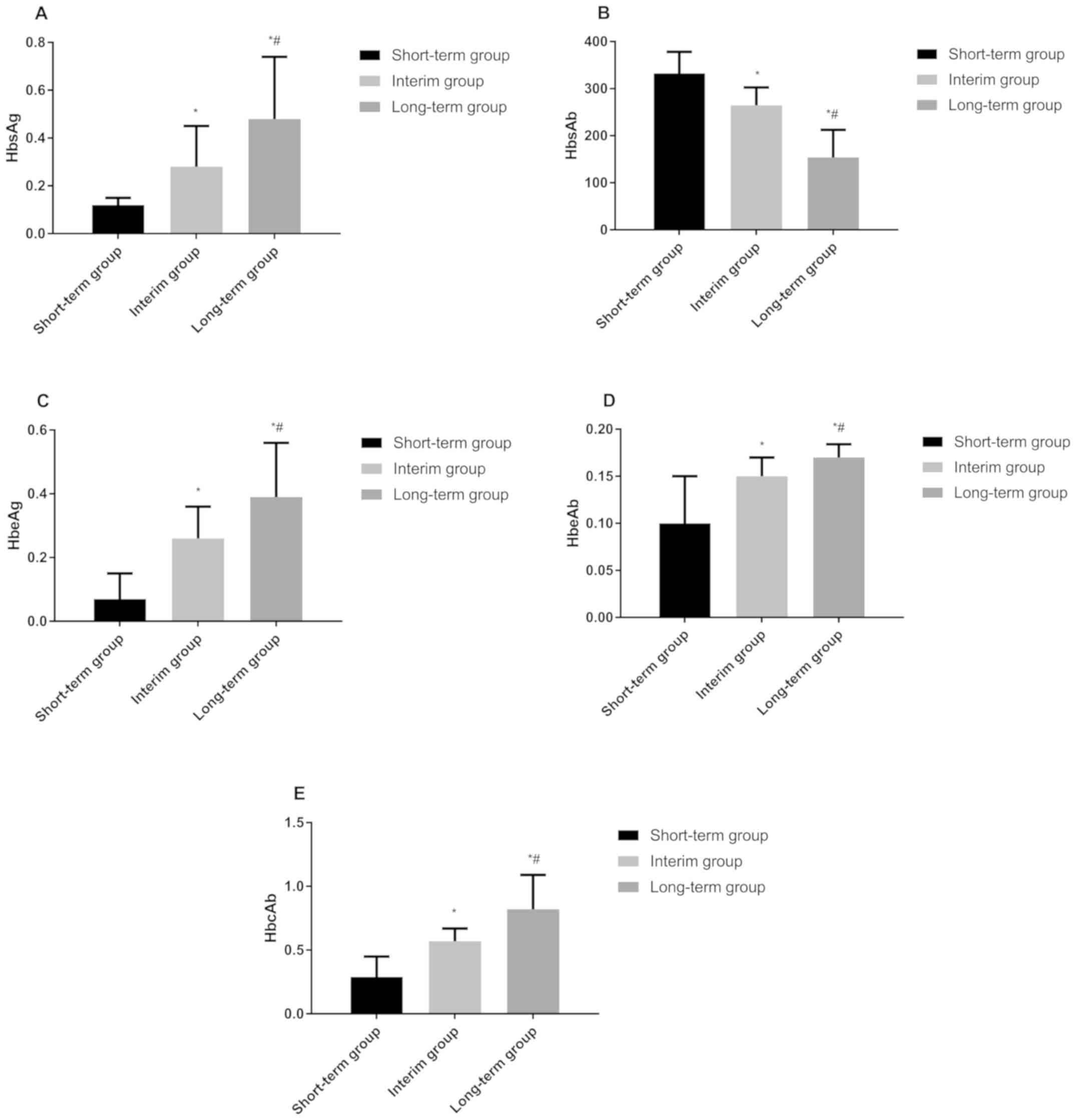
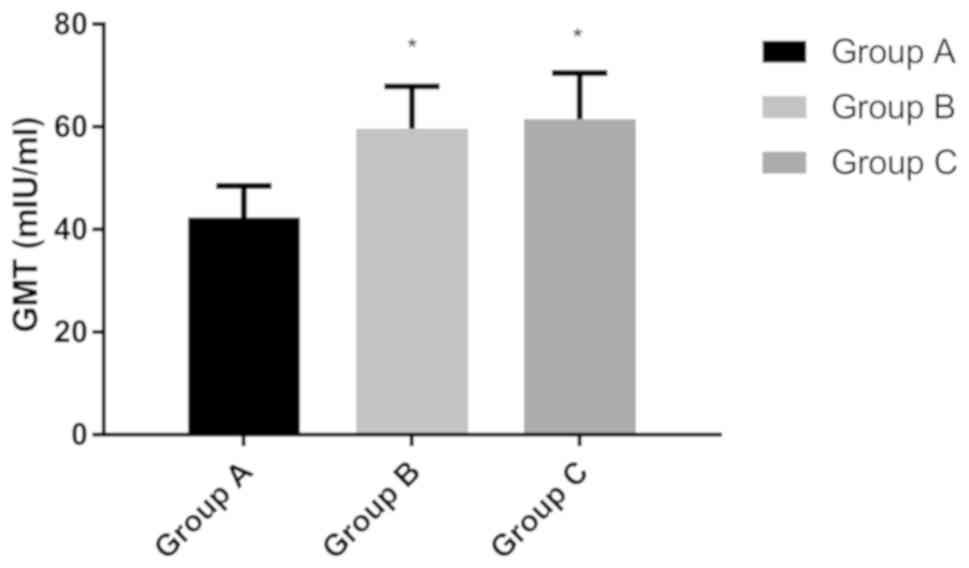
|
1
|
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan
HL, Chen CJ, Chen DS, Chen HL, Chen PJ, Chien RN, et al:
Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of
hepatitis B: A 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 10:1–98. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang
JP, Jonas MM and Murad MH: American Association for the Study of
Liver Diseases. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis
B. Hepatology. 63:261–283. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lok AS, McMahon BJ, Brown RS Jr, Wong JB,
Ahmed AT, Farah W, Almasri J, Alahdab F, Benkhadra K, Mouchli MA,
et al: Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B viral infection in
adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology.
63:284–306. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang C, Ji D, Chen J, Shao Q, Li B, Liu J,
Wu V, Wong A, Wang Y, Zhang X, et al: Hepatitis due to reactivation
of hepatitis B virus in endemic areas among patients with hepatitis
C treated with direct-acting antiviral agents. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 15:132–136. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Brown RS Jr, McMahon BJ, Lok AS, Wong JB,
Ahmed AT, Mouchli MA, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, Murad MH and Mohammed K:
Antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B viral infection during
pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology.
63:319–333. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ye B, Liu X, Li X, Kong H, Tian L and Chen
Y: T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: Current
knowledge and clinical significance. Cell Death Dis.
6(e1694)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bruce MG, Bruden D, Hurlburt D, Zanis C,
Thompson G, Rea L, Toomey M, Townshend-Bulson L, Rudolph K, Bulkow
L, et al: Antibody levels and protection after hepatitis B vaccine:
Results of a 30-year follow-up study and response to a booster
dose. J Infect Dis. 214:16–22. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hernán MA, Jick SS, Olek MJ and Jick H:
Recombinant hepatitis B vaccine and the risk of multiple sclerosis:
A prospective study. Neurology. 63:838–842. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Van Damme P: Long-term protection after
hepatitis B vaccine. J Infect Dis. 214:1–3. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Qiu Y, Guo L, Zhang S, Xu B, Gao Y, Hu Y,
Hou J, Bai B, Shen H and Mao P: DNA-based vaccination against
hepatitis B virus using dissolving microneedle arrays adjuvanted by
cationic liposomes and CpG ODN. Drug Deliv. 23:2391–2398.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nelson NP, Easterbrook PJ and McMahon BJ:
Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection and impact of
vaccination on disease. Clin Liver Dis. 20:607–628. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guirguis-Blake JM, Senger CA, Webber EM,
Mularski RA and Whitlock EP: Screening for chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease: Evidence report and systematic review for the US
preventive services task force. JAMA. 315:1378–1393.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Eichelberger MC, Couzens L, Gao Y, Levine
M, Katz J, Wagner R, Thompson CI, Höschler K, Laurie K, Bai T, et
al: ELLA study participants: Comparability of neuraminidase
inhibition antibody titers measured by enzyme-linked lectin assay
(ELLA) for the analysis of influenza vaccine immunogenicity.
Vaccine. 34:458–465. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lampertico P, Agarwal K, Berg T, Buti M,
Janssen HLA, Papatheodoridis G, Zoulim F and Tacke F: European
Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address:
easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the
Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of
hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 67:370–398. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim WR, Berg T, Asselah T, Flisiak R, Fung
S, Gordon SC, Janssen HL, Lampertico P, Lau D, Bornstein JD, et al:
Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 scoring systems for non-invasive
assessment of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients. J
Hepatol. 64:773–780. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Buti M, Gane E, Seto WK, Chan HL, Chuang
WL, Stepanova T, Hui AJ, Lim YS, Mehta R, Janssen HL, et al:
GS-US-320-0108 Investigators: Tenofovir alafenamide versus
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of patients with
HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A randomised,
double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 1:196–206. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Roberts H, Kruszon-Moran D, Ly KN, Hughes
E, Iqbal K, Jiles RB and Holmberg SD: Prevalence of chronic
hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in U.S. households: National
Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1988-2012.
Hepatology. 63:388–397. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Paul S, Saxena A, Terrin N, Viveiros K,
Balk EM and Wong JB: Hepatitis B virus reactivation and prophylaxis
during solid tumor chemotherapy: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 164:30–40. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Decorsière A, Mueller H, van Breugel PC,
Abdul F, Gerossier L, Beran RK, Livingston CM, Niu C, Fletcher SP,
Hantz O, et al: Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6
complex as a host restriction factor. Nature. 531:386–389.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lok AS, Pan CQ, Han SH, Trinh HN, Fessel
WJ, Rodell T, Massetto B, Lin L, Gaggar A, Subramanian GM, et al:
Randomized phase II study of GS-4774 as a therapeutic vaccine in
virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol.
65:509–516. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Harris AM, Iqbal K, Schillie S, Britton J,
Kainer MA, Tressler S and Vellozzi C: Increases in acute hepatitis
B virus infections - Kentucky, Tennessee, and West Virginia,
2006-2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 65:47–50. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Park JJ, Wong DK, Wahed AS, Lee WM, Feld
JJ, Terrault N, Khalili M, Sterling RK, Kowdley KV, Bzowej N, et
al: Hepatitis B Research Network: Hepatitis B Virus-specific and
global T-cell dysfunction in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology.
150:684–695.e5. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Takayama H, Sato T, Ikeda F and Fujiki S:
Reactivation of hepatitis B virus during interferon-free therapy
with daclatasvir and asunaprevir in patient with hepatitis B
virus/hepatitis C virus co-infection. Hepatol Res. 46:489–491.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hayashi K, Ishigami M, Ishizu Y, Kuzuya T,
Honda T, Nishimura D, Goto H and Hirooka Y: A case of acute
hepatitis B in a chronic hepatitis C patient after daclatasvir and
asunaprevir combination therapy: Hepatitis B virus reactivation or
acute self-limited hepatitis? Clin J Gastroenterol. 9:252–256.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xiang KH, Michailidis E, Ding H, Peng YQ,
Su MZ, Li Y, Liu XE, Dao Thi VL, Wu XF, Schneider WM, et al:
Effects of amino acid substitutions in hepatitis B virus surface
protein on virion secretion, antigenicity, HBsAg and viral DNA. J
Hepatol. 66:288–296. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fries LF, Smith GE and Glenn GM: A
recombinant viruslike particle influenza A (H7N9) vaccine. N Engl J
Med. 369:2564–2566. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Patel M, Glass RI, Jiang B, Santosham M,
Lopman B and Parashar U: A systematic review of anti-rotavirus
serum IgA antibody titer as a potential correlate of rotavirus
vaccine efficacy. J Infect Dis. 208:284–294. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
van Assen S, Holvast A, Telgt DSC, Benne
CA, de Haan A, Westra J, Kallenberg CG and Bijl M: Patients with
humoral primary immunodeficiency do not develop protective
anti-influenza antibody titers after vaccination with trivalent
subunit influenza vaccine. Clin Immunol. 136:228–235.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Folaranmi T, Rubin L, Martin SW, Patel M
and MacNeil JR: Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Use of serogroup
B meningococcal vaccines in persons aged ≥10 years at increased
risk for serogroup B meningococcal disease: Recommendations of the
Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2015. MMWR Morb
Mortal Wkly Rep. 64:608–612. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Benoit A, Beran J, Devaster JM, Esen M,
Launay O, Leroux-Roels G, McElhaney JE, Oostvogels L, van Esse GA
and Gaglani M: Hemagglutination inhibition antibody titers as a
correlate of protection against seasonal A/H3N2 influenza disease.
Open Forum Infect Dis 2: ofv067. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofv067.
eCollection 2015 Apr.
|
|
31
|
Yang S, Tian G, Cui Y, Ding C, Deng M, Yu
C, Xu K, Ren J, Yao J, Li Y, et al: Factors influencing immunologic
response to hepatitis B vaccine in adults. Sci Rep.
6(27251)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|