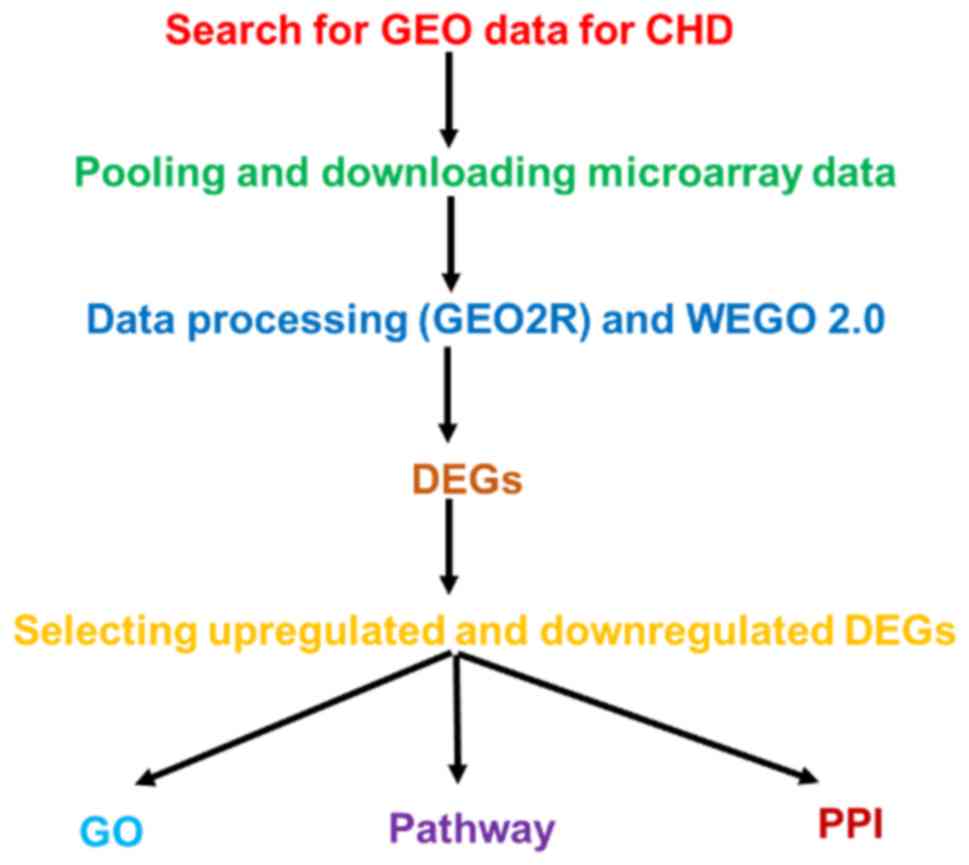
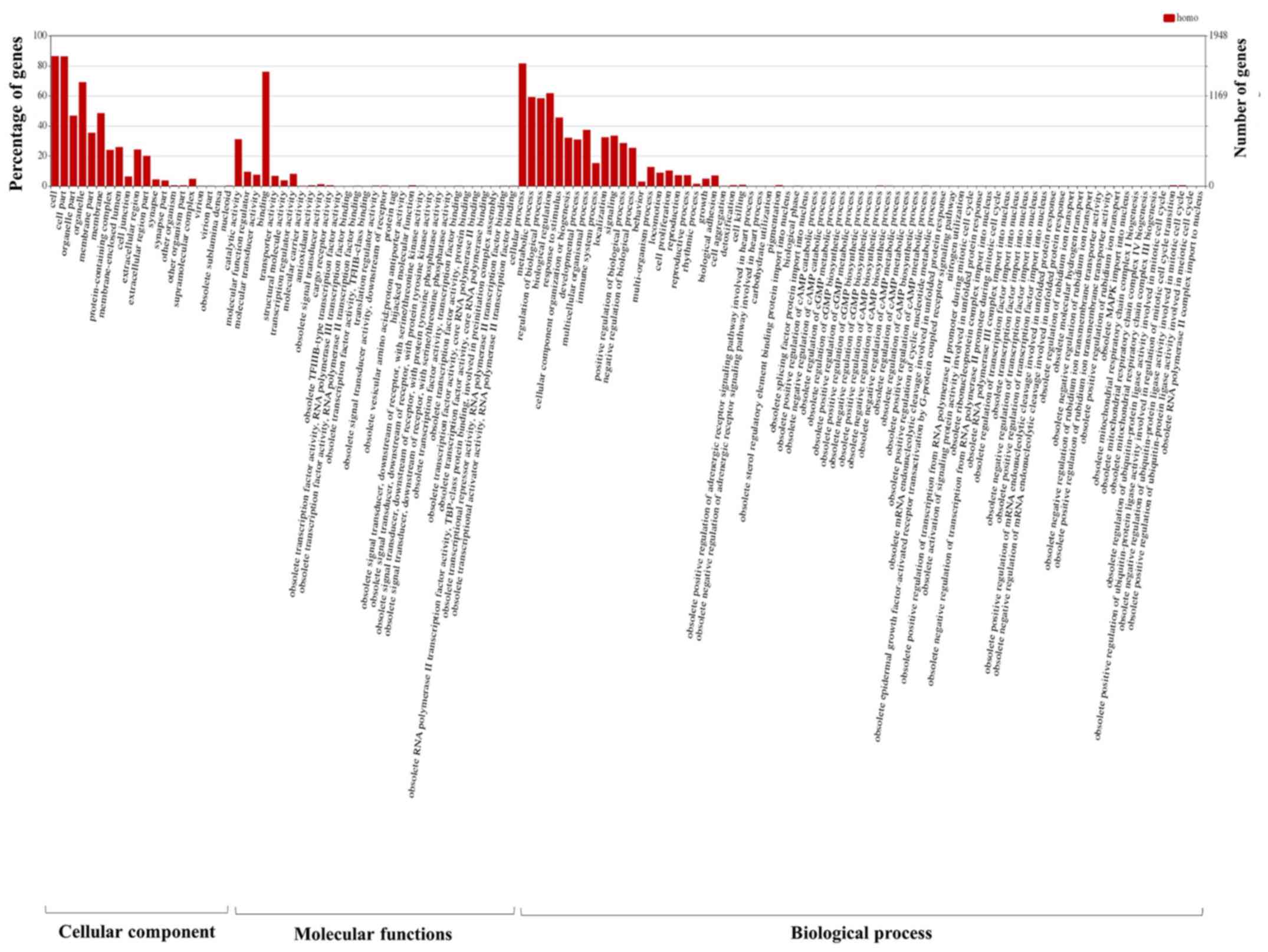
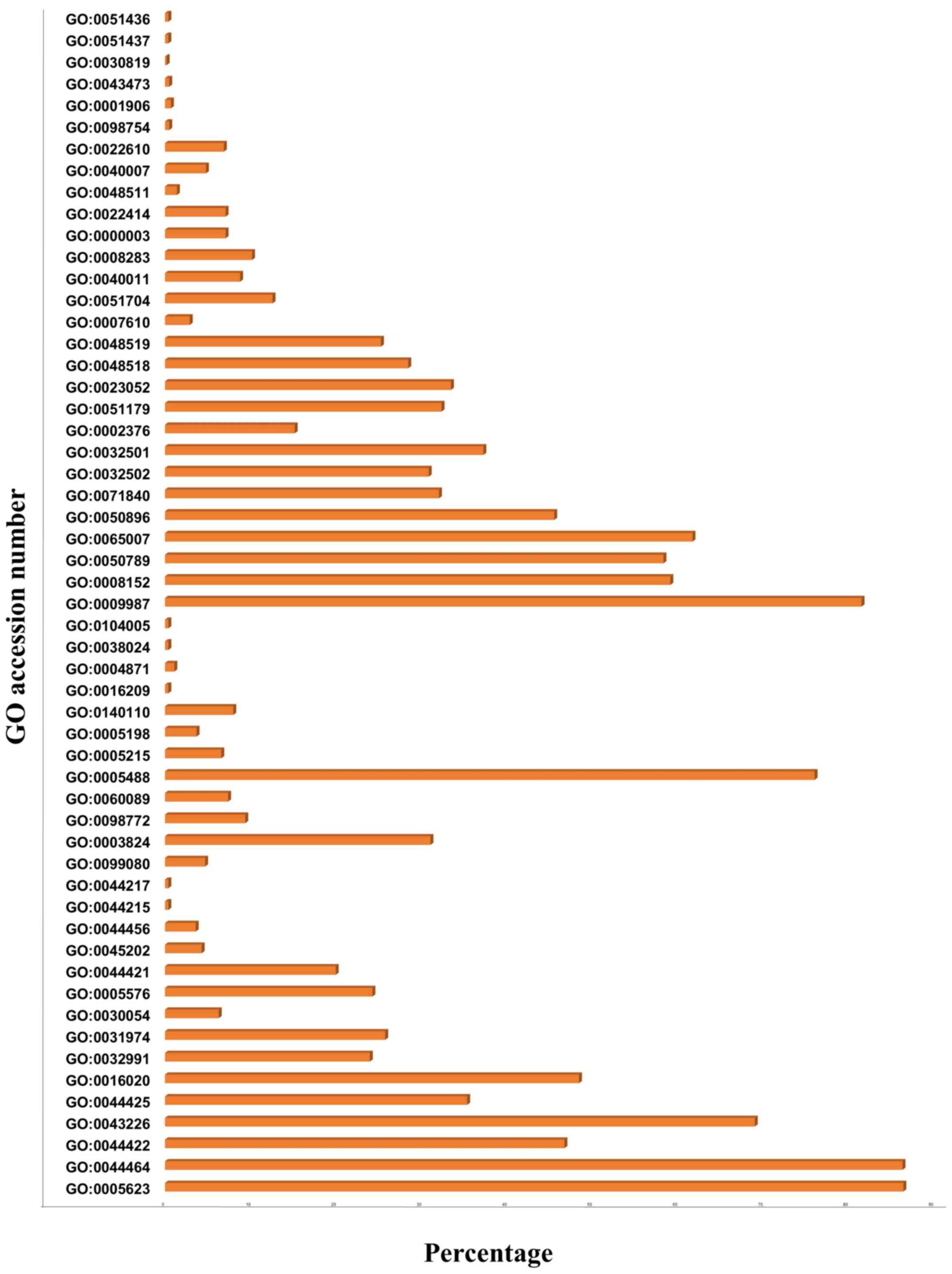
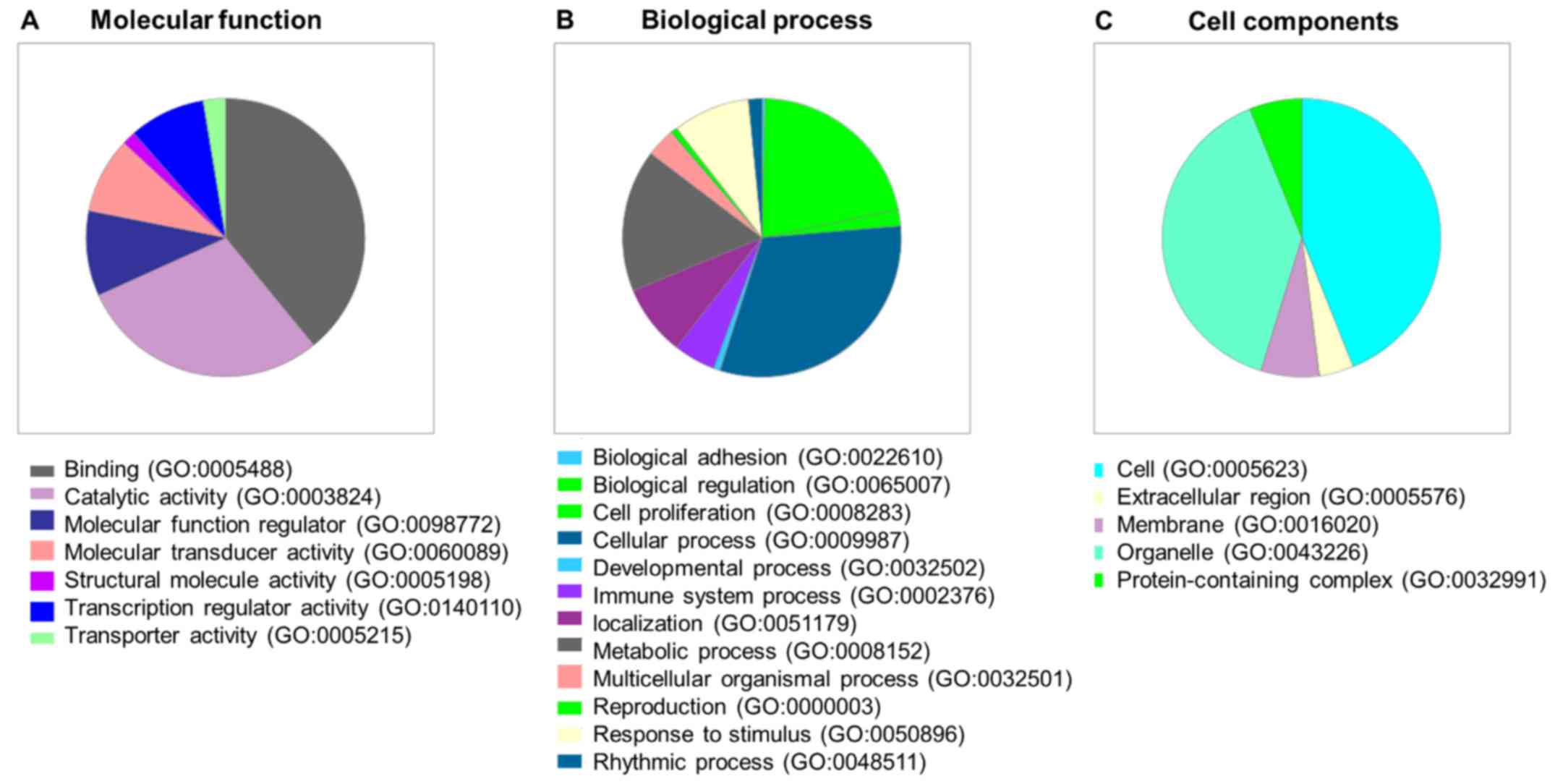
|
1
|
Underlying Cause of Death 1999-2017.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 24/7.
|
|
2
|
Haukilahti MAE, Holmström L, Vähätalo J,
Kenttä T, Tikkanen J, Pakanen L, Kortelainen ML, Perkiömäki J,
Huikuri H, Myerburg RJ, et al: Sudden cardiac death in women.
Circulation. 139:1012–1021. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ding D, Wang M, Su D, Hong C, Li X, Yang
Y, Zhang Y, Hu G and Ling W: Body mass index, high-sensitivity
C-reactive protein and mortality in Chinese with coronary artery
disease. PLoS One. 10(e0135713)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
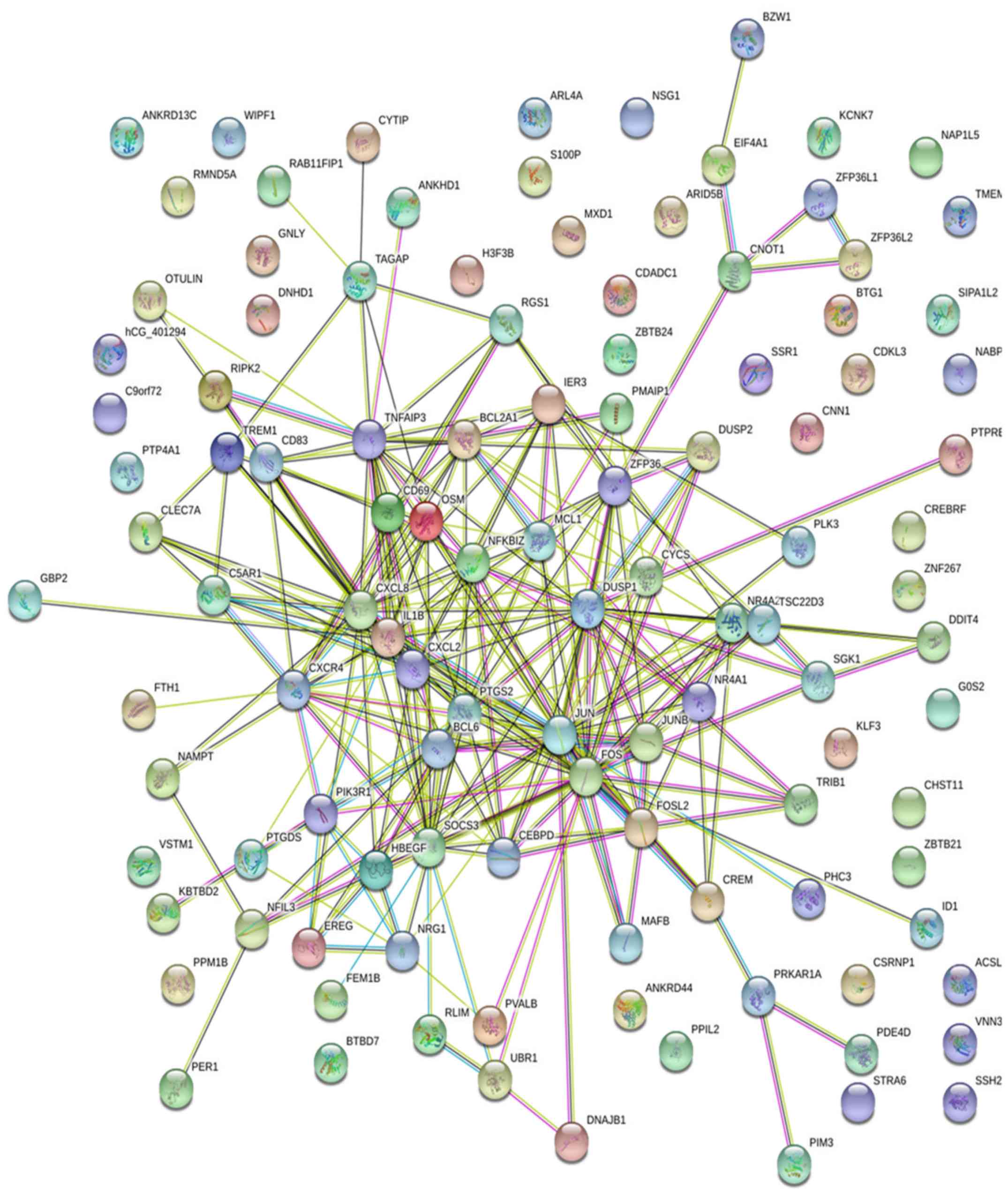
Yusuf S, Rangarajan S, Teo K, Islam S, Li
W, Liu L, Bo J, Lou Q, Lu F, Liu T, et al: Cardiovascular risk and
events in 17 low-, middle-, and high-income countries. N Engl J
Med. 371:818–827. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman
M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C,
et al: American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017
Update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
135:e146–e603. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mehta LS, Beckie TM, DeVon HA, Grines CL,
Krumholz HM, Johnson MN, Lindley KJ, Vaccarino V, Wang TY, Watson
KE, et al: American Heart Association Cardiovascular Disease in
Women and Special Populations Committee of the Council on Clinical
Cardiology, Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, Council on
Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, and Council on Quality of Care
and Outcomes Research: Acute myocardial infarction in women: A
scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
Circulation. 133:916–947. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fyyaz S, Rauf A, Hudson J and Olabintan O:
107 Nice 2016 stable chest pain guidelines: Improved yield of
severe coronary artery disease at invasive coronary angiography.
Heart. 105(88)2019.
|
|
8
|
Timmis A, Townsend N, Gale C, Grobbee R,
Maniadakis N, Flather M, Wilkins E, Wright L, Vos R, Bax J, et al:
ESC Scientific Document Group: European Society of Cardiology:
Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017. Eur Heart J. 39:508–579.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, Bossone E,
Bartolomeo RD, Eggebrecht H, Evangelista A, Falk V, Frank H,
Gaemperli O, et al: ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: 2014 ESC
Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases:
Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic
and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 35:2873–2926.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, Albus C,
Brotons C, Catapano AL, Cooney MT, Corrà U, Cosyns B, Deaton C, et
al: ESC Scientific Document Group: 2016 European guidelines on
cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth
Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other
Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice
(constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited
experts) Developed with the special contribution of the European
Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation
(EACPR). Eur Heart J. 37:2315–2381. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kwak BR, Bäck M, Bochaton-Piallat ML,
Caligiuri G, Daemen MJAP, Davies PF, Hoefer IE, Holvoet P, Jo H and
Krams R: Biomechanical factors in atherosclerosis: Mechanisms and
clinical implications. Eur Heart J. 35:3013–3020. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
CARDIoGRAMplusC4D Consortium. Deloukas P,
Kanoni S, Willenborg C, Farrall M, Assimes TL, Thompson JR,
Ingelsson E, Saleheen D and Erdmann J: Large-scale association
analysis identifies new risk loci for coronary artery disease. Nat
Genet. 45:25–33. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nikpay M, Goel A, Won H-H, Hall LM,
Willenborg C, Kanoni S, Saleheen D, Kyriakou T, Nelson CP, Hopewell
JC, et al: A comprehensive 1,000 genomes-based genome-wide
association meta-analysis of coronary artery disease. Nat Genet.
47:1121–1130. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kessler T, Vilne B and Schunkert H: The
impact of genome-wide association studies on the pathophysiology
and therapy of cardiovascular disease. EMBO Mol Med. 8:688–701.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Roberts R: Genetics of coronary artery
disease. Circ Res. 114:1890–1903. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhao Y, Chen J, Freudenberg JM, Meng Q,
Rajpal DK and Yang X: Network-based identification and
prioritization of key regulators of coronary artery disease loci.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:928–941. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Miller CL, Pjanic M and Quertermous T:
From locus association to mechanism of gene causality: The devil is
in the details. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:2079–2080.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cheng Y and Zhang C: MicroRNA-21 in
cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 3:251–255.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF and Bartel DP:
MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science.
303:83–86. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G,
Byrom M, Kelnar K, Ovcharenko D, Wilson M, Wang X, Shelton J,
Shingara J, et al: The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation
pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. 67:7713–7722. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Smyth GK, Michaud J and Scott HS: Use of
within-array replicate spots for assessing differential expression
in microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 21:2067–2075.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT and
Thomas PD: Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER
classification system. Nat Protoc. 8:1551–1566. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jupe S, Fabregat A and Hermjakob H:
Expression data analysis with reactome. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics
49: 8.20.1-8.20.9, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0820s49.
|
|
25
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rana JS, Nieuwdorp M, Jukema JW and
Kastelein JJ: Cardiovascular metabolic syndrome - an interplay of,
obesity, inflammation, diabetes and coronary heart disease.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 9:218–232. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kessler T, Vilne B and Schunkert H: The
impact of genome-wide association studies on the pathophysiology
and therapy of cardiovascular disease. EMBO Mol Med. 8:688–701.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Torre-Amione G: Immune activation in
chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 95 (11A):3C–8C; discussion
38C-40C. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Brenes-Castro D, Castillo EC,
Vázquez-Garza E, Torre-Amione G and García-Rivas G: Temporal frame
of immune cell infiltration during heart failure establishment:
Lessons from animal models. Int J Mol Sci. 19(19)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Flores-Arredondo JH, García-Rivas G and
Torre-Amione G: Immune modulation in heart failure: Past challenges
and future hopes. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 8:28–37. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gu X, Li B, Jiang M, Fang M, Ji J, Wang A,
Wang M, Jiang X and Gao C: RNA sequencing reveals differentially
expressed genes as potential diagnostic and prognostic indicators
of gallbladder carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:20661–20671.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Barth AS, Kuner R, Buness A, Ruschhaupt M,
Merk S, Zwermann L, Kääb S, Kreuzer E, Steinbeck G, Mansmann U, et
al: Identification of a common gene expression signature in dilated
cardiomyopathy across independent microarray studies. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 48:1610–1617. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Satterthwaite G, Francis SE, Suvarna K,
Blakemore S, Ward C, Wallace D, Braddock M and Crossman D:
Differential gene expression in coronary arteries from patients
presenting with ischemic heart disease: Further evidence for the
inflammatory basis of atherosclerosis. Am Heart J. 150:488–499.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sinnaeve PR, Donahue MP, Grass P, Seo D,
Vonderscher J, Chibout SD, Kraus WE, Sketch M Jr, Nelson C,
Ginsburg GS, et al: Gene expression patterns in peripheral blood
correlate with the extent of coronary artery disease. PLoS One.
4(e7037)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gotoh T, Endo M and Oike Y: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress-related inflammation and cardiovascular diseases.
Int J Inflam. 2011:1–9. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Haas MJ and Mooradian AD: Regulation of
high-density lipoprotein by inflammatory cytokines: Establishing
links between immune dysfunction and cardiovascular disease.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 26:90–99. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Costa THR, de Figueiredo Neto JA, de
Oliveira AEF, Lopes e Maia MF and de Almeida AL: Association
between chronic apical periodontitis and coronary artery disease. J
Endod. 40:164–167. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jensen MK, Pers TH, Dworzynski P, Girman
CJ, Brunak S and Rimm EB: Protein interaction-based genome-wide
analysis of incident coronary heart disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.
4:549–556. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Duan S, Luo X and Dong C: Identification
of susceptibility modules for coronary artery disease using a
genome wide integraded network analysis. Gene:. 531:347–357.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|