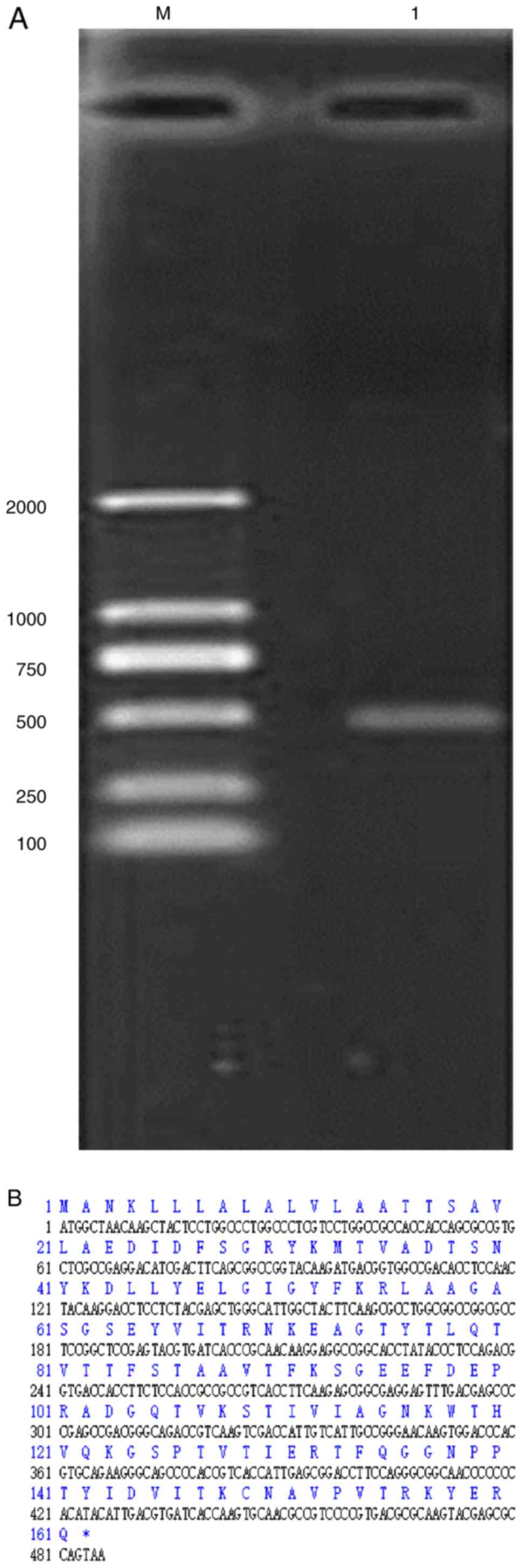
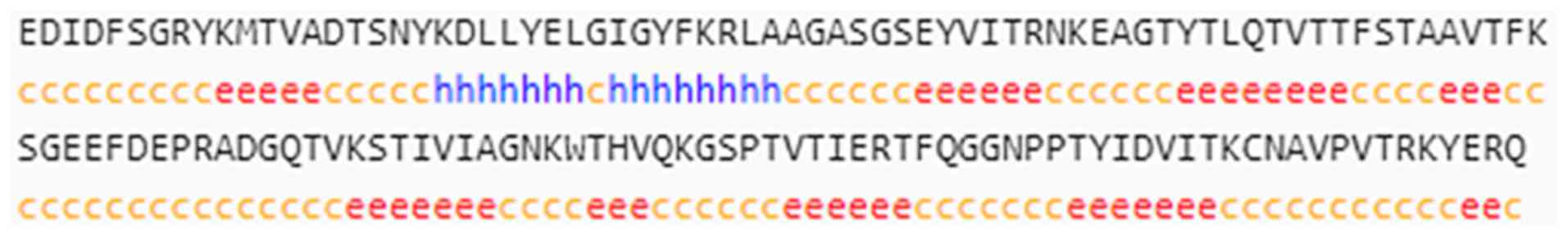
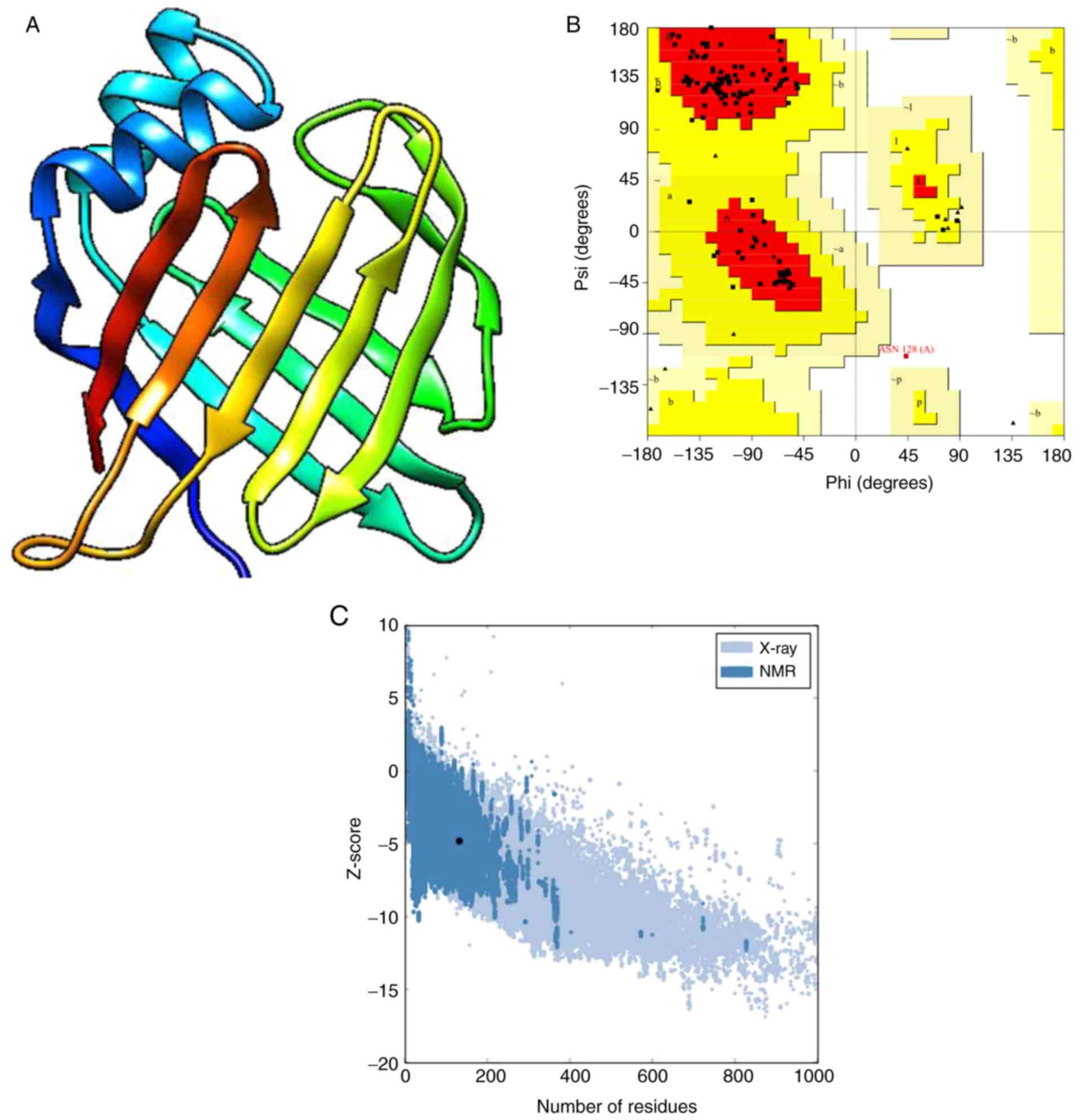
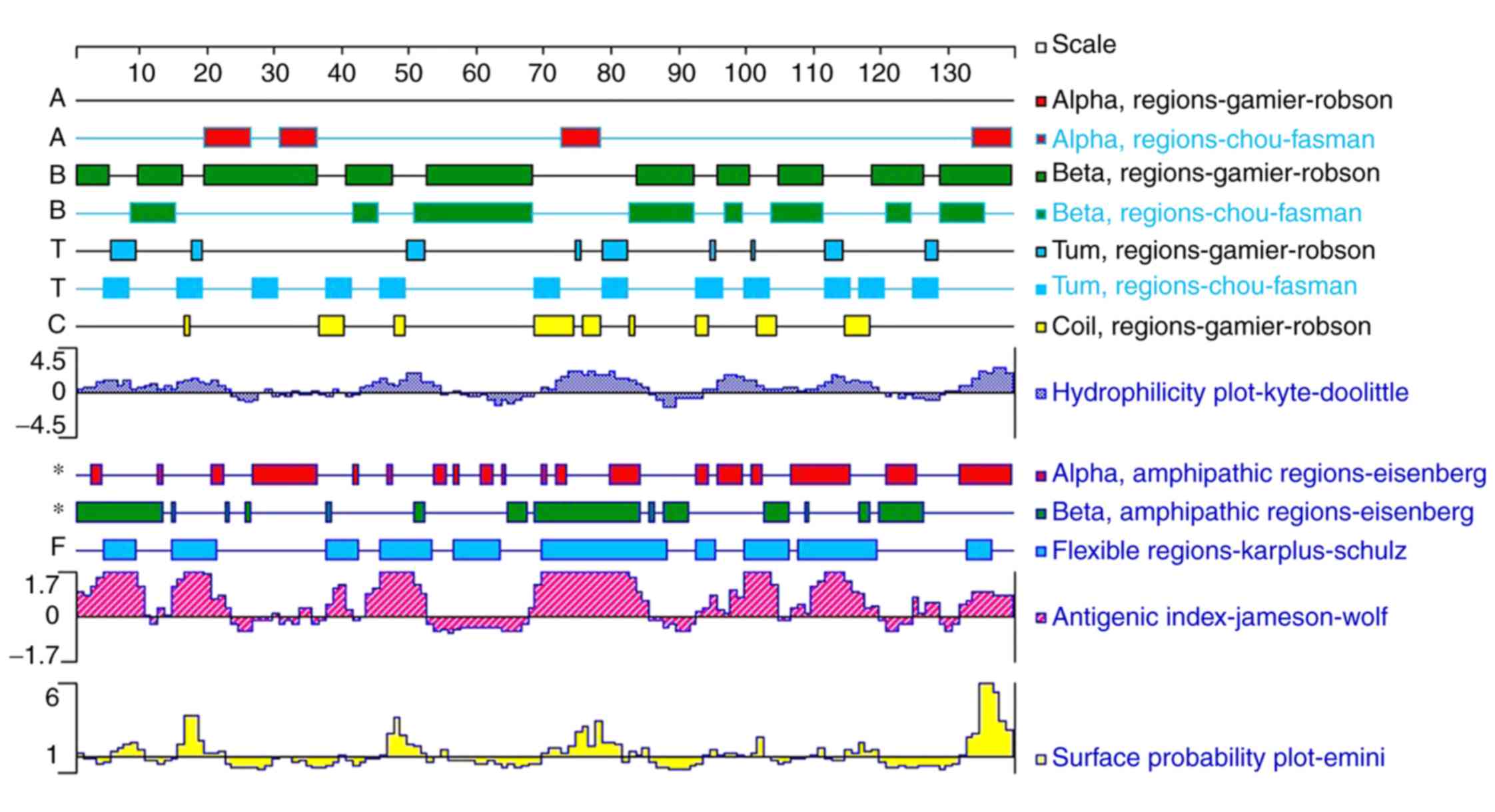
|
1
|
Jeong KY, Lee H, Lee JS, Lee J, Lee IY,
Ree HI, Hong CS and Yong TS: Molecular cloning and the allergenic
characterization of tropomyosin from Tyrophagus
putrescentiae. Protein Pept. Lett. 14:431–436. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Aygun O, Yaman M and Durmaz H: A survey on
occurrence of Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Acari: Acaridae) in
Surk, a traditional Turkish dairy product. J Food Eng. 78:878–881.
2007.
|
|
3
|
Uzunoğlu Karagöz E, Akdemir C, Direkel Ş
and Cebeci Guler N: The investigation of the presence of mites in
some served dry foodstuffs. Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 41:92–95.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liao EC, Hsu EL, Tsai JJ and Ho CM:
Immunologic characterization and allergenicity of recombinant Tyr p
3 allergen from the storage mite Tyrophagus putrescentiae. Int Arch
Allergy Immunol. 150:15–24. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mondal P, Dey D, Sarkar T, Laha A, Moitra
S, Bhattacharyya S, Saha NC, Saha GK and Podder S: Evaluation of
sensitivity toward storage mites and house dust mites among
nasobronchial allergic patients of kolkata, india. J Med Entomol.
56:347–352. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Szilman E, Szilman P, Solarz K,
Brewczyński P and Sieroń AL: Sensitization to the storage mite
Tyrophagus putrescentiae in urban population of Upper
Silesia (Poland). Wiad Parazytol. 50:471–476. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tabesh S, Fanuel S, Fazlollahi MR,
Yekaninejad MS, Kardar GA and Razavi SA: Design and evaluation of a
hypoallergenic peptide-based vaccine for Salsola kali allergy. Int
Immunopharmacol. 66:62–68. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Niederberger V and Valenta R: Molecular
approaches for new vaccines against allergy. Expert Rev Vaccines.
5:103–110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ramos JD, Valmonte GR and de Guia RM:
Recombinant proteins and peptides as diagnostic and therapeutic
reagents for arthropod allergies. Protein Pept Lett. 14:992–1002.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang L and Kulis M: Hypoallergenic
proteins for the treatment of food allergy. Curr Allergy Asthma
Rep. 19(15)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cui Y: Immunoglobulin E-binding epitopes
of mite allergens: from characterization to immunotherapy. Clin Rev
Allergy Immunol. 47:344–353. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Teng FX, Huang HF, Ge DZ, Yu LL, Xu C and
Cui YB: Tyrophagus putrescentiae group 4 allergen
allergenicity and epitope prediction. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr):
2020.
|
|
13
|
Cui Y, Yu L, Teng F, Zhang C, Wang N, Yang
L and Zhou Y: Transcriptomic/proteomic identification of allergens
in the mite Tyrophagus putrescentiae. Allergy. 71:1635–1639.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nicklas RA: National and international
guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of asthma. Curr Opin
Pulm Med. 3:51–55. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Guifang M, Qisong L, Yubao C and
Jinfang S: Use of a multimedia diagnostic microscope to
morphologically identify adult Tyrophagus putrescentiae. J
Pathogen Biology. 13:164–167. 2018.
|
|
16
|
Cui YB, Zhou P, Peng JL, Peng M, Zhou Y,
Lin YZ and Liu L: Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of
cDNA coding for the major house dust mite allergen, Der f 1, in
Escherichia coli. Braz J Med Biol Res. 41:380–388.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mitchell A, Chang HY, Daugherty L, Fraser
M, Hunter S, Lopez R, McAnulla C, McMenamin C, Nuka G, Pesseat S,
et al: The InterPro protein families database: The classification
resource after 15 years. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D213–D221.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
de Castro E, Sigrist CJ, Gattiker A,
Bulliard V, Langendijk-Genevaux PS, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A and Hulo
N: ScanProsite: Detection of PROSITE signature matches and
ProRule-associated functional and structural residues in proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res. 34:W362–W365. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cui YB, Yu LL, Teng FX, Wang N, Zhou Y,
Yang L and Zhang CB: Dust mite allergen Der f 4: Expression,
characterization, and IgE binding in pediatric asthma. Pediatr
Allergy Immunol. 27:391–397. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G and
Sonnhammer EL: Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a
hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol.
305:567–580. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Teng F, Yu L, Sun J, Wang N and Cui Y:
Homology modeling and prediction of Bcell and Tcell epitopes of the
house dust mite allergen Der f 20. Mol Med Rep. 17:1807–1812.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shahsavani N, Sheikhha MH, Yousefi H and
Sefid F: In silico homology modeling and epitope prediction of NadA
as a potential vaccine candidate in neisseria meningitidis. Int J
Mol Cell Med. 7:53–68. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tong X, Guo M, Jin M, Chen H, Li Y and Wei
JF: In silico epitope prediction, expression and functional
analysis of Per a 10 allergen from the American cockroach. Int J
Mol Med. 38:1806–1814. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sikic K, Tomic S and Carugo O: Systematic
comparison of crystal and NMR protein structures deposited in the
protein data bank. Open Biochem J. 4:83–95. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang C, Li J, Lai X, Zheng Y, Gjesing B,
Spangfort MD and Zhong N: House dust mite and storage mite IgE
reactivity in allergic patients from Guangzhou, China. Asian Pac J
Allergy Immunol. 30:294–300. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zakzuk J, Jiménez S, Cheong N, Puerta L,
Lee BW, Chua KY and Caraballo L: Immunological characterization of
a Blo t 12 isoallergen: identification of immunoglobulin E
epitopes. Clin Exp Allergy. 39:608–616. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cui Y, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Ma G and Yang L:
The group 10 allergen of Dermatophagoides farinae (Acari:
Pyroglyphidae): cDNA cloning, sequence analysis, and expression in
Escherichia coli BL21. J Med Entomol. 50:205–208.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|