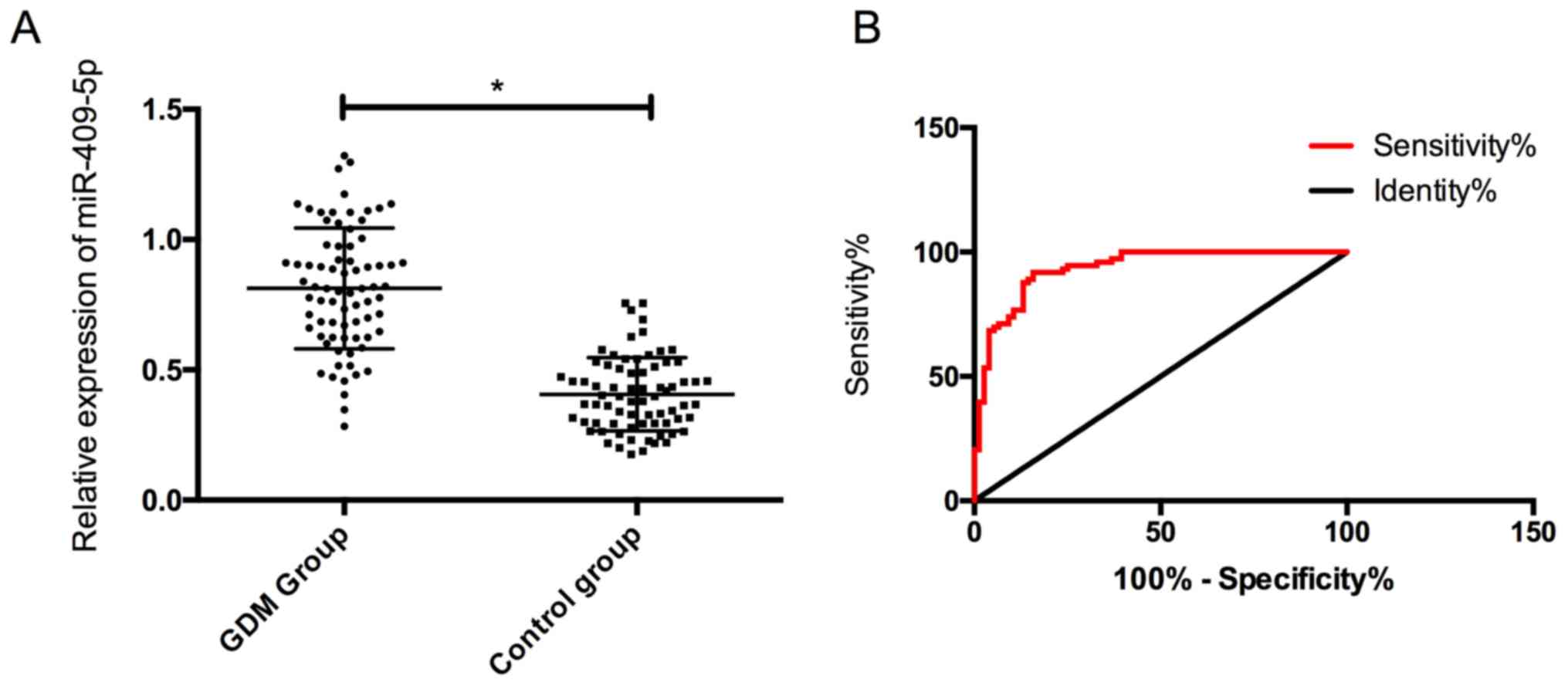
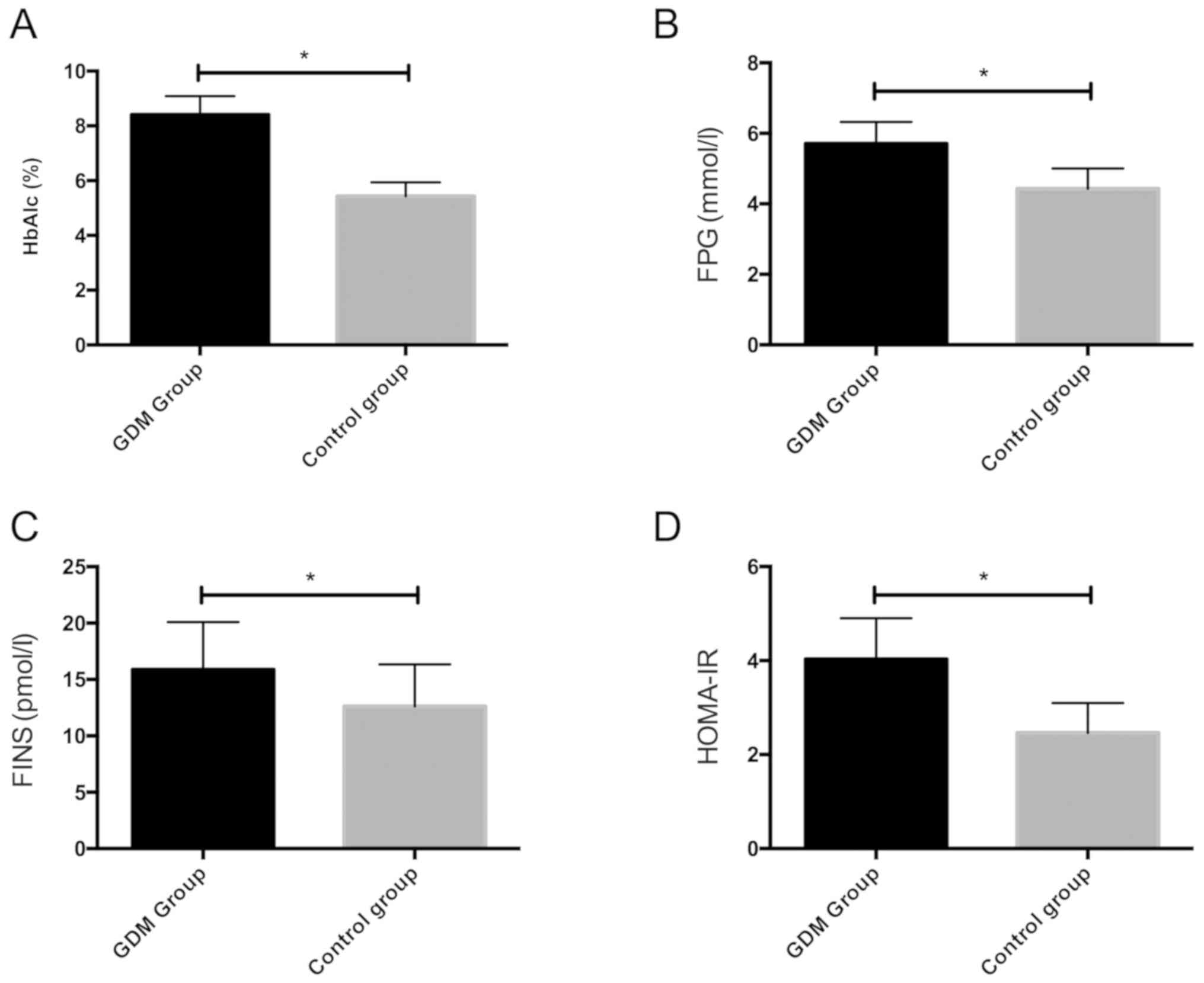
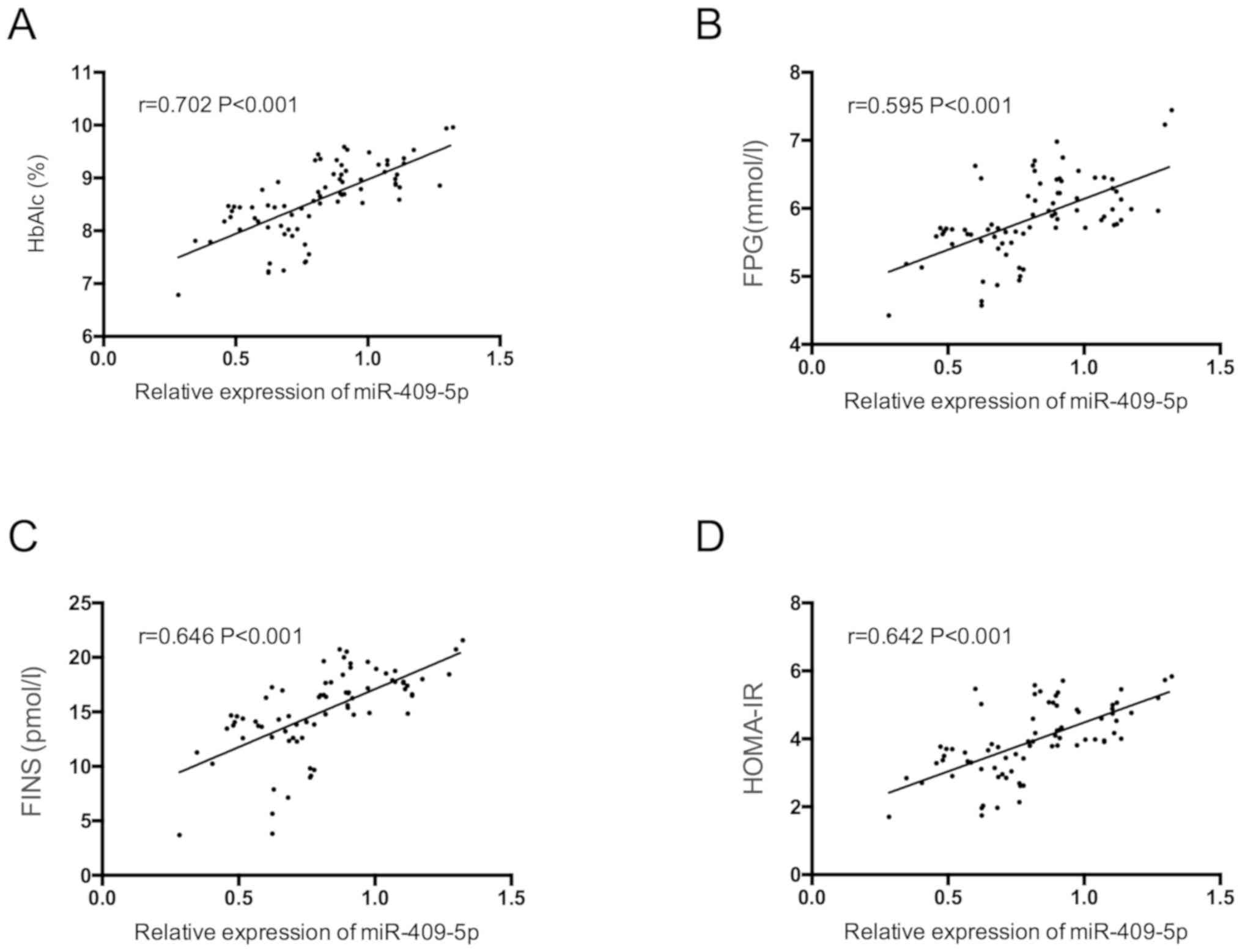
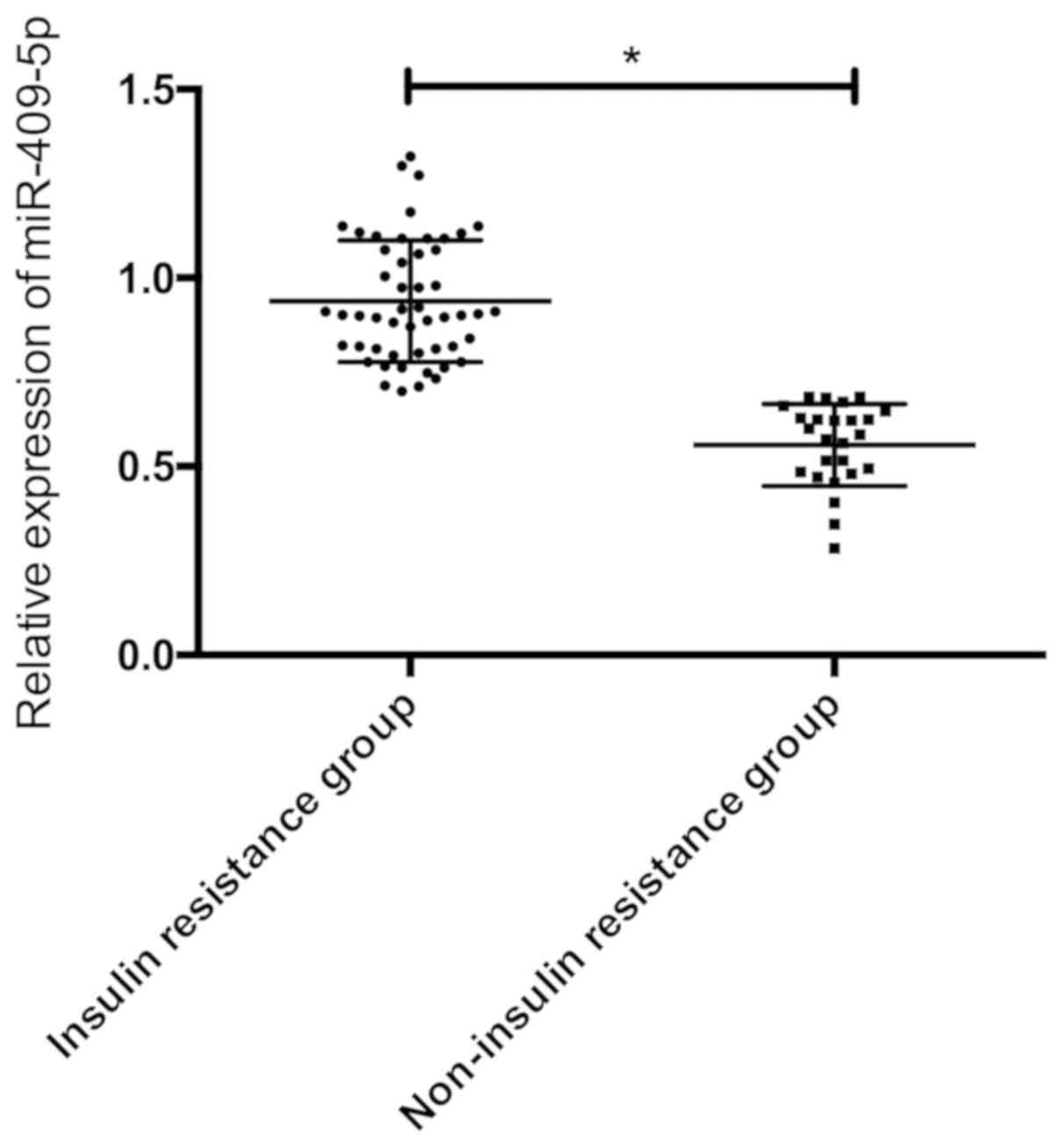
|
1
|
Ranheim T, Haugen F, Staff AC, Braekke K,
Harsem NK and Drevon CA: Adiponectin is reduced in gestational
diabetes mellitus in normal weight women. Acta Obstet Gynecol
Scand. 83:341–347. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
O'Sullivan EP, Avalos G, O'Reilly MW,
Dennedy MC, Gaffney G and Dunne F: Atlantic DIP collaborators:
Erratum to. Atlantic Diabetes in Pregnancy (DIP): the prevalence
and outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus using new diagnostic
criteria. Diabetologia. 59:873. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee KH, Han YJ, Chung JH, Kim MY, Ryu HM,
Kim JH, Kwak DW, Kim SH, Yang S and Kim M: Treatment of gestational
diabetes diagnosed by the IADPSG criteria decreases excessive fetal
growth. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 63:19–26. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li J, Leng J, Li W, Zhang C, Feng L, Wang
P, Chan JCN, Hu G, Yu Z and Yang X: Roles of insulin resistance and
beta cell dysfunction in macrosomia among Chinese women with
gestational diabetes mellitus. Prim Care Diabetes. 12:565–573.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shaat N, Ignell C, Katsarou A and Berntorp
K: Glucose homeostasis, beta cell function, and insulin resistance
in relation to vitamin D status after gestational diabetes
mellitus. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 96:821–827. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bartolo S, Vambergue A and Deruelle P:
Screening for gestational diabetes: Still many unsolved issues. J
Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 45:105–111. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In French).
|
|
7
|
Pheiffer C, Dias S, Rheeder P and Adam S:
Decreased expression of circulating miR-20a-5p in South African
women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol Diagn Ther.
22:345–352. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Feng J, Xing W and Xie L: Regulation of
microorganisms in diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 17(1729)2016.
|
|
9
|
Tang XW and Qin QX: miR-335-5p induces
insulin resistance and pancreatic islet β-cell secretion in
gestational diabetes mellitus mice through VASH1-mediated TGF-β
signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 234:6654–6666. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sebastiani G, Guarino E, Grieco GE,
Formichi C, Delli Poggi C, Ceccarelli E and Dotta F: Circulating
microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling in plasma of patients with
pestational diabetes mellitus reveals upregulation of miRNA
miR-330-3p. Front Endocrinol. 8(345)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
He Y, Bai J, Liu P, Dong J, Tang Y, Zhou
J, Han P, Xing J, Chen Y and Yu X: miR-494 protects pancreatic
β-cell function by targeting PTEN in gestational diabetes mellitus.
EXCLI J. 16:1297–1307. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yu H, Xing H, Han W, Wang Y, Qi T, Song C,
Xu Z, Li H and Huang Y: MicroRNA-409-5p is upregulated in breast
cancer and its downregulation inhibits cancer development through
downstream target of RSU1. Tumour Biol.
39(1010428317701647)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Massaro JD, Polli CD, Costa E Silva M,
Alves CC, Passos GA, Sakamoto-Hojo ET, Rodrigues de Holanda Miranda
W, Bispo Cezar NJ, Rassi DM, Crispim F, et al: Post-transcriptional
markers associated with clinical complications in Type 1 and Type 2
diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 490:1–14. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Metzger BE, Gabbe SG, Persson B, Buchanan
TA, Catalano PA, Damm P, Dyer AR, Leiva A, Hod M, Kitzmiler JL, et
al: International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study
Groups Consensus Panel: International association of diabetes and
pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and
classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care.
33:676–682. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Demir E, Ozkan H, Seckin KD, Sahtiyancı B,
Demir B, Tabak O, Kumbasar A and Uzun H: Plasma zonulin levels as a
non-invasive biomarker of intestinal permeability in women with
gestational diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules: Jan 11, 2019 (Epub
ahead of print). doi: 10.3390/biom9010024.
|
|
16
|
Van Winden K, Montoro M, Korst LM and
Ouzounian JG: A homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance
(HOMA-IR) relates to gestational diabetes, glycemic control [1K].
Obstet Gynecol. 129(112S)2017.
|
|
17
|
Wei YM, Yan J and Yang HX: Identification
of severe gestational diabetes mellitus after new criteria used in
China. J Perinatol. 36:90–94. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Yang T, Miao J, Liu H, Wu K, Guo
J, Chen J and Li T: Correlation between maternal and fetal insulin
resistance in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus.
Clin Lab. 64:945–953. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ebert T, Hindricks J, Kralisch S, Lossner
U, Jessnitzer B, Richter J, Blüher M, Stumvoll M and Fasshauer M:
Serum levels of fractalkine are associated with markers of insulin
resistance in gestational diabetes. Diabet Med. 31:1014–1017.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wander PL, Boyko EJ, Hevner K, Parikh VJ,
Tadesse MG, Sorensen TK, Williams MA and Enquobahrie DA:
Circulating early- and mid-pregnancy microRNAs and risk of
gestational diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 132:1–9.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li L, Wang S, Li H, Wan J, Zhou Q, Zhou Y
and Zhang C: microRNA-96 protects pancreatic β-cell function by
targeting PAK1 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Biofactors.
44:539–547. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou X, Xiang C and Zheng X: miR-132
serves as a diagnostic biomarker in gestational diabetes mellitus
and its regulatory effect on trophoblast cell viability. Diagn
Pathol. 14(119)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zheng B, Liang L, Huang S, Zha R, Liu L,
Jia D, Tian Q, Wang Q, Wang C, Long Z, et al: MicroRNA-409
suppresses tumour cell invasion and metastasis by directly
targeting radixin in gastric cancers. Oncogene. 31:4509–4516.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Song Q, Ji Q, Xiao J, Li F, Wang L, Chen
Y, Xu Y and Jiao S: miR-409 inhibits human non-small-cell lung
cancer progression by directly targeting SPIN1. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 13:154–163. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Retnakaran R, Ye C, Connelly PW, Hanley
AJ, Sermer M and Zinman B: Serum apoA1 (Apolipoprotein A-1),
insulin resistance, and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus
in human pregnancy - brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
39:2192–2197. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kraus M, Greither T, Wenzel C,
Bräuer-Hartmann D, Wabitsch M and Behre HM: Inhibition of
adipogenic differentiation of human SGBS preadipocytes by
androgen-regulated microRNA miR-375. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
414:177–185. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dooley J, Garcia-Perez JE, Sreenivasan J,
Schlenner SM, Vangoitsenhoven R, Papadopoulou AS, Tian L,
Schonefeldt S, Serneels L, Deroose C, et al: The microRNA-29 family
dictates the balance between homeostatic and pathological glucose
handling in diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 65:53–61.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Andersson-Hall U, Gustavsson C, Pedersen
A, Malmodin D, Joelsson L and Holmäng A: Higher concentrations of
BCAAs and 3-HIB are associated with insulin resistance in the
transition from gestational diabetes to type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes
Res. 2018(4207067)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li J-Y, Wu G-M, Hou Z and Cao YM:
Expression of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP3) in serum of
patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and its relationship
with insulin resistance. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:5702–5710.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|