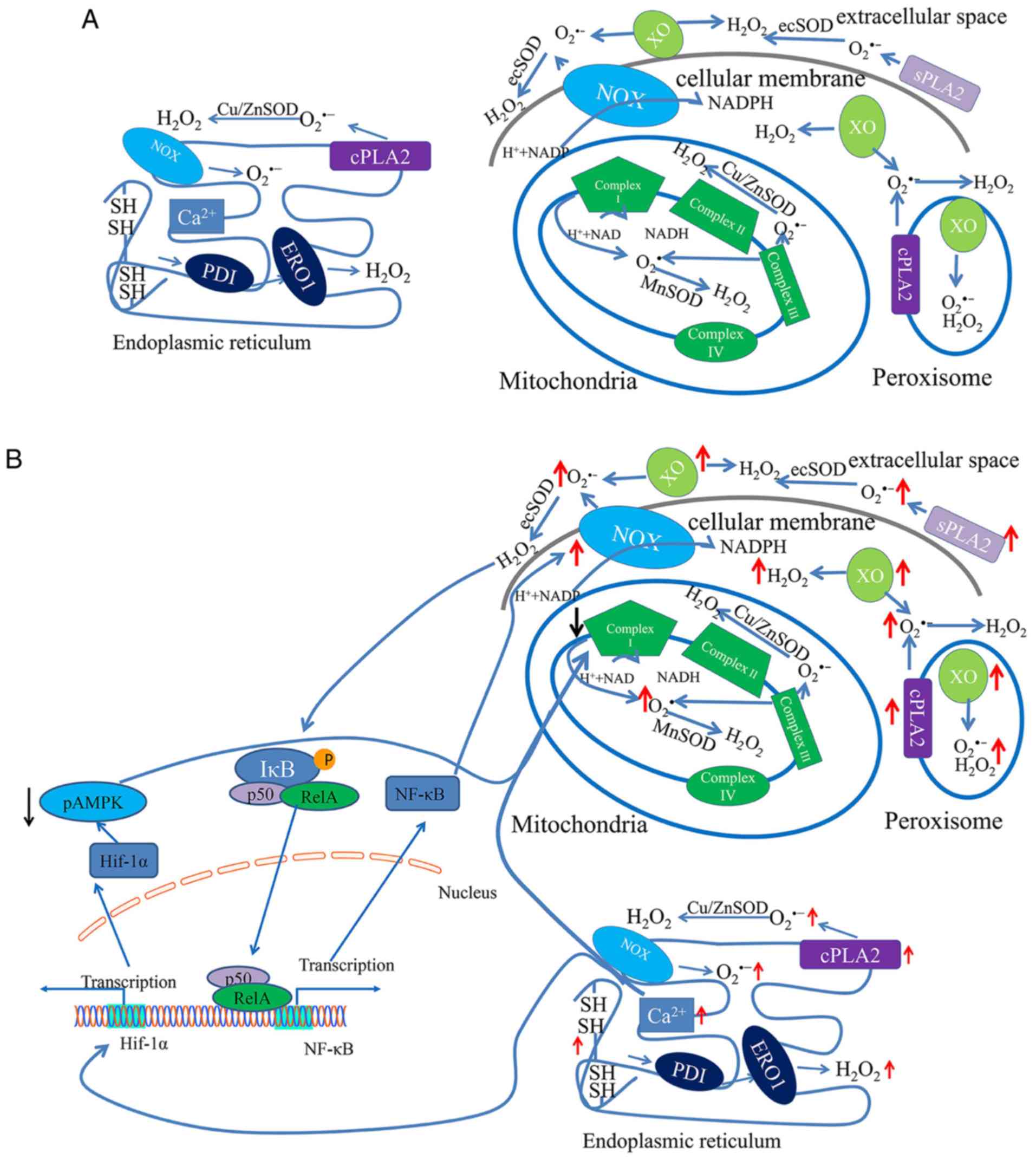
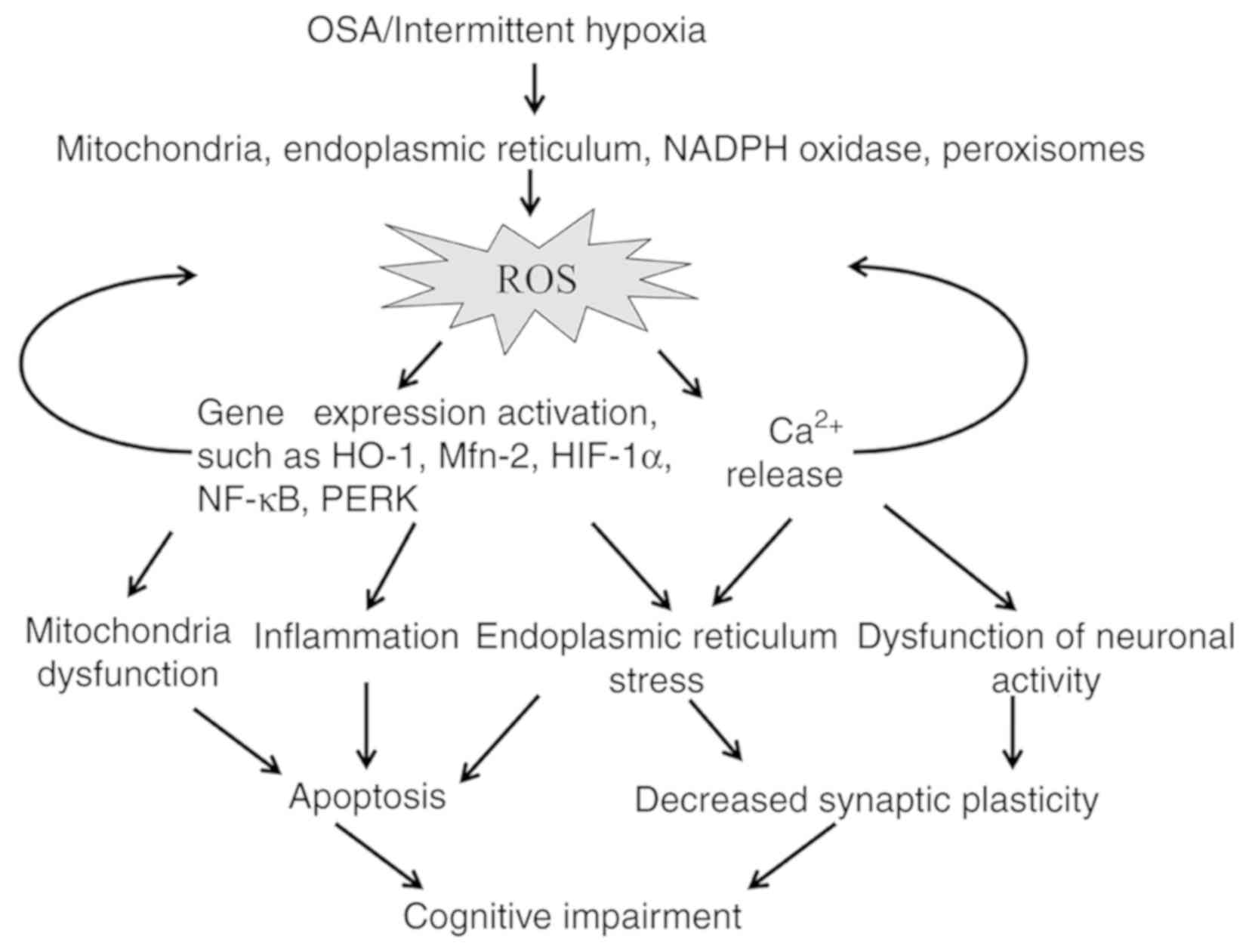
|
1
|
Dewan NA, Nieto FJ and Somers VK:
Intermittent hypoxemia and OSA: Implications for comorbidities.
Chest. 147:266–274. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Vaessen TJ, Overeem S and Sitskoorn MM:
Cognitive complaints in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med Rev.
19:51–58. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lal C, Strange C and Bachman D:
Neurocognitive impairment in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest.
141:1601–1610. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Zhang SX and Gozal D: Reactive
oxygen species and the brain in sleep apnea. Respir Physiol
Neurobiol. 174:307–316. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dayyat EA, Zhang SX, Wang Y, Cheng ZJ and
Gozal D: Exogenous erythropoietin administration attenuates
intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits in a murine model
of sleep apnea. BMC Neurosci. 13(77)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Roy J, Galano JM, Durand T, Le Guennec JY
and Lee JC: Physiological role of reactive oxygen species as
promoters of natural defenses. FASEB J. 31:3729–3745.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pilkauskaite G, Miliauskas S and
Sakalauskas R: Reactive oxygen species production in peripheral
blood neutrophils of obstructive sleep apnea patients.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2013(421763)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Schulz R, Mahmoudi S, Hattar K, Sibelius
U, Olschewski H, Mayer K, Seeger W and Grimminger F: Enhanced
release of superoxide from polymorphonuclear neutrophils in
obstructive sleep apnea. Impact of continuous positive airway
pressure therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 162:566–570.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Vatansever E, Surmen-Gur E, Ursavas A and
Karadag M: Obstructive sleep apnea causes oxidative damage to
plasma lipids and proteins and decreases adiponectin levels. Sleep
Breath. 15:275–282. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lavie L: Oxidative stress inflammation and
endothelial dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea. Front Biosci
(Elite Ed). 4:1391–1403. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zou Z, Chang H, Li H and Wang S: Induction
of reactive oxygen species: An emerging approach for cancer
therapy. Apoptosis. 22:1321–1335. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bonekamp NA, Völkl A, Fahimi HD and
Schrader M: Reactive oxygen species and peroxisomes: Struggling for
balance. Biofactors. 35:346–355. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fransen M, Nordgren M, Wang B and
Apanasets O: Role of peroxisomes in ROS/RNS-metabolism:
Implications for human disease. Biochimica et biophysica Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1822:1363–1373. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kubota C, Torii S, Hou N, Saito N,
Yoshimoto Y, Imai H and Takeuchi T: Constitutive reactive oxygen
species generation from autophagosome/lysosome in neuronal
oxidative toxicity. J Biol Chem. 285:667–674. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Santos CX, Tanaka LY, Wosniak J and
Laurindo FR: Mechanisms and implications of reactive oxygen species
generation during the unfolded protein response: Roles of
endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductases, mitochondrial electron
transport, and NADPH oxidase. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:2409–2427.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Angelova PR and Abramov AY: Role of
mitochondrial ROS in the brain: From physiology to
neurodegeneration. FEBS Lett. 592:692–702. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Oyewole AO and Birch-Machin MA:
Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants. FASEB J. 29:4766–4771.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Halliwell B: Oxidative stress and
neurodegeneration: Where are we now? J Neurochem. 97:1634–1658.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K,
Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S
and Ohta S: Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by
selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med.
13:688–694. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Prabhakar NR: Sensory plasticity of the
carotid body: Role of reactive oxygen species and physiological
significance. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 178:375–380.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhao RZ, Jiang S, Zhang L and Yu ZB:
Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and
uncoupling (Review). Int J Mol Med. 44:3–15. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Khan SA, Nanduri J, Yuan G, Kinsman B,
Kumar GK, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B and Prabhakar R: NADPH oxidase 2
mediates intermittent hypoxia-induced mitochondrial complex I
inhibition: Relevance to blood pressure changes in rats. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 14:533–542. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kang PT, Chen CL, Lin P, Zhang L, Zweier
JL and Chen YR: Mitochondrial complex I in the post-ischemic heart:
Reperfusion-mediated oxidative injury and protein cysteine
sulfonation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 121:190–204. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yuan G, Adhikary G, McCormick AA, Holcroft
JJ, Kumar GK and Prabhakar NR: Role of oxidative stress in
intermittent hypoxia-induced immediate early gene activation in rat
PC12 cells. J Physiol. 557:773–783. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Higa A and Chevet E: Redox signaling loops
in the unfolded protein response. Cell Signal. 24:1548–1555.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Görlach A, Bertram K, Hudecova S and
Krizanova O: Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay. Redox Biol.
6:260–271. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bhandary B, Marahatta A, Kim HR and Chae
HJ: An involvement of oxidative stress in endoplasmic reticulum
stress and its associated diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 14:434–456.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yong J, Bischof H, Burgstaller S, Siirin
M, Murphy A, Malli R and Kaufman RJ: Mitochondria supply ATP to the
ER through a mechanism antagonized by cytosolic Ca2.
Elife. 8: pii(e49682)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and oxidative stress: A vicious cycle or a
double-edged sword? Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:2277–2293.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mello T, Zanieri F, Ceni E and Galli A:
Oxidative stress in the healthy and wounded hepatocyte: A cellular
organelles perspective. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016(8327410)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tu BP and Weissman JS: The FAD- and
O(2)-dependent reaction cycle of Ero1-mediated oxidative protein
folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cell. 10:983–994.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Panday A, Sahoo MK, Osorio D and Batra S:
NADPH oxidases: An overview from structure to innate
immunity-associated pathologies. Cell Mol Immunol. 12:5–23.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kaur G, Sharma A, Guruprasad K and Pati
PK: Versatile roles of plant NADPH oxidases and emerging concepts.
Biotechnol Adv. 32:551–563. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Konior A, Schramm A, Czesnikiewicz-Guzik M
and Guzik TJ: NADPH oxidases in vascular pathology. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:2794–2814. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nisimoto Y, Motalebi S, Han CH and Lambeth
JD: The p67(phox) activation domain regulates electron flow from
NADPH to flavin in flavocytochrome b(558). J Biol Chem.
274:22999–23005. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li L, Ren F, Qi C, Xu L, Fang Y, Liang M,
Feng J, Chen B, Ning W and Cao J: Intermittent hypoxia promotes
melanoma lung metastasis via oxidative stress and inflammation
responses in a mouse model of obstructive sleep apnea. Respir Res.
19(28)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Del Ben M, Fabiani M, Loffredo L, Polimeni
L, Carnevale R, Baratta F, Brunori M, Albanese F, Augelletti T,
Violi F and Angelico F: Oxidative stress mediated arterial
dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea and the
effect of continuous positive airway pressure treatment. BMC Pulm
Med. 12(36)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schulz R, Murzabekova G, Egemnazarov B,
Kraut S, Eisele HJ, Dumitrascu R, Heitmann J, Seimetz M, Witzenrath
M, Ghofrani HA, et al: Arterial hypertension in a murine model of
sleep apnea: Role of NADPH oxidase 2. J Hypertens. 32:300–305.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nair D, Dayyat EA, Zhang SX, Wang Y and
Gozal D: Intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits are
mediated by NADPH oxidase activity in a murine model of sleep
apnea. PLoS One. 6(e19847)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Nair D, Ramesh V and Gozal D: Adverse
cognitive effects of high-fat diet in a murine model of sleep apnea
are mediated by NADPH oxidase activity. Neuroscience. 227:361–369.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Reddy JK and Mannaerts GP: Peroxisomal
lipid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 14:343–370. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lodhi IJ and Semenkovich CF: Peroxisomes:
A nexus for lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Cell Metab.
19:380–392. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Suzuki J: Short-duration intermittent
hypoxia enhances endurance capacity by improving muscle fatty acid
metabolism in mice. Physiol Rep. 4: pii(e12744)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cantu-Medellin N and Kelley EE: Xanthine
oxidoreductase-catalyzed reactive species generation: A process in
critical need of reevaluation. Redox Biol. 1:353–358.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Harris CM and Massey V: The reaction of
reduced xanthine dehydrogenase with molecular oxygen. Reaction
kinetics and measurement of superoxide radical. J Biol Chem.
272:8370–8379. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Harris CM and Massey V: The oxidative
half-reaction of xanthine dehydrogenase with NAD; Reaction kinetics
and steady-state mechanism. J Biol Chem. 272:28335–28341.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang S, Li Y, Song X, Wang X, Zhao C, Chen
A and Yang P: Febuxostat pretreatment attenuates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via mitochondrial apoptosis. J Transl
Med. 13(209)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Nanduri J, Vaddi DR, Khan SA, Wang N,
Makerenko V and Prabhakar NR: Xanthine oxidase mediates
hypoxia-inducible factor-2α degradation by intermittent hypoxia.
PLoS One. 8(e75838)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Morgan BJ, Bates ML, Rio RD, Wang Z and
Dopp JM: Oxidative stress augments chemoreflex sensitivity in rats
exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol.
234:47–59. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
El Solh AA, Saliba R, Bosinski T, Grant
BJ, Berbary E and Miller N: Allopurinol improves endothelial
function in sleep apnoea: A randomised controlled study. Eur Respir
J. 27:997–1002. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Griscavage JM, Rogers NE, Sherman MP and
Ignarro LJ: Inducible nitric oxide synthase from a rat alveolar
macrophage cell line is inhibited by nitric oxide. J Immunol.
151:6329–6337. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kumar A, Chen SH, Kadiiska MB, Hong JS,
Zielonka J, Kalyanaraman B and Mason RP: Inducible nitric oxide
synthase is key to peroxynitrite-mediated, LPS-induced protein
radical formation in murine microglial BV2 cells. Free Radic Biol
Med. 73:51–59. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Contestabile A: Role of nitric oxide in
cerebellar development and function: Focus on granule neurons.
Cerebellum. 11:50–61. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li S, Hafeez A, Noorulla F, Geng X, Shao
G, Ren C, Lu G, Zhao H, Ding Y and Ji X: Preconditioning in
neuroprotection: From hypoxia to ischemia. Prog Neurobiol.
157:79–91. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yuan X, Guo X, Deng Y, Zhu D, Shang J and
Liu H: Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced neuronal apoptosis in
the hippocampus is attenuated by telmisartan through suppression of
iNOS/NO and inhibition of lipid peroxidation and inflammatory
responses. Brain Res. 1596:48–57. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Varadharaj S, Porter K, Pleister A,
Wannemacher J, Sow A, Jarjoura D, Zweier JL and Khayat RN:
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling: A novel pathway in
OSA induced vascular endothelial dysfunction. Respir Physiol
Neurobiol. 207:40–47. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sun GY, Shelat PB, Jensen MB, He Y, Sun AY
and Simonyi A: Phospholipases A2 and inflammatory responses in the
central nervous system. Neuromolecular Med. 12:133–148.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Akiba S and Sato T: Cellular function of
calcium-independent phospholipase A2. Biol Pharm Bull.
27:1174–1178. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Radogna F, Sestili P, Martinelli C,
Paolillo M, Paternoster L, Albertini MC, Accorsi A, Gualandi G and
Ghibelli L: Lipoxygenase-mediated pro-radical effect of melatonin
via stimulation of arachidonic acid metabolism. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 238:170–177. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Rordorf G, Uemura Y and Bonventre JV:
Characterization of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity in gerbil
brain: Enhanced activities of cytosolic, mitochondrial, and
microsomal forms after ischemia and reperfusion. J Neurosci.
11:1829–1836. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Stephenson D, Rash K, Smalstig B, Roberts
E, Johnstone E, Sharp J, Panetta J, Little S, Kramer R and Clemens
J: Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is induced in reactive glia following
different forms of neurodegeneration. Glia. 27:110–128.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Arai K, Ikegaya Y, Nakatani Y, Kudo I,
Nishiyama N and Matsuki N: Phospholipase A2 mediates ischemic
injury in the hippocampus: A regional difference of neuronal
vulnerability. Eur J Neurosci. 13:2319–2323. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Lauritzen I, Heurteaux C and Lazdunski M:
Expression of group II phospholipase A2 in rat brain after severe
forebrain ischemia and in endotoxic shock. Brain Res. 651:353–356.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Elliot-Portal E, Laouafa S, Arias-Reyes C,
Janes TA, Joseph V and Soliz J: Brain-derived erythropoietin
protects from intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiorespiratory
dysfunction and oxidative stress in mice. Sleep: 41, 2018 doi:
10.1093/sleep/zsy072.
|
|
65
|
Kim YS, Kwak JW, Lee KE, Cho HS, Lim SJ,
Kim KS, Yang HS and Kim HJ: Can mitochondrial dysfunction be a
predictive factor for oxidative stress in patients with obstructive
sleep apnea? Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:1285–1288. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Slonkova J, Bar M, Nilius P, Berankova D,
Salounova D and Sonka K: Spontaneous improvement in both
obstructive sleep apnea and cognitive impairment after stroke.
Sleep Med. 32:137–142. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Quan SF, Chan CS, Dement WC, Gevins A,
Goodwin JL, Gottlieb DJ, Green S, Guilleminault C, Hirshkowitz M,
Hyde PR, et al: The association between obstructive sleep apnea and
neurocognitive performance-the Apnea Positive Pressure Long-term
Efficacy Study (APPLES). Sleep. 34:303–314B. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Gagnon K, Baril AA, Gagnon JF, Fortin M,
Décary A, Lafond C, Desautels A, Montplaisir J and Gosselin N:
Cognitive impairment in obstructive sleep apnea. Pathol Biol
(Paris). 62:233–240. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Xu LH, Xie H, Shi ZH, Du LD, Wing YK, Li
AM, Ke Y and Yung WH: Critical role of endoplasmic reticulum stress
in chronic intermittent Hypoxia-induced deficits in synaptic
plasticity and Long-term memory. Antioxid Redox Signal. 23:695–710.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Xie H, Leung KL, Chen L, Chan YS, Ng PC,
Fok TF, Wing YK, Ke Y, Li AM and Yung WH: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor rescues and prevents chronic intermittent
hypoxia-induced impairment of hippocampal long-term synaptic
plasticity. Neurobiol Dis. 40:155–162. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Feng J, Wu Q, Zhang D and Chen BY:
Hippocampal impairments are associated with intermittent hypoxia of
obstructive sleep apnea. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:696–701.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Milton VJ and Sweeney ST: Oxidative stress
in synapse development and function. Dev Neurobiol. 72:100–110.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Lin WC, Huang CC, Chen HL, Chou KH, Chen
PC, Tsai NW, Chen MH, Friedman M, Lin HC and Lu CH: Longitudinal
brain structural alterations and systemic inflammation in
obstructive sleep apnea before and after surgical treatment. J
Transl Med. 14(139)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
O'Donoghue FJ, Wellard RM, Rochford PD,
Dawson A, Barnes M, Ruehland WR, Jackson ML, Howard ME, Pierce RJ
and Jackson GD: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and neurocognitive
dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea before and after CPAP
treatment. Sleep. 35:41–48. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Canessa N, Castronovo V, Cappa SF, Aloia
MS, Marelli S, Falini A, Alemanno F and Ferini-Strambi L:
Obstructive sleep apnea: Brain structural changes and
neurocognitive function before and after treatment. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 183:1419–1426. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Torelli F, Moscufo N, Garreffa G, Placidi
F, Romigi A, Zannino S, Bozzali M, Fasano F, Giulietti G, Djonlagic
I, et al: Cognitive profile and brain morphological changes in
obstructive sleep apnea. NeuroImage. 54:787–793. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Nizari S, Carare RO, Romero IA and Hawkes
CA: 3D reconstruction of the neurovascular unit reveals
differential loss of cholinergic innervation in the cortex and
hippocampus of the adult mouse brain. Front Aging Neurosci.
11(172)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Han Q, Li G, Ip MS, Zhang Y, Zhen Z, Mak
JC and Zhang N: Haemin attenuates intermittent hypoxia-induced
cardiac injury via inhibiting mitochondrial fission. J Cell Mol
Med. 22:2717–2726. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Hull TD, Boddu R, Guo L, Tisher CC,
Traylor AM, Patel B, Joseph R, Prabhu SD, Suliman HB, Piantadosi
CA, et al: Heme oxygenase-1 regulates mitochondrial quality control
in the heart. JCI Insight. 1(e85817)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Delbarba A, Abate G, Prandelli C, Marziano
M, Buizza L, Arce Varas N, Novelli A, Cuetos F, Martinez C, Lanni
C, et al: Mitochondrial alterations in peripheral mononuclear blood
cells from Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment
patients. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016(5923938)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Petersen MH, Budtz-Jørgensen E, Sørensen
SA, Nielsen JE, Hjermind LE, Vinther-Jensen T, Nielsen SM and
Nørremølle A: Reduction in mitochondrial DNA copy number in
peripheral leukocytes after onset of Huntington's disease.
Mitochondrion. 17:14–21. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Leuner K, Pantel J, Frey C, Schindowski K,
Schulz K, Wegat T, Maurer K, Eckert A and Müller WE: Enhanced
apoptosis, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in
lymphocytes as potential biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. J
Neural Transm. Suppl:207–215. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Ciccone MM, Scicchitano P, Zito A, Cortese
F, Boninfante B, Falcone VA, Quaranta VN, Ventura VA, Zucano A, Di
Serio F, et al: Correlation between inflammatory markers of
atherosclerosis and carotid intima-media thickness in Obstructive
Sleep Apnea. Molecules. 19:1651–1662. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Yang Q, Wang Y, Feng J, Cao J and Chen B:
Intermittent hypoxia from obstructive sleep apnea may cause
neuronal impairment and dysfunction in central nervous system: The
potential roles played by microglia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
9:1077–1086. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Lee EJ, Heo W, Kim JY, Kim H, Kang MJ, Kim
BR, Kim JH, Park DY, Kim CH, Yoon JH and Cho HJ: Alteration of
inflammatory mediators in the upper and lower airways under chronic
intermittent hypoxia: Preliminary animal study. Mediators Inflamm.
2017(4327237)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Ryan S, Taylor CT and McNicholas WT:
Selective activation of inflammatory pathways by intermittent
hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Circulation.
112:2660–2667. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Morgan MJ and Liu ZG: Crosstalk of
reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Schoonbroodt S, Ferreira V, Best-Belpomme
M, Boelaert JR, Legrand-Poels S, Korner M and Piette J: Crucial
role of the amino-terminal tyrosine residue 42 and the
carboxyl-terminal PEST domain of I kappa B alpha in NF-kappa B
activation by an oxidative stress. J Immunol. 164:4292–4300.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Fang L, Choudhary S, Zhao Y, Edeh CB, Yang
C, Boldogh I and Brasier AR: ATM regulates NF-κB-dependent
immediate-early genes via RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation coupled to
CDK9 promoter recruitment. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:8416–8432.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Williams A and Scharf SM: Obstructive
sleep apnea, cardiovascular disease, and inflammation-is NF-kappaB
the key? Sleep Breath. 11:69–76. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Anrather J, Racchumi G and Iadecola C:
NF-kappaB regulates phagocytic NADPH oxidase by inducing the
expression of gp91phox. J Biol Chem. 281:5657–5667. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Vasconcelos AR, Yshii LM, Viel TA, Buck
HS, Mattson MP, Scavone C and Kawamoto EM: Intermittent fasting
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and memory
impairment. J Neuroinflammation. 11(85)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Do K, Laing BT, Landry T, Bunner W,
Mersaud N, Matsubara T, Li P, Yuan Y, Lu Q and Huang H: The effects
of exercise on hypothalamic neurodegeneration of Alzheimer's
disease mouse model. PLoS One. 13(e0190205)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Wang J, Ming H, Chen R, Ju JM, Peng WD,
Zhang GX and Liu CF: CIH-induced neurocognitive impairments are
associated with hippocampal Ca(2+) overload, apoptosis, and
dephosphorylation of ERK1/2 and CREB that are mediated by
overactivation of NMDARs. Brain Res. 1625:64–72. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Qi G, Mi Y, Wang Y, Li R, Huang S, Li X
and Liu X: Neuroprotective action of tea polyphenols on oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of the
TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in SH-SY5Y
cells and mice brain. Food Funct. 8:4421–4432. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Yin X, Zhang X, Lv C, Li C, Yu Y, Wang X
and Han F: Protocatechuic acid ameliorates neurocognitive functions
impairment induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia. Sci Rep.
5(14507)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Cervellati F, Cervellati C, Romani A,
Cremonini E, Sticozzi C, Belmonte G, Pessina F and Valacchi G:
Hypoxia induces cell damage via oxidative stress in retinal
epithelial cells. Free Radic Res. 48:303–312. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Semenza GL and Prabhakar NR:
HIF-1-dependent respiratory, cardiovascular, and redox responses to
chronic intermittent hypoxia. Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:1391–1396.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Jung SN, Yang WK, Kim J, Kim HS, Kim EJ,
Yun H, Park H, Kim SS, Choe W, Kang I and Ha J: Reactive oxygen
species stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha protein and
stimulate transcriptional activity via AMP-activated protein kinase
in DU145 human prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:713–721.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Rabinovitch RC, Samborska B, Faubert B, Ma
EH, Gravel SP, Andrzejewski S, Raissi TC, Pause A, St-Pierre J and
Jones RG: AMPK maintains cellular metabolic homeostasis through
regulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Cell Rep.
21:1–9. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Guo H, Cao J, Li J, Yang X, Jiang J, Feng
J, Li S, Zhang J and Chen B: Lymphocytes from intermittent
hypoxia-exposed rats increase the apoptotic signals in endothelial
cells via oxidative and inflammatory injury in vitro. Sleep Breath.
19:969–976. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Bianchi G, Di Giulio C, Rapino C, Rapino
M, Antonucci A and Cataldi A: p53 and p66 proteins compete for
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha stabilization in young and old rat
hearts exposed to intermittent hypoxia. Gerontology. 52:17–23.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
da Rosa DP, Forgiarini LF, e Silva MB,
Fiori CZ, Andrade CF, Martinez D and Marroni NP: Antioxidants
inhibit the inflammatory and apoptotic processes in an intermittent
hypoxia model of sleep apnea. Inflamm Res. 64:21–29.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Pan W and Kastin AJ: Can sleep apnea cause
Alzheimer's disease? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 47:656–669.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Andrade AG, Bubu OM, Varga AW and Osorio
RS: The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and
Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 64 (Suppl 1):S255–S270.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Casagrande R, Stern P, Diehn M, Shamu C,
Osario M, Zúñiga M, Brown PO and Ploegh H: Degradation of proteins
from the ER of S. cerevisiae requires an intact unfolded protein
response pathway. Mol cell. 5:729–735. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Walter P and Ron D: The unfolded protein
response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science.
334:1081–1086. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Chou YT, Zhan G, Zhu Y, Fenik P, Panossian
L, Li Y, Zhang J and Veasey S: C/EBP homologous binding protein
(CHOP) underlies neural injury in sleep apnea model. Sleep.
36:481–492. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Yao ZH, Kang X, Yang L, Niu Y, Lu Y, Gong
CX, Tian Q and Wang JZ: Phenylbutyric acid protects against spatial
memory deficits in a model of repeated electroconvulsive therapy.
Curr Neurovasc Res. 11:156–167. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Nosyreva E and Kavalali ET:
Activity-dependent augmentation of spontaneous neurotransmission
during endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Neurosci. 30:7358–7368.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Archbold KH, Borghesani PR, Mahurin RK,
Kapur VK and Landis CA: Neural activation patterns during working
memory tasks and OSA disease severity: Preliminary findings. J Clin
Sleep Med. 5:21–27. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Miller JF, Neufang M, Solway A, Brandt A,
Trippel M, Mader I, Hefft S, Merkow M, Polyn SM, Jacobs J, et al:
Neural activity in human hippocampal formation reveals the spatial
context of retrieved memories. Science. 342:1111–1114.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Pena F and Ramirez JM: Hypoxia-induced
changes in neuronal network properties. Mol Neurobiol. 32:251–283.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Dixon CE, Chen M,
Marion DW, Heineman S, DeKosky ST and Graham SH: Early
neuropathologic effects of mild or moderate hypoxemia after
controlled cortical impact injury in rats. J Neurotrauma.
14:179–189. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Fung SJ, Xi MC, Zhang JH, Sampogna S,
Yamuy J, Morales FR and Chase MH: Apnea promotes glutamate-induced
excitotoxicity in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1179:42–50.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Socodato R, Portugal CC, Rodrigues A,
Henriques J, Rodrigues C, Figueira C and Relvas JB: Redox tuning of
Ca2+ signaling in microglia drives glutamate release
during hypoxia. Free Radic Biol Med. 118:137–149. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Macey PM, Sarma MK, Nagarajan R, Aysola R,
Siegel JM, Harper RM and Thomas MA: Obstructive sleep apnea is
associated with low GABA and high glutamate in the insular cortex.
J Sleep Res. 25:390–394. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Opie GM, Catcheside PG, Usmani ZA, Ridding
MC and Semmler JG: Motor cortex plasticity induced by theta burst
stimulation is impaired in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea.
Eur J Neurosci. 37:1844–1852. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Gozal D, Nair D and Goldbart AD: Physical
activity attenuates intermittent hypoxia-induced spatial learning
deficits and oxidative stress. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
182:104–112. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Toraldo DM, Di Michele L, Ralli M,
Arigliani M, Passali GC, De Benedetto M and Passali D: Obstructive
sleep apnea syndrome in the pediatric age: The role of the
pneumologist. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23 (1 Suppl):S15–S18.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Li Y, Ye J, Han D, Zhao D, Cao X, Orr J,
Jen R, Deacon-Diaz N, Sands SA, Owens R and Malhotra A: The effect
of upper airway surgery on loop gain in obstructive sleep apnea. J
Clin Sleep Med. 15:907–913. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Epstein LJ, Kristo D, Strollo PJ Jr,
Friedman N, Malhotra A, Patil SP, Ramar K, Rogers R, Schwab RJ,
Weaver EM, et al: Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management
and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J Clin
Sleep Med. 5:263–276. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Carlucci A, Ceriana P, Mancini M, Cirio S,
Pierucci P, D'Artavilla Lupo N, Gadaleta F, Morrone E and Fanfulla
F: Efficacy of Bilevel-auto treatment in patients with obstructive
sleep apnea not responsive to or intolerant of continuous positive
airway pressure ventilation. J Clin Sleep Med. 11:981–985.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|