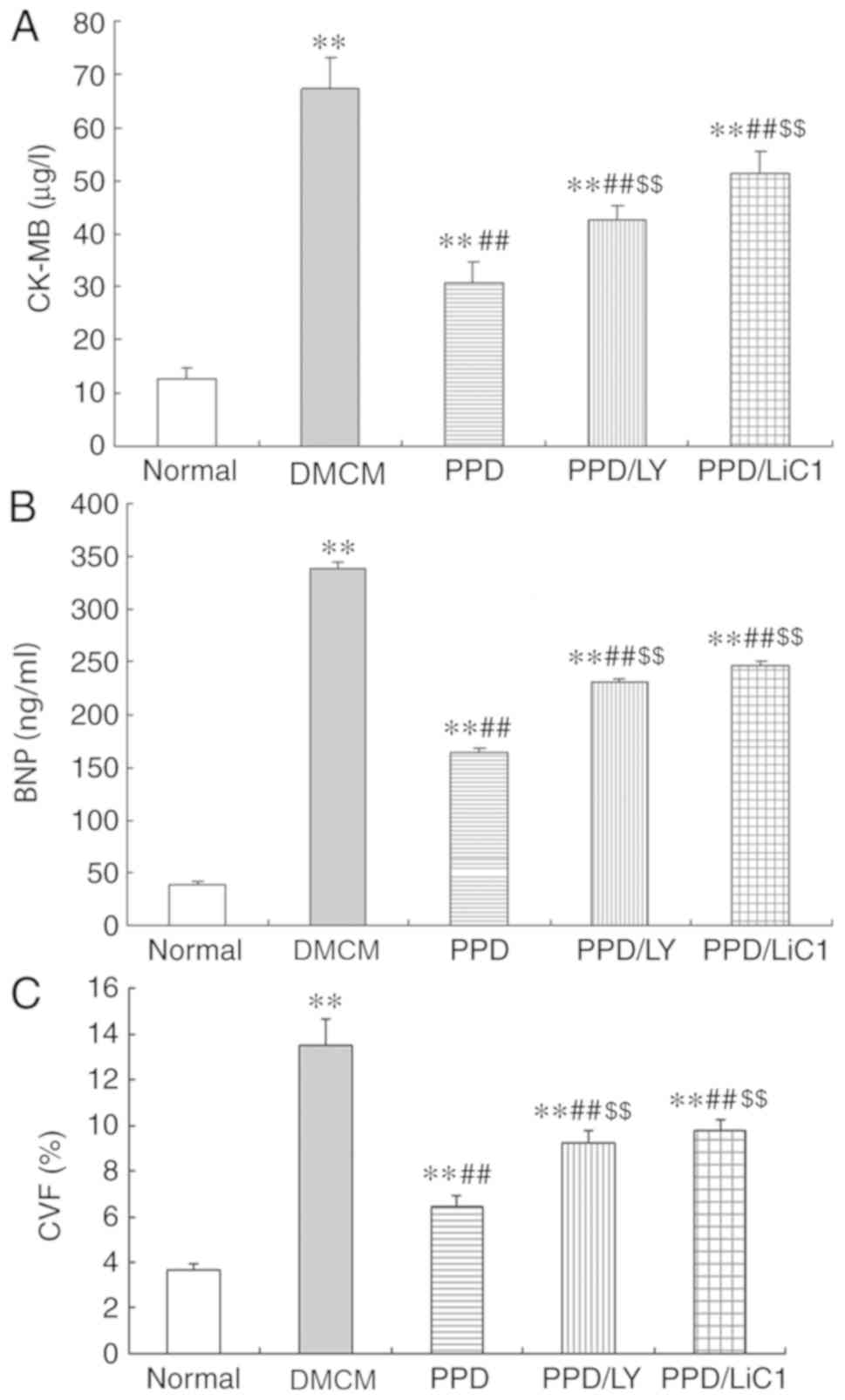
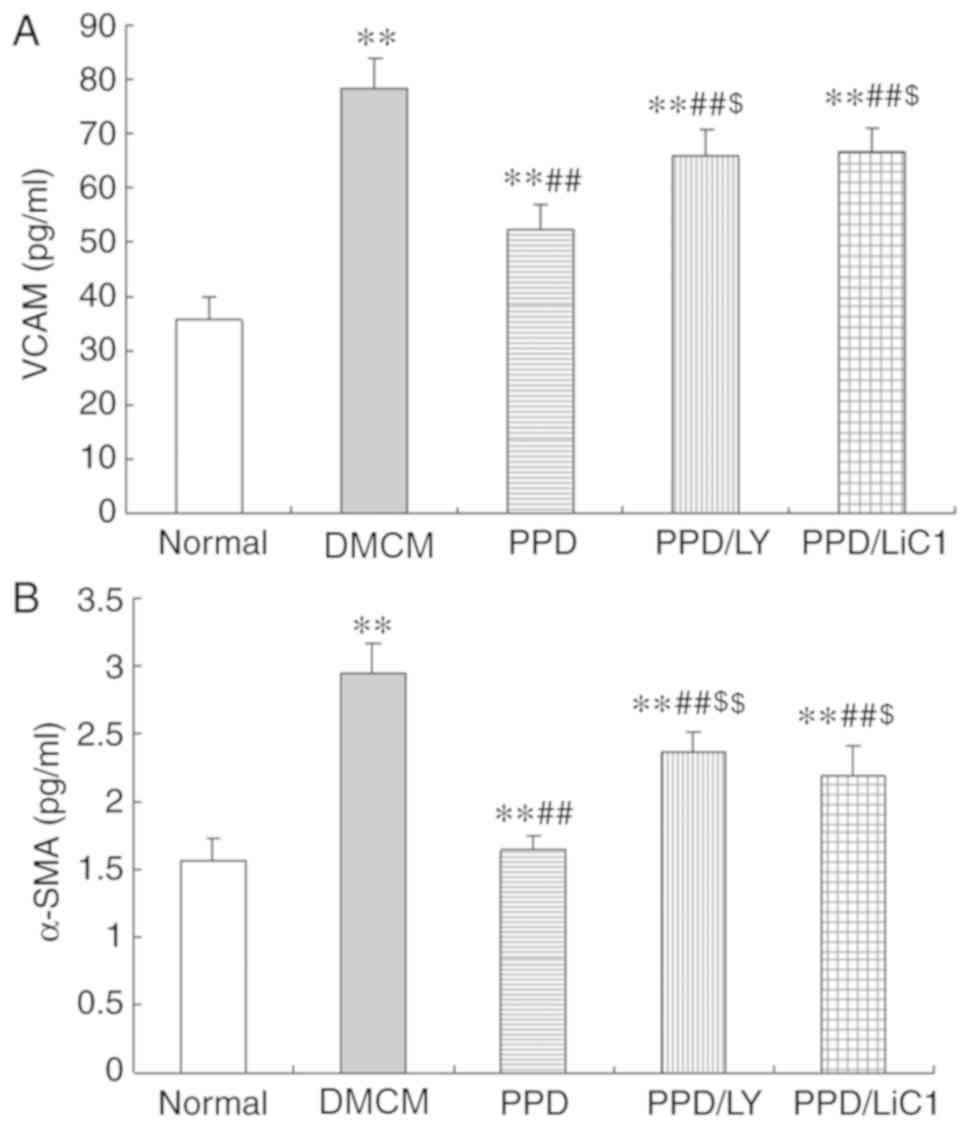
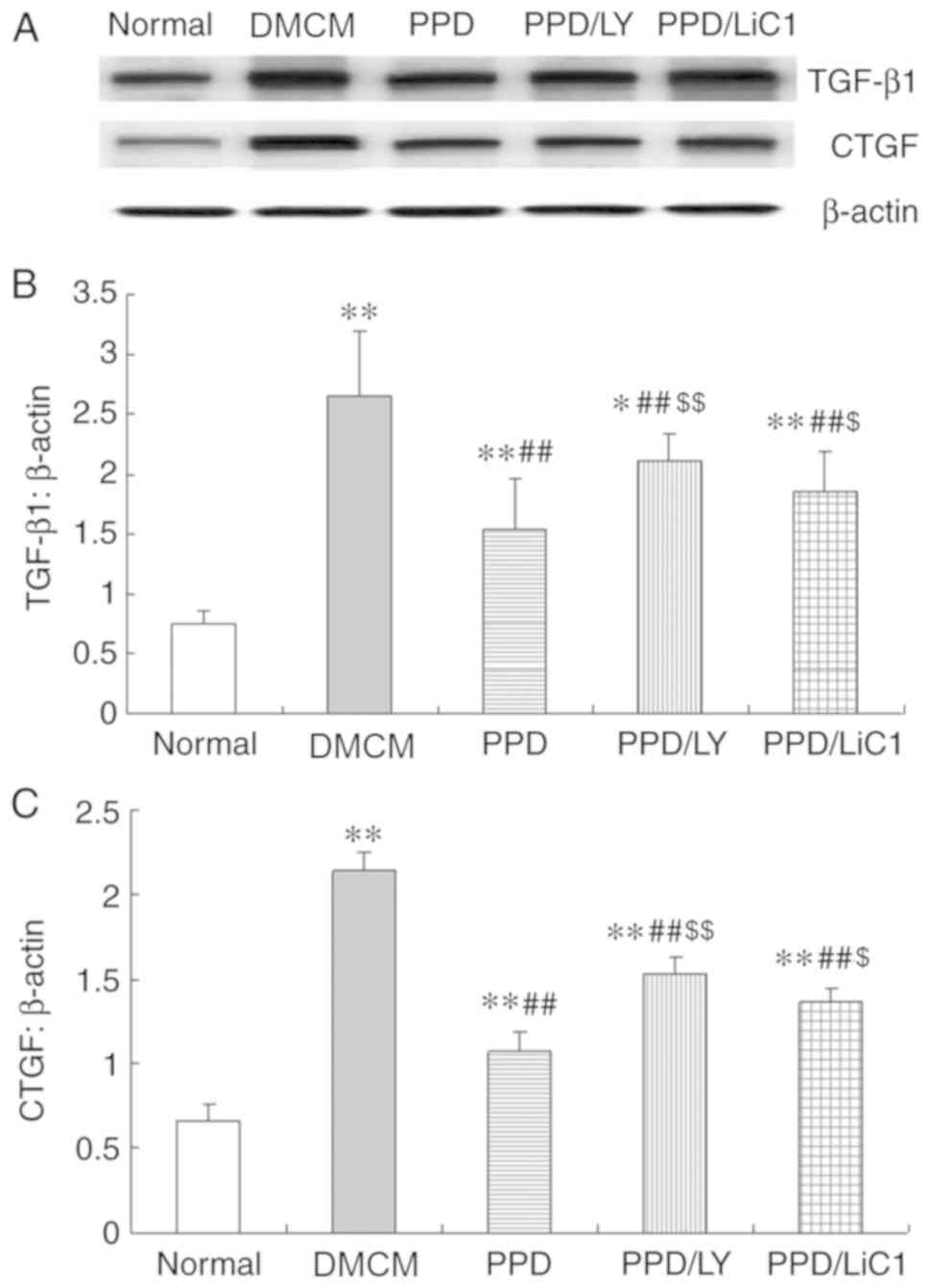
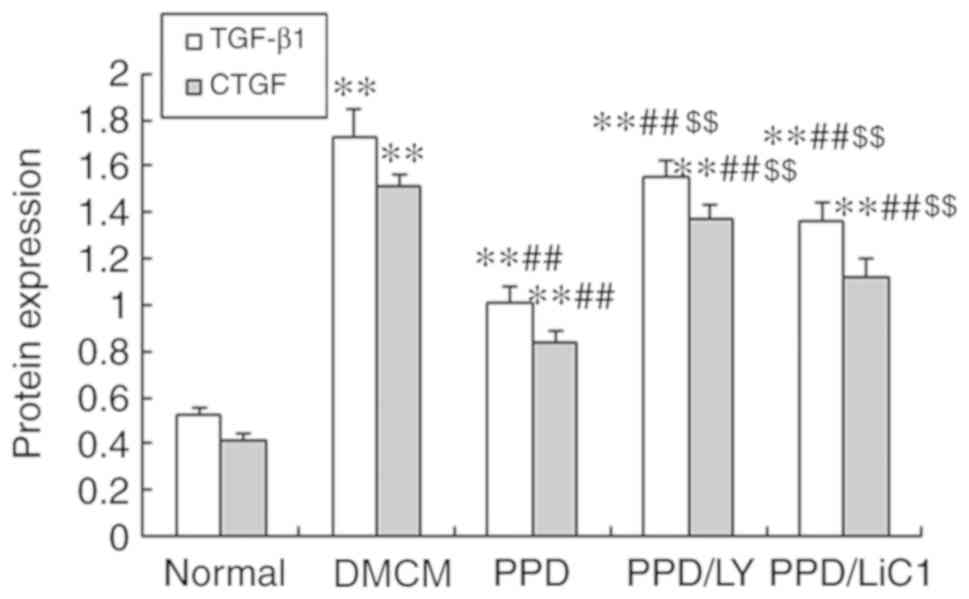
|
1
|
Gregg EW, Cheng YJ, Srinivasan M, Lin J,
Geiss LS, Albright AL and Imperatore G: Trends in cause-specific
mortality among adults with and without diagnosed diabetes in the
USA: An epidemiological analysis of linked national survey and
vital statistics data. Lancet. 16:2430–2440. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jun JE, Lee SE, Choi MS, Park SW, Hwang YC
and Kim JH: Clinical factors associated with the recovery of
cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 18:29–30. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mahajan UB, Chandrayan G, Patil CR, Arya
DS, Suchal K, Agrawal Y, Ojha S and Goyal SN: Eplerenone attenuates
myocardial infarction in diabetic rats via modulation of the
PI3K-Akt pathway and phosphorylation of GSK-3β. Am J Transl Res.
10:2810–2821. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hölscher ME, Bode C and Bugger H: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: Does the type of diabetes matter? Int J Mol Sci.
17(2136)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Furuya F, Ishii T and Kitamura K: Chronic
inflammation and progression of diabetic kidney disease. Contrib
Nephrol. 198:33–39. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lombardi C, Spigoni V, Gorga E and Dei Cas
A: Novel insight into the dangerous connection between diabetes and
heart failure. Herz. 41:201–207. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huber SA: Viral myocarditis and dilated
cardiomyopathy: Etiology and pathogenesis. Curr Pharm Des.
22:408–426. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yoshida Y, Boren SA, Soares J, Popescu M,
Nielson SD, Koopman RJ, Kennedy DR and Simoes EJ: Effect of health
information technologies on cardiovascular risk factors among
patients with diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 19(28)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Guo X, Xue M, Li CJ, Yang W, Wang SS, Ma
ZJ, Zhang XN, Wang XY, Zhao R and Chang BC: Protective effects of
triptolide on TLR4 mediated autoimmune and inflammatory response
induced myocardial fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J
Ethnopharmacol. 193:333–344. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kitamura K, Takamura Y, Iwamoto T, Nomura
M, Iwasaki H, Ohdera M, Murakoshi M, Sugiyama K, Matsuyama K,
Manabe Y, et al: Dammarane-type triterpene extracts of Panax
notoginseng root ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity
by enhancing glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 81:335–342. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hu S, Liu T, Wu Y, Yang W, Hu S, Sun Z, Li
P1 and Du S: Panax notoginseng saponins suppress
lipopolysaccharide-induced barrier disruption and monocyte adhesion
on bEnd.3 cells via the opposite modulation of Nrf2 antioxidant and
NF-κB inflammatory pathways. Phytother Res. 33:3163–3176.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jin X, Luo Y, Chen Y, Ma Y, Yue P and Yang
M: Novel breviscapine nanocrystals modified by panax notoginseng
saponins for enhancing bioavailability and synergistic
anti-platelet aggregation effect. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.
175:333–342. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yu J, Liu C, Li Z, Zhang C, Wang Z and Liu
X: Inhibitory effects and mechanism of 25-OH-PPD on glomerular
mesangial cell proliferation induced by high glucose. Environ
Toxicol Pharmacol. 44:93–98. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shi X, Yu W, Yang T, Qiu S, Yao C, Feng Z,
Wei W, Wu W and Guo D: Panax notoginseng saponins provide
neuroprotection by regulating NgR1/RhoA/ROCK2 pathway expression,
in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 190:301–312.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Liu C, Li J, Zhang X, Song F and Xu
J: Urocortin attenuates myocardial fibrosis in diabetic rats via
the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Endocr Res. 41:148–157.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xie W, Meng X, Zhai Y, Zhou P, Ye T, Wang
Z, Sun G and Sun X: Panax notoginseng saponins: A review of its
mechanisms of antidepressant or anxiolytic effects and network
analysis on phytochemistry and pharmacology. Molecules.
17(940)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Loh YC, Tan CS, Ch'ng YS, Ng CH, Yeap ZQ
and Yam MF: Mechanisms of action of Panax notoginseng ethanolic
extract for its vasodilatory effects and partial characterization
of vasoactive compounds. Hypertens Res. 42:182–194. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chan YS, Wong JH and Ng TB: Bioactive
proteins in Panax notoginseng roots and other panax species. Curr
Protein Pept Sci. 20:231–239. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yin Z, Ma L, Xu J, Xia J and Luo D:
Pustular drug eruption due to Panax notoginseng saponins. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 16:957–961. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Joubert M, Manrique A, Cariou B and Prieur
X: Diabetes-related cardiomyopathy: The sweet story of glucose
overload from epidemiology to cellular pathways. Diabetes Metab.
45:238–247. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Guo X, Sun W, Luo G, Xia J and Luo D:
Panax notoginseng saponins alleviate skeletal muscle insulin
resistance by regulating the IRS1-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and
GLUT4 expression. FEBS Open Bio. 9:1008–1019. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ding W, Chang WG, Guo XC, Liu Y, Xiao DD,
Ding D, Wang JX and Zhang XJ: Exenatide protects against cardiac
dysfunction by attenuating oxidative stress in the diabeticmouse
heart. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10(202)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shinde AV, Humeres C and Frangogiannis NG:
The role of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix
contraction and remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:298–309.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guo SJ, Zhang P, Wu LY, Zhang GN, Chen WD
and Gao PJ: Adenovirus-Mediated overexpression of septin 2
attenuates α-Smooth muscle actin expression and adventitial
myofibroblast migration induced by angiotensin II. J Vasc Res.
53:309–316. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sun KH, Chang Y, Reed NI and Sheppard D:
α-Smooth muscle actin is an inconsistent marker of fibroblasts
responsible for force-dependent TGFβ activation or collagen
production across multiple models of organ fibrosis. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 310:L824–L836. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huang H, Zheng F, Dong X, Wu F, Wu T and
Li H: Allicin inhibits tubular epithelial-myofibroblast
transdifferentiation under high glucose conditions in vitro.
Exp Ther Med. 13:254–262. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Chu HR, Guo Y, Liu JH, Li WP, Li
H and Cheng M: The effects and mechanisms of high glucose on the
phenotype transformation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells.
Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 31:458–461. 2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Yu GI, Jun SE and Shin DH: Associations of
VCAM-1 gene polymorphisms with obesity and inflammation markers.
Inflamm Res. 66:217–225. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Weber ZA, Kaur P, Hundal A, Ibriga SH and
Bhatwadekar AD: Effect of the pharmacist-managed cardiovascular
risk reduction services on diabetic retinopathy outcome measures.
Pharm Pract (Granada). 17(1319)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang SQ, Li D and Yuan Y: Long-term
moderate intensity exercise alleviates myocardial fibrosis in type
2 diabetic rats via inhibitions of oxidative stress and TGF-β1/Smad
pathway. J Physiol Sci. 69:861–873. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Abdel-Hamid AAM and Firgany AEL: Favorable
outcomes of metformin on coronary microvasculature in experimental
diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Histol. 49:639–649. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao B, Guan H, Liu JQ, Zheng Z, Zhou Q,
Zhang J, Su LL and Hu DH: Hypoxia drives the transition of human
dermal fibroblasts to a myofibroblast-like phenotype via the
TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 39:153–159. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Zhao L, Jiao FZ, Zhang WB, Chen Q
and Gong ZJ: Histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide
hydroxamic acid alleviates liver fibrosis by suppressing the
transforming growth factor-β1 signal pathway. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 17:423–429. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim KK, Sheppard D and Chapman HA: TGF-β1
Signaling and tissue fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
2(a022293)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen JQ, Guo YS, Chen Q, Cheng XL, Xiang
GJ, Chen MY, Wu HL, Huang QL, Zhu PL and Zhang JC: TGFβ1 and HGF
regulate CTGF expression in human atrial fibroblasts and are
involved in atrial remodelling in patients with rheumatic heart
disease. J Cell Mol Med. 23:3032–3039. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tsai CC, Wu SB, Kau HC and Wei YH:
Essential role of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in
transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-induced myofibroblast
transdifferentiation from Graves' orbital fibroblasts. Sci Rep.
8(7276)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Pan J, Liu D, Zhang M, Li X, Tian
J, Liu M, Jin T and An F: Nicorandil alleviates apoptosis in
diabetic cardiomyopathy through PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
23:5349–5359. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zheng W, Shang X, Zhang C, Gao X, Robinson
B and Liu J: The effects of carvedilol on cardiac function and the
AKT/XIAP signaling pathway in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats.
Cardiology. 136:204–211. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shang L, Pin L, Zhu S, Zhong X, Zhang Y,
Shun M, Liu Y and Hou M: Plantamajoside attenuates
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy associated with the HDAC2
and AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 307:21–28.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang CY, Li XD, Hao ZH and Xu D:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves diabetic cardiomyopathy
through antioxidative and anti-inflammatory processes along with
modulation of Akt/GSK-3β signaling in rats. Korean J Physiol
Pharmacol. 20:613–619. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Liu C, Zhang X, Zhao J and Xu J:
Urocortin ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats via the
Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 9:667–674.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yang Q, Huang DD, Li DG, Chen B, Zhang LM,
Yuan CL and Huang HH: Tetramethylpyrazine exerts a protective
effect against injury from acute myocardial ischemia by regulating
the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
24(17)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|