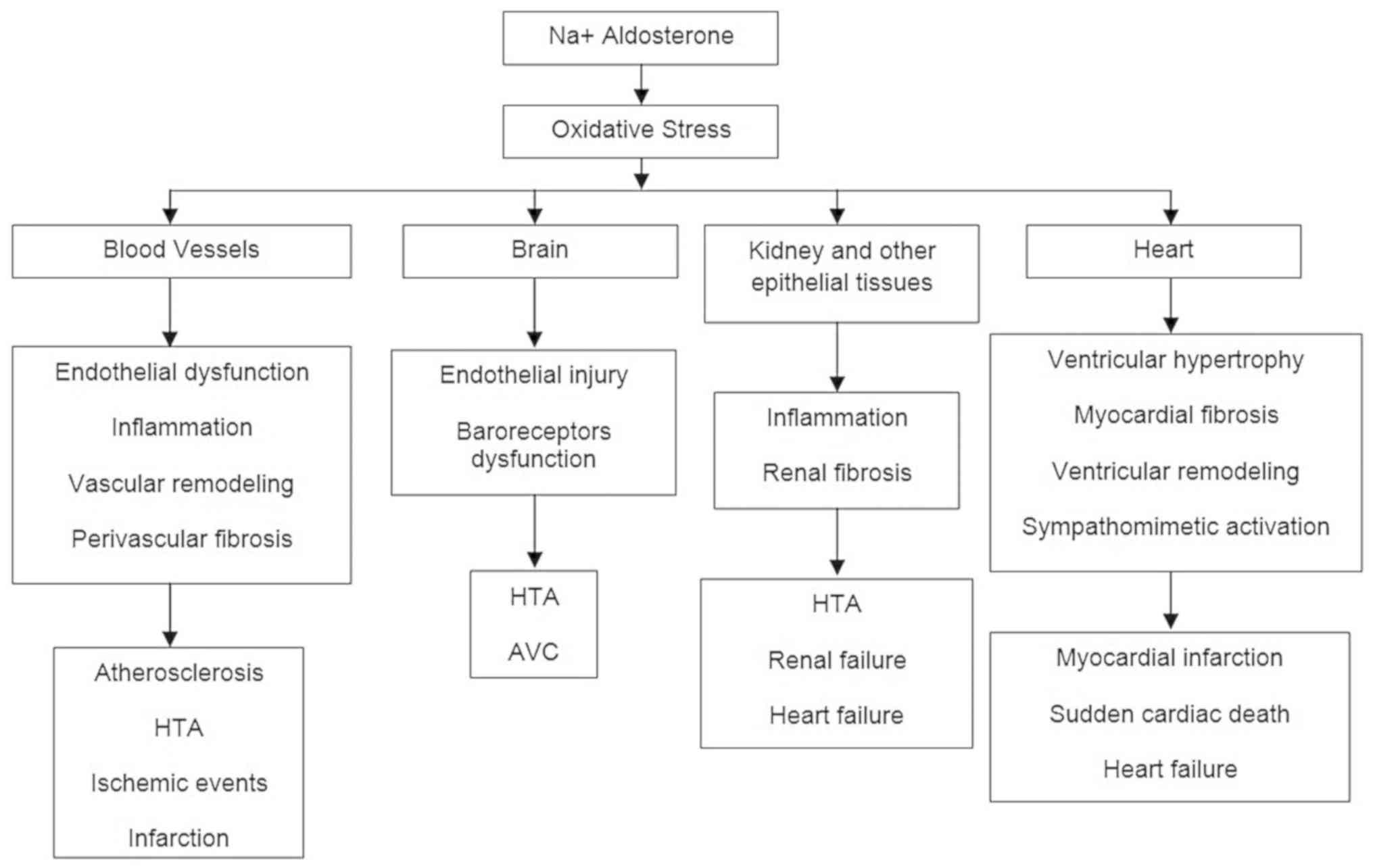
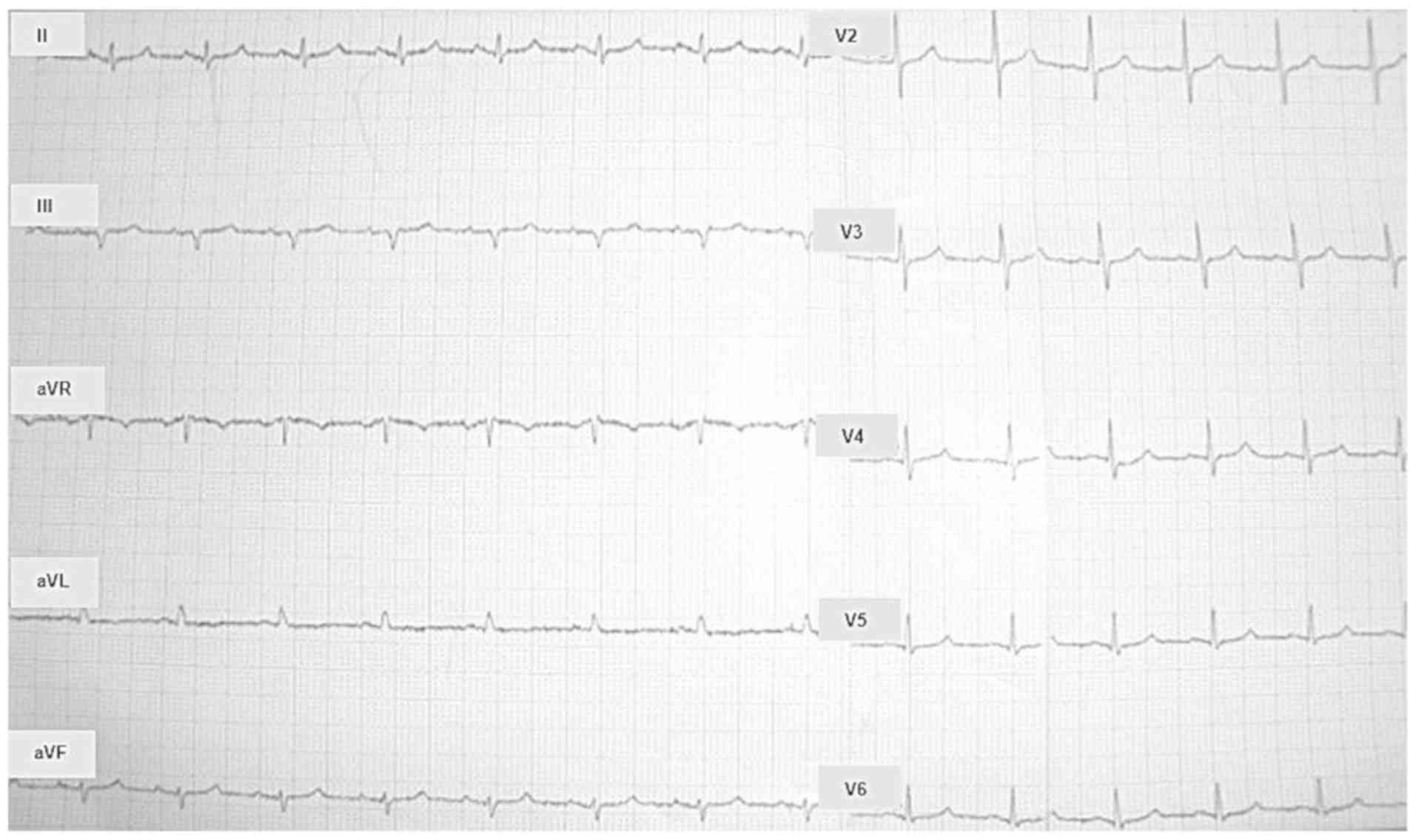
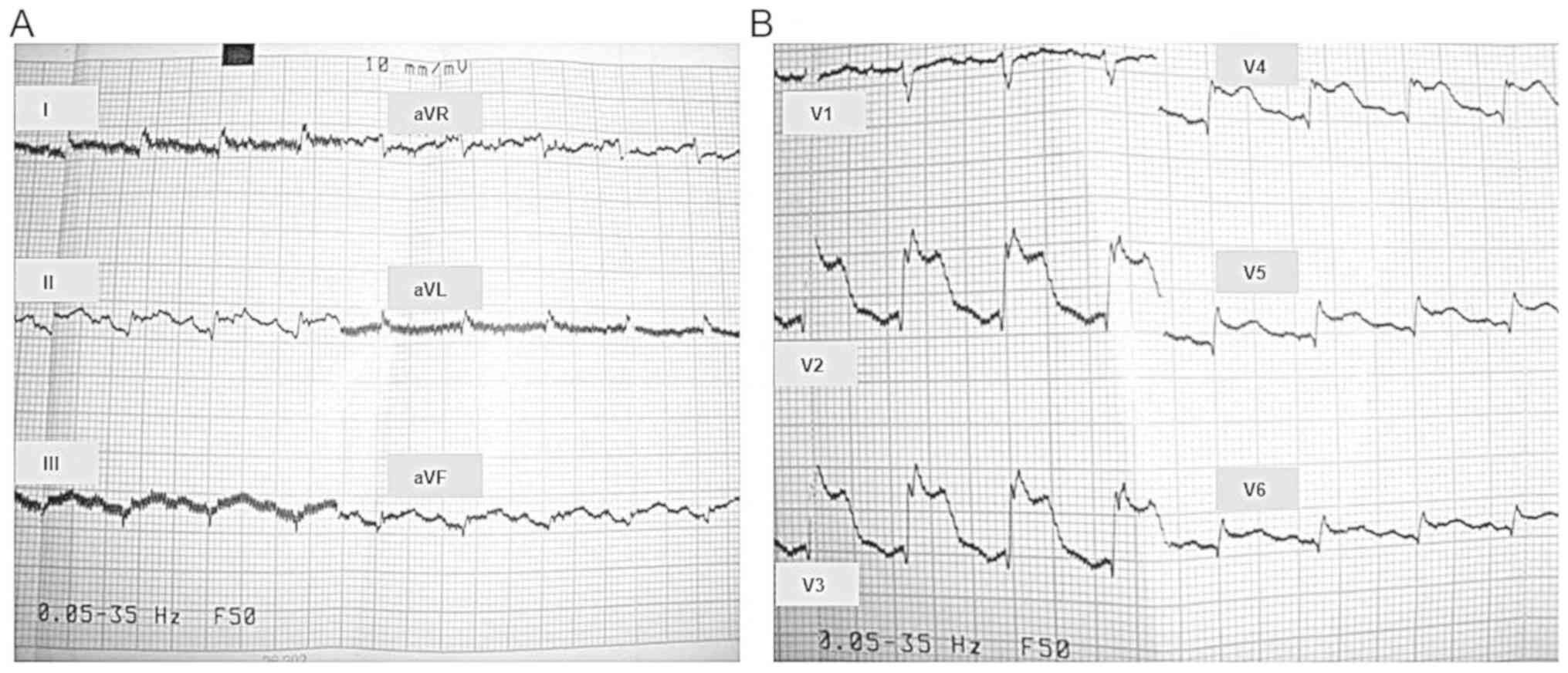
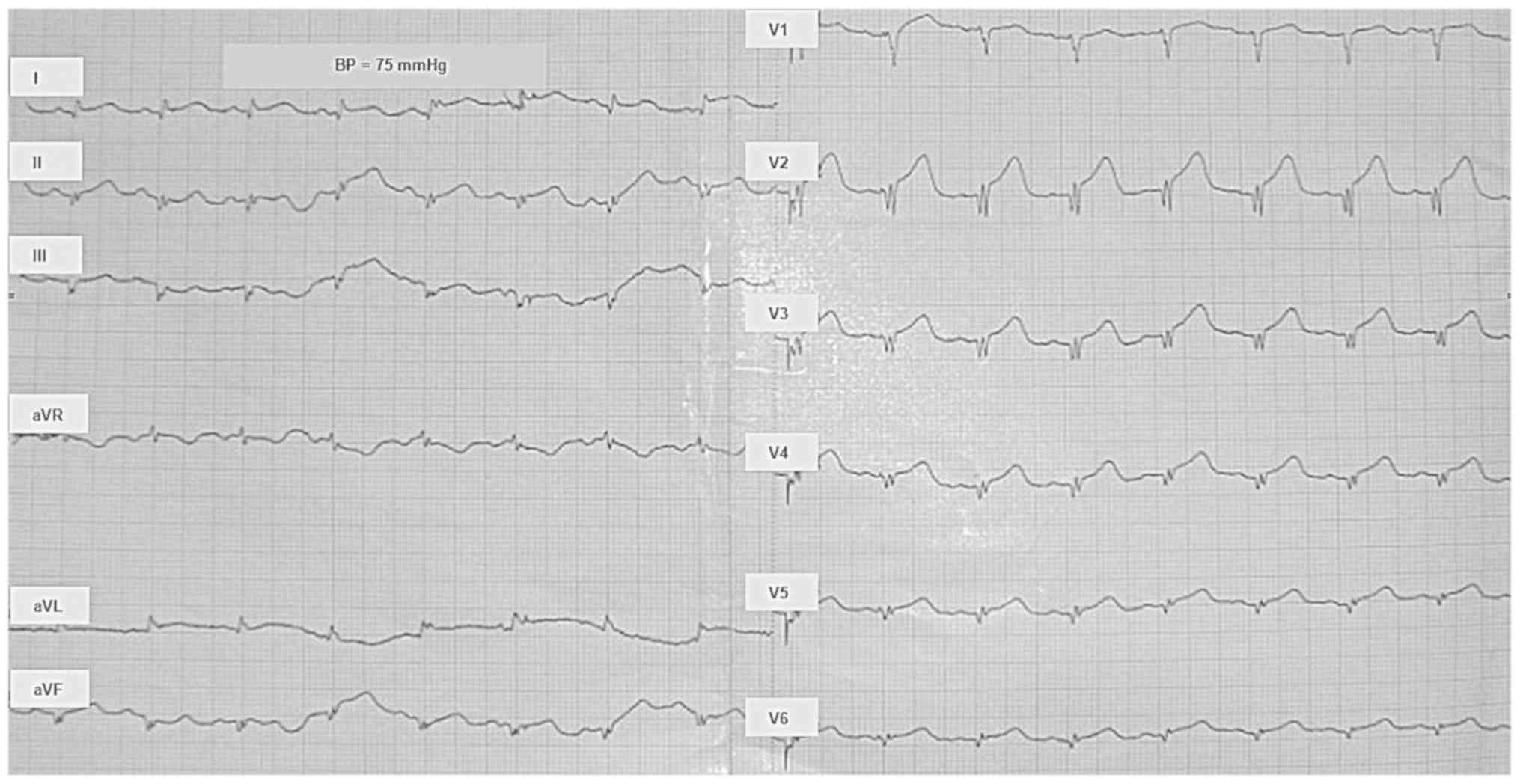
Spandidos Publications style
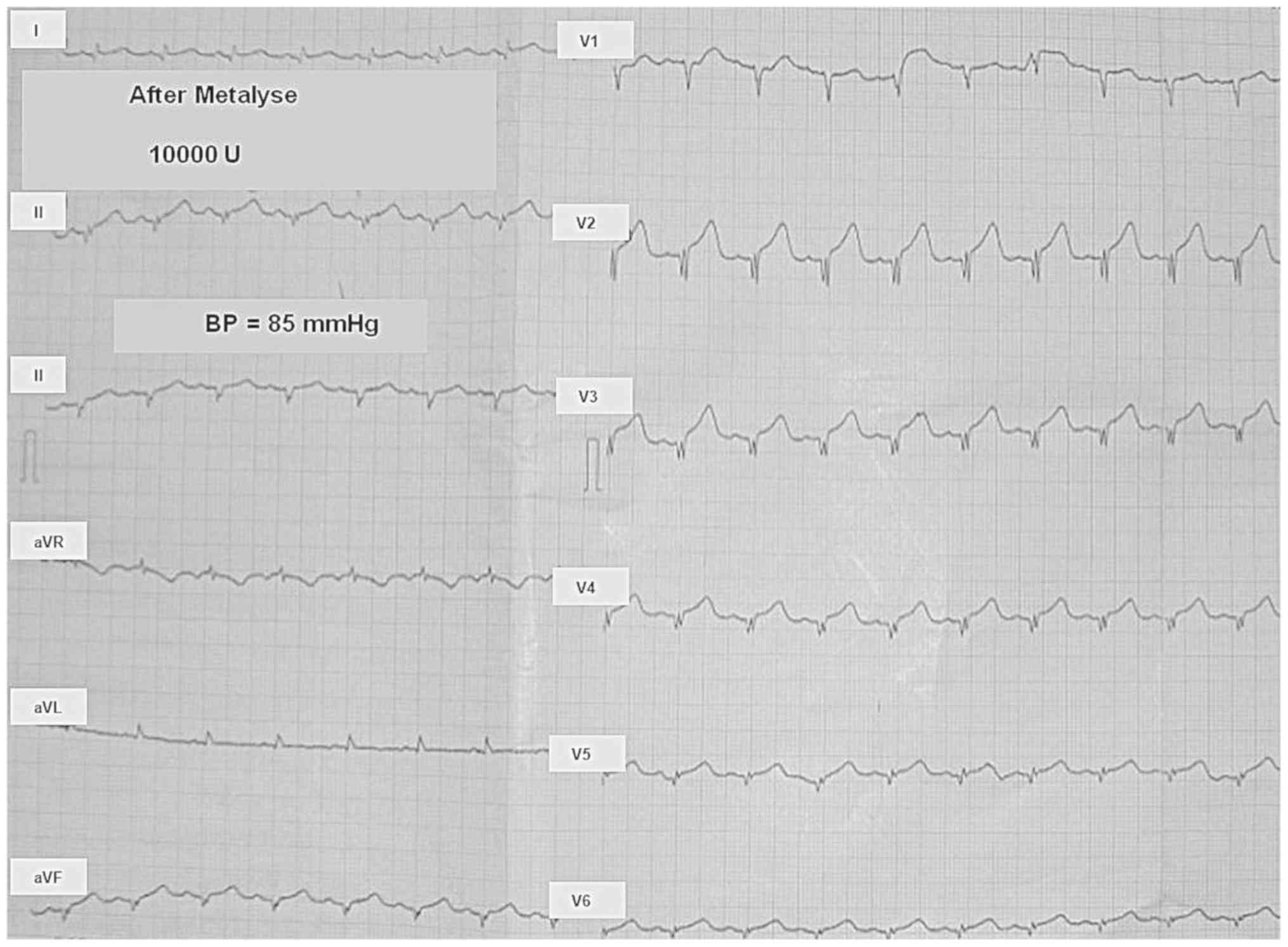
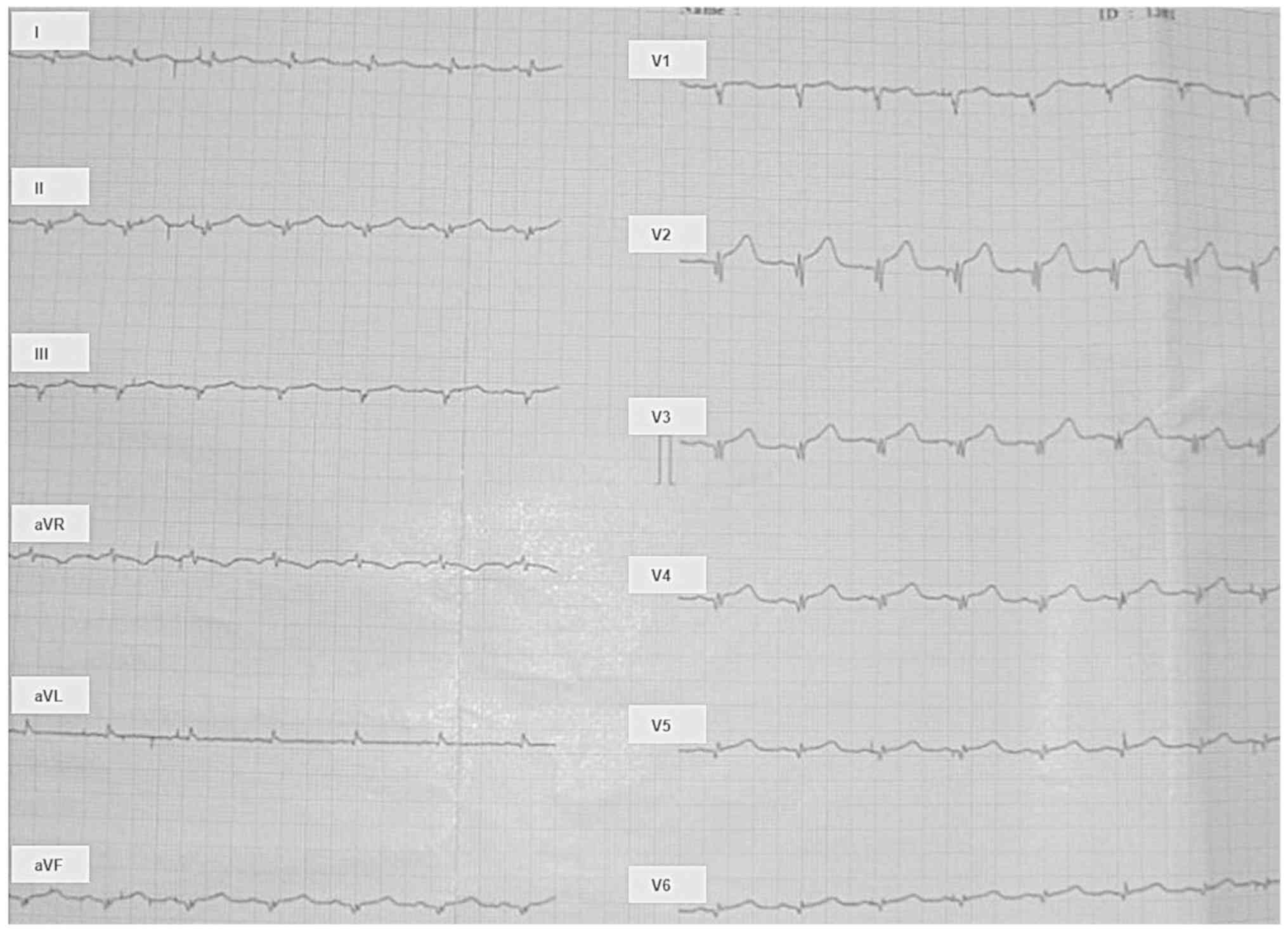
Maranduca MA, Statescu C, Sascau RA, Dima N, Hurjui LL, Serban DN and Serban IL: Acute coronary syndrome with ST segment elevation in a patient with Addison disease: Case report and brief review of physiopathological mechanisms: A case study. Exp Ther Med 20: 1230-1236, 2020.
APA
Maranduca, M.A., Statescu, C., Sascau, R.A., Dima, N., Hurjui, L.L., Serban, D.N., & Serban, I.L. (2020). Acute coronary syndrome with ST segment elevation in a patient with Addison disease: Case report and brief review of physiopathological mechanisms: A case study. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 20, 1230-1236. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8855
MLA
Maranduca, M. A., Statescu, C., Sascau, R. A., Dima, N., Hurjui, L. L., Serban, D. N., Serban, I. L."Acute coronary syndrome with ST segment elevation in a patient with Addison disease: Case report and brief review of physiopathological mechanisms: A case study". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 20.2 (2020): 1230-1236.
Chicago
Maranduca, M. A., Statescu, C., Sascau, R. A., Dima, N., Hurjui, L. L., Serban, D. N., Serban, I. L."Acute coronary syndrome with ST segment elevation in a patient with Addison disease: Case report and brief review of physiopathological mechanisms: A case study". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 20, no. 2 (2020): 1230-1236. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8855