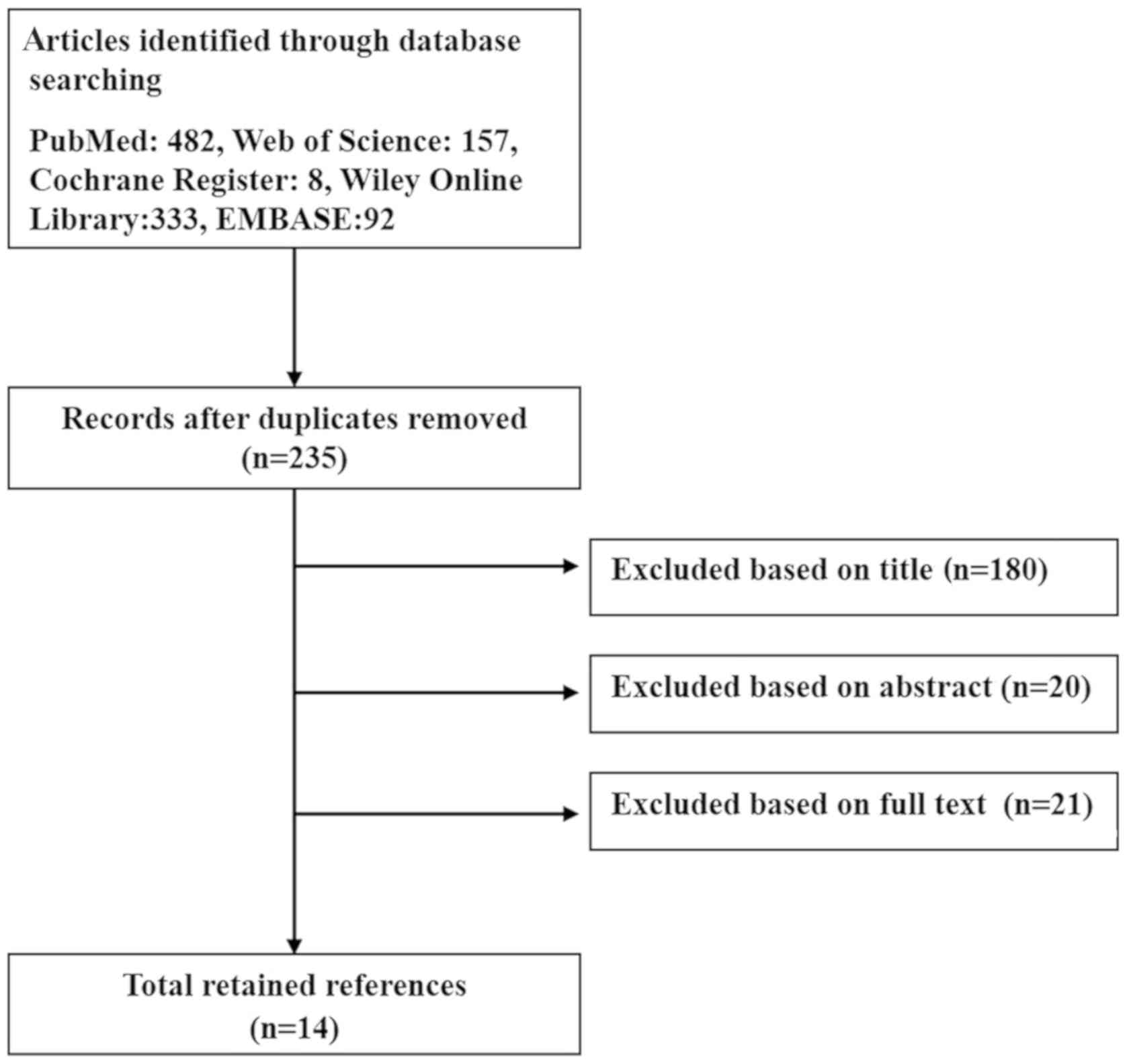
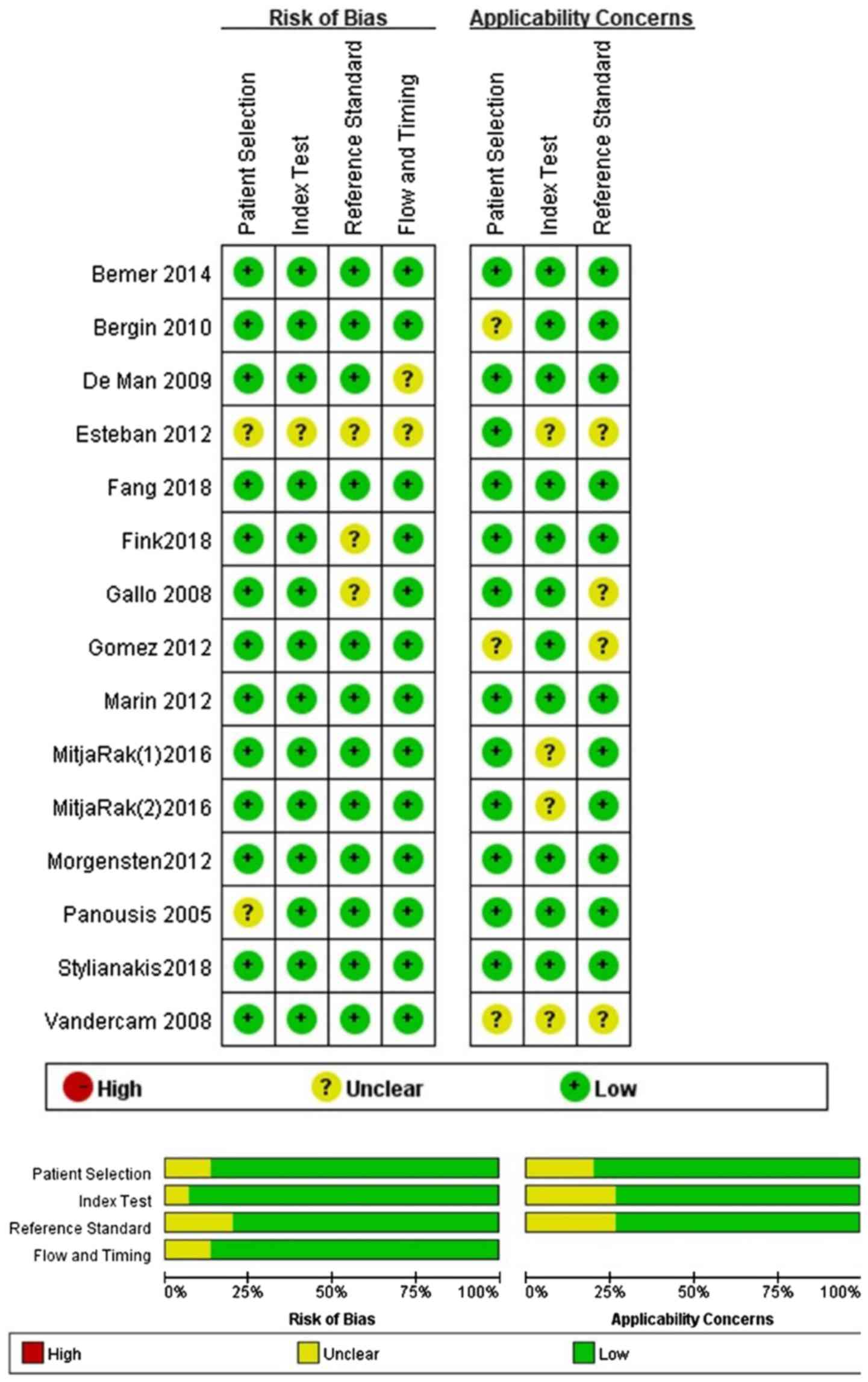
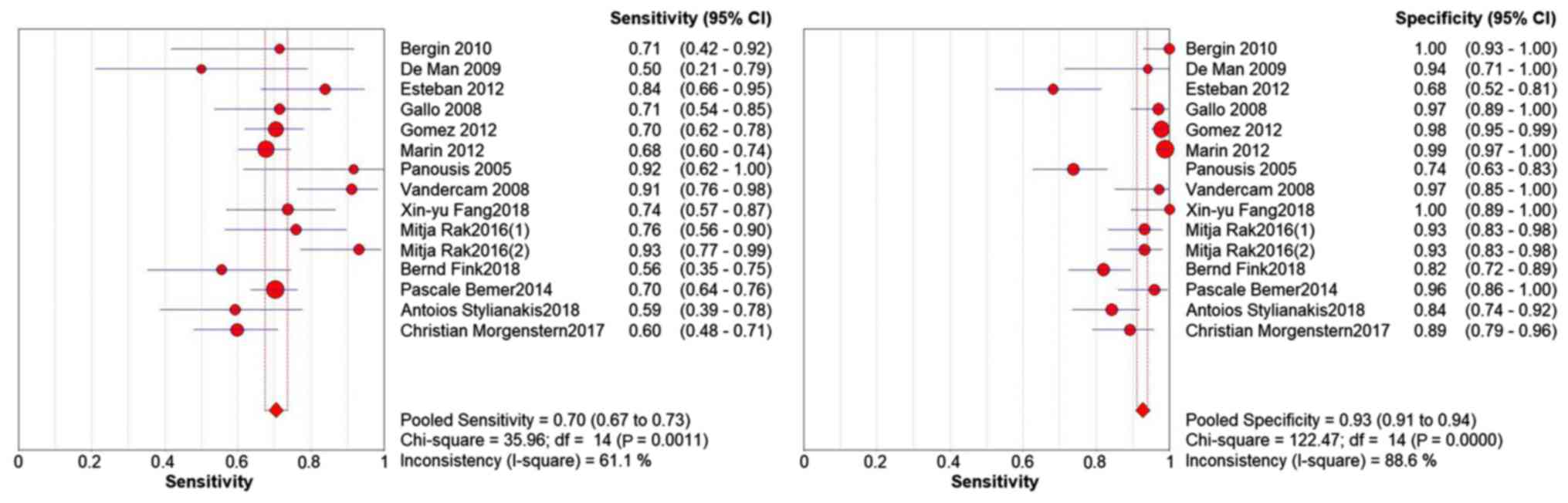
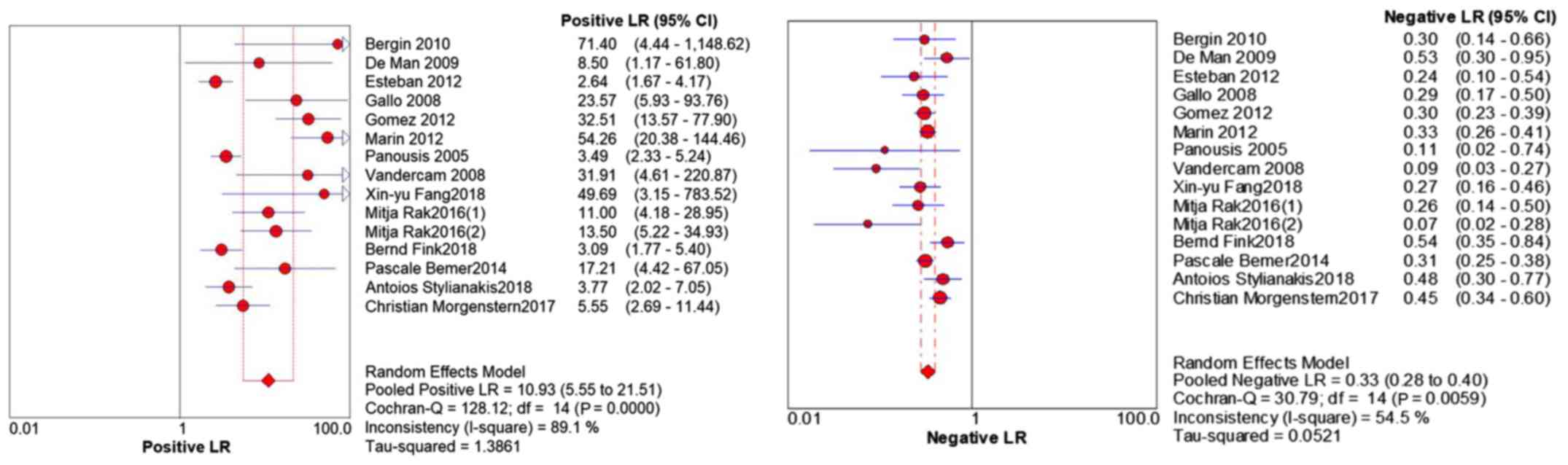
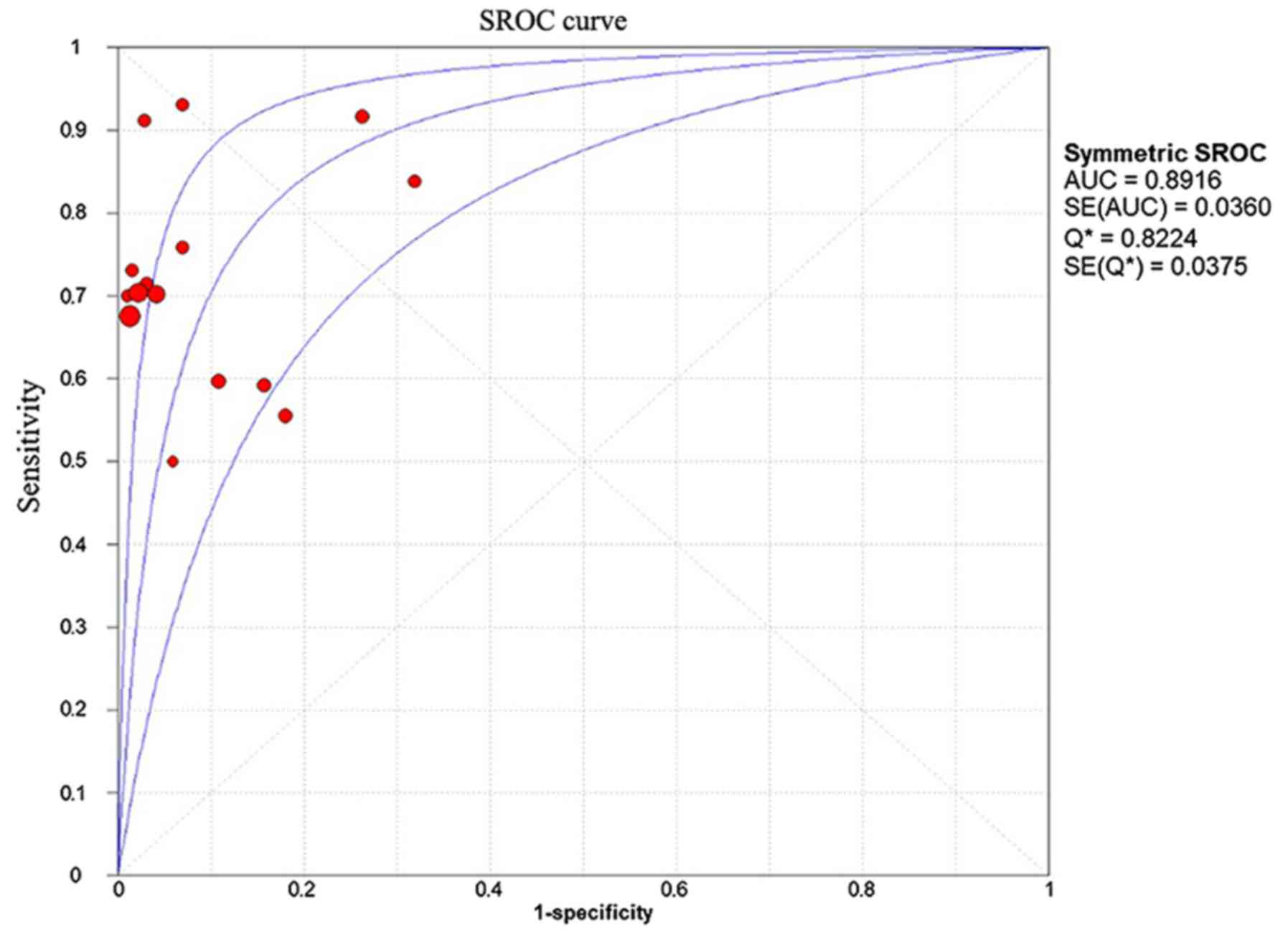
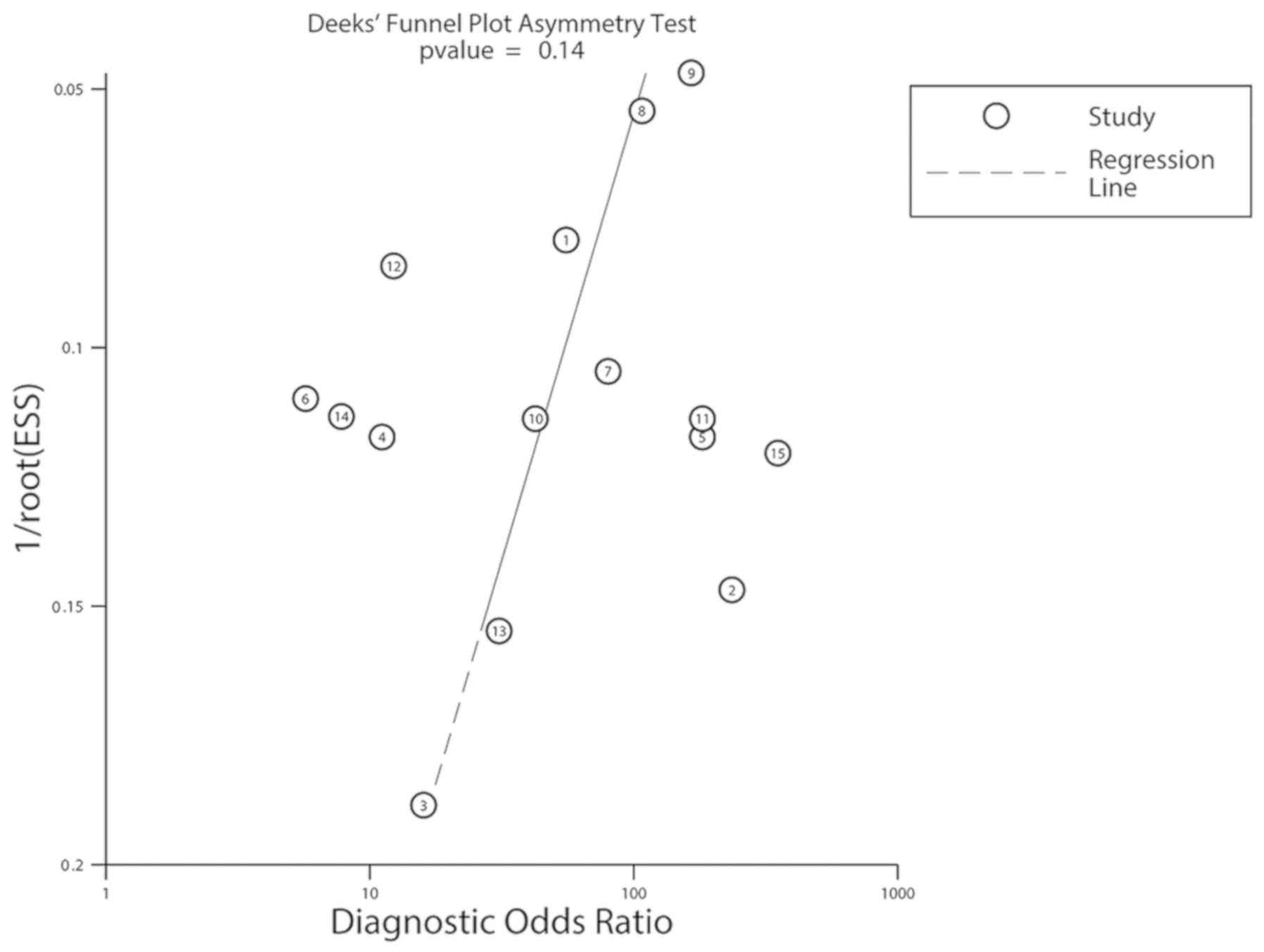
|
1
|
Jones CA, Beaupre LA, Johnston DW and
Suarez-Almazor ME: Total joint arthroplasties: Current concepts of
patient outcomes after surgery. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 33:71–86.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lavernia CJ, Guzman JF and Gachupin-Garcia
A: Cost effectiveness and quality of life in knee arthroplasty.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 134–139. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pivec R, Johnson AJ, Mears SC and Mont MA:
Hip arthroplasty. Lancet. 380:1768–1777. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Van Manen MD, Nace J and Mont MA:
Management of primary knee osteoarthritis and indications for total
knee arthroplasty for general practitioners. J Am Osteopath Assoc.
112:709–715. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clohisy JC, Calvert G, Tull F, McDonald D
and Maloney WJ: Reasons for revision hip surgery: A retrospective
review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 188–192. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH, Shastri
S and Jacoby SM: Insall Award paper. Why are total knee
arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 7–13.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Munjal S, Phillips MJ and Krackow KA:
Revision total knee arthroplasty: Planning, controversies, and
management-infection. Instr Course Lect. 50:367–377.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mortazavi SM, Molligan J, Austin MS,
Purtill JJ, Hozack WJ and Parvizi J: Failure following revision
total knee arthroplasty: Infection is the major cause. Int Orthop.
35:1157–1164. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shi S and Zhang X: Interaction of
staphylococcus aureus with osteoblasts (Review). Exp Ther
Med. 3:367–370. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Peel TN, Buising KL and Choong PF:
Prosthetic joint infection: Challenges of diagnosis and treatment.
ANZ J Surg. 81:32–39. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bozic KJ and Ries MD: The impact of
infection after total hip arthroplasty on hospital and surgeon
resource utilization. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 87:1746–1751.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kuo FC, Lu YD, Wu CT, You HL, Lee GB and
Lee MS: Comparison of molecular diagnosis with serum markers and
synovial fluid analysis in patients with prosthetic joint
infection. Bone Joint J. 100B:1345–1351. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Berbari EF, Hanssen AD, Duffy MC,
Steckelberg JM, Ilstrup DM, Harmsen WS and Osmon DR: Risk factors
for prosthetic joint infection: Case-control study. Clin Infect
Dis. 27:1247–1254. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Corvec S, Portillo ME, Pasticci BM, Borens
O and Trampuz A: Epidemiology and new developments in the diagnosis
of prosthetic joint infection. Int J Artif Organs. 35:923–934.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cobo J and Del Pozo JL: Prosthetic joint
infection: Diagnosis and management. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther.
9:787–802. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Matthews PC, Berendt AR, McNally MA and
Byren I: Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection.
BMJ. 338(b1773)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tsukayama DT, Goldberg VM and Kyle R:
Diagnosis and management of infection after total knee
arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85-A(Suppl 1):S75–S80.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shaw JD, Miller S, Plourde A, Shaw DL,
Wustrack R and Hansen EN: Methylene blue-guided debridement as an
intraoperative adjunct for the surgical treatment of periprosthetic
joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 32:3718–3723. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Peel TN, Buising KL and Choong PF:
Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection. Curr Opin
Infect Dis. 25:670–676. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cataldo MA, Petrosillo N, Cipriani M,
Cauda R and Tacconelli E: Prosthetic joint infection: Recent
developments in diagnosis and management. J Infect. 61:443–448.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ouyang Z, Zhai Z, Qin AN, Li H, Liu X, Qu
X and Dai K: Limitations of Gram staining for the diagnosis of
infections following total hip or knee arthroplasty. Exp Ther Med.
9:1857–1864. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Patel R, Osmon DR and Hanssen AD: The
diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection: Current techniques and
emerging technologies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 55–58.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Panousis K, Grigoris P, Butcher I, Rana B,
Reilly JH and Hamblen DL: Poor predictive value of broad-range PCR
for the detection of arthroplasty infection in 92 cases. Acta
Orthop. 76:341–346. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qu X, Zhai Z, Li H, Li H, Liu X, Zhu Z,
Wang Y, Liu G and Dai K: PCR-based diagnosis of prosthetic joint
infection. J Clin Microbiol. 51:2742–2746. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D,
Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P and Stewart LA: PRISMA-P Group.
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 4(1)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Devillé WL, Buntinx F, Bouter LM, Montori
VM, de Vet HC, van der Windt DA and Bezemer PD: Conducting
systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: Didactic guidelines. BMC
Med Res Methodol. 2(9)2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang J and Leeflang M: Recommended
software/packages for meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Lab
Precision Med. 4:2019.
|
|
28
|
Walter SD: Properties of the summary
receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for diagnostic test
data. Stat Med. 21:1237–1256. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Jones CM and Athanasiou T: Summary
receiver operating characteristic curve analysis techniques in the
evaluation of diagnostic tests. Ann Thorac Surg. 79:16–20.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rak M, KavčIč M, Trebše R and CőR A:
Detection of bacteria with molecular methods in prosthetic joint
infection: Sonication fluid better than periprosthetic tissue. Acta
Orthop. 87:339–345. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Spangehl MJ, Masri BA, O'Connell JX and
Duncan CP: Prospective analysis of preoperative and intraoperative
investigations for the diagnosis of infection at the sites of two
hundred and two revision total hip arthroplasties. J Bone Joint
Surg Am. 81:672–683. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Parvizi J, Zmistowski B, Berbari EF, Bauer
TW, Springer BD, Della Valle CJ, Garvin KL, Mont MA, Wongworawat MD
and Zalavras CG: New definition for periprosthetic joint infection:
From the workgroup of the musculoskeletal infection society. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 469:2992–2994. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Atkins BL, Athanasou N, Deeks JJ, Crook
DW, Simpson H, Peto TE, McLardy-Smith P and Berendt AR: Prospective
evaluation of criteria for microbiological diagnosis of
prosthetic-joint infection at revision arthroplasty. The OSIRIS
collaborative study group. J Clin Microbiol. 36:2932–2939.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gallo J, Kolar M, Dendis M, Loveckova Y,
Sauer P, Zapletalova J and Koukalova D: Culture and PCR analysis of
joint fluid in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. New
Microbiol. 31:97–104. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Esteban J, Alonso-Rodriguez N, del-Prado
G, Ortiz-Pérez A, Molina-Manso D, Cordero-Ampuero J, Sandoval E,
Fernández-Roblas R and Gómez-Barrena E: PCR-hybridization after
sonication improves diagnosis of implant-related infection. Acta
Orthop. 83:299–304. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gomez E, Cazanave C, Cunningham SA,
Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Steckelberg JM, Uhl JR, Hanssen AD, Karau
MJ, Schmidt SM, Osmon DR, et al: Prosthetic joint infection
diagnosis using broad-range PCR of biofilms dislodged from knee and
hip arthroplasty surfaces using sonication. J Clin Microbiol.
50:3501–3508. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Marin M, Garcia-Lechuz JM, Alonso P,
Villanueva M, Alcalá L, Gimeno M, Cercenado E, Sánchez-Somolinos M,
Radice C and Bouza E: Role of universal 16S rRNA gene PCR and
sequencing in diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. J Clin
Microbiol. 50:583–589. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fang XY, Li WB, Zhang CF, Huang ZD, Zeng
HY, Dong Z and Zhang WM: Detecting the presence of bacterial DNA
and RNA by polymerase chain reaction to diagnose suspected
periprosthetic joint infection after antibiotic therapy. Orthop
Surg. 10:40–46. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Trampuz A, Osmon DR, Hanssen AD,
Steckelberg JM and Patel R: Molecular and antibiofilm approaches to
prosthetic joint infection. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 69–88.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Arciola CR, Collamati S, Donati E and
Montanaro L: A rapid PCR method for the detection of
slime-producing strains of staphylococcus epidermidis and S-aureus
in periprosthesis infections. Diagn Mol Pathol. 10:130–137.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Tarkin IS, Henry TJ, Fey PI, Iwen PC,
Hinrichs SH and Garvin KL: PCR rapidly detects
methicillin-resistant staphylococci periprosthetic infection. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 89–94. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gallo J, Kolar M, Koukalova D, Sauer P,
Loveckova Y and Zapletalova J: P1407. Cultivation versus PCR
analysis of joint fluid samples in prosthetic joint infection. Int
J Antimicrobial Agents. 29:S391–S392. 2007.
|
|
43
|
Clarke MT, Roberts CP, Lee PT, Gray J,
Keene GS and Rushton N: Polymerase chain reaction can detect
bacterial DNA in aseptically loose total hip arthroplasties. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 132–137. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Millar BC, Xu J and Moore JE: Risk
assessment models and contamination management: Implications for
broad-range ribosomal DNA PCR as a diagnostic tool in medical
bacteriology. J Clin Microbiol. 40:1575–1580. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fink B, Steurer M, Hofäecker S, Schäfer P,
Sandow D, Schuster P and Oremek D: Preoperative PCR analysis of
synovial fluid has limited value for the diagnosis of
periprosthetic joint infections of total knee arthroplasties. Arch
Orthop Trauma Surg. 138:871–878. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Mariaux S, Tafin UF and Borens O:
Diagnosis of persistent infection in prosthetic two-stage exchange:
PCR analysis of sonication fluid from bone cement spacers. J Bone
Jt Infect. 2:218–223. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sebastian S, Malhotra R, Sreenivas V,
Kapil A, Chaudhry R and Dhawan B: Utility of 16S rRNA PCR in the
synovial fluid for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. Ann
Lab Med. 38:610–612. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Bergin PF, Doppelt JD, Hamilton WG, Mirick
GE, Jones AE, Sritulanondha S, Helm JM and Tuan RS: Detection of
periprosthetic infections with use of ribosomal RNA-based
polymerase chain reaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 92:654–663.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
De Man FHR, Graber P, Lüem M, Zimmerli W,
Ochsner PE and Sendi P: Broad-range PCR in selected episodes of
prosthetic joint infection. Infection. 37:292–294. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Vandercam B, Jeumont S, Cornu O, Yombi JC,
Lecouvet F, Lefèvre P, Irenge LM and Gala JL: Amplification-based
DNA analysis in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. J Mol
Diagn. 10:537–543. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bemer P, Plouzeau C, Tande D, Léger J,
Giraudeau B, Valentin AS, Jolivet-Gougeon A, Vincent P, Corvec S,
Gibaud S, et al: Evaluation of 16S rRNA gene PCR sensitivity and
specificity for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection: A
prospective multicenter cross-sectional study. J Clin Microbiol.
52:3583–3589. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Stylianakis A, Schinas G, Thomaidis PC,
Papaparaskevas J, Ziogas DC, Gamaletsou MN, Daikos GL, Pneumaticos
S and Sipsas NV: Combination of conventional culture, vial culture,
and broad-range PCR of sonication fluid for the diagnosis of
prosthetic joint infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 92:13–18.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Morgenstern C, Cabric S, Perka C, Trampuz
A and Renz N: Synovial fluid multiplex PCR is superior to culture
for detection of low-virulent pathogens causing periprosthetic
joint infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 90:115–119.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Arciola CR, Campoccia D, Baldassarri L,
Donati ME, Pirini V, Gamberini S and Montanaro L: Detection of
biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis from implant
infections. Comparison of a PCR-method that recognizes the presence
of ica genes with two classic phenotypic methods. J Biomed Mater
Res Part A. 76:425–430. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Montanaro L, Arciola CR, Borsetti E,
Brigotti M and Baldassarri L: A polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
method for the identification of collagen adhesin gene (CNA) in
staphylo coccus-induced prosthesis infections. New Microbiol.
21:359–363. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Miao Q, Ma Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Zhang Y, Jin
W, Yao Y, Su Y, Huang Y, Wang M, et al: Microbiological diagnostic
performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing when applied
to clinical practice. Clin Infect Dis. 67(Suppl 2):S231–S240.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Frank KL, Hanssen AD and Patel R: icaA is
not a useful diagnostic marker for prosthetic joint infection. J
Clin Microbiol. 42:4846–4849. 2004.
|
|
58
|
Birmingham P, Helm JM, Manner PA and Tuan
RS: Simulated joint infection assessment by rapid detection of live
bacteria with real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain
reaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 90:602–608. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Portillo ME, Salvadó M, Sorli L, Alier A,
Martínez S, Trampuz A, Gómez J, Puig L and Horcajada JP: Multiplex
PCR of sonication fluid accurately differentiates between
prosthetic joint infection and aseptic failure. J Infect.
65:541–548. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|