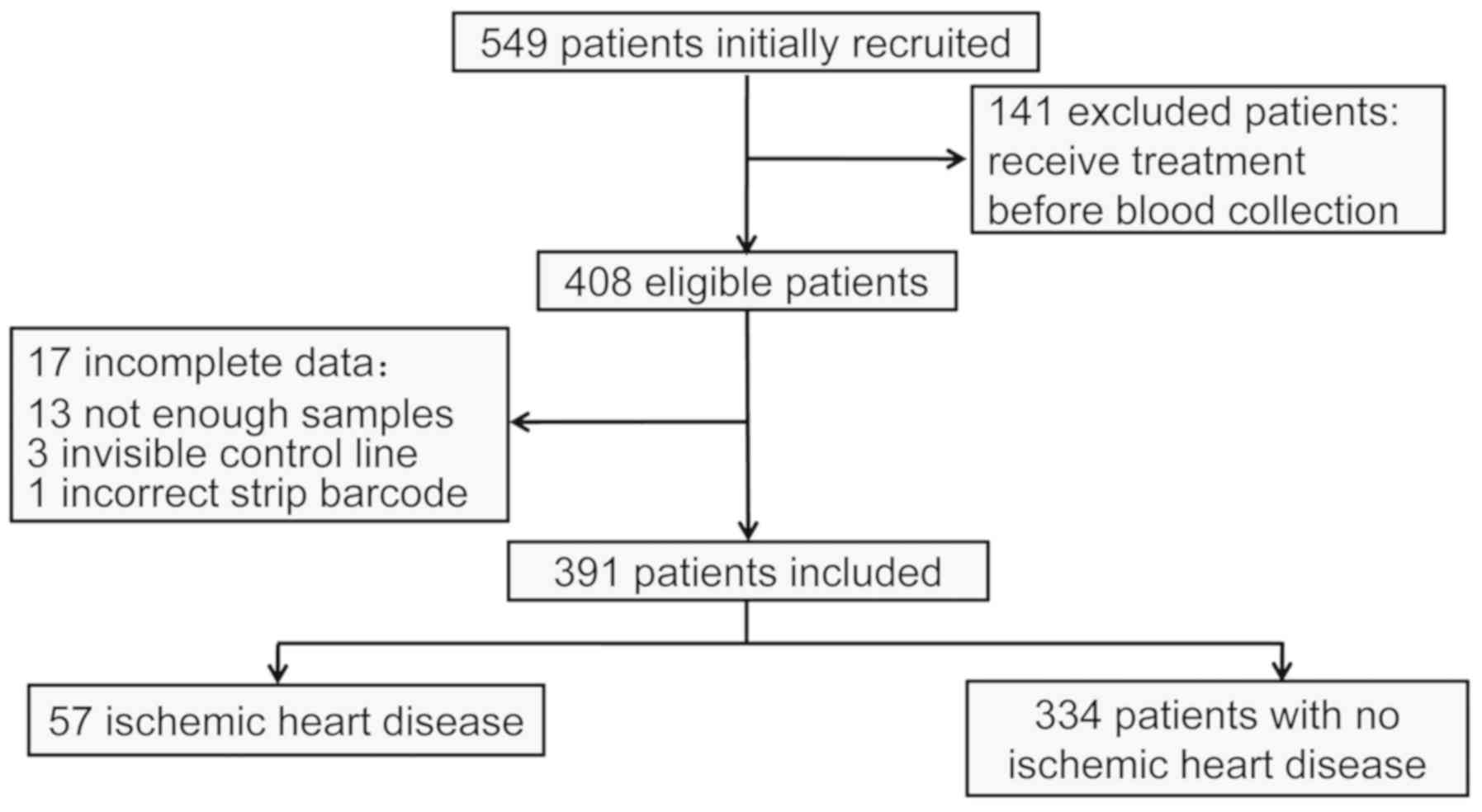
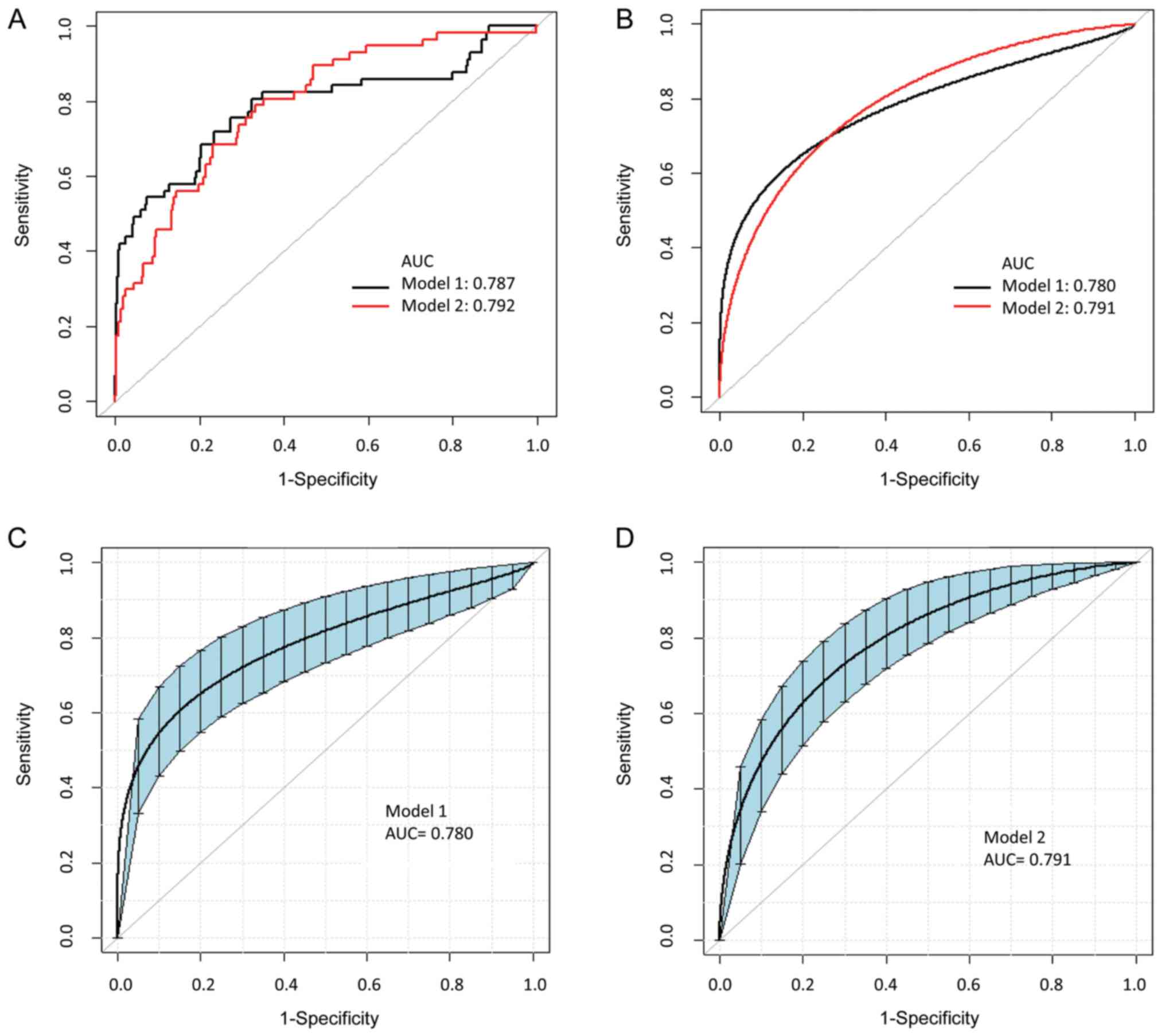
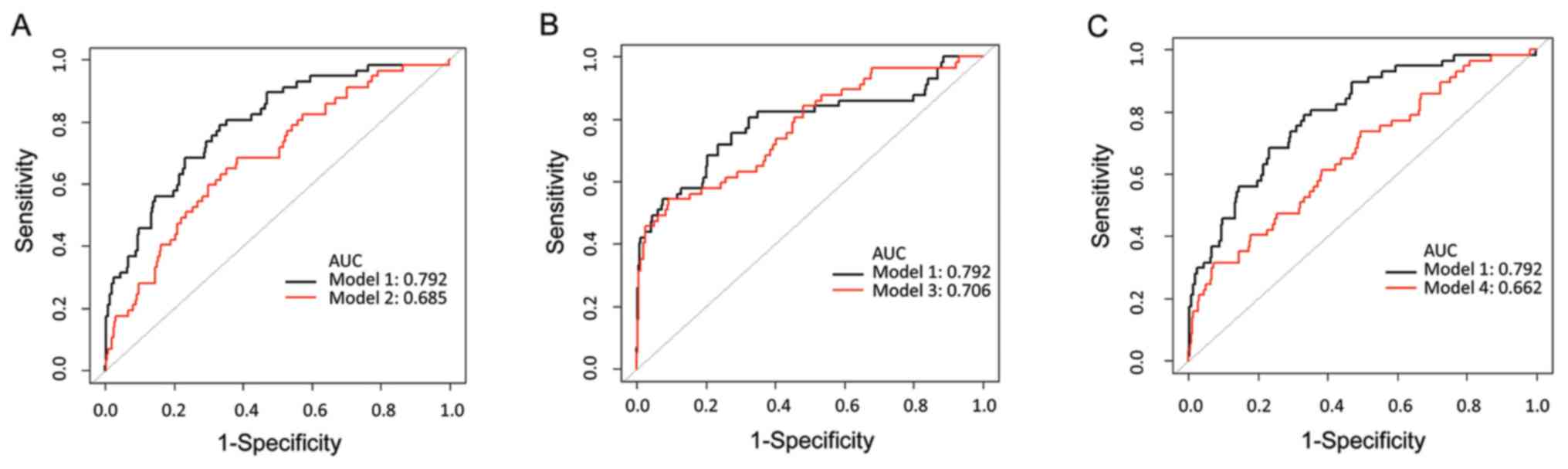
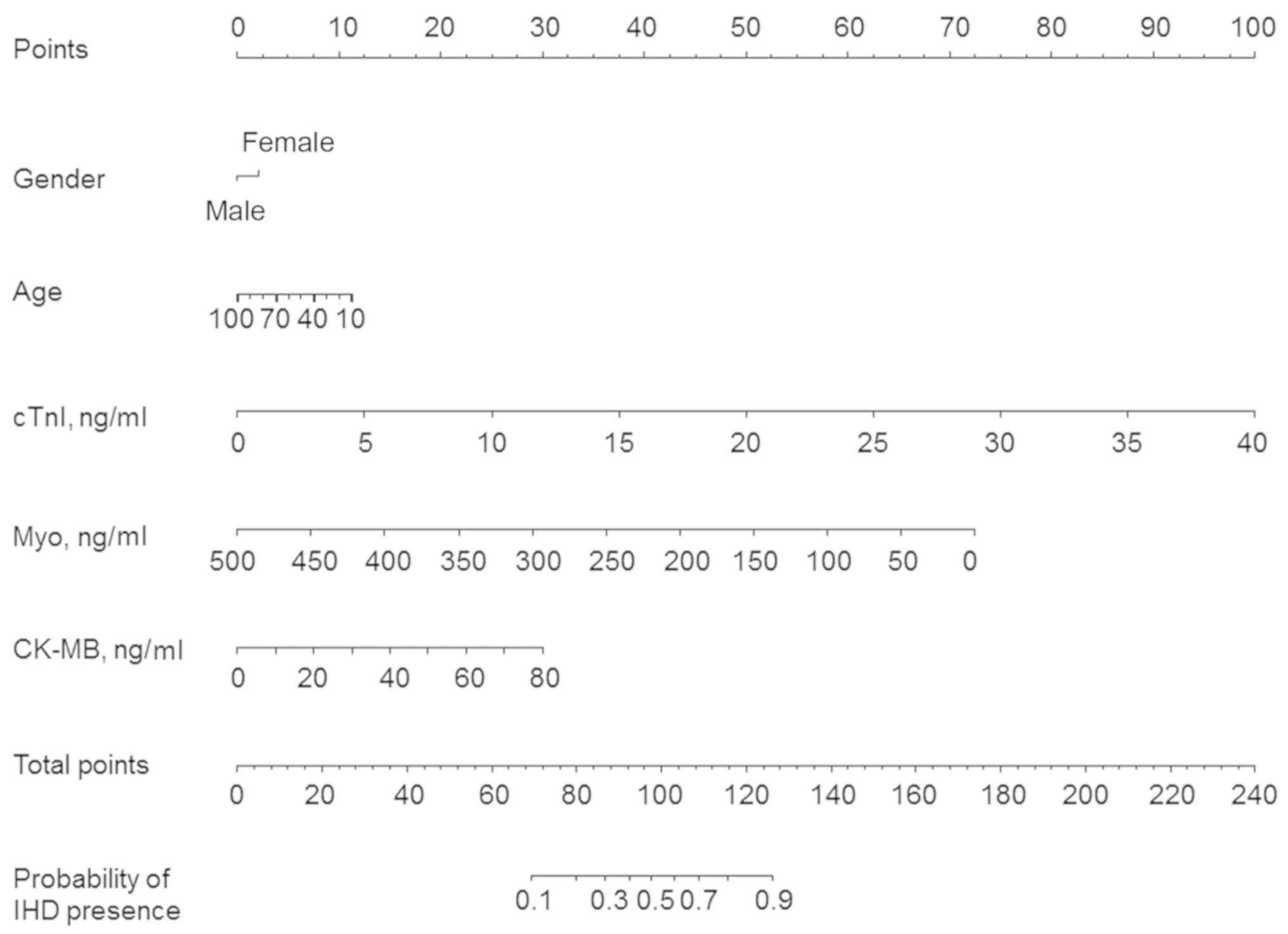
|
1
|
Joseph P, Leong D, McKee M, Anand SS,
Schwalm JD, Teo K, Mente A and Yusuf S: Reducing the global burden
of cardiovascular disease, part 1: The epidemiology and risk
factors. Circ Res. 121:677–694. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lamelas PM, Yusuf S and Schwalm JD:
Effective approaches to address the global cardiovascular disease
burden. Curr Opin Cardiol. 32:557–566. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett
DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Despres JP,
Fullerton HJ, et al: Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2016 update: A report from the American heart
association. Circulation. 133:447–454. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Roth GA, Johnson C, Abajobir A, Abd-Allah
F, Abera SF, Abyu G, Ahmed M, Aksut B, Alam T, Alam K, et al:
Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases
for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J Am Coll Cardiol. 70:1–25.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
World Health Organization (WHO): Global
health estimates: Deaths by cause, age, sex and country, 2000-2012.
WHO, Geneva, 2014.
|
|
6
|
Lippi G, Franchini M and Cervellin G:
Diagnosis and management of ischemic heart disease. Semin Thromb
Hemost. 39:202–213. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Safdar B, Nagurney JT, Anise A, DeVon HA,
D'Onofrio G, Hess EP, Hollander JE, Legato MJ, McGregor AJ, Scott
J, et al: Gender-specific research for emergency diagnosis and
management of ischemic heart disease: Proceedings from the 2014
academic emergency medicine consensus conference cardiovascular
research workgroup. Acad Emerg Med. 21:1350–1360. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
de Winter RJ, Koster RW, Sturk A and
Sanders GT: Value of myoglobin, troponin T, and CK-MBmass in ruling
out an acute myocardial infarction in the emergency room.
Circulation. 92:3401–3407. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Scebba F, Papale M, Rocchiccioli S,
Ucciferri N, Bigazzi F, Sampietro T, Carpeggiani C, L'Abbate A,
Coceani F and Angeloni D: Differential proteome profile in ischemic
heart disease: Prognostic value in chronic angina versus myocardial
infarction. A proof of concept. Clin Chim Acta. 471:68–75.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hachey BJ, Kontos MC, Newby LK,
Christenson RH, Peacock WF, Brewer KC and Mccord J: Trends in use
of biomarker protocols for the evaluation of possible myocardial
infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 6(e005852)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Haeck JD, Verouden NJ, Kuijt WJ, Koch KT,
Van Straalen JP, Fischer J, Groenink M, Bilodeau L, Tijssen JG,
Krucoff MW and De Winter RJ: Comparison of usefulness of N-terminal
pro-brain natriuretic peptide as an independent predictor of
cardiac function among admission cardiac serum biomarkers in
patients with anterior wall versus nonanterior wall ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 105:1065–1069.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hetland O and Dickstein K: Cardiac markers
in the early hours of acute myocardial infarction: Clinical
performance of creatine kinase, creatine kinase MB isoenzyme
(activity and mass concentration), creatine kinase MM and MB
subform ratios, myoglobin and cardiac troponin T. Scand J Clin Lab
Invest. 56:701–713. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jolly SS, Shenkman H, Brieger D, Fox KA,
Yan AT, Eagle KA, Steg PG, Lim KD, Quill A and Goodman SG: GRACE
Investigators. Quantitative troponin and death, cardiogenic shock,
cardiac arrest and new heart failure in patients with
non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes (NSTE ACS):
Insights from the global registry of acute coronary events. Heart.
97:197–202. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zeller T, Ojeda F, Brunner FJ, Peitsmeyer
P, Munzel T, Binder H, Pfeiffer N, Michal M, Wild PS, Blankenberg S
and Lackner KJ: High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I in the general
population-defining reference populations for the determination of
the 99th percentile in the gutenberg health study. Clin Chem Lab
Med. 53:699–706. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Penttila I, Penttila K and Rantanen T:
Laboratory diagnosis of patients with acute chest pain. Clin Chem
Lab Med. 38:187–197. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Weigl B, Domingo G, Labarre P and Gerlach
J: Towards non- and minimally instrumented, microfluidics-based
diagnostic devices. Lab Chip. 8:1999–2014. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen A and Yang S: Replacing antibodies
with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron.
71:230–242. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen J, Zhou S and Wen J: Disposable strip
biosensor for visual detection of Hg(2+) based on Hg(2+)-triggered
toehold binding and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification.
Anal Chem. 86:3108–3114. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yu L, Shi Z, Fang C, Zhang Y, Liu Y and Li
C: Disposable lateral flow-through strip for smartphone-camera to
quantitatively detect alkaline phosphatase activity in milk.
Biosens Bioelectron. 69:307–315. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Weng CW, Hsieh BC, Hou YT and Cheng TJ:
Determination of hematocrit by voltage-induced hemolysis on a
disposable electrochemical sensing strip. Analyst. 140:6619–6624.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li X, Wang X, Fang T, Zhang L and Gong J:
Disposable photoelectrochemical sensing strip for highly sensitive
determination of perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride on
functionalized screen-printed carbon electrode. Talanta.
181:147–153. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Braunwald E, Antman EM, Beasley JW, Califf
RM, Cheitlin MD, Hochman JS, Jones RH, Kereiakes D, Kupersmith J,
Levin TN, et al: ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for the management
of patients with unstable angina and non-ST-segment elevation
myocardial infarction-summary article: A report of the American
college of cardiology/American heart association task force on
practice guidelines (committee on the management of patients with
unstable angina). J Am Coll Cardiol. 40:1366–1374. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Christenson RH and Azzazy HM: Cardiac
point of care testing: A focused review of current national academy
of clinical biochemistry guidelines and measurement platforms. Clin
Biochem. 42:150–157. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Storrow AB, Apple FS, Wu AHB, Jesse RL,
Francis GS, Christenson RH, Cannon CP, Morrow DA, Newby LK,
Ravkilde J, et al: National academy of clinical biochemistry
laboratory medicine practice guidelines: Point of care testing,
oversight, and administration of cardiac biomarkers for acute
coronary syndromes. Point Care. 6:215–222. 2007.
|
|
25
|
McRae AD, Innes G, Graham M, Lang E,
Andruchow JE, Yang H, Ji Y, Vatanpour S, Southern DA, Wang D, et
al: Comparative evaluation of 2-hour rapid diagnostic algorithms
for acute myocardial infarction using high-sensitivity cardiac
troponin T. Can J Cardiol. 33:1006–1012. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mancini GB, Gosselin G, Chow B, Kostuk W,
Stone J, Yvorchuk KJ, Abramson BL, Cartier R, Huckell V, Tardif JC,
et al: Canadian cardiovascular society guidelines for the diagnosis
and management of stable ischemic heart disease. Can J Cardiol.
30:837–849. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|