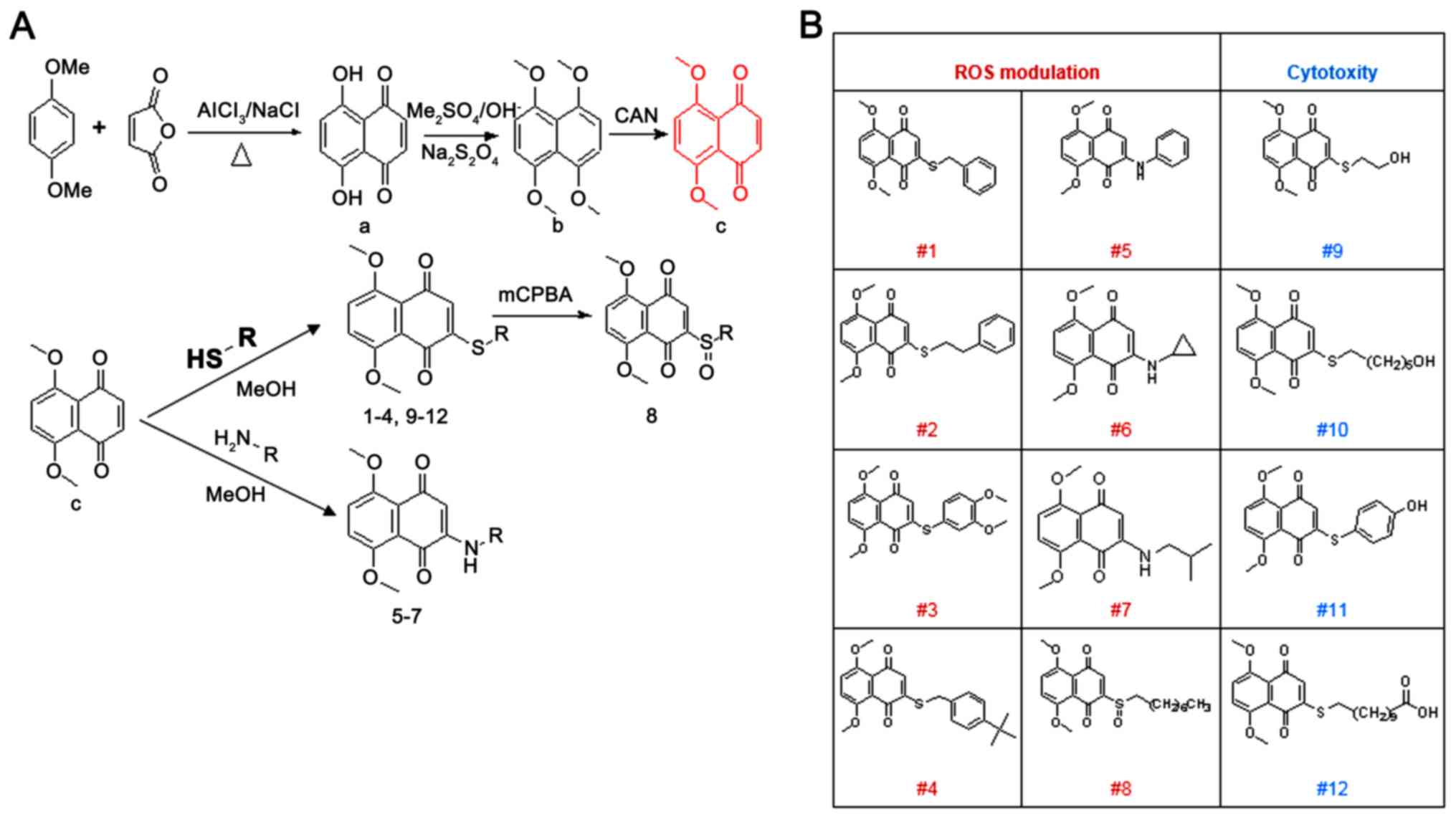
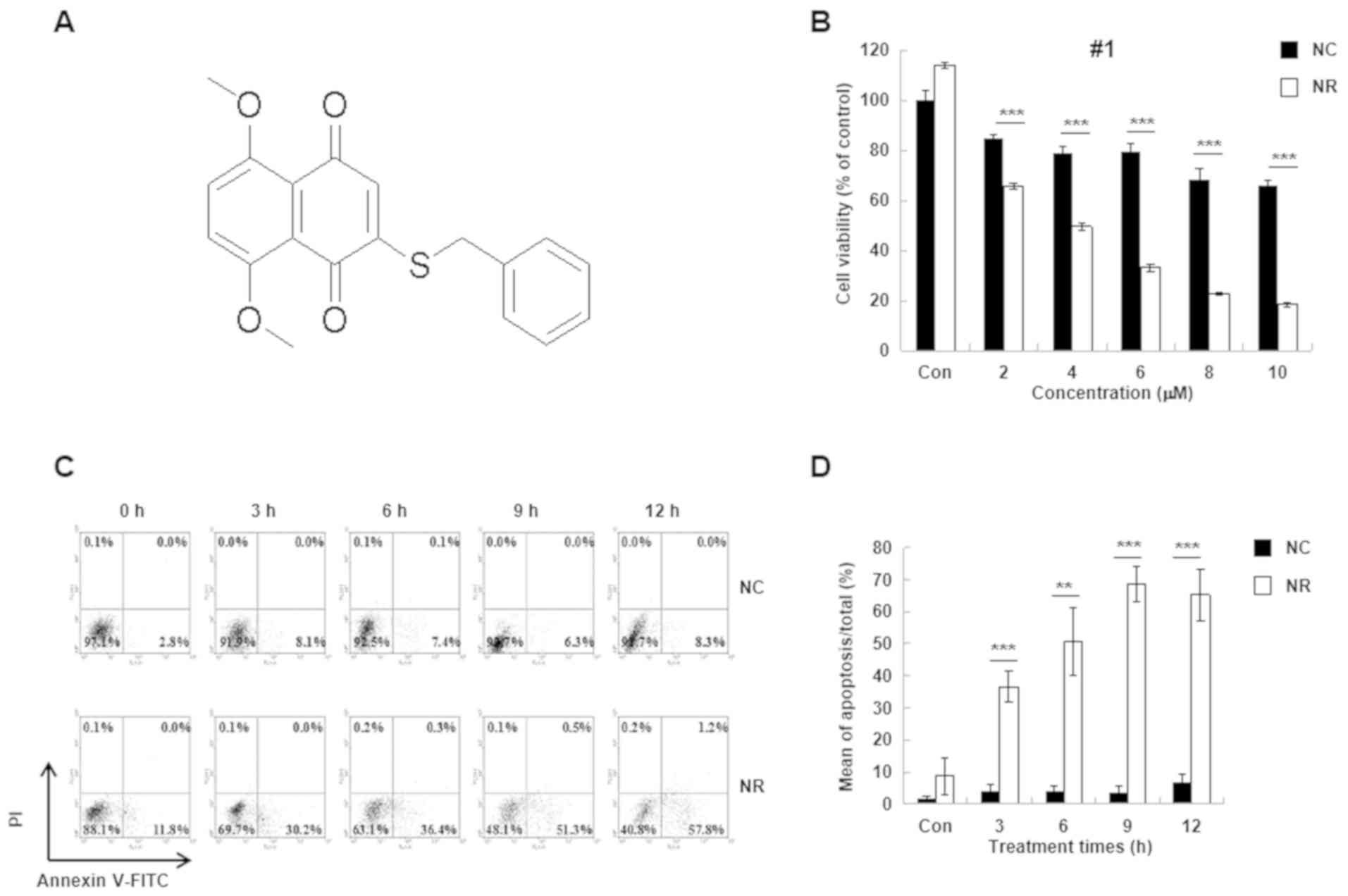
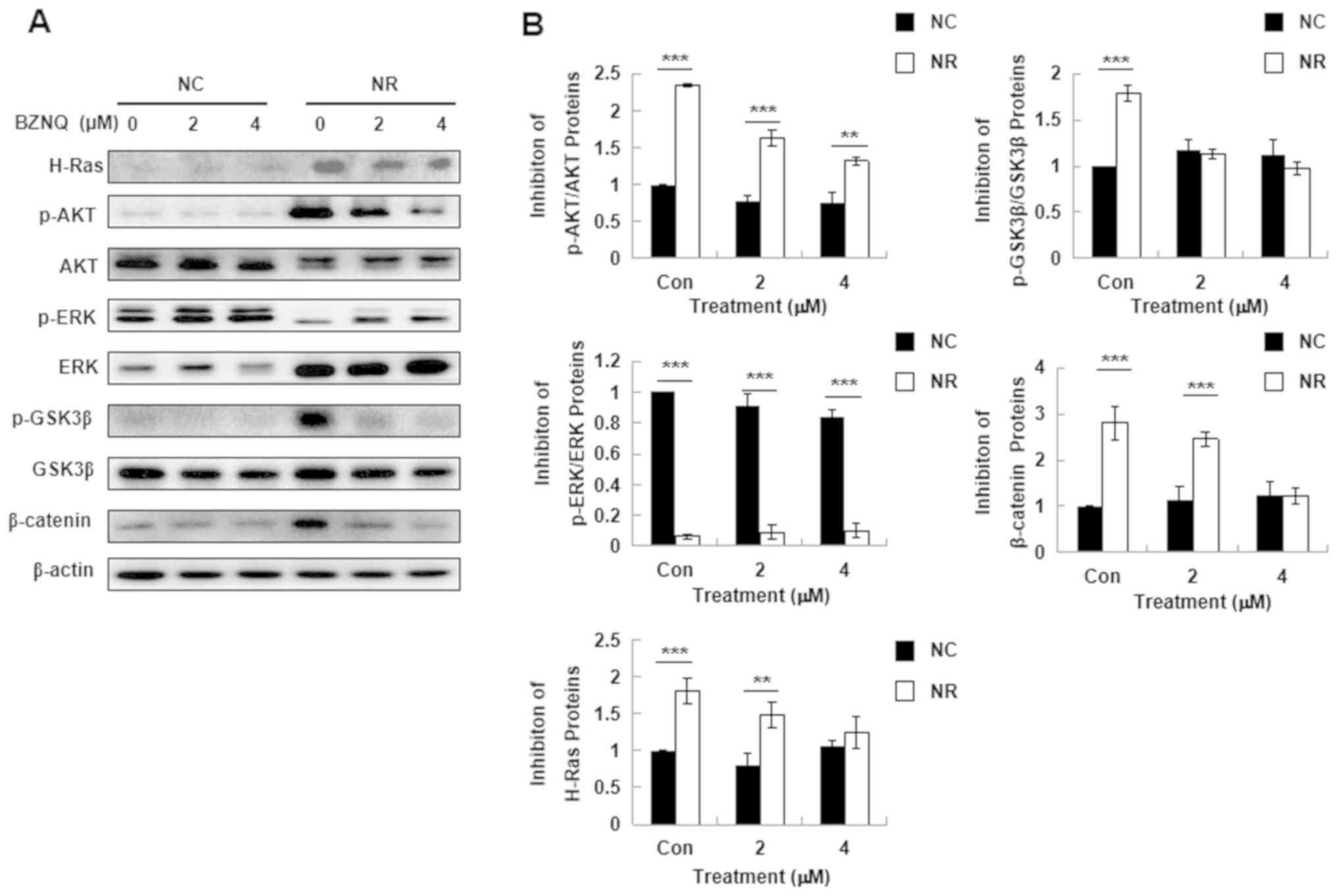
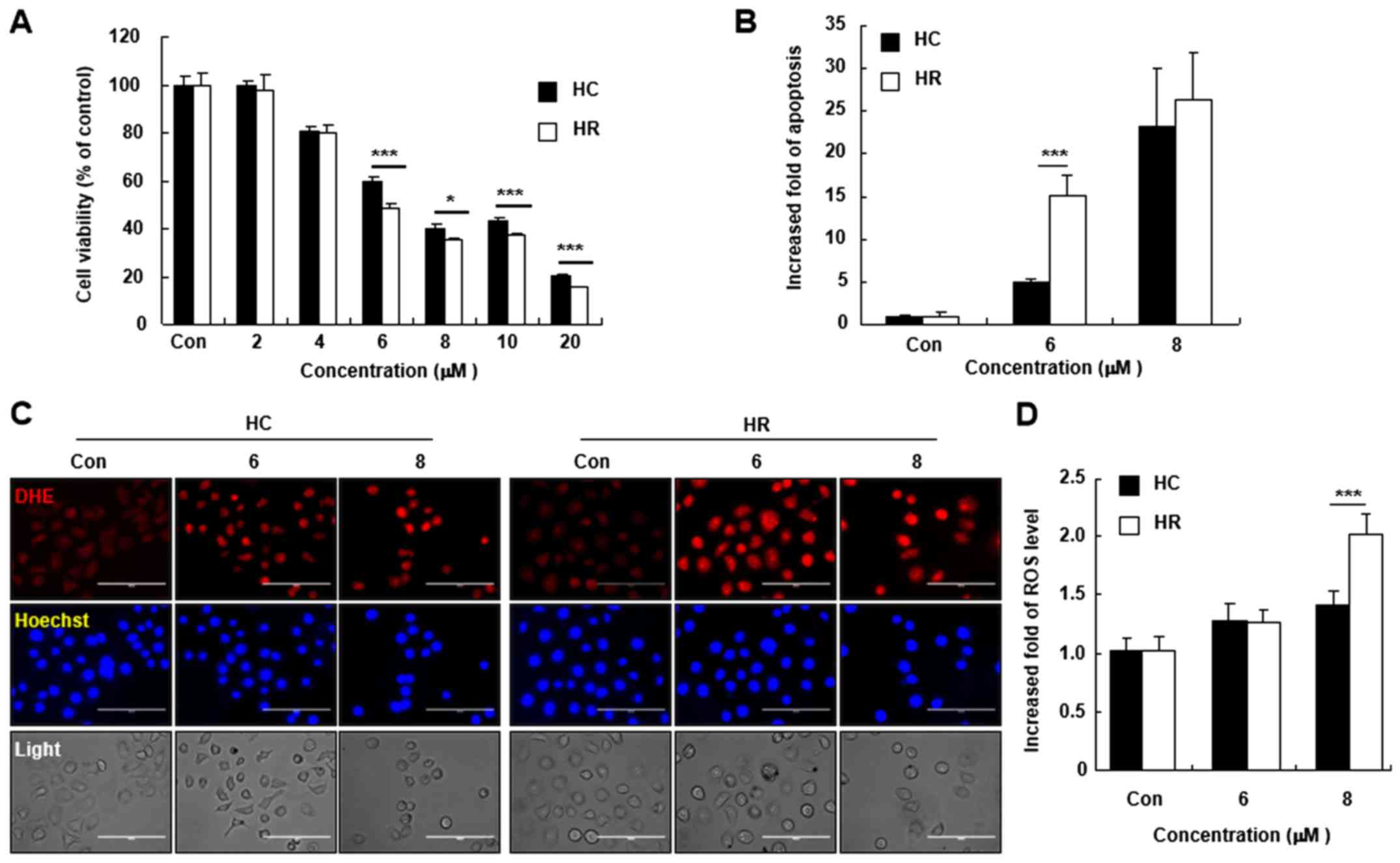
|
1
|
Prior IA, Hood FE and Hartley JL: The
frequency of ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res.
80(2969)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yaeger R, Cowell E, Chou JF, Gewirtz AN,
Borsu L, Vakiani E, Solit DB, Rosen N, Capanu M, Ladanyi M and
Kemeny N: RAS mutations affect pattern of metastatic spread and
increase propensity for brain metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Cancer. 121:1195–1203. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Maertens O and Cichowski K: An expanding
role for RAS GTPase activating proteins (RAS GAPs) in cancer. Adv
Biol Regul. 55:1–14. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Grewal T, Koese M, Tebar F and Enrich C:
Differential regulation of RasGAPs in cancer. Genes Cancer.
2:288–297. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Maurya HK, Gautam SK, Pratap R, Tandon VK,
Kumar A, Kumar B, Saxena S, Tripathi D, Rajwanshi M, Das M and Ram
VJ: Regioselective synthesis of polycyclic aza-oxa and aza-oxa-thia
heteroarenes as Colo-205 and HepG2 carcinoma cells growth
inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 81:367–377. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Inamdar GS, Madhunapantula SV and
Robertson GP: Targeting the MAPK pathway in melanoma: Why some
approaches succeed and other fail. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:624–637.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ledford H: Cancer: The Ras renaissance.
Nature. 520:278–280. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Luo YH, Piao XJ, Shen GN, Wang
JR, Feng YC, Li JQ, Xu WT, Zhang Y, Zhang T, et al: The design of
1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives and mechanisms underlying apoptosis
induction through ROS-dependent MAPK/Akt/STAT3 pathways in human
lung cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 27:1577–1587. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lin HY, Han HW, Wang YS, He DL, Sun WX,
Feng L, Wen ZL, Yang MK, Lu GH, Wang XM, et al: Shikonin and
4-hydroxytamoxifen synergistically inhibit the proliferation of
breast cancer cells through activating apoptosis signaling pathway
in vitro and in vivo. Chin Med. 15(23)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Seetha A, Devaraj H and Sudhandiran G:
Indomethacin and juglone inhibit inflammatory molecules to induce
apoptosis in colon cancer cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
34(e22433)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vukic MD, Vukovic NL, Obradovic A, Matic
M, Djukic M and Avdovic E: Redox status, DNA and HSA binding study
of naturally occurring naphthoquinone derivatives. EXCLI J.
19:48–70. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guo C, He J, Song X, Tan L, Wang M, Jiang
P, Li Y, Cao Z and Peng C: Pharmacological properties and
derivatives of shikonin-A review in recent years. Pharmacol Res.
149(104463)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lim ES, Rhee YH, Park MK, Shim BS, Ahn KS,
Kang H, Yoo HS and Kim SH: DMNQ S-64 induces apoptosis via caspase
activation and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in human nonsmall lung
cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1095:7–18. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
PLOS ONE Editors. Retraction:
Ramentaceone, a naphthoquinone derived from drosera sp., induces
apoptosis by suppressing PI3K/Akt signaling in breast cancer cells.
PLoS One. 14(e0226703)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Dong J, Cui J, Huang G, Meng Q
and Li S: Cytotoxicity of synthesized 1,4-naphthoquinone oxime
derivatives on selected human cancer cell lines. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 66:612–619. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shahsavari Z, Karami-Tehrani F and Salami
S: Shikonin induced necroptosis via reactive oxygen species in the
T-47D breast cancer cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
16:7261–7266. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Qiao C, Bi S, Sun Y, Song D, Zhang H and
Zhou W: Study of interactions of anthraquinones with DNA using
ethidium bromide as a fluorescence probe. Spectrochim Acta A Mol
Biomol Spectrosc. 70:136–143. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kobayashi K, Nishiumi S, Nishida M, Hirai
M, Azuma T, Yoshida H, Mizushina Y and Yoshida M: Effects of
quinone derivatives, such as 1,4-naphthoquinone, on DNA polymerase
inhibition and anti-inflammatory action. Med Chem. 7:37–44.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu C, Shen GN, Luo YH, Piao XJ, Jiang XY,
Meng LQ, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang JR, Wang H, et al: Novel
1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives induce apoptosis via ROS-mediated
p38/MAPK, Akt and STAT3 signaling in human hepatoma Hep3B cells.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 96:9–19. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Moore AR, Rosenberg SC, McCormick F and
Malek S: RAS-targeted therapies: Is the undruggable drugged? Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 19:533–552. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Aly AA, El-Sheref EM, Bakheet MEM, Mourad
MAE, Bräse S, Ibrahim MAA, Nieger M, Garvalov BK, Dalby KN and
Kaoud TS: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of fused
naphthofuro[3,2-c] quinoline-6,7,12-triones and
pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline-6,7,8,13-tetraones derivatives as ERK
inhibitors with efficacy in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Bioorg Chem.
82:290–305. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kabakci Z, Käppeli S, Cantù C, Jensen LD,
König C, Toggweiler J, Gentili C, Ribaudo G, Zagotto G, Basler K,
et al: Pharmacophore-guided discovery of CDC25 inhibitors causing
cell cycle arrest and tumor regression. Sci Rep.
9(1335)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jeung YJ, Kim HG, Ahn J, Lee HJ, Lee SB,
Won M, Jung CR, Im JY, Kim BK, Park SK, et al: Shikonin induces
apoptosis of lung cancer cells via activation of FOXO3a/EGR1/SIRT1
signaling antagonized by p300. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2584–2593. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gara RK, Srivastava VK, Duggal S, Bagga
JK, Bhatt M, Sanyal S and Mishra DP: Shikonin selectively induces
apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through the endoplasmic
reticulum stress and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J Biomed Sci.
22(26)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chandimali N, Sun HN, Kong LZ, Zhen X, Liu
R, Kwon T and Lee DS: Shikonin-induced apoptosis of colon cancer
cells is reduced by peroxiredoxin V expression. Anticancer Res.
39:6115–6123. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ahn BZ, Baik KU, Kweon GR, Lim K and Hwang
BD: Acylshikonin analogues: Synthesis and inhibition of DNA
topoisomerase-I. J Med Chem. 38:1044–1047. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lu Q, Liu W, Ding J, Cai J and Duan W:
Shikonin derivatives: Synthesis and inhibition of human telomerase.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 12:1375–1378. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li W, Zhang C, Ren A, Li T, Jin R, Li G,
Gu X, Shi R and Zhao Y: Shikonin suppresses skin carcinogenesis via
inhibiting cell proliferation. PLoS One.
10(e0126459)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wiench B, Eichhorn T, Paulsen M and
Efferth T: Shikonin directly targets mitochondria and causes
mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer cells. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012(726025)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang F, Yao X, Zhang Y and Tang J:
Synthesis, biological function and evaluation of Shikonin in cancer
therapy. Fitoterapia. 134:329–339. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Andújar I, Ríos JL, Giner RM and Recio MC:
Pharmacological properties of shikonin-a review of literature since
2002. Planta Med. 79:1685–1697. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liang W, Cui J, Zhang K, Xi H, Cai A, Li
J, Gao Y, Hu C, Liu Y, Lu Y, et al: Shikonin induces ROS-based
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in colon cancer. Oncotarget.
8:109094–109106. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Boulos JC, Rahama M, Hegazy MF and Efferth
T: Shikonin derivatives for cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer
Lett. 459:248–267. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ali A, Assimopoulou AN, Papageorgiou VP
and Kolodziej H: Structure/antileishmanial activity relationship
study of naphthoquinones and dependency of the mode of action on
the substitution patterns. Planta Med. 77:2003–2012.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee SH, Shen GN, Jung YS, Lee SJ, Chung
JY, Kim HS, Xu Y, Choi Y, Lee JW, Ha NC, et al: Antitumor effect of
novel small chemical inhibitors of Snail-p53 binding in
K-Ras-mutated cancer cells. Oncogene. 29:4576–4587. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen X, Yang L, Oppenheim JJ and Howard
MZ: Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives.
Phytother Res. 16:199–209. 2020.
|
|
37
|
Elferink JG and Deierkauf M: Inhibition of
polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions by fluorinated nitrobenzenes.
Chem Biol Interact. 52:163–72. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sun HN, Shen GN, Jin YZ, Jin Y, Han YH,
Feng L, Liu L, Jin MH, Luo YH, Kwon TH, et al:
2-Cyclohexylamino-5,8-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone inhibits
LPS-induced BV2 microglial activation through MAPK/NF-kB signaling
pathways. Heliyon. 2(e00132)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gaascht F, Teiten MH, Cerella C, Dicato M,
Bagrel D and Diederich M: Plumbagin modulates leukemia cell redox
status. Molecules. 19:10011–10032. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang J, Peng S, Li X, Liu R, Han X and
Fang J: Targeting thioredoxin reductase by plumbagin contributes to
inducing apoptosis of HL-60 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 619:16–26.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sharma A, Santos IO, Gaur P, Ferreira VF,
Garcia CR and da Rocha DR: Addition of thiols to o-quinone methide:
New 2-hydroxy-3-phenylsulfanylmethyl[1,4]naphthoquinones and their
activity against the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
(3D7). Eur J Med Chem. 59:48–53. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pandey SK, Naware NB, Trivedi P and Saxena
AK: Molecular modeling and 3D-QSAR studies in 2-aziridinyl-and
2,3-bis(aziridinyl)-1,4-naphthoquinonyl sulfonate and acylate
derivatives as potential antimalarial agents. SAR QSAR Environ Res.
12:547–564. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Bielitza M, Belorgey D, Ehrhardt K, Johann
L, Lanfranchi DA, Gallo V, Schwarzer E, Mohring F, Jortzik E,
Williams DL, et al: Antimalarial NADPH-consuming redox-cyclers as
superior glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency copycats.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:1337–1351. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Edenharder R and Grünhage D: Free radical
scavenging abilities of flavonoids as mechanism of protection
against mutagenicity induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide or cumene
hydroperoxide in Salmonella typhimurium TA102. Mutat Res. 540:1–18.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fukushi S, Yoshino H, Yoshizawa A and
Kashiwakura I: p53-independent structure-activity relationships of
3-ring mesogenic compounds' activity as cytotoxic effects against
human non-small cell lung cancer lines. BMC Cancer.
16(521)2006.
|
|
46
|
Gao M, Wang R, Yu F and Chen L: Evaluation
of sulfane sulfur bioeffects via a mitochondria-targeting
selenium-containing near-infrared fluorescent probe. Biomaterials.
160:1–14. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Santarpia L, Lippman SM and El-Naggar AK:
Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF signaling pathway in cancer therapy.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:103–119. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhu J, Blenis J and Yuan J: Activation of
PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways regulates Myc-mediated transcription by
phosphorylating and promoting the degradation of Mad1. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:6584–6589. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Kempf
RC, Long J, Laidler P, Mijatovic S, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Stivala F,
Mazzarino MC, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and
PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity
to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging (Albany NY).
3:192–222. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Asati V, Mahapatra DK and Bharti SK:
PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways inhibitors as
anticancer agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur
J Med Chem. 109:314–341. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Romashkova JA and Makarov SS: NF-kappaB is
a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signalling. Nature.
401:86–90. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Gingery A, Bradley EW, Pederson L, Ruan M,
Horwood NJ and Oursler MJ: TGF-beta coordinately activates
TAK1/MEK/AKT/NFkB and SMAD pathways to promote osteoclast survival.
Exp Cell Res. 314:2725–2738. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Delire B and Stärkel P: The Ras/MAPK
pathway and hepatocarcinoma: Pathogenesis and therapeutic
implications. Eur J Clin Invest. 45:609–63. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Rommel C, Clarke BA, Zimmermann S, Nuñez
L, Rossman R, Reid K, Moelling K, Yancopoulos GD and Glass DJ:
Differentiation stage-specific inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK
pathway by Akt. Science. 286:1738–1741. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Balmanno K, Chell SD, Gillings AS, Hayat S
and Cook SJ: Intrinsic resistance to the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244
(ARRY-142886) is associated with weak ERK1/2 signalling and/or
strong PI3K signalling in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int J
Cancer. 125:2332–2341. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Gholampour M, Ranjbar S, Edraki N,
Mohabbati M, Firuzi O and Khoshneviszadeh M: Click
chemistry-assisted synthesis of novel
aminonaphthoquinone-1,2,3-triazole hybrids and investigation of
their cytotoxicity and cancer cell cycle alterations. Bioorg Chem.
88(102967)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|