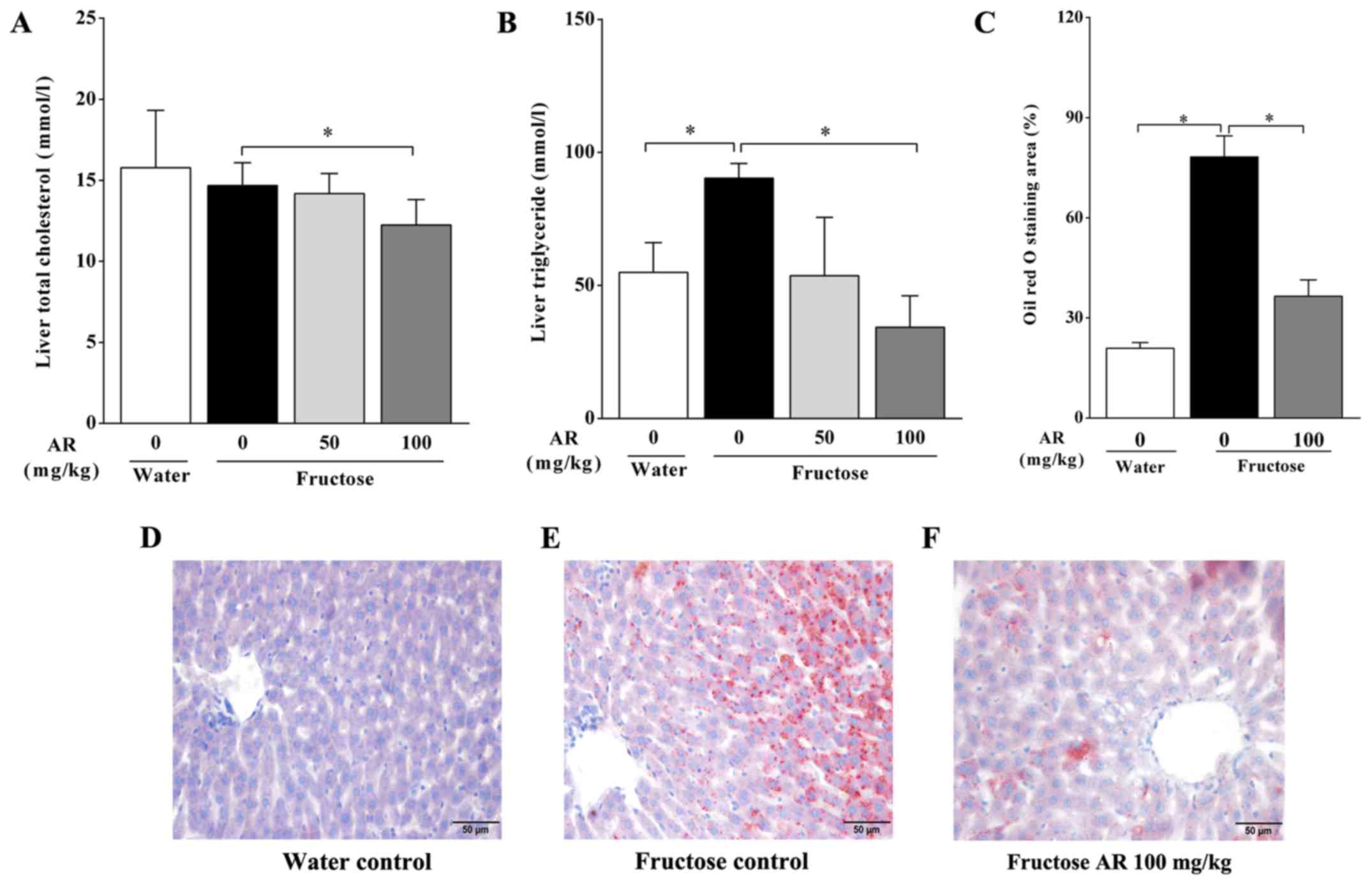
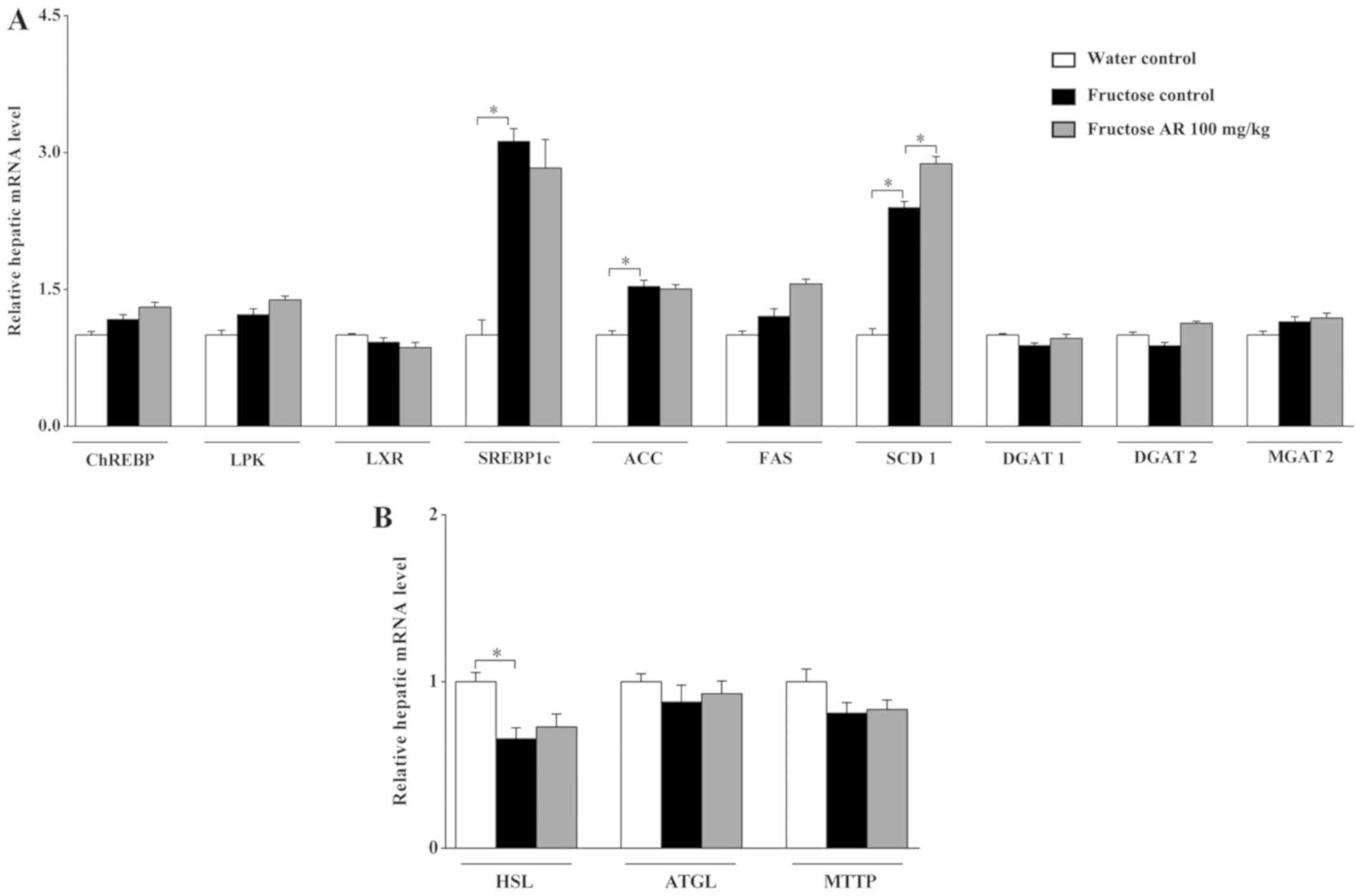
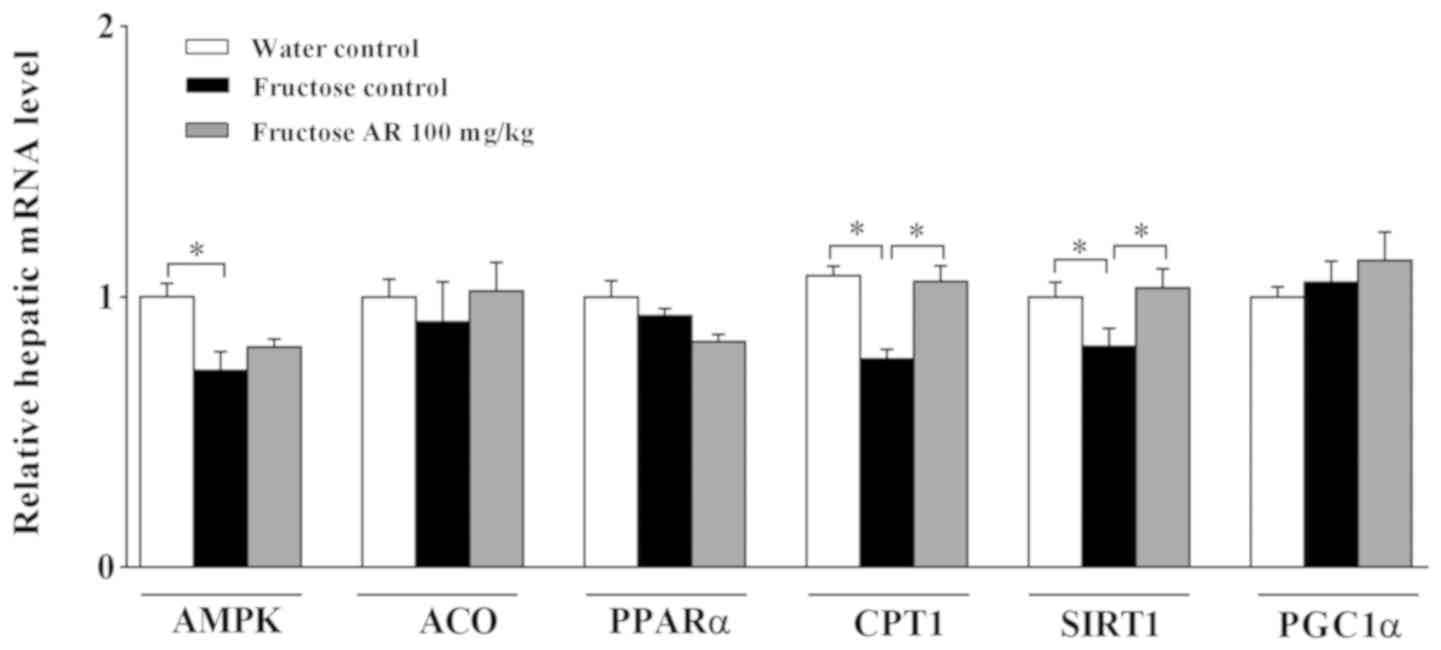
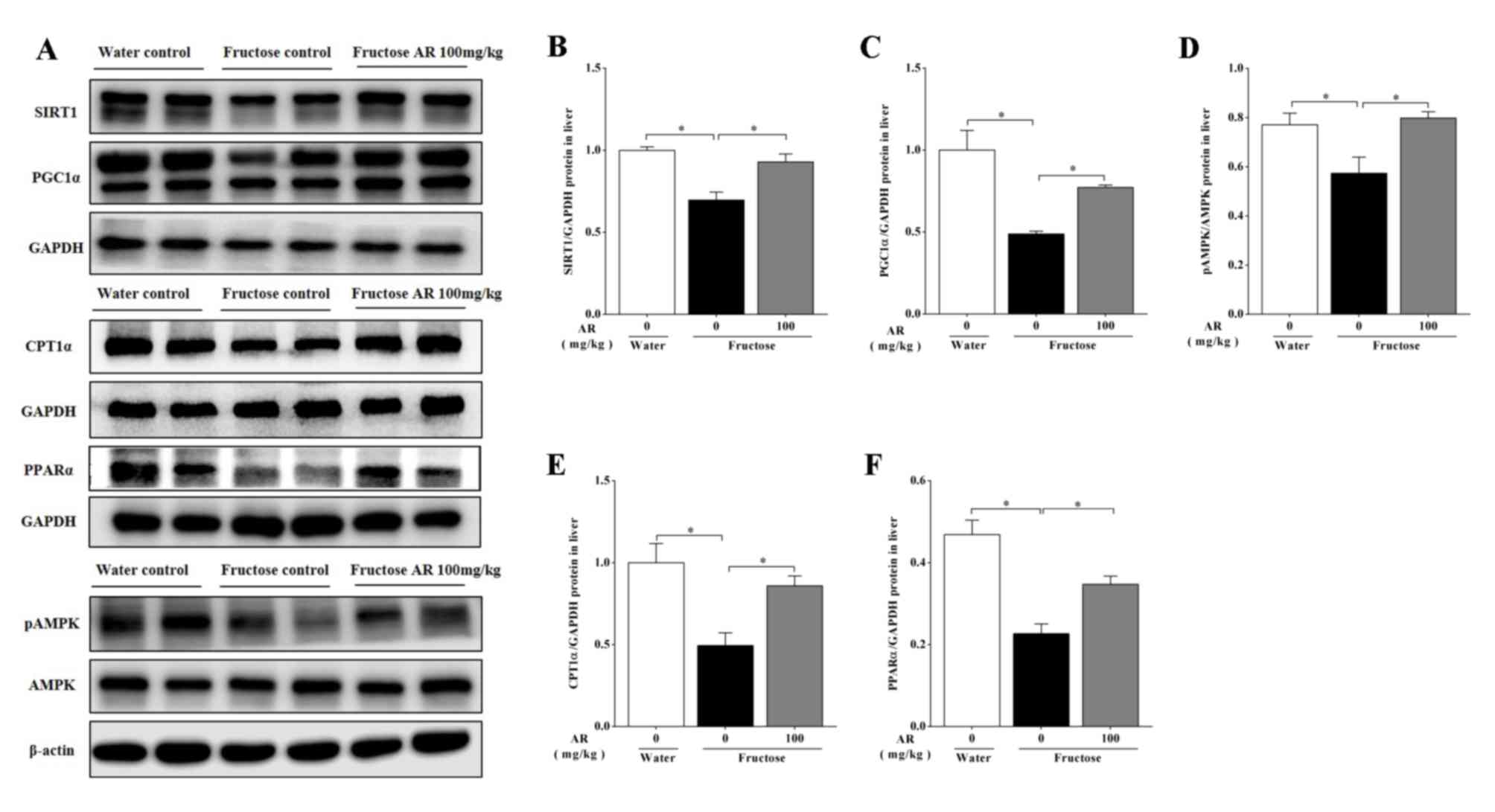
|
1
|
Hassan K, Bhalla V, El Regal ME and
A-Kader HH: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive
review of a growing epidemic. World J Gastroenterol.
20:12082–12101. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray GA, Nielsen SJ and Popkin BM:
Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a
role in the epidemic of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 79:537–543.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Trindade CT, Kurokawa , Cilmery
Barreiros RC, Bossolan and Grasiela : High-fructose
consumption and metabolic diseases. Fructose: Synthesis, Functions
and Health Implications. 37–60. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Kuzma JN, Cromer G, Hagman DK, Breymeyer
KL, Roth CL, Foster-Schubert KE, Holte SE, Weigle DS and Kratz M:
Consuming glucose-sweetened, not fructose-sweetened, beverages
increases fasting insulin in healthy humans. Eur J Clin Nutr.
73:487–490. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Aeberli I, Hochuli M, Gerber PA, Sze L,
Murer SB, Tappy L, Spinas GA and Berneis K: Moderate amounts of
fructose consumption impair insulin sensitivity in healthy young
men: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 36:150–156.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tappy L and Lê KA: Metabolic effects of
fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol Rev.
90:23–46. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
DiNicolantonio JJ, Mehta V, Onkaramurthy N
and O'Keefe JH: Fructose-induced inflammation and increased
cortisol: A new mechanism for how sugar induces visceral adiposity.
Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 61:3–9. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhu L, Baker SS, Liu W, Tao MH, Patel R,
Nowak NJ and Baker RD: Lipid in the livers of adolescents with
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Combined effects of pathways on
steatosis. Metabolism. 60:1001–1011. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kohjima M, Enjoji M, Higuchi N, Kato M,
Kotoh K, Yoshimoto T, Fujino T, Yada M, Yada R, Harada N, et al:
Re-evaluation of fatty acid metabolism-related gene expression in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Med. 20:351–358.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kasper W, ter Horst ID and Mireille J:
Serlie: Fructose consumption, lipogenesis, and non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease. Nutrients. 9(981)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Shimomura I, Bashmakov Y, Ikemoto S,
Horton JD, Brown MS and Goldstein JL: Insulin selectively increases
SREBP-1c mRNA in the livers of rats with streptozotocin-induced
diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:13656–13661. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Filhoulaud G, Guilmeau S, Dentin R, Girard
J and Postic C: Novel insights into ChREBP regulation and function.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 24:257–268. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shimano H, Horton JD, Shimomura I, Hammer
RE, Brown MS and Goldstein JL: Isoform 1c of sterol regulatory
element binding protein is less active than isoform 1a in livers of
transgenic mice and in cultured cells. J Clin Invest. 99:846–854.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Higuchi N, Kato M, Shundo Y, Tajiri H,
Tanaka M, Yamashita N, Kohjima M, Kotoh K, Nakamuta M, Takayanagi
R, et al: Liver X receptor in cooperation with SREBP-1c is a major
lipid synthesis regulator in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Hepatol Res. 38:1122–1129. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xie Z, Li H, Wang K, Lin J, Wang Q, Zhao
G, Jia W and Zhang Q: Analysis of transcriptome and metabolome
profiles alterations in fatty liver induced by high-fat diet in
rat. Metabolism. 59:554–560. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Postic C and Girard J: Contribution of de
novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin
resistance: Lessons from genetically engineered mice. J Clin
Invest. 118:829–838. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ipsen DH, Lykkesfeldt J and Tveden-Nyborg
P: Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:3313–3327.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yamaguchi T, Omatsu N, Matsushita S and
Osumi T: CGI-58 interacts with perilipin and is localized to lipid
droplets. Possible involvement of CGI-58 mislocalization in
Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome. J Biol Chem. 279:30490–30497.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ding J, Li M, Wan X, Jin X, Chen S, Yu C
and Li Y: Effect of miR-34a in regulating steatosis by targeting
PPARα expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep.
5(13729)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Reddy JK and Hashimoto T: Peroxisomal
beta-oxidation and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
alpha: An adaptive metabolic system. Annu Rev Nutr. 21:193–230.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cao Y, Xue Y, Xue L, Jiang X, Wang X,
Zhang Z, Yang J, Lu J, Zhang C, Wang W, et al: Hepatic menin
recruits SIRT1 to control liver steatosis through histone
deacetylation. J Hepatol. 59:1299–1306. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xu F, Gao Z, Zhang J, Rivera CA, Yin J,
Weng J and Ye J: Lack of SIRT1 (Mammalian Sirtuin 1) activity leads
to liver steatosis in the SIRT1+/- mice: A role of lipid
mobilization and inflammation. Endocrinology. 151:2504–2514.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hernández-Rodas MC, Valenzuela R,
Echeverría F, Rincón-Cervera MÁ, Espinosa A, Illesca P, Muñoz P,
Corbari A, Romero N, Gonzalez-Mañan D, et al: Supplementation with
docosahexaenoic acid and extra virgin olive oil prevents liver
steatosis induced by a high-fat diet in mice through PPAR-α and
Nrf2 upregulation with concomitant SREBP-1c and NF-κB
downregulation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 61(61)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Valenzuela R, Illesca P, Echeverría F,
Espinosa A, Rincón-Cervera MÁ, Ortiz M, Hernandez-Rodas MC,
Valenzuela A and Videla LA: Molecular adaptations underlying the
beneficial effects of hydroxytyrosol in the pathogenic alterations
induced by a high-fat diet in mouse liver: PPAR-α and Nrf2
activation, and NF-κB down-regulation. Food Funct. 8:1526–1537.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Munteanu MA, Nagy GA and Mircea PA:
Current management of NAFLD. Clujul Med. 89:19–23. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li S, Xu Y, Guo W, Chen F, Zhang C, Tan
HY, Wang N and Feng Y: The impacts of herbal medicines and natural
products on regulating the hepatic lipid metabolism. Front
Pharmacol. 11(351)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kammerer DR, Kammerer J, Valet R and Carle
R: Recovery of polyphenols from the by-products of plant food
processing and application as valuable food ingredients. Food Res
Int. 65:2–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hyson DA: A comprehensive review of apples
and apple components and their relationship to human health. Adv
Nutr. 2:408–420. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bhushan S, Kalia K, Sharma M, Singh B and
Ahuja PS: Processing of apple pomace for bioactive molecules. Crit
Rev Biotechnol. 28:285–296. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Skinner RC, Warren DC, Lateef SN, Benedito
VA and Tou JC: Apple pomace consumption favorably alters hepatic
lipid metabolism in young female Sprague-Dawley rats fed a western
diet. Nutrients. 10(10)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cho KD, Han CK and Lee BH: Loss of body
weight and fat and improved lipid profiles in obese rats fed apple
pomace or apple juice concentrate. J Med Food. 16:823–830.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jeong JW, Shim JJ, Choi ID, Kim SH, Ra J,
Ku HK, Lee DE, Kim TY, Jeung W, Lee JH, et al: Apple pomace extract
improves endurance in exercise performance by increasing strength
and weight of skeletal muscle. J Med Food. 18:1380–1386.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Makarova E, Górnaś P, Konrade I, Tirzite
D, Cirule H, Gulbe A, Pugajeva I, Seglina D and Dambrova M: Acute
anti-hyperglycaemic effects of an unripe apple preparation
containing phlorizin in healthy volunteers: A preliminary study. J
Sci Food Agric. 95:560–568. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bakirel T, Bakirel U, Keleş OU, Ulgen SG
and Yardibi H: In vivo assessment of antidiabetic and antioxidant
activities of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) in
alloxan-diabetic rabbits. J Ethnopharmacol. 116:64–73. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nazem F, Farhangi N and Neshat-Gharamaleki
M: Beneficial effects of endurance exercise with Rosmarinus
officinalis Labiatae leaves extract on blood antioxidant enzyme
activities and lipid peroxidation in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Can J Diabetes. 39:229–234. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ramadan KS, Khalil OA, Danial EN, Alnahdi
HS and Ayaz NO: Hypoglycemic and hepatoprotective activity of
Rosmarinus officinalis extract in diabetic rats. J Physiol
Biochem. 69:779–783. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jäger S, Trojan H, Kopp T, Laszczyk MN and
Scheffler A: Pentacyclic triterpene distribution in various plants
- rich sources for a new group of multi-potent plant extracts.
Molecules. 14:2016–2031. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ma P, Yao L, Lin X, Gu T, Rong X, Batey R,
Yamahara J, Wang J and Li Y: A mixture of apple pomace and rosemary
extract improves fructose consumption-induced insulin resistance in
rats: Modulation of sarcolemmal CD36 and glucose transporter-4. Am
J Transl Res. 8:3791–3801. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao H, Guan T, Li C, Zuo G, Yamahara J,
Wang J and Li Y: Treatment with ginger ameliorates fructose-induced
fatty liver and hypertriglyceridemia in rats: Modulation of the
hepatic carbohydrate response element-binding pro-tein-mediated
pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012(570948)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu C and Li Y, Zuo G, Xu W, Gao H, Yang
Y, Yamahara J, Wang J and Li Y: Oleanolic acid diminishes liquid
fructose-induced fatty liver in rats: role of modulation of hepatic
sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c-mediated expression of
genes responsible for de novo fatty acid synthesis. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013(534084)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang J, Gao H, Ke D, Zuo G, Yang Y,
Yamahara J and Li Y: Improvement of liquid fructose-induced adipose
tissue insulin resistance by ginger treatment in rats is associated
with suppression of adipose macrophage-related proinflammatory
cytokines. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013(590376)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li Y, Wang J, Gu T, Yamahara J and Li Y:
Oleanolic acid supplement attenuates liquid fructose-induced
adipose tissue insulin resistance through the insulin receptor
substrate-1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in
rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 277:155–163. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Xing X, Li D, Chen D, Zhou L, Chonan R,
Yamahara J, Wang J and Li Y: Mangiferin treatment inhibits hepatic
expression of acyl-coenzyme A: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase-2 in
fructose-fed spontaneously hypertensive rats: a link to
amelioration of fatty liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 280:207–215.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Villena JA, Roy S, Sarkadi-Nagy E, Kim KH
and Sul HS: Desnutrin, an adipocyte gene encoding a novel patatin
domain-containing protein, is induced by fasting and
glucocorticoids: Ectopic expression of desnutrin increases
triglyceride hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 279:47066–47075.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
van Rijn JM, Ardy RC, Kuloğlu Z, Härter B,
van Haaften-Visser DY, van der Doef HP, van Hoesel M, Kansu A, van
Vugt AH, Thian M, et al: Intestinal failure and aberrant lipid
metabolism in patients with DGAT1 deficiency. Gastroenterology.
155(130-143.e15)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kraus-Friedmann N and Feng L: The role of
intracellular Ca2+ in the regulation of gluconeogenesis.
Metabolism. 45:389–403. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Horton JD, Bashmakov Y, Shimomura I and
Shimano H: Regulation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins
in livers of fasted and refed mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:5987–5992. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Vasiljević A, Bursać B, Djordjevic A,
Milutinović DV, Nikolić M, Matić G and Veličković N: Hepatic
inflammation induced by high-fructose diet is associated with
altered 11βHSD1 expression in the liver of Wistar rats. Eur J Nutr.
53:1393–1402. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mary C Sugden, Paul W Caton and Mark J
Holness: PPAR control: It's SIRTainly as easy as PGC. J Endocrinol.
204:93–104. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lee WJ, Kim M, Park HS, Kim HS, Jeon MJ,
Oh KS, Koh EH, Won JC, Kim MS, Oh GT, et al: AMPK activation
increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle by activating
PPARalpha and PGC-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 340:291–295.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Haigis MC and Sinclair DA: Mammalian
sirtuins: Biological insights and disease relevance. Annu Rev
Pathol. 5:253–295. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hall JA, Dominy JE, Lee Y and Puigserver
P: The sirtuin family's role in aging and age-associated
pathologies. J Clin Invest. 123:973–979. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Houtkooper RH, Cantó C, Wanders RJ and
Auwerx J: The secret life of NAD+: An old metabolite
controlling new metabolic signaling pathways. Endocr Rev.
31:194–223. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Michishita E, Park JY, Burneskis JM,
Barrett JC and Horikawa I: Evolutionarily conserved and
nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT
proteins. Mol Biol Cell. 16:4623–4635. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Verdin E, Hirschey MD, Finley LW and
Haigis MC: Sirtuin regulation of mitochondria: Energy production,
apoptosis, and signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 35:669–675.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Gariani K, Menzies KJ, Ryu D, Wegner CJ,
Wang X, Ropelle ER, Moullan N, Zhang H, Perino A, Lemos V, et al:
Eliciting the mitochondrial unfolded protein response by
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide repletion reverses fatty liver
disease in mice. Hepatology. 63:1190–1204. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Cantó C, Menzies KJ and Auwerx J: NAD(+)
metabolism and the control of energy homeostasis: A balancing act
between mitochondria and the nucleus. Cell Metab. 22:31–53. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ruan Q, Ruan J, Zhang W, Qian F and Yu Z:
Targeting NAD+ degradation: The therapeutic potential of
flavonoids for Alzheimer's disease and cognitive frailty. Pharmacol
Res. 128:345–358. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Echeverría F, Valenzuela R, Bustamante A,
Álvarez D, Ortiz M, Espinosa A, Illesca P, Gonzalez-Mañan D and
Videla LA: High-fat diet induces mouse liver steatosis with a
concomitant decline in energy metabolism: Attenuation by
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) or hydroxytyrosol (HT) supplementation
and the additive effects upon EPA and HT co-administration. Food
Funct. 10:6170–6183. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Jäger S, Handschin C, St-Pierre J and
Spiegelman BM: AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) action in
skeletal muscle via direct phosphorylation of PGC-1alpha. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:12017–12022. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Wahli W and Michalik L: PPARs at the
crossroads of lipid signaling and inflammation. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 23:351–363. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Alcendor RR, Gao S, Zhai P, Zablocki D,
Holle E, Yu X, Tian B, Wagner T, Vatner SF and Sadoshima J: Sirt1
regulates aging and resistance to oxidative stress in the heart.
Circ Res. 100:1512–1521. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wan X, Wen JJ, Koo SJ, Liang LY and Garg
NJ: SIRT1-PGC1α-NFκB Pathway of oxidative and inflammatory stress
during Trypanosoma cruzi infection: Benefits of
SIRT1-targeted therapy in improving heart function in chagas
disease. PLoS Pathog. 12(e1005954)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Köhler UA, Böhm F, Rolfs F, Egger M,
Hornemann T, Pasparakis M, Weber A and Werner S: NF-κB/RelA and
Nrf2 cooperate to maintain hepatocyte integrity and to prevent
development of hepatocellular adenoma. J Hepatol. 64:94–102.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Bayram B, Ozcelik B, Grimm S, Roeder T,
Schrader C, Ernst IM, Wagner AE, Grune T, Frank J and Rimbach G: A
diet rich in olive oil phenolics reduces oxidative stress in the
heart of SAMP8 mice by induction of Nrf2-dependent gene expression.
Rejuvenation Res. 15:71–81. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|