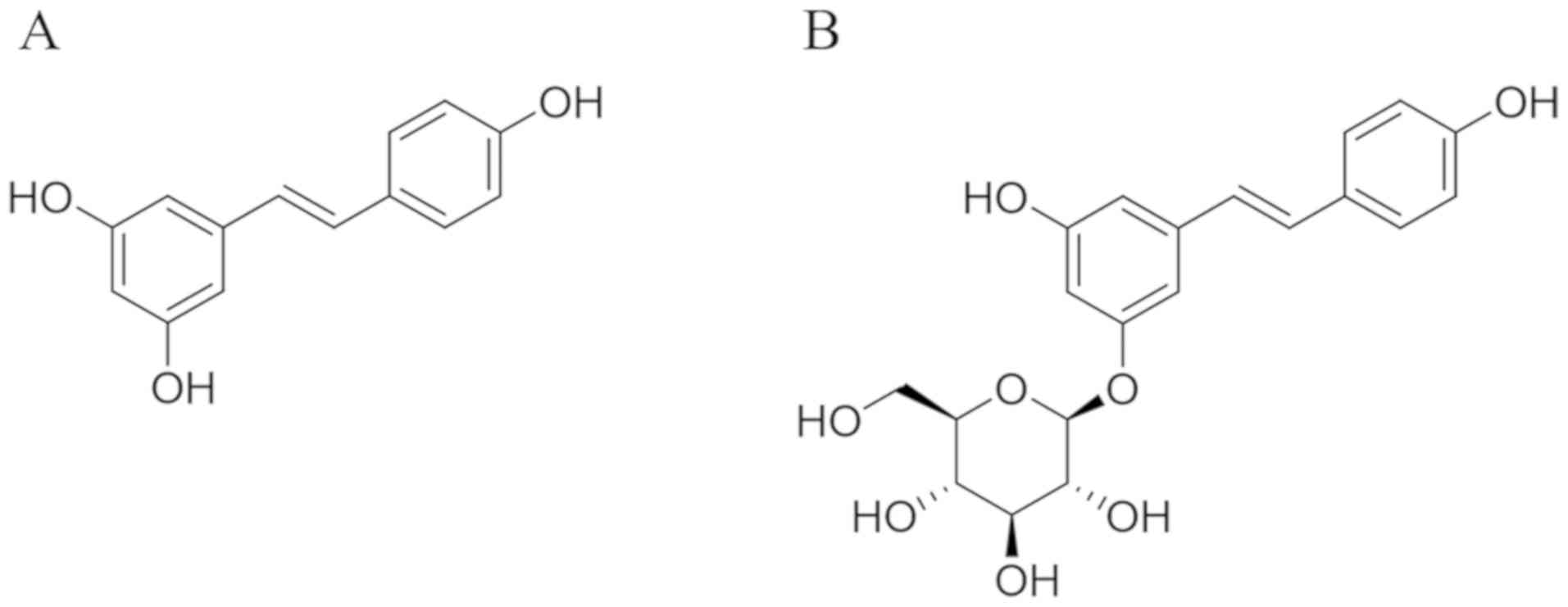
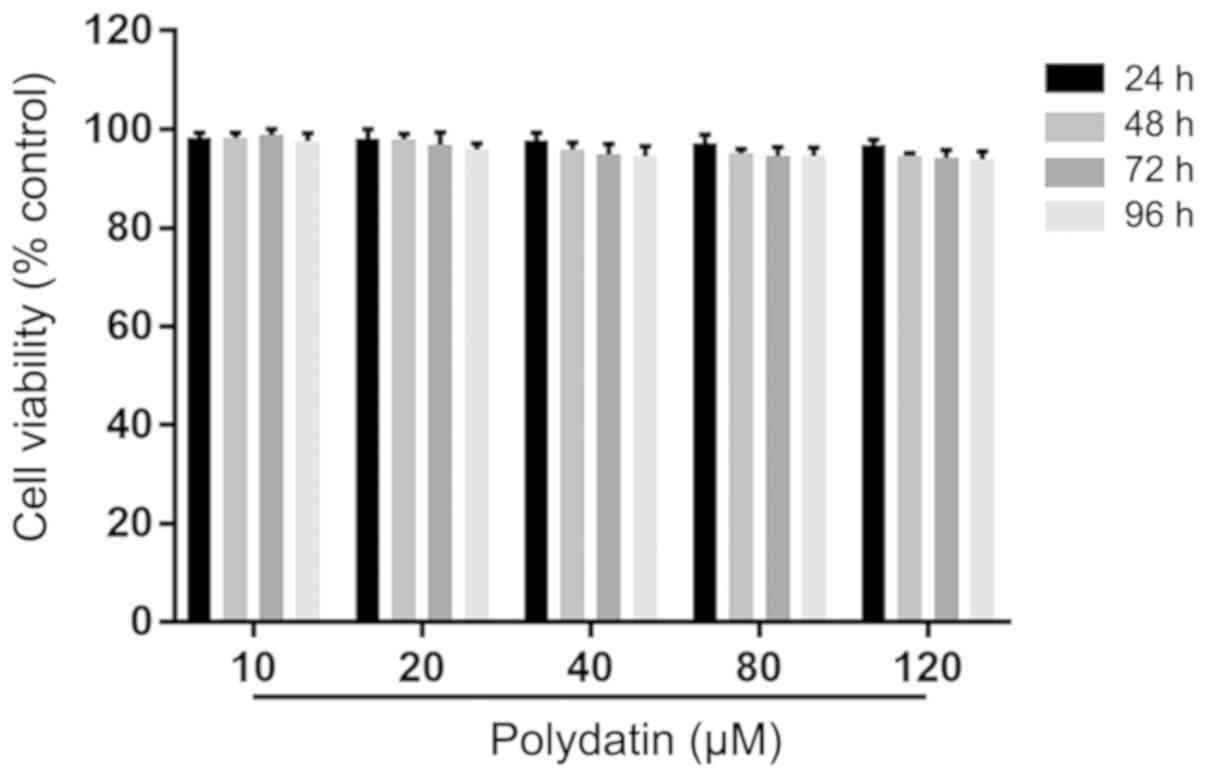
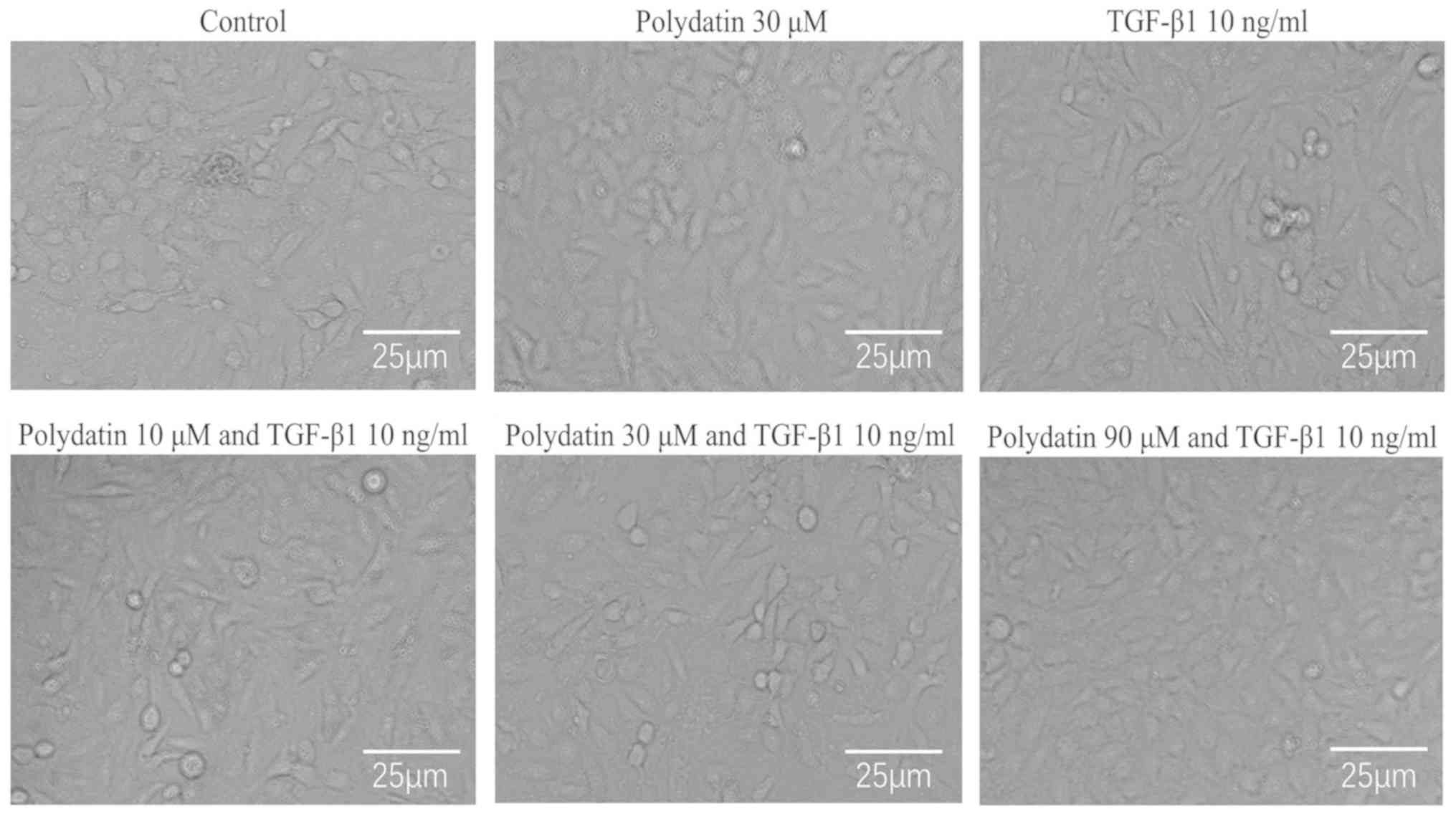
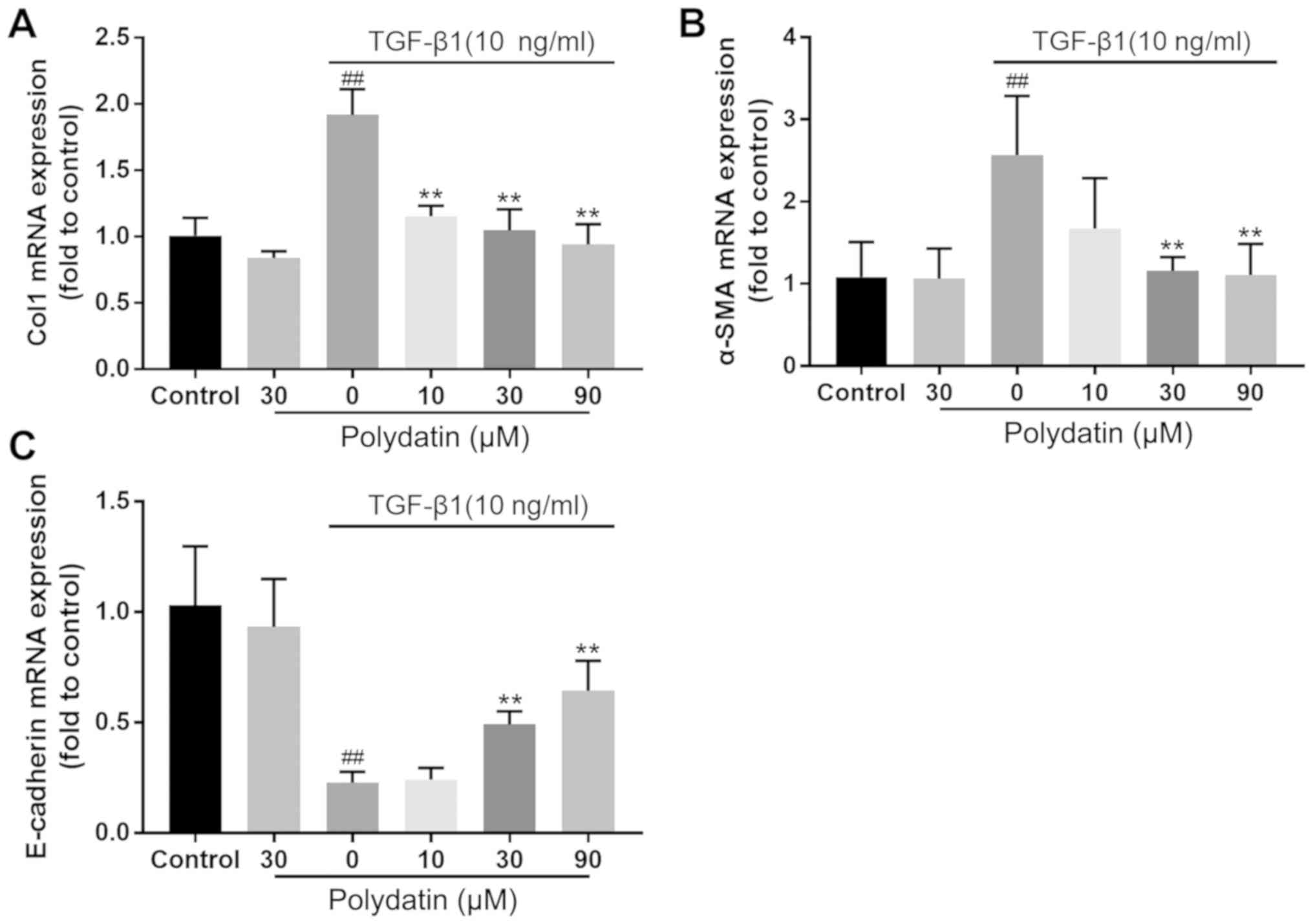
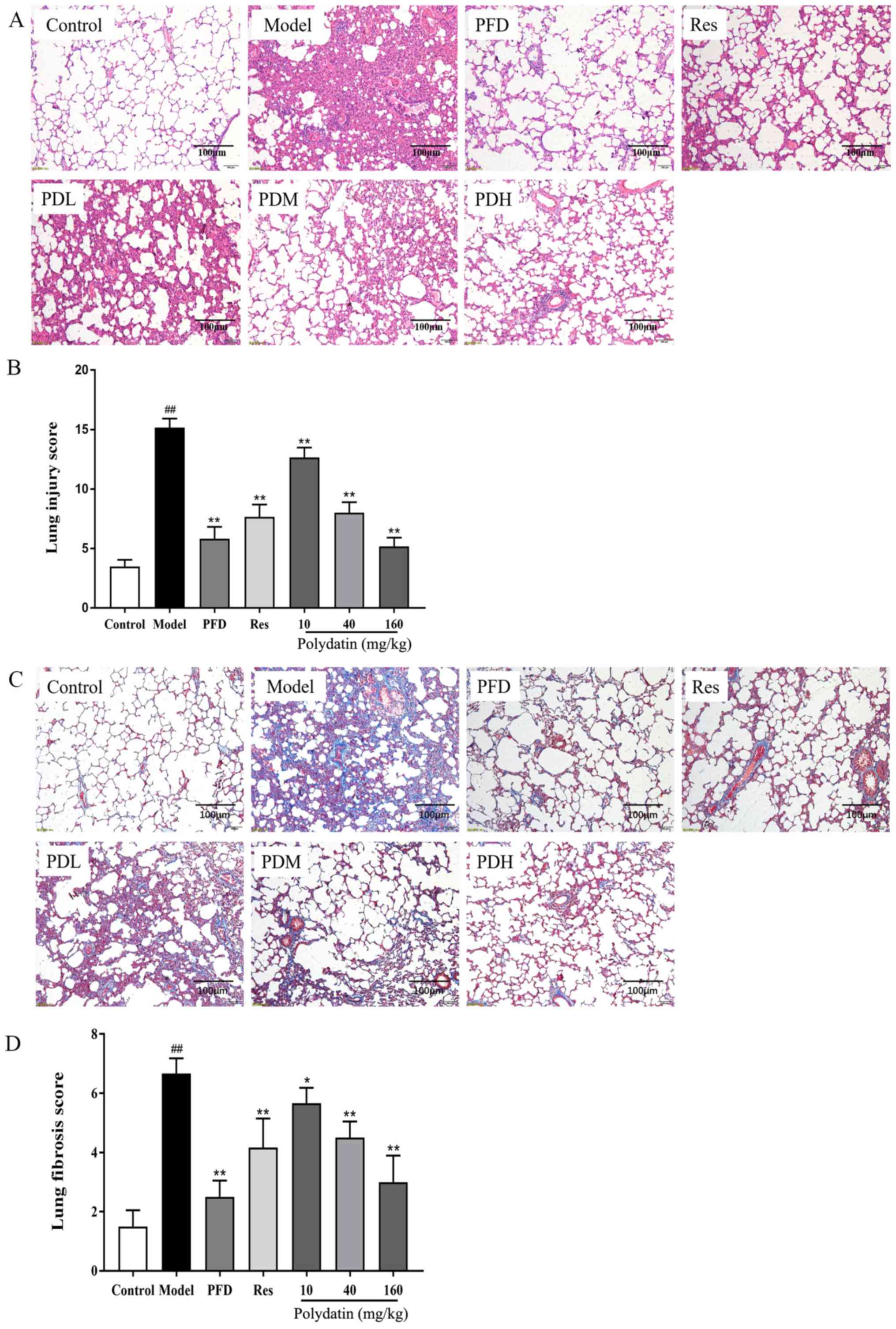
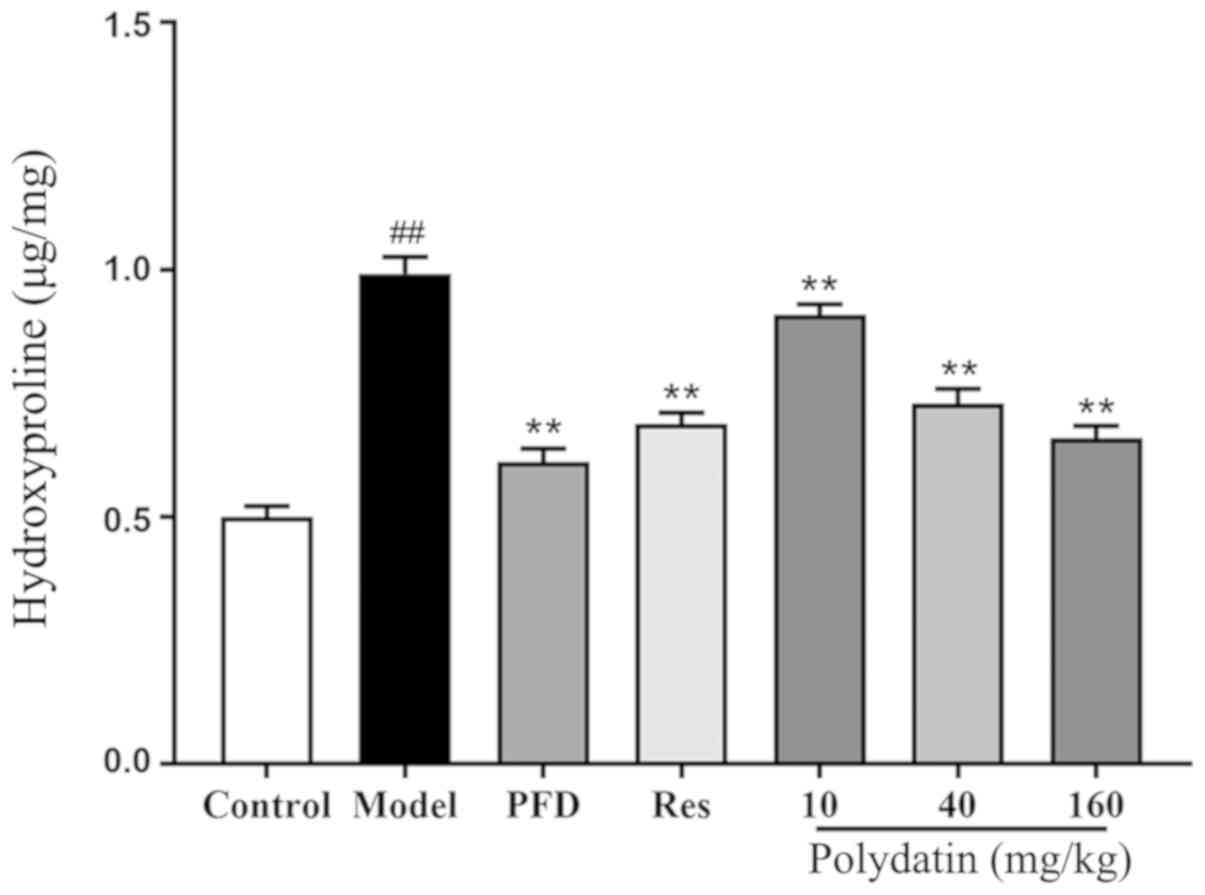
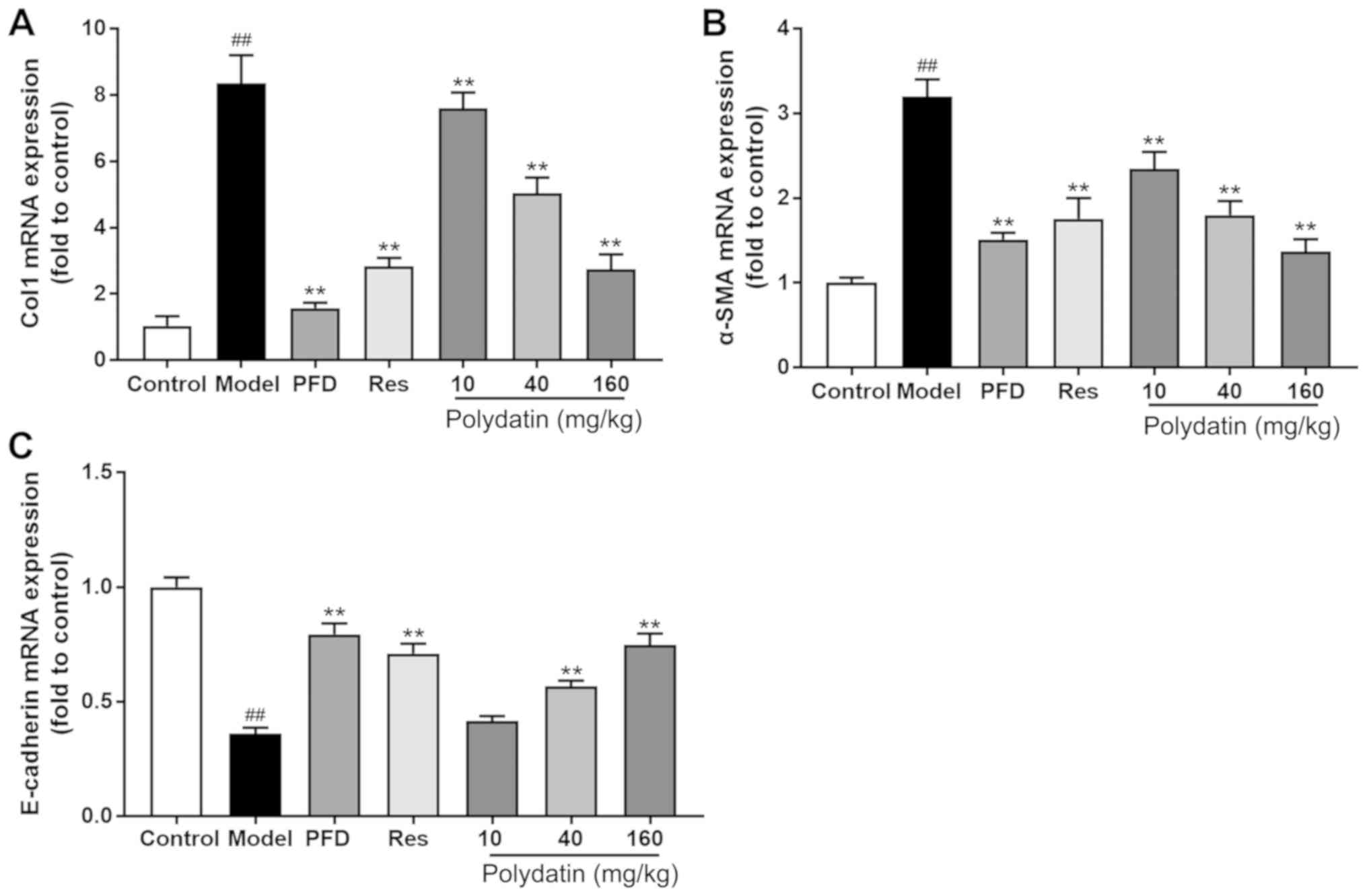
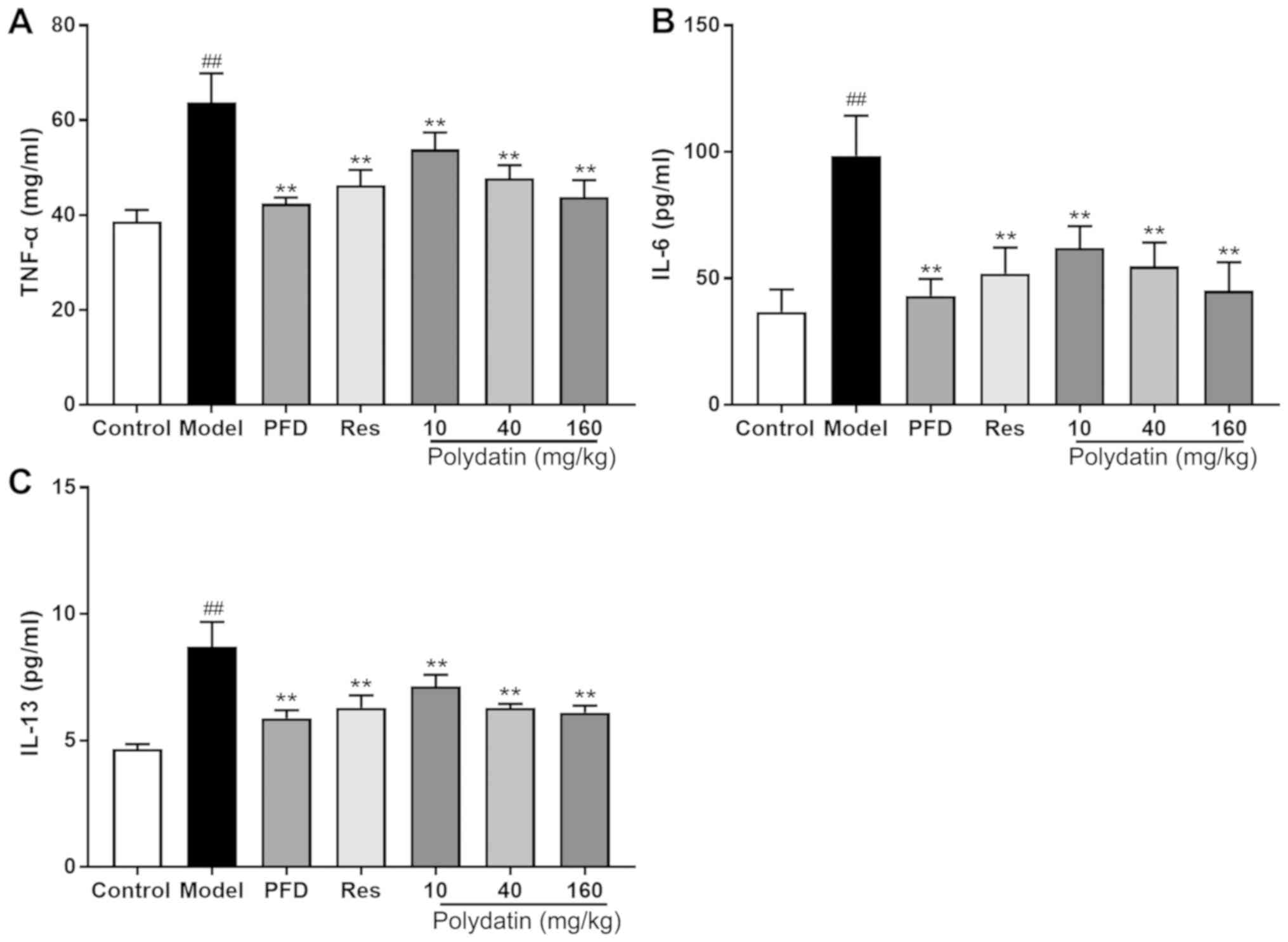
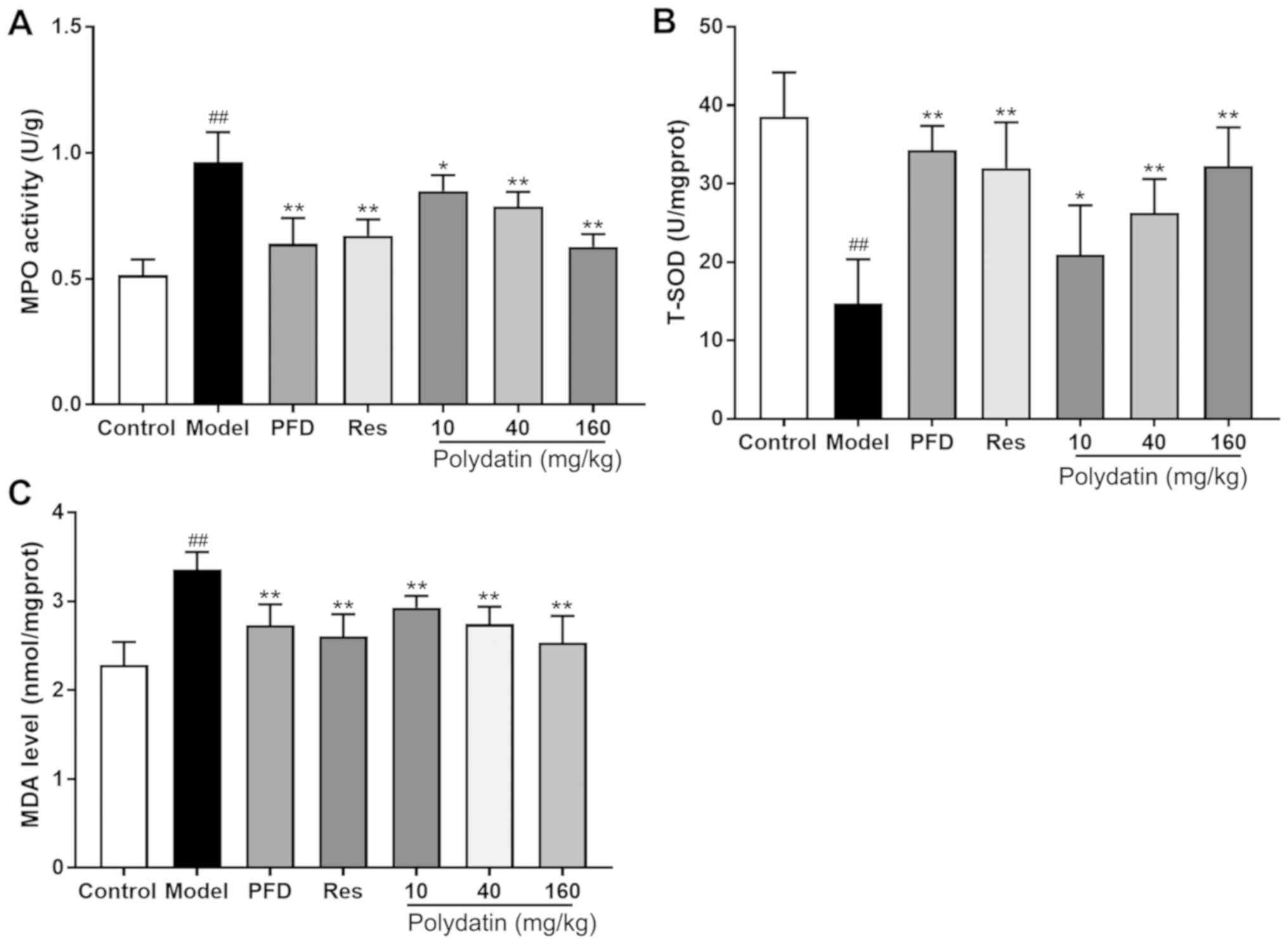
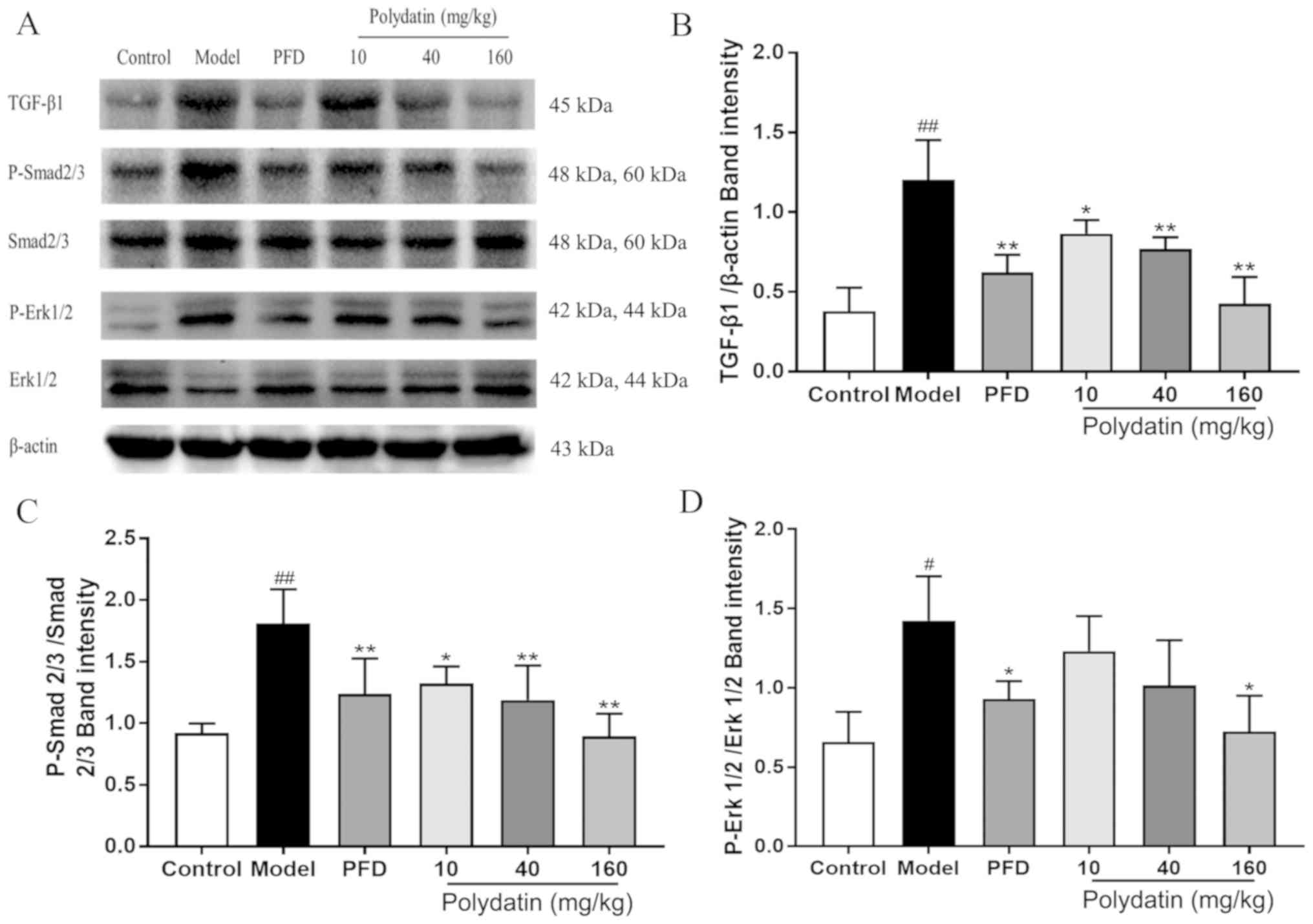
|
1
|
Luppi F, Spagnolo P, Cerri S and Richeldi
L: The big clinical trials in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr
Opin Pulm Med. 18:428–432. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang X, Ouyang Z, You Q, He S, Meng Q, Hu
C, Wu X, Shen Y, Sun Y, Wu X and Xu Q: Obaculactone protects
against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 303:21–29. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gouda MM and Bhandary YP: Curcumin
down-regulates IL-17A mediated p53-fibrinolytic system in bleomycin
induced acute lung injury in vivo. J Cell Biochem. 119:7285–7299.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
You XY, Xue Q, Fang Y, Liu Q, Zhang CF,
Zhao C, Zhang M and Xu XH: Preventive effects of ecliptae herba
extract and its component, ecliptasaponin a, on bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 175:172–180.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pardo A and Selman M: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: New insights in its pathogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 34:1534–1538. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Manali ED, Stathopoulos GT, Kollintza A,
Kalomenidis I, Emili JM, Sotiropoulou C, Daniil Z, Roussos C and
Papiris SA: The medical research council chronic dyspnea score
predicts the survival of patients with idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Respir Med. 102:586–592. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Krein PM and Winston BW: Roles for
insulin-like growth factor I and transforming growth factor-beta in
fibrotic lung disease. Chest. 122 (6 Suppl):289S–293S.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Handa T and Azuma A: Pharmacotherapy of
IPF using antifibrotic compounds. In: Idiopathic Pulmonary
Fibrosis. Nakamura H and Aoshiba K (eds). Springer, Japan,
pp147-159, 2016.
|
|
9
|
Truong VL, Jun M and Jeong WS: Role of
resveratrol in regulation of cellular defense systems against
oxidative stress. Biofactors. 44:36–49. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Brasnyó P, Molnár GA, Mohás M, Markó L,
Laczy B, Cseh J, Mikolás E, Szijártó IA, Mérei A, Halmai R, et al:
Resveratrol improves insulin sensitivity, reduces oxidative stress
and activates the Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic patients. Br J
Nutr. 106:383–389. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vargas JE, Souto AA, Pitrez PMC, Stein RT
and Porto BN: Modulatory potential of resveratrol during lung
inflammatory disease. Med Hypotheses. 96:61–65. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Haobo L, Guangfeng Z and Xiao Z: OP0216
resveratrol ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis and inhibits human lung
fibroblasts activation via modulating SIRT1 and GLI1 signaling. Ann
Rheumatic Diseases. 74:152–153. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Chávez E, Reyes-Gordillo K, Segovia J,
Shibayama M, Tsutsumi V, Vergara P, Moreno MG and Muriel P:
Resveratrol prevents fibrosis, NF-kappaB activation and TGF-beta
increases induced by chronic CCl4 treatment in rats. J Appl
Toxicol. 28:35–43. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Di Benedetto A, Posa F, De Maria S,
Ravagnan G, Ballini A, Porro C, Trotta T, Grano M, Muzio LL and
Mori G: Polydatin, natural precursor of resveratrol, promotes
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Med
Sci. 15:944–952. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang LP, Yang CY, Wang YP, Cui F and
Zhang Y: Protective effect of polydatin against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat heart. Sheng Li Xue Bao.
60:161–168. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koneru M, Sahu BD, Gudem S, Kuncha M,
Ravuri HG, Kumar JM, Kilari EK and Sistla R: Polydatin alleviates
alcohol-induced acute liver injury in mice: Relevance of matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) and hepatic antioxidants. Phytomedicine.
27:23–32. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cremon C, Stanghellini V, Barbaro MR,
Cogliandro RF, Bellacosa L, Santos J, Vicario M, Pigrau M, Alonso
Cotoner C, Lobo B, et al: Randomised clinical trial: The analgesic
properties of dietary supplementation with palmitoylethanolamide
and polydatin in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
45:909–922. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Martano M, Stiuso P, Facchiano A, De Maria
S, Vanacore D, Restucci B, Rubini C, Caraglia M, Ravagnan G and Lo
Muzio L: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor, a tumor grade-associated marker
of oral cancer, is directly downregulated by polydatin: A pilot
study. Oncol Rep. 40:1435–1442. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jiang Q, Yi M, Guo Q, Wang C, Wang H, Meng
S, Liu C, Fu Y, Ji H and Chen T: Protective effects of polydatin on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through
TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:370–376.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu W, Chen P, Deng J, Lv J and Liu J:
Resveratrol and polydatin as modulators of Ca2+
mobilization in the cardiovascular system. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1403:82–91. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang YS, Zhuang ZX, Jiao Y, Xu JY, Fan SJ
and Qin SB: Polydatin inhibits metastasis of human breast cancer
and underlying mechanisms. China J Cancer Prev Treat. 21:1788–1793.
2014.
|
|
22
|
Pan JH, Wang HB, Du XF, Liu JY and Zhang
DJ: Polydatin induces human cervical cancer cell apoptosis via
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
42:2345–2349. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Mo JF, Wu JY, Zheng L, Yu YW, Zhang TX,
Guo L and Bao Y: Therapeutic efficacy of polydatin for nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease via regulating inflammatory response in obese
mice. RSC Adv. 8:31194–31200. 2018.
|
|
24
|
Li R, Li J, Huang Y, Li H, Yan S, Lin J,
Chen Y, Wu L, Liu B, Wang G and Lan T: Polydatin attenuates
diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Int
J Biol Sci. 14:1411–1425. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shiyu S, Zhiyu L, Mao Y, Lin B, Lijia W,
Tianbao Z, Jie C and Tingyu L: Polydatin up-regulates clara cell
secretory protein to suppress phospholipase A2 of lung induced by
LPS in vivo and in vitro. BMC Cell Biol. 12(31)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yan XD, Wang QM, Tie C, Jin HT, Han YX,
Zhang JL, Yu XM, Hou Q, Zhang PP, Wang AP, et al: Polydatin
protects the respiratory system from PM2.5 exposure. Sci
Rep. 7(40030)2017.
|
|
27
|
Cao K, Lei X, Liu H, Zhao H, Guo J, Chen
Y, Xu Y, Cheng Y, Liu C, Cui J, et al: Polydatin alleviated
radiation-induced lung injury through activation of Sirt3 and
inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Mol Med.
21:3264–3276. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Qiu Y, Pan X and Hu Y: Polydatin
ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing inflammation and the
epithelial mesenchymal transition via inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad
signaling pathway. RSC Adv. 9:8104–8112. 2019.
|
|
29
|
Gong LK, Li XH, Wang H, Zhang L, Cai Y, Qi
XM, Liu LL, Liu YZ, Wu XF, Chen FP, et al: Feitai attenuates
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Biol Pharm Bull.
27:634–640. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou C, Han W, Zhang P, Cai M, Wei D and
Zhang C: Lycopene from tomatoes partially alleviates the
bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Nutr
Res. 28:122–130. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hübner RH, Gitter W, El Mokhtari NE,
Mathiak M, Both M, Bolte H, Freitag-Wolf S and Bewig B:
Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological
samples. Biotechniques. 44:507–511, 514-517. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Robbe A, Tassin A, Carpentier J, Declèves
AE, Mekinda Ngono ZL, Nonclercq D and Legrand A: Intratracheal
bleomycin aerosolization: The best route of administration for a
scalable and homogeneous pulmonary fibrosis rat model? BioMed Res
Int. 2015(198418)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang F, Zhang Z, Chen L, Kong D, Zhang X,
Lu C, Lu Y and Zheng S: Curcumin attenuates angiogenesis in liver
fibrosis and inhibits angiogenic properties of hepatic stellate
cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1392–1406. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Selman M, King TE Jr and Pardo A: American
Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society; American College of
Chest Physicians. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Prevailing and
evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for
therapy. Ann Intern Med. 134:136–151. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fioret D: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
Diagnosis, management, and the search for a cure Electronic Theses
and Dissertations, University of Louisville. Paper.
437(394)2012.doi:10.18297/etd/437.
|
|
38
|
McCormack FX, King TE Jr, Voelker DR,
Robinson PC and Mason RJ: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Abnormalities in the bronchoalveolar lavage content of surfactant
protein A. Am Rev Respir Dis. 144:160–166. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Williamson JD, Sadofsky LR and Hart SP:
The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced lung injury in animals and
its applicability to human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung
Res. 41:57–73. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ramirez AM, Wongtrakool C, Welch T,
Steinmeyer A, Zügel U and Roman J: Vitamin D inhibition of
pro-fibrotic effects of transforming growth factor beta1 in lung
fibroblasts and epithelial cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
118:142–150. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yu WN, Sun LF and Yang H: Inhibitory
effects of astragaloside IV on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation.
Inflammation. 39:1835–1841. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Adegunsoye A, Balachandran J and Ivanovska
N: Inflammatory response mechanisms exacerbating hypoxemia in
coexistent pulmonary fibrosis and sleep apnea. Mediators Inflamm.
2015(510105)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hong JS, Ko HH, Han ES and Lee CS:
Inhibition of bleomycin-induced cell death in rat alveolar
macrophages and human lung epithelial cells by ambroxol. Biochem
Pharmacol. 66:1297–1306. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Uchida M, Shiraishi H, Ohta S, Arima K,
Taniguchi K, Suzuki S, Okamoto M, Ahlfeld SK, Ohshima K, Kato S, et
al: Periostin, a matricellular protein, plays a role in the
induction of chemokines in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 46:677–686. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li L, Wu W, Huang W, Hu G, Yuan W and Li
W: NF-κB RNAi decreases the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and inhibits
TNF-α-induced apoptosis in human alveolar epithelial cells. Inflamm
Res. 62:387–397. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Dong SH, Liu YW, Wei F, Tan HZ and Han ZD:
Asiatic acid ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin
(BLM) via suppressing pro-fibrotic and inflammatory signaling
pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:1297–1309. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Grounds MD: Complexity of extracellular
matrix and skeletal muscle regeneration. Adv Muscle Res. 3:269–302.
2008.
|
|
48
|
Matute-Bello G, Winn RK, Jonas M, Chi EY,
Martin TR and Liles WC: Fas (CD95) induces alveolar epithelial cell
apoptosis in vivo: Implications for acute pulmonary inflammation.
Am J Pathol. 158:153–161. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hirano Y, Aziz M, Yang WL, Wang Z, Zhou M,
Ochani M, Khader A and Wang P: Neutralization of osteopontin
attenuates neutrophil migration in sepsis-induced acute lung
injury. Crit Care. 19(53)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Van Der Vliet A, Nguyen MN, Shigenaga MK,
Eiserich JP, Marelich GP and Cross CE: Myeloperoxidase and protein
oxidation in cystic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
279:L537–L546. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Siqueira RF, Weigel RA, Nunes GR, Mori CS
and Fernandes WR: Oxidative profiles of endurance horses racing
different distances. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec. 66:455–461. 2014.
|
|
52
|
Kosters M, Kothari S, Ghaly T and Dhamoon
A: Unmasking a rare rheumatological disease with the atypical
presentation of acute onset shortness of breath. Chest J. 146
(Suppl 4)(414A)2014.
|
|
53
|
Teixeira KC, Soares FS, Rocha LGC,
Silveira PCL, Silva LA, Valença SS, Dal Pizzol F, Streck EL and
Pinho RA: Attenuation of bleomycin-induced lung injury and
oxidative stress by N-acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine. Pulm
Pharmacol Ther. 21:309–316. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lee YM, Rhee JS, Hwang DS, Kim IC,
Raisuddin S and Lee JS: Mining of biomarker genes from expressed
sequence tags and differential display reverse
transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in the self-fertilizing
fish, kryptolebias marmoratus and their expression patterns in
response to exposure to an endocrine-disrupting alkylphenol,
bisphenol A. Mol Cells. 23:287–303. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Culcasi M, Benameur L, Mercier A, Lucchesi
C, Rahmouni H, Asteian A, Casano G, Botta A, Kovacic H and Pietri
S: EPR spin trapping evaluation of ROS production in human
fibroblasts exposed to cerium oxide nanoparticles: Evidence for
NADPH oxidase and mitochondrial stimulation. Chem Biol Interact.
199:161–176. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Long LL, Yi YJ, Zhou JW, Cheng YD and Xia
YB: Microbial transformation of polydatin by endophytic fungi
isolated from polygonum cuspidatum and antioxidant activity
of the products. Mod Food Sci Technol. 31:76–83, and 162. 2015.
|
|
57
|
Massagué J, Blain SW and Lo RS: TGFbeta
signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell.
103:295–309. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Derynck R and Akhurst RJ: Differentiation
plasticity regulated by TGF-beta family proteins in development and
disease. Nat Cell Biol. 9:1000–1004. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Branton MH and Kopp JB: TGF-beta and
fibrosis. Microbes Infect. 1:1349–1365. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Jin M, Wang L, Wu Y, Zang BX and Tan L:
Protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on bleomycin-induced
pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in rats. Chin J Integr Med.
24:32–39. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Khalil N and Greenberg AH: The role of
TGF-beta in pulmonary fibrosis. Ciba Found Symp. 157:194–207;
discussion 207-211. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zhou Y, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Tan M, Zheng R,
Zhao L and Zhang X: Induced pluripotent stem cell-conditioned
medium suppresses pulmonary fibroblast-to-myofibroblast
differentiation via the inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Int J
Mol Med. 41:473–484. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Tobar N, Villar V and Santibanez JF:
ROS-NFkappaB mediates TGF-beta1-induced expression of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator, matrix metalloproteinase-9
and cell invasion. Mol Cell Biochem. 340:195–202. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Verrecchia F and Mauviel A: TGF-beta and
TNF-alpha: Antagonistic cytokines controlling type I collagen gene
expression. Cell Signal. 16:873–880. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Feng XH and Derynck R: Specificity and
versatility in TGF-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 21:659–693. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Roberts AB, Tian F, Byfield SD, Stuelten
C, Ooshima A, Saika S and Flanders KC: Smad3 is key to
TGF-beta-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, fibrosis,
tumor suppression and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
17:19–27. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhao J, Shi W, Wang YL, Chen H, Bringas P
Jr, Datto MB, Frederick JP, Wang XF and Warburton D: Smad3
deficiency attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 282:L585–L593. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Shou J, Cao J, Zhang S, Sun R, Zhao M,
Chen K, Su SB, Yang J and Yang T: SIS3, a specific inhibitor of
smad3, attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:757–762. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Wang S, Wilkes MC, Leof EB and Hirschberg
R: Imatinib mesylate blocks a non-Smad TGF-beta pathway and reduces
renal fibrogenesis in vivo. FASEB J. 19:1–11. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Zhang M, Fraser D and Phillips A: ERK,
p38, and Smad signaling pathways differentially regulate
transforming growth factor-beta1 autoinduction in proximal tubular
epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 169:1282–1293. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Chun JN, Park S, Lee S, Kim JK, Park EJ,
Kang M, Kim HK, Park JK, So I and Jeon JH: Schisandrol B and
schisandrin B inhibit TGFβ1-mediated NF-κB activation via a
Smad-independent mechanism. Oncotarget. 9:3121–3130.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Hartsough MT and Mulder KM: Transforming
growth factor beta activation of p44mapk in proliferating cultures
of epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 270:7117–7124. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Mucsi I, Skorecki KL and Goldberg HJ:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and the small GTP-binding
protein, Rac, contribute to the effects of transforming growth
factor-beta1 on gene expression. J Biol Chem. 271:16567–16572.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
González MN, de Mello W, Butler-Browne GS,
Silva-Barbosa SD, Mouly V, Savino W and Riederer I: HGF potentiates
extracellular matrix-driven migration of human myoblasts:
Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases and MAPK/ERK pathway.
Skelet Muscle. 7(20)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Hu X, Wang H, Liu J, Fang X, Tao K, Wang
Y, Li N, Shi J, Wang Y, Ji P, et al: The role of ERK and JNK
signaling in connective tissue growth factor induced extracellular
matrix protein production and scar formation. Arch Dermatol Res.
305:433–445. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Hough C, Radu M and Doré JJ: TGF-beta
induced Erk phosphorylation of smad linker region regulates smad
signaling. PLoS One. 7(e42513)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Matsuura I, Wang G, He D and Liu F:
Identification and characterization of ERK MAP kinase
phosphorylation sites in Smad3. Biochemistry. 44:12546–12553.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Kretzschmar M, Doody J, Timokhina I and
Massagué J: A mechanism of repression of TGFbeta/Smad signaling by
oncogenic Ras. Genes Dev. 13:804–816. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Wang G, Jiao H, Zheng JN and Sun X: HSP27
regulates TGF-β mediated lung fibroblast differentiation through
the Smad3 and ERK pathways. Int J Mol Med. 39:183–190.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Conte E, Gili E, Fagone E, Fruciano M,
Iemmolo M and Vancheri C: Effect of pirfenidone on proliferation,
TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation and fibrogenic activity
of primary human lung fibroblasts. Eur J Pharm Sci. 58:13–19.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Li C, Rezov V, Joensuu E, Vartiainen V,
Rönty M, Yin M, Myllärniemi M and Koli K: Pirfenidone decreases
mesothelioma cell proliferation and migration via inhibition of ERK
and AKT and regulates mesothelioma tumor microenvironment in vivo.
Sci Rep. 8(10070)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|