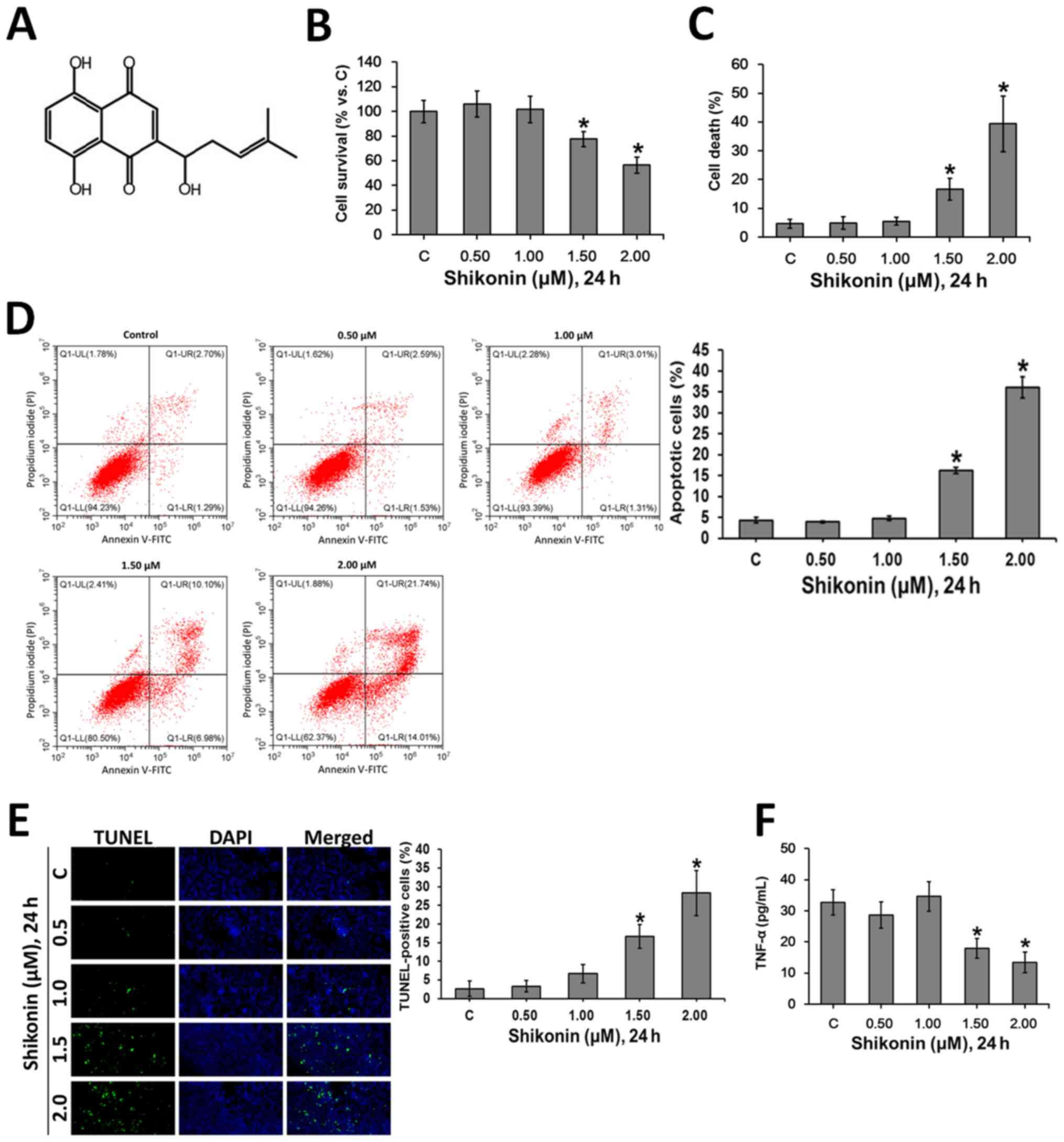
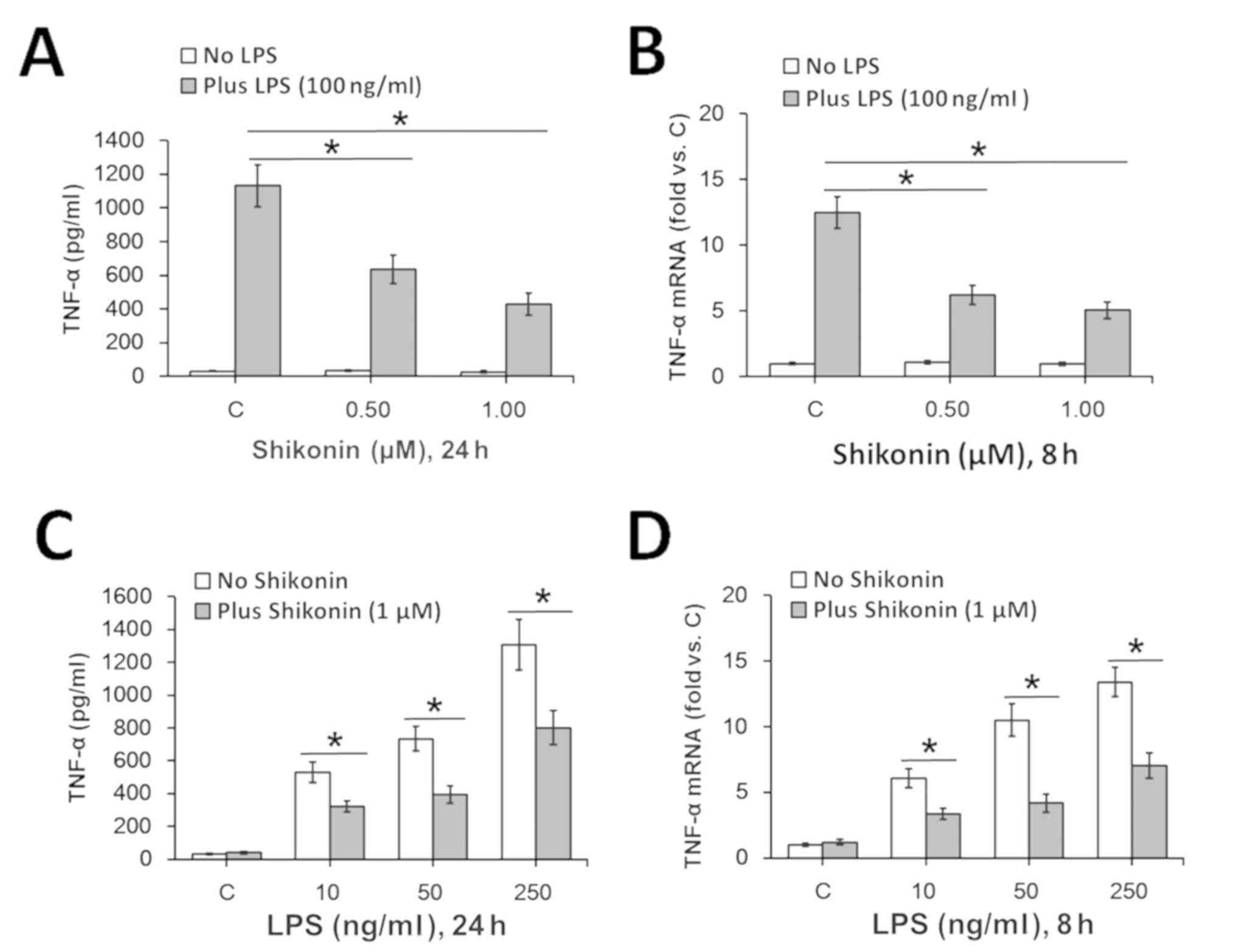
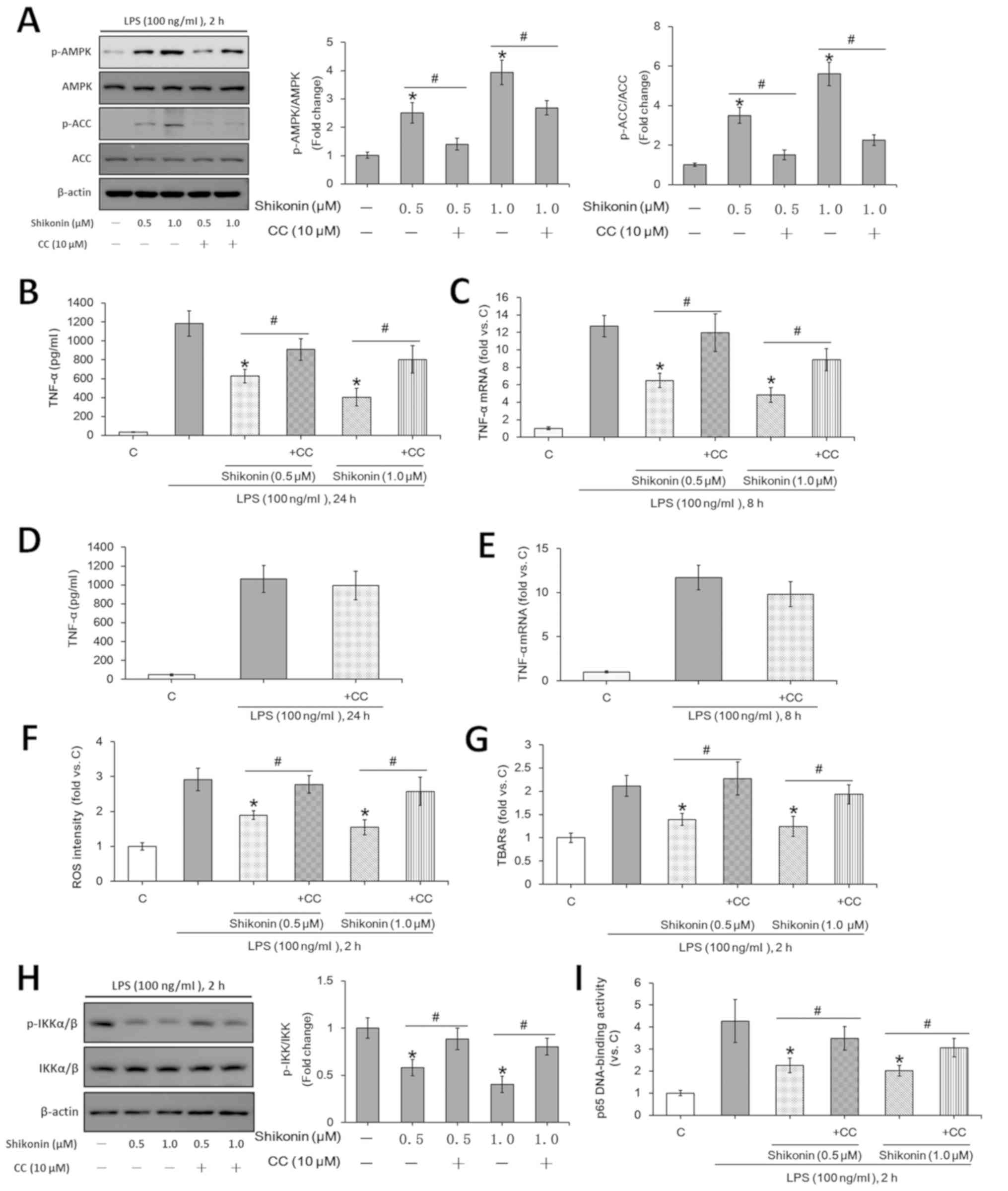
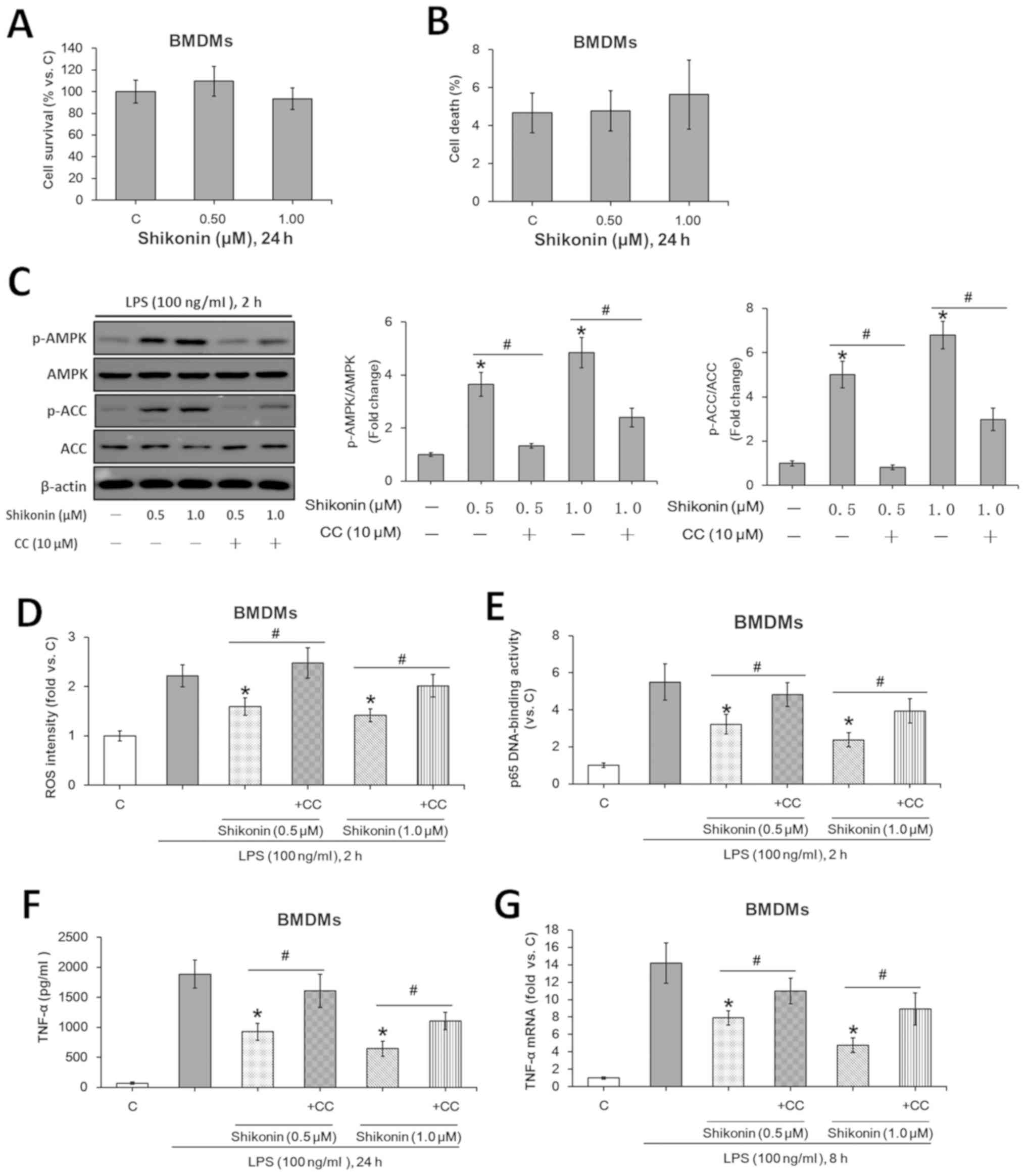
|
1
|
Lu Y, Chang R, Yao J, Xu X, Teng Y and
Cheng N: Effectiveness of long-term using statins in COPD-a network
meta-analysis. Respir Res. 20(17)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Park HY, Kang D, Lee H, Shin SH, Kang M,
Kong S, Rhee CK, Cho J and Yoo KH: Impact of chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease on mortality: A large national cohort study.
Respirology. 25:726–734. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lopez AD, Shibuya K, Rao C, Mathers CD,
Hansell AL, Held LS, Schmid V and Buist S: Chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease: Current burden and future projections. Eur
Respir J. 27:397–412. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li P, Wu Y, Li M, Qiu X, Bai X and Zhao X:
AS-703026 inhibits LPS-induced TNFα production through MEK/ERK
dependent and independent mechanisms. PLoS One.
10(e0137107)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Barnes PJ: New anti-inflammatory targets
for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
12:543–559. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Brusasco V and Martinez F: Chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Compr Physiol. 4:1–31.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Roversi S, Roversi P, Spadafora G, Rossi R
and Fabbri LM: Coronary artery disease concomitant with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 44:93–102.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cosio MG, Saetta M and Agusti A:
Immunologic aspects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N
Engl J Med. 360:2445–2454. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lamela J and Vega F: Immunologic aspects
of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med.
361(1024)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Singh D, Smyth L, Borrill Z, Sweeney L and
Tal-Singer R: A randomized, placebo-controlled study of the effects
of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB-681323 on blood biomarkers of
inflammation in COPD patients. J Clin Pharmacol. 50:94–100.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ouagued M, Martin-Chouly CA, Brinchault G,
Leportier-Comoy C, Depincé A, Bertrand C, Lagente V, Belleguic C
and Pruniaux MP: The novel phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, CI-1044,
inhibits LPS-induced TNF-alpha production in whole blood from COPD
patients. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 18:49–54. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rabinovich RA, Figueras M, Ardite E, Carbó
N, Troosters T, Filella X, Barberà JA, Fernandez-Checa JC, Argilés
JM and Roca J: Increased tumour necrosis factor-alpha plasma levels
during moderate-intensity exercise in COPD patients. Eur Respir J.
21:789–794. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Profita M, Chiappara G, Mirabella F, Di
Giorgi R, Chimenti L, Costanzo G, Riccobono L, Bellia V, Bousquet J
and Vignola AM: Effect of cilomilast (Ariflo) on TNF-alpha, IL-8,
and GM-CSF release by airway cells of patients with COPD. Thorax.
58:573–579. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jeon S-M, Chandel NS and Hay N: AMPK
regulates NADPH homeostasis to promote tumour cell survival during
energy stress. Nature. 485:661–665. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jansen T, Kvandová M, Daiber A, Stamm P,
Frenis K, Schulz E, Münzel T and Kröller-Schön S: The AMP-activated
protein kinase plays a role in antioxidant defense and regulation
of vascular inflammation. Antioxidants (Basel).
9(525)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Saisho Y: Metformin and inflammation: Its
potential beyond glucose-lowering effect. Endocr Metab Immune
Disord Drug Targets. 15:196–205. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Salt IP and Palmer TM: Exploiting the
anti-inflammatory effects of AMP-activated protein kinase
activation. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 21:1155–1167.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dandapani M and Hardie DG: AMPK: Opposing
the metabolic changes in both tumour cells and inflammatory cells?
Biochem Soc Trans. 41:687–693. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bai A, Ma AG, Yong M, Weiss CR, Ma Y, Guan
Q, Bernstein CN and Peng Z: AMPK agonist downregulates innate and
adaptive immune responses in TNBS-induced murine acute and
relapsing colitis. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1708–1717. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang Z, Kahn BB, Shi H and Xue BZ:
Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK)
antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J Biol
Chem. 285:19051–19059. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang S, Zhang M, Liang B, Xu J, Xie Z, Liu
C, Viollet B, Yan D and Zou MH: AMPKalpha2 deletion causes aberrant
expression and activation of NAD(P)H oxidase and consequent
endothelial dysfunction in vivo: Role of 26S proteasomes. Circ Res.
106:1117–1128. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Salminen A, Hyttinen JM and Kaarniranta K:
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-κB signaling and
inflammation: Impact on healthspan and lifespan. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:667–676. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
O'Neill LA and Hardie DG: Metabolism of
inflammation limited by AMPK and pseudo-starvation. Nature.
493:346–355. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jeon SM: Regulation and function of AMPK
in physiology and diseases. Exp Mol Med. 48(e245)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Galic S, Fullerton MD, Schertzer JD,
Sikkema S, Marcinko K, Walkley CR, Izon D, Honeyman J, Chen ZP, van
Denderen BJ, et al: Hematopoietic AMPK β1 reduces mouse adipose
tissue macrophage inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. J
Clin Invest. 121:4903–4915. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J,
Kaarniranta K and Salminen A: Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB
and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic
disorders. Cell Signal. 25:1939–1948. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shen J, Liang L and Wang C: Perifosine
inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-α production via regulation multiple signaling pathways: New
implication for Kawasaki disease (KD) treatment. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 437:250–255. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wu YH, Li Q, Li P and Liu B: GSK621
activates AMPK signaling to inhibit LPS-induced TNFα production.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 480:289–295. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ducommun S, Ford RJ, Bultot L, Deak M,
Bertrand L, Kemp BE, Steinberg GR and Sakamoto K: Enhanced
activation of cellular AMPK by dual-small molecule treatment: AICAR
and A769662. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 306:E688–E696.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang JL, Xu Y and Shen J: Cordycepin
inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-α production via activating amp-activated protein kinase
(AMPK) signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12119–12134. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li P, Li X, Wu Y, Li M and Wang X: A novel
AMPK activator hernandezine inhibits LPS-induced TNFα production.
Oncotarget. 8:67218–67226. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Guo C, He J, Song X, Tan L, Wang M, Jiang
P, Li Y, Cao Z and Peng C: Pharmacological properties and
derivatives of shikonin-A review in recent years. Pharmacol Res.
149(104463)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen X, Yang L, Oppenheim JJ and Howard
MZ: Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives.
Phytother Res. 16:199–209. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhou G, Yang Z, Wang X, Tao R and Zhou Y:
TRAIL enhances shikonin induced apoptosis through ROS/JNK signaling
in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:1073–1086.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Velliquette RA, Rajgopal A, Rebhun J and
Glynn K: Lithospermum erythrorhizon Root and its
naphthoquinones repress SREBP1c and activate PGC1α through AMPKα.
Obesity (Silver Spring). 26:126–134. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang R, Yin R, Zhou W, Xu D and Li S:
Shikonin and its derivatives: A patent review. Expert Opin Ther
Pat. 22:977–997. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Liu Y, Liu Y
and Xu G: Pioglitazone increases VEGFR3 expression and promotes
activation of M2 macrophages via the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ. Mol Med Rep. 19:2740–2748.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shi-Lin D, Yuan X, Zhan S, Luo-Jia T and
Chao-Yang T: Trametinib, a novel MEK kinase inhibitor, suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α production
and endotoxin shock. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:667–673.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wright CJ, Agboke F, Muthu M, Michaelis
KA, Mundy MA, La P, Yang G and Dennery PA: Nuclear factor-κB
(NF-κB) inhibitory protein IκBβ determines apoptotic cell death
following exposure to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 287:6230–6239.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Si H, Zhang Y, Song Y and Li L:
Overexpression of adrenomedullin protects mesenchymal stem cells
against hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis via the
Akt/GSK3β and Bcl-2 signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med.
41:3342–3352. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhu X, Jiang Y, Shan PF, Shen J, Liang QH,
Cui RR, Liu Y, Liu GY, Wu SS, Lu Q, et al: Vaspin attenuates the
apoptosis of human osteoblasts through ERK signaling pathway. Amino
Acids. 44:961–968. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hu YB, Wu X, Qin XF, Wang L and Pan PH:
Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in silica-induced apoptosis in
RAW264.7 cells. Biomed Environ Sci. 30:591–600. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Pan T, Zhang M, Zhang F, Yan G, Ru Y, Wang
Q, Zhang Y, Wei X, Xu X, Shen L, et al: NDRG2 overexpression
suppresses hepatoma cells survival during metabolic stress through
disturbing the activation of fatty acid oxidation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 483:860–866. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pan T, Zhang F, Li F, Gao X, Li Z, Li X
and Ren X: Shikonin blocks human lung adenocarcinoma cell migration
and invasion in the inflammatory microenvironment via the
IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 44:1049–1063.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cortizo AM, Bruzzone L, Molinuevo S and
Etcheverry SB: A possible role of oxidative stress in the
vanadium-induced cytotoxicity in the MC3T3E1 osteoblast and UMR106
osteosarcoma cell lines. Toxicology. 147:89–99. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Qian J, Jiang F, Wang B, Yu Y, Zhang X,
Yin Z and Liu C: Ophiopogonin D prevents H2O2-induced injury in
primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
128:438–445. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Watcharanurak K, Zang L, Nishikawa M,
Yoshinaga K, Yamamoto Y, Takahashi Y, Ando M, Saito K, Watanabe Y
and Takakura Y: Effects of upregulated indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase
1 by interferon γ gene transfer on interferon γ-mediated antitumor
activity. Gene Ther. 21:794–801. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ji G, Zhang Y, Yang Q, Cheng S, Hao J,
Zhao X and Jiang Z: Genistein suppresses LPS-induced inflammatory
response through inhibiting NF-κB following AMP kinase activation
in RAW 264.7 macrophages. PLoS One. 7(e53101)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Dumitru CD, Ceci JD, Tsatsanis C,
Kontoyiannis D, Stamatakis K, Lin JH, Patriotis C, Jenkins NA,
Copeland NG, Kollias G and Tsichlis PN: TNF-alpha induction by LPS
is regulated posttranscriptionally via a Tpl2/ERK-dependent
pathway. Cell. 103:1071–1083. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Thakur R, Trivedi R, Rastogi N, Singh M
and Mishra DP: Inhibition of STAT3, FAK and Src mediated signaling
reduces cancer stem cell load, tumorigenic potential and metastasis
in breast cancer. Sci Rep. 5(10194)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Andújar I, Rios JL, Giner RM and Recio MC:
Pharmacological properties of shikonin-a review of literature since
2002. Planta Med. 79:1685–1697. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Neumann D: Is TAK1 a direct upstream
kinase of AMPK? Int J Mol Sci. 19(2412)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Jiang T, Yu JT, Zhu XC, Wang HF, Tan MS,
Cao L, Zhang QQ, Gao L, Shi JQ, Zhang YD and Tan L: Acute metformin
preconditioning confers neuroprotection against focal cerebral
ischaemia by pre-activation of AMPK-dependent autophagy. Br J
Pharmacol. 171:3146–3157. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kurumbail RG and Calabrese MF: Structure
and regulation of AMPK. Exp Suppl. 107:3–22. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhou X, Cao Y, Ao G, Hu L, Liu H, Wu J,
Wang X, Jin M, Zheng S, Zhen X, et al: CaMKKβ-dependent activation
of AMP-activated protein kinase is critical to suppressive effects
of hydrogen sulfide on neuroinflammation. Antioxid Redox Signal.
21:1741–1758. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
She C, Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, Wang XD and Dong
QR: Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced
osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH
maintenance: New implications for osteonecrosis treatment? Cell
Signal. 26:1–8. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Lu B, Gong X, Wang ZQ, Ding Y, Wang C, Luo
TF, Piao MH, Meng FK, Chi GF, Luo YN and Ge PF: Shikonin induces
glioma cell necroptosis in vitro by ROS overproduction and
promoting RIP1/RIP3 necrosome formation. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
38:1543–1553. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhang X, Cui JH, Meng QQ, Li SS, Zhou W
and Xiao S: Advance in anti-tumor mechanisms of shikonin, alkannin
and their derivatives. Mini Rev Med Chem. 18:164–172.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Gasparrini M, Forbes-Hernandez TY,
Giampieri F, Afrin S, Alvarez-Suarez JM, Mazzoni L, Mezzetti B,
Quiles JL and Battino M: Anti-inflammatory effect of strawberry
extract against LPS-induced stress in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food
Chem Toxicol. 102:1–10. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Jung EH, Lee JH, Kim SC and Kim YW: AMPK
activation by liquiritigenin inhibited oxidative hepatic injury and
mitochondrial dysfunction induced by nutrition deprivation as
mediated with induction of farnesoid X receptor. Eur J Nutr.
56:635–647. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Kajiwara C, Kusaka Y, Kimura S, Yamaguchi
T, Nanjo Y, Ishii Y, Udono H, Standiford TJ and Tateda K: Metformin
mediates protection against legionella pneumonia through activation
of AMPK and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. J Immunol.
200:623–631. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
GBD 2015 Chronic Respiratory Disease
Collaborators. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence,
disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990-2015: A
systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015.
Lancet Respir Med. 5:691–706. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|