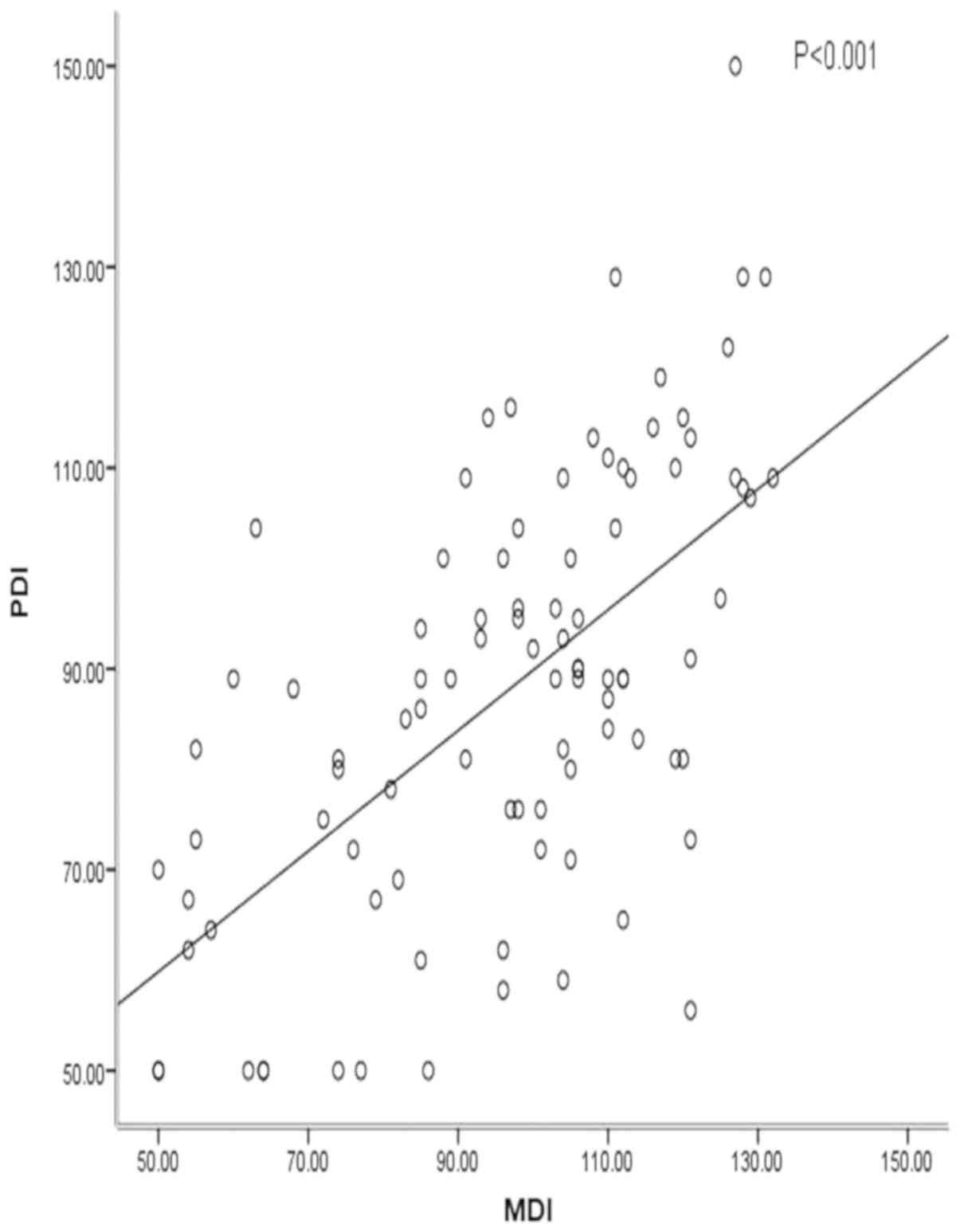
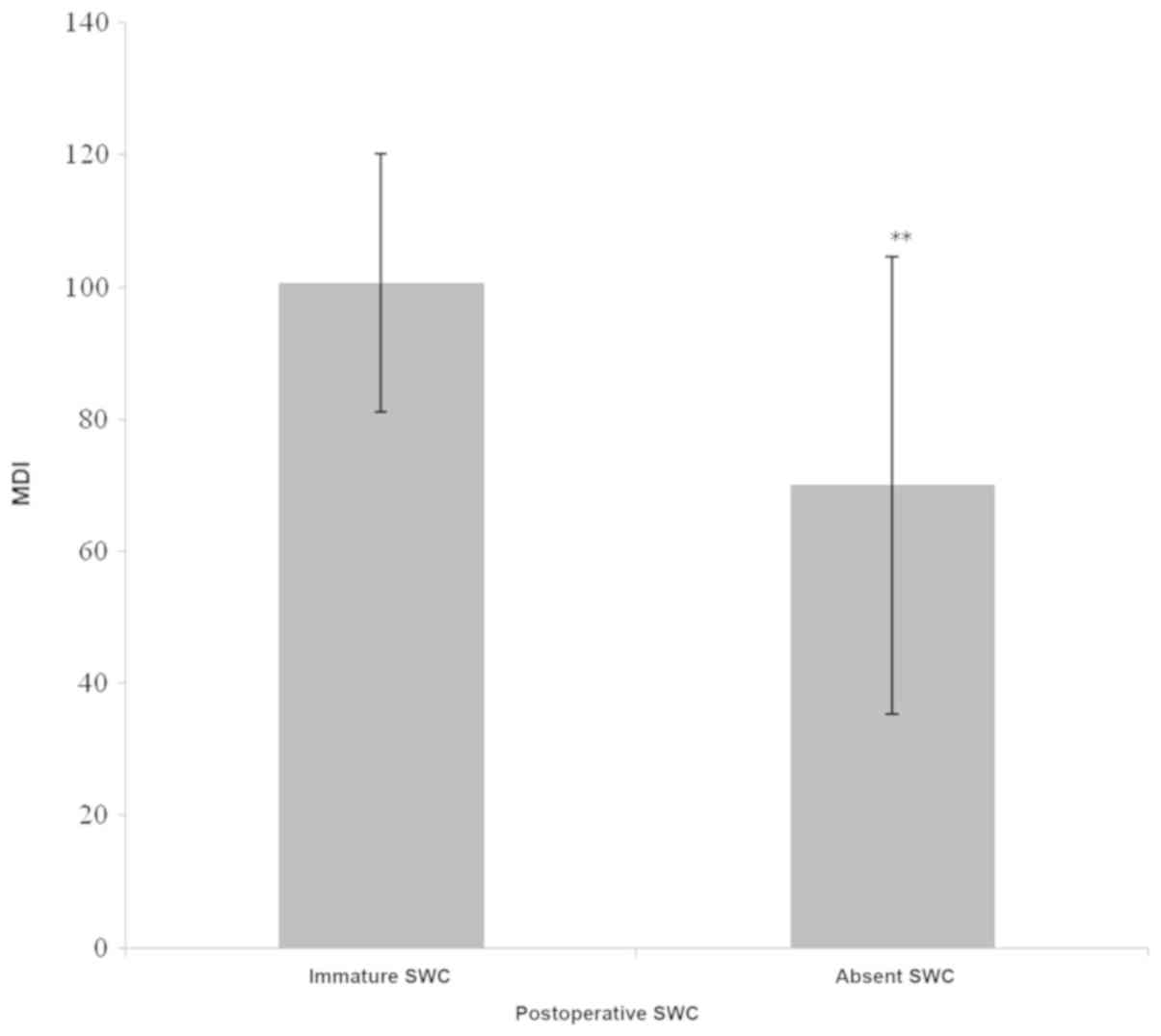
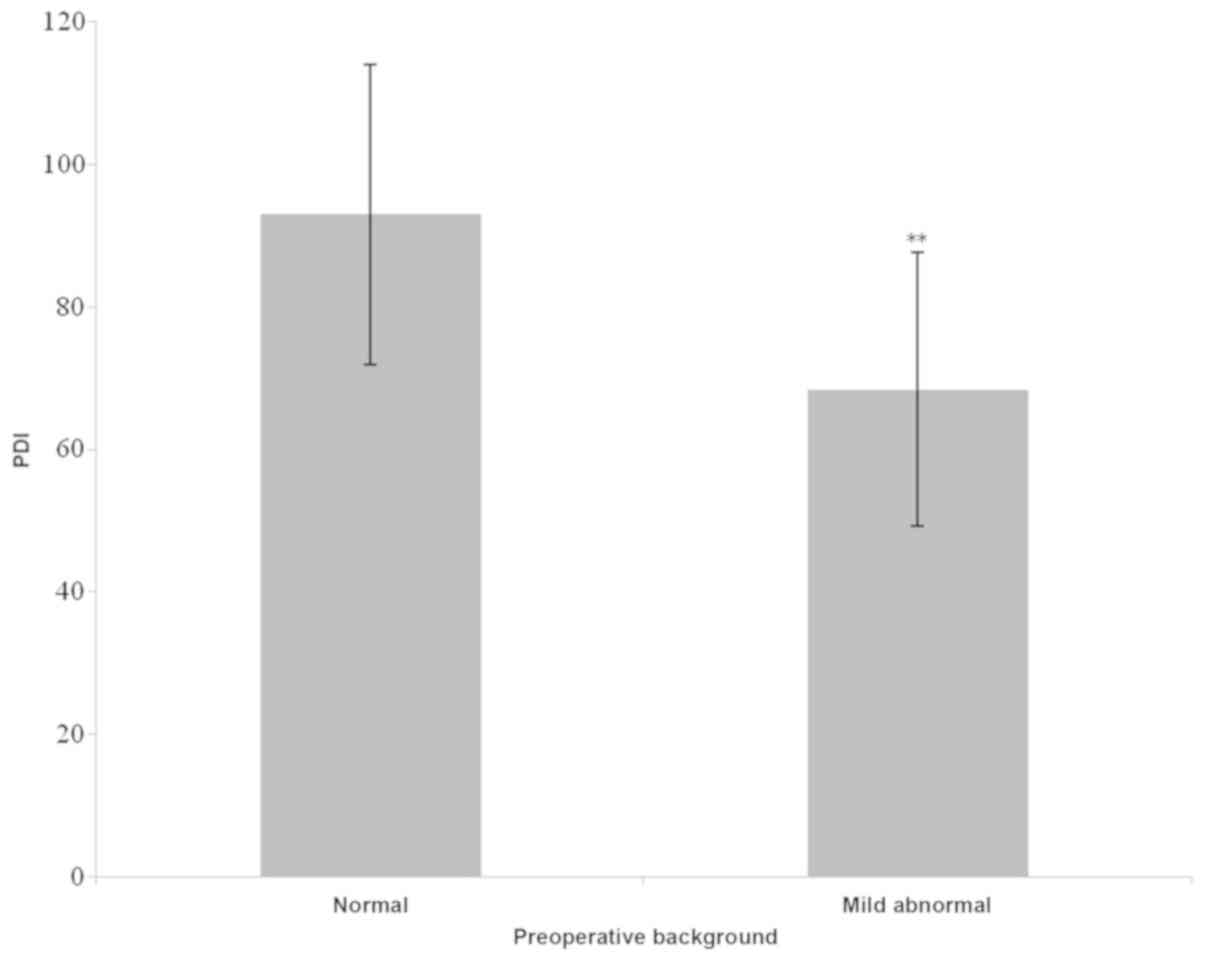
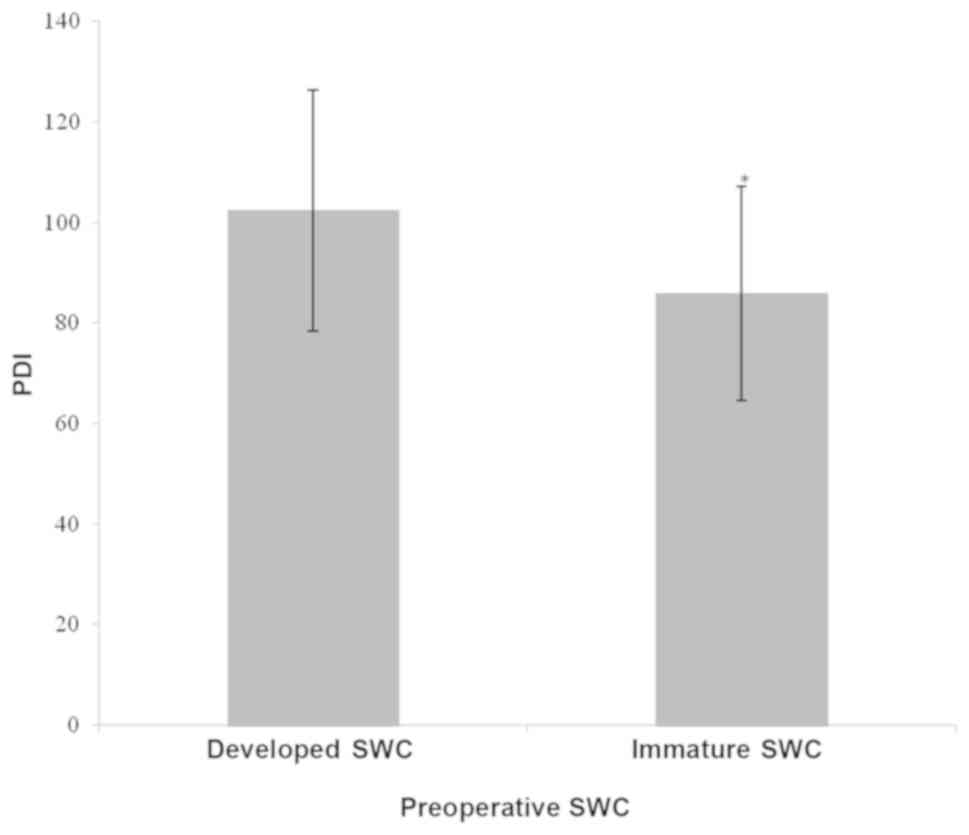
|
1
|
Mandalenakis Z, Rosengren A, Skoglund K,
Lappas G, Eriksson P and Dellborg M: Survivorship in children and
young adults with congenital heart disease in Sweden. JAMA Intern
Med. 177:224–230. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Matthiesen NB, Henriksen TB, Gaynor JW,
Agergaard P, Bach CC, Hjortdal VE and Østergaard JR: Congenital
heart defects and indices of fetal cerebral growth in a nationwide
cohort of 924 422 liveborn infants. Circulation. 133:566–575.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Qu Y, Liu X, Zhuang J, Chen G, Mai J, Guo
X, Ou Y, Chen J, Gong W, Gao X, et al: Incidence of congenital
heart disease: The 9-year experience of the Guangdong registry of
congenital heart disease, China. PLoS One.
11(e0159257)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Massaro AN, El-Dib M, Glass P and Aly H:
Factors associated with adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes in
infants with congenital heart disease. Brain Dev. 30:437–446.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Komur M, Ozen S, Okuyaz C, Makharoblıdze K
and Erdogan S: Neurodevelopment evaluation in children with
congenital hypothyroidism by Bayley-III. Brain Dev. 35:392–397.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kono Y, Yonemoto N, Kusuda S, Hirano S,
Iwata O, Tanaka K and Nakazawa J: Developmental assessment of VLBW
infants at 18 months of age: A comparison study between KSPD and
Bayley III. Brain Dev. 38:377–385. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Luo XR, Yang ZW and Wan GB: National
Collaboration Group. Revision of bailey infant and child
development scale in China (City Edition). Chin J Clin Psychol.
1:71–75. 1993.
|
|
8
|
Massaro AN, Tsuchida T, Kadom N, El-Dib M,
Glass P, Baumgart S and Chang T: aEEG evolution during therapeutic
hypothermia and prediction of NICU outcome in encephalopathic
neonates. Neonatology. 102:197–202. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Davis AS, Gantz MG, Do B, Shankaran S,
Hamrick SE, Kennedy KA, Tyson JE, Chalak LF, Laptook AR, Goldstein
RF, et al: Serial aEEG recordings in a cohort of extremely preterm
infants: Feasibility and safety. J Perinatol. 35:373–378.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fogtmann EP, Plomgaard AM, Greisen G and
Gluud C: Prognostic accuracy of electroencephalograms in preterm
infants: A systematic review. Pediatrics.
139(e20161951)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rakshasbhuvankar A, Paul S, Nagarajan L,
Ghosh S and Rao S: Amplitude-integrated EEG for detection of
neonatal seizures: A systematic review. Seizure. 33:90–98.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gunn JK, Beca J, Hunt RW, Olischar M and
Shekerdemian LS: Perioperative amplitude-integrated EEG and
neurodevelopment in infants with congenital heart disease.
Intensive Care Med. 38:1539–1547. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Homsy J, Zaidi S, Shen Y, Ware JS, Samocha
KE, Karczewski KJ, DePalma SR, McKean D, Wakimoto H, Gorham J, et
al: De novo mutations in congenital heart disease with
neurodevelopmental and other congenital anomalies. Science.
350:1262–1266. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Iliodromiti S, Mackay DF, Smith GC, Pell
JP and Nelson SM: Apgar score and the risk of cause-specific infant
mortality: A population-based cohort study. Lancet. 384:1749–1755.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
O'Brien SM, Clarke DR, Jacobs JP, Jacobs
ML, Lacour-Gayet FG, Pizarro C, Welke KF, Maruszewski B, Tobota Z,
Miller WJ, et al: An empirically based tool for analyzing mortality
associated with congenital heart surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
138:1139–1153. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lacour-Gayet F, Clarke D, Jacobs J, Comas
J, Daebritz S, Daenen W, Gaynor W, Hamilton L, Jacobs M,
Maruszsewski B, et al: The Aristotle score: A complexity-adjusted
method to evaluate surgical results. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
25:911–924. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tekgul H, Bourgeois BF, Gauvreau K and
Bergin AM: Electroencephalography in neonatal seizures: Comparison
of a reduced and a full 10/20 montage. Pediatr Neurol. 32:155–161.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shah NA and Wusthoff CJ: How to use:
Amplitude-integrated EEG (aEEG). Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed.
100:75–81. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
al Naqeeb N, Edwards AD, Cowan FM and
Azzopardi D: Assessment of neonatal encephalopathy by
amplitude-integrated electroencephalography. Pediatrics.
103:1263–1271. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Horst HJ, Mud M, Roofthooft MT and Bos AF:
Amplitude integrated electroencephalographic activity in infants
with congenital heart disease before surgery. Early Hum Dev.
86:759–764. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Fogtmann EP, Plomgaard AM, Greisen G and
Gluud C: Prognostic accuracy of electroencephalograms in preterm
infants: A systematic review. Pediatrics. 139(pii:
e20161951)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Latal B, Wohlrab G, Brotschi B, Beck I,
Knirsch W and Bernet V: Postoperative amplitude-integrated
electroencephalography predicts four-year neurodevelopmental
outcome in children with complex congenital heart disease. J
Pediatr. 178(55-60.e1)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Drury PP, Gunn AJ, Bennet L,
Ganeshalingham A, Finucane K, Buckley D and Beca J: Deep
hypothermic circulatory arrest during the arterial switch operation
is associated with reduction in cerebral oxygen extraction but no
increase in white matter injury. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
146:1327–1333. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Clancy RR, Sharif U, Ichord R, Spray TL,
Nicolson S, Tabbutt S, Wernovsky G and Gaynor JW: Electrographic
neonatal seizures after infant heart surgery. Epilepsia. 46:84–90.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bertholdt S, Latal B, Liamlahi R, Pretre
R, Scheer I, Goetti R, Dave H, Bernet V, Schmitz A, von Rhein M, et
al: Cerebral lesions on magnetic resonance imaging correlate with
preoperative neurological status in neonates undergoing
cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
45:625–632. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gunn JK, Beca J, Penny DJ, Horton SB,
d'Udekem YA, Brizard CP, Finucane K, Olischar M, Hunt RW and
Shekerdemian LS: Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography and
brain injury in infants undergoing Norwood-type operations. Ann
Thorac Surg. 93:170–176. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dimitropoulos A, McQuillen PS, Sethi V,
Moosa A, Chau V, Xu D, Brant R, Azakie A, Campbell A, Barkovich AJ,
et al: Brain injury and development in newborns with critical
congenital heart disease. Neurology. 81:241–248. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bellinger DC, Wypij D, Rivkin MJ, DeMaso
DR, Robertson RL Jr, Dunbar-Masterson C, Rappaport LA, Wernovsky G,
Jonas RA and Newburger JW: Adolescents with d-transposition of the
great arteries corrected with the arterial switch procedure:
Neuropsychological assessment and structural brain imaging.
Circulation. 124:1361–1369. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mulkey SB, Yap VL, Bai S, Ramakrishnaiah
RH, Glasier CM, Bornemeier RA, Schmitz ML and Bhutta AT:
Amplitude-integrated EEG in newborns with critical congenital heart
disease predicts preoperative brain magnetic resonance imaging
findings. Pediatr Neurol. 52:599–605. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Latal B, Kellenberger C, Dimitropoulos A,
Hagmann C, Balmer C, Beck I and Bernet V: Can preoperative cranial
ultrasound predict early neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with
congenital heart disease? Dev Med Child Neurol. 57:639–644.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Algra SO, Schouten AN, Jansen NJ, van
Oeveren W, Haas F, Groenendaal F, Lemmers PM, van Haastert IC, Toet
MC and de Vries LS: Perioperative and bedside cerebral monitoring
identifies cerebral injury after surgical correction of congenital
aortic arch obstruction. Intensive Care Med. 41:2011–2012.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Juan G, Suixin L, Shaoru H, Yunxia S,
Yumei L, Yuan R, Chen C and Bi W: Postoperative brain functions in
infants with critical congenital heart disease via aEEG. Chin J
Thoracic Cardiovascular Surg. 34:581–585. 2018.
|
|
33
|
Gaynor JW, Nicolson SC, Jarvik GP,
Wernovsky G, Montenegro LM, Burnham NB, Hartman DM, Louie A, Spray
TL and Clancy RR: Increasing duration of deep hypothermic
circulatory arrest is associated with an increased incidence of
postoperative electroencephalographic seizures. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 130:1278–1286. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
von Rhein M, Dimitropoulos A,
Valsangiacomo Buechel ER, Landolt MA and Latal B: Risk factors for
neurodevelopmental impairments in school-age children after cardiac
surgery with full-flow cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 144:577–583. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gaynor JW, Jarvik GP, Bernbaum J, Gerdes
M, Wernovsky G, Burnham NB, D'Agostino JA, Zackai E,
McDonald-McGinn DM, Nicolson SC, et al: The relationship of
postoperative electrographic seizures to neurodevelopmental outcome
at 1 year of age after neonatal and infant cardiac surgery. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 131:181–249. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|