Article
Open Access
Effects of diabetes on the rebleeding rate following endoscopic treatment in patients with liver cirrhosis
- Authors:
- Xi Wang
- Xuecan Mei
- Derun Kong
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui 230022, P.R. China
-
Pages:
1299-1306
|
Published online on:
June 11, 2020
https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8876
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
In the present study, the effects of diabetes on rebleeding following endoscopic treatment were assessed in patients with liver cirrhosis. A retrospective analysis of patients who underwent endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) or endoscopic injection sclerotherapy (EIS) at the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University (Hefei, China) between June 2015 and March 2018 was performed. The patients were divided into the EVL and the EIS groups and each group was subdivided into diabetic and non‑diabetic groups. The post‑operative rebleeding rate was compared between the EVL and the EIS groups and between the diabetic and non‑diabetic patients. The differences in the post‑operative rebleeding rate of diabetic patients with hepatogenic and non‑hepatogenic diabetes and in patients with different liver function grades were also determined. In the total patient cohort, the rebleeding rate in the EVL subgroup (11.3, 16.5 and 23.5%) was not significantly different compared with that in the EIS subgroup (9.8, 17.4 and 29.3%) at 1, 3 and 6 months following surgery, respectively (P=0.724, 0.868 and 0.339). In the total diabetic group, the rebleeding rate in the EVL subgroup (25.0, 36.1 and 44.4%) was not significantly different compared with that in the EIS subgroup (20.6, 32.4 and 47.1%) at 1, 3 and 6 months following surgery (P=0.660, 0.741 and 0.826, respectively). In the EVL group, the rebleeding rate in the diabetic subgroup (25.0, 36.1 and 44.4%) was higher than that in the non‑diabetic subgroup (5.1, 7.6 and 13.9%) at 1, 3, and 6 months following surgery and the differences were significant (P=0.005, <0.001 and <0.001, respectively). In the EIS group, the rebleeding rate in the diabetic subgroup (20.6, 32.4 and 47.1%) was significantly higher than that in the non‑diabetic subgroup (3.4, 8.6 and 19.0%) at 1, 3 and 6 months following surgery (P=0.021, 0.004 and 0.004, respectively). Adjustment for age and liver function grade in the EVL and EIS groups was performed using binary logistic regression and the parameter diabetes was indicated to be a risk factor for post‑operative rebleeding (P<0.05). No significant difference was noted in the rate of rebleeding between patients with hepatogenic diabetes and non‑hepatogenic diabetes at 1, 3 and 6 months following surgery (P=0.634, 0.726 and 0.446, respectively). In the total diabetic group, the rebleeding rate in the Child‑Pugh grade A subgroup (14.3, 17.9 and 25.0%) was lower than that in the Child‑Pugh grade B/C subgroup (28.6, 45.2 and 59.5%) at 1, 3 and 6 months following surgery, respectively. No significant difference was noted between the two groups at 1 month following surgery (P=0.163). However, the differences were significant at 3 and 6 months following surgery (P=0.018 and 0.005, respectively). The results suggested that diabetes is a risk factor for post‑operative rebleeding in patients with cirrhosis. Diabetic patients with poor liver function were more likely to bleed following surgery and the post‑operative bleeding rate was not significantly different between patients with hepatogenic and non‑hepatogenic diabetes. The study was registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (no. ChiCTR1800017772).
View Figures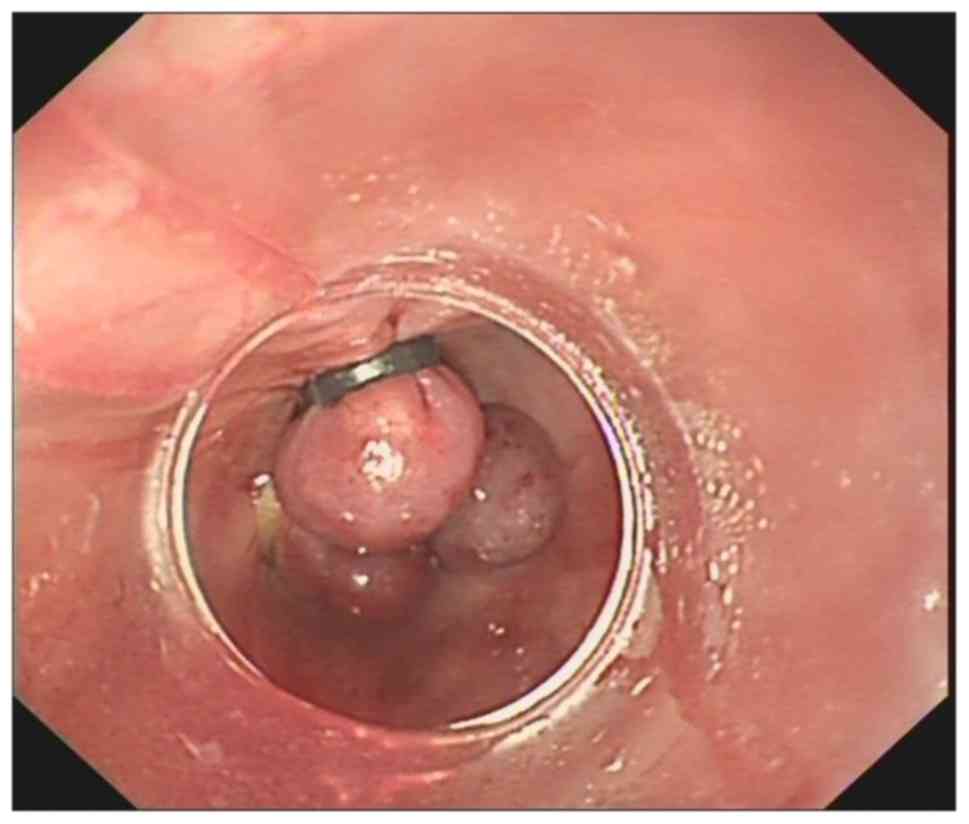 |
Figure 1
|
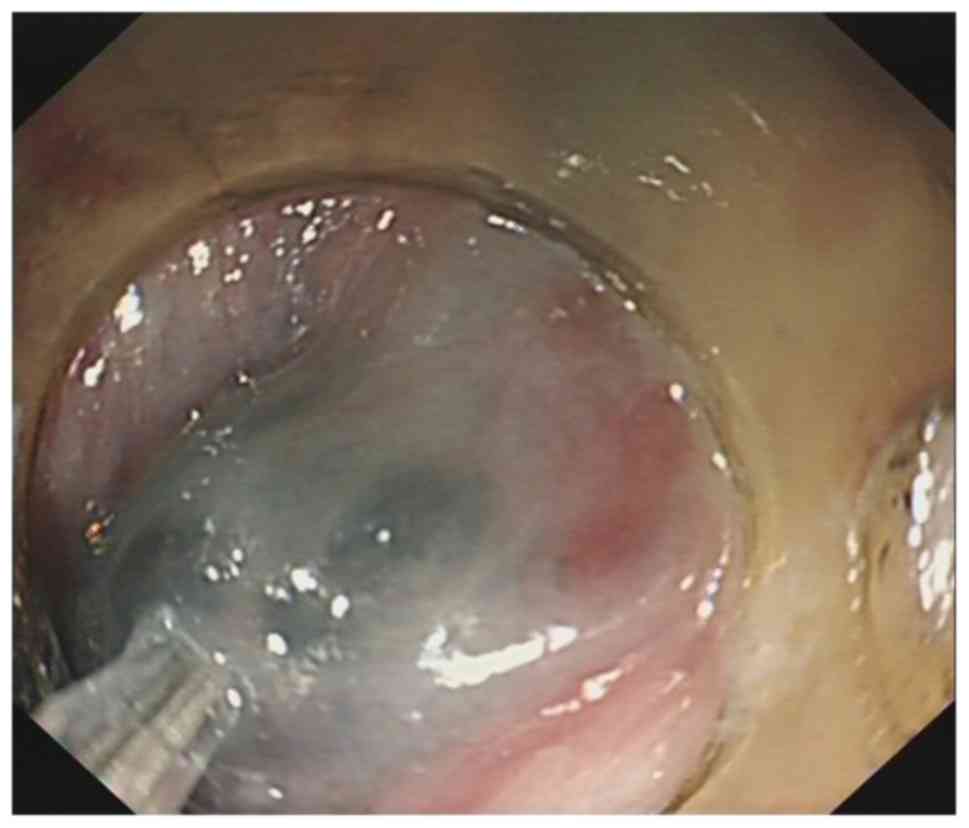 |
Figure 2
|
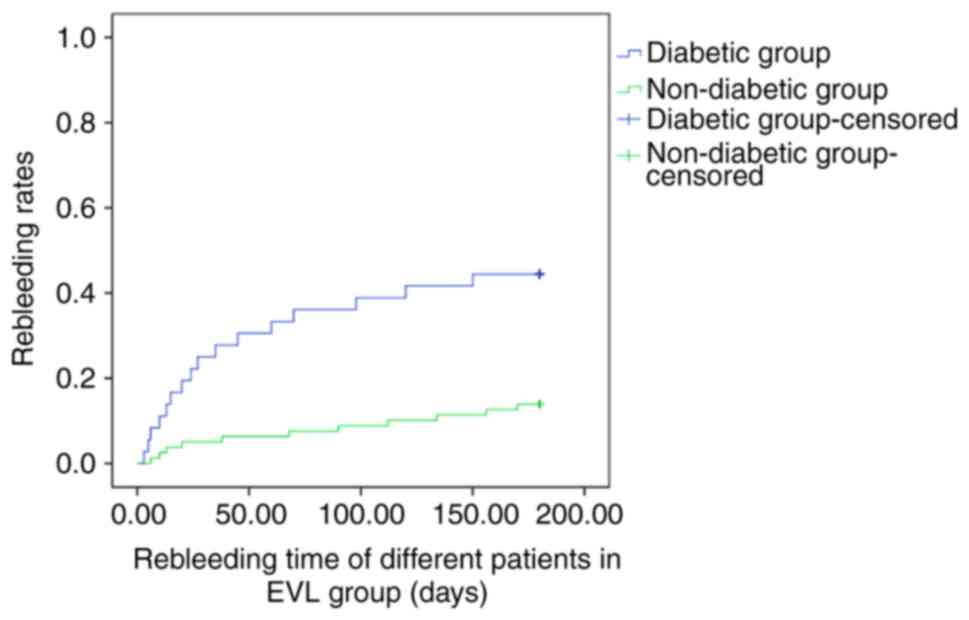 |
Figure 3
|
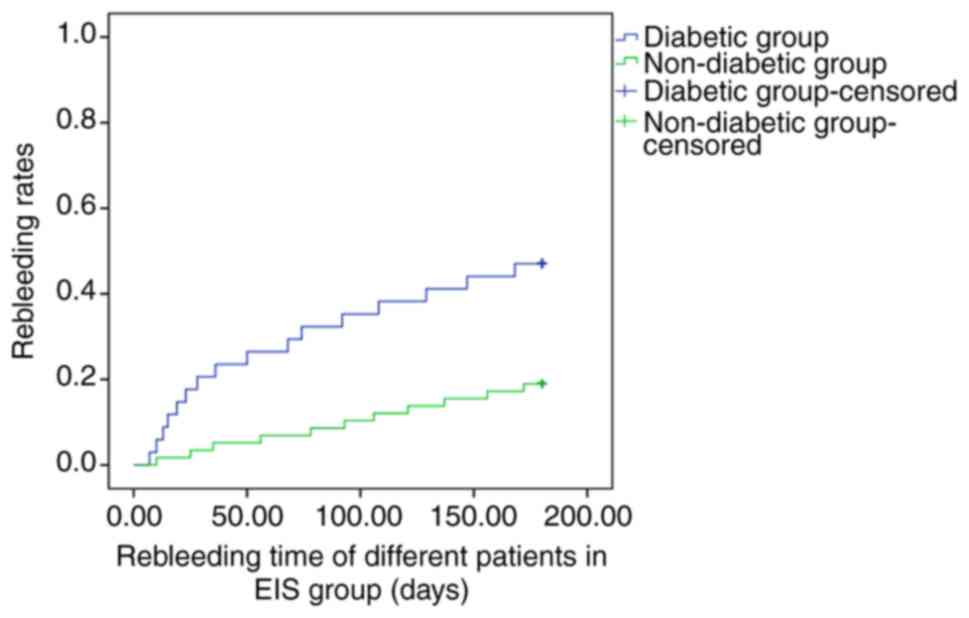 |
Figure 4
|
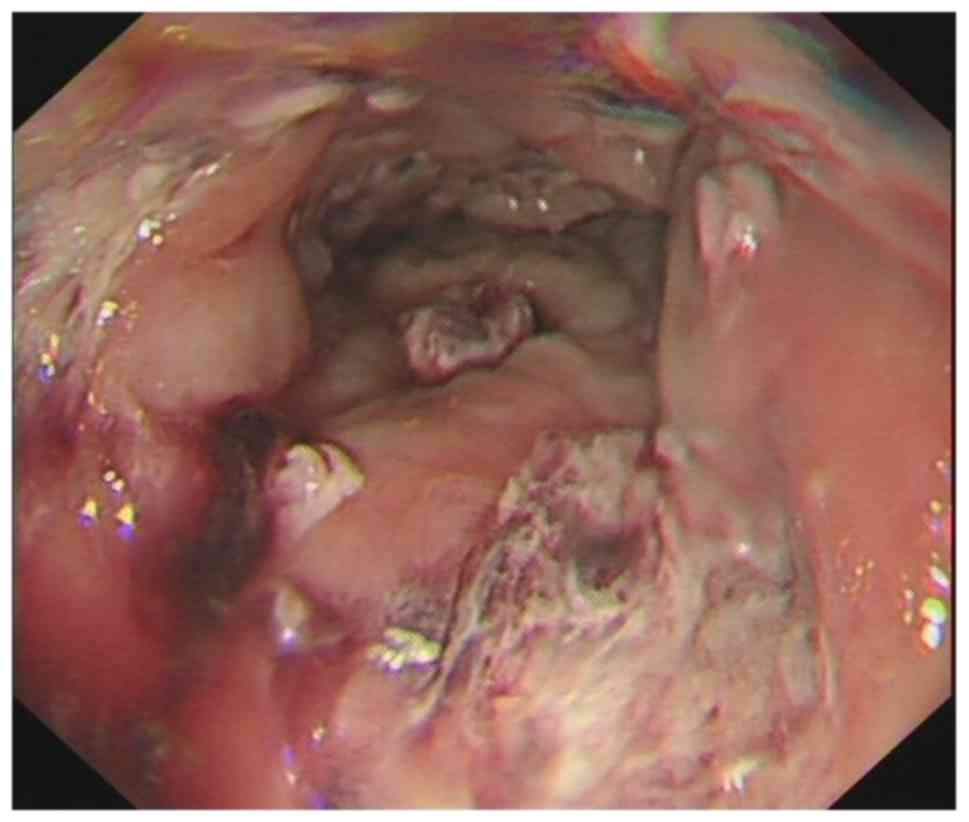 |
Figure 5
|
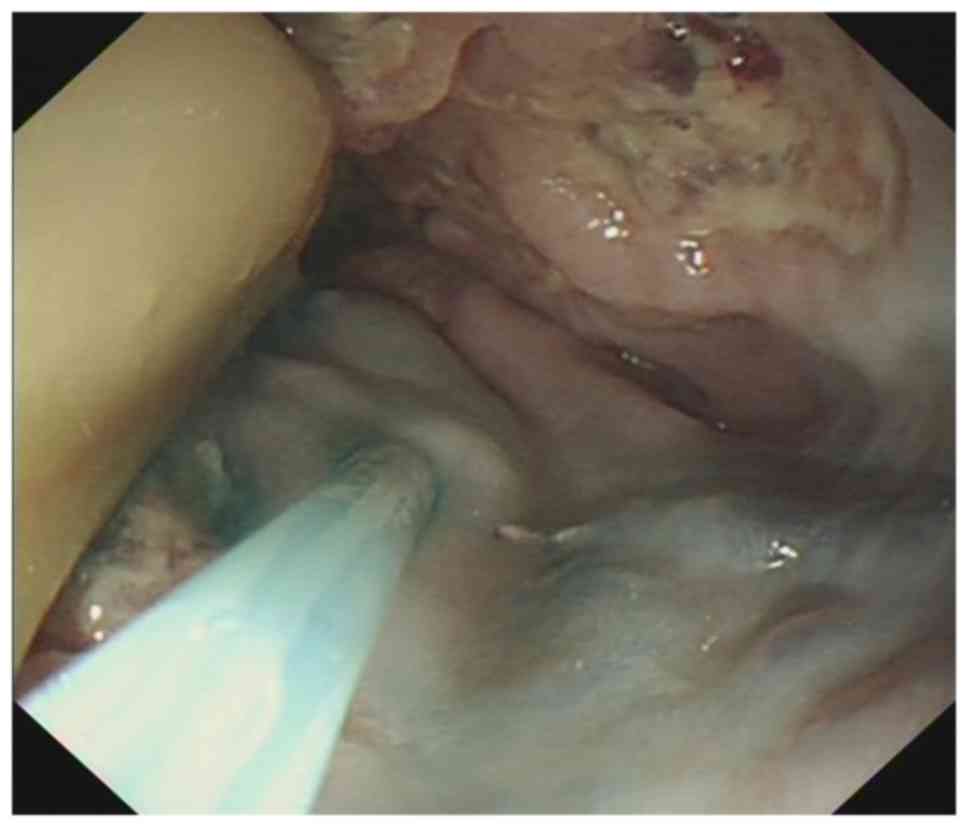 |
Figure 6
|
View References
|
1
|
Kumar S, Asrani SK and Kamath PS:
Epidemiology, diagnosis and early patient management of
esophagogastric hemorrhage. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
43:765–782. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ali SM, Wu S, Xu H, Liu H, Hao J and Qin
C: A prospective study of endoscopic injection sclerotherapy and
endoscopic variceal ligation in the treatment of esophageal
varices. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 27:333–341.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zargar SA, Javid G, Khan BA, Shah OJ,
Yattoo GN, Shah AH, Gulzar GM, Singh J, Shah NA and Shafi HM:
Endoscopic ligation vs. sclerotherapy in adults with extrahepatic
portal venous obstruction: A prospective randomized study.
Gastrointest Endosc. 61:58–66. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A
and Bosch J: Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk
stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance
by the American Association for the study of liver diseases.
Hepatology. 65:310–335. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu L, Ji F, Xu QW and Zhang MQ: Risk
factors for predicting early variceal rebleeding after endoscopic
variceal ligation. World J Gastroenterol. 17:3347–3352.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nishida T, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Arimitsu S,
Haruna Y, Imano E, Suzuki M, Kanda T, Kawano S, Hiramatsu N, et al:
Oral glucose tolerance test predicts prognosis of patients with
liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 101:70–75. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hickman IJ and Macdonald GA: Impact of
diabetes on the severity of liver disease. Am J Med. 120:829–834.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Quintana JO, García-Compean D, González
JA, Pérez JZ, González FJ, Espinosa LE, Hernández PL, Cabello ER,
Villarreal ER, Rendón RF and Garza HM: The impact of diabetes
mellitus in mortality of patients with compensated liver
cirrhosis-a prospective study. Ann Hepatol. 10:56–62.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi X, Peng Y, Li H, Dai J and Guo X:
Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of in-hospital
mortality in liver cirrhosis with acute upper gastrointestinal
bleeding. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:476–477. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bai Z, Li B, Lin S, Liu B, Li Y, Zhu Q, Wu
Y, Yang Y, Tang S, Meng F, et al: Development and validation of
CAGIB score for evaluating the prognosis of cirrhosis with acute
gastrointestinal bleeding: A retrospective multicenter study. Adv
Ther. 36:3211–3220. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Khangholi S, Majid FA, Berwary NJ, Ahmad F
and Aziz RB: The mechanisms of inhibition of advanced glycation end
products formation through polyphenols in hyperglycemic condition.
Planta Med. 82:32–45. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tian M, Qing C, Niu Y, Dong J, Cao X, Song
F, Ji X and Lu S: The relationship between inflammation and
impaired wound healing in a diabetic rat burn model. J Burn Care
Res. 37:e115–e124. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
García-Compeán D, Jáquez-Quintana JO,
González-González JA, Lavalle-González FJ, Villarreal-Pérez JZ and
Maldonado-Garza HJ: Diabetes in liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 36:473–482. 2013.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gundling F, Schepp W and Schumm-Draeger
PM: Hepatogenous diabetes in cirrhosis: Academic sport or a
neglected disease? Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 120:469–471.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hunter SS and Hamdy S: Predictors of early
re-bleeding and mortality after acute variceal haemorrhage. Arab J
Gastroenterol. 14:63–67. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|




















