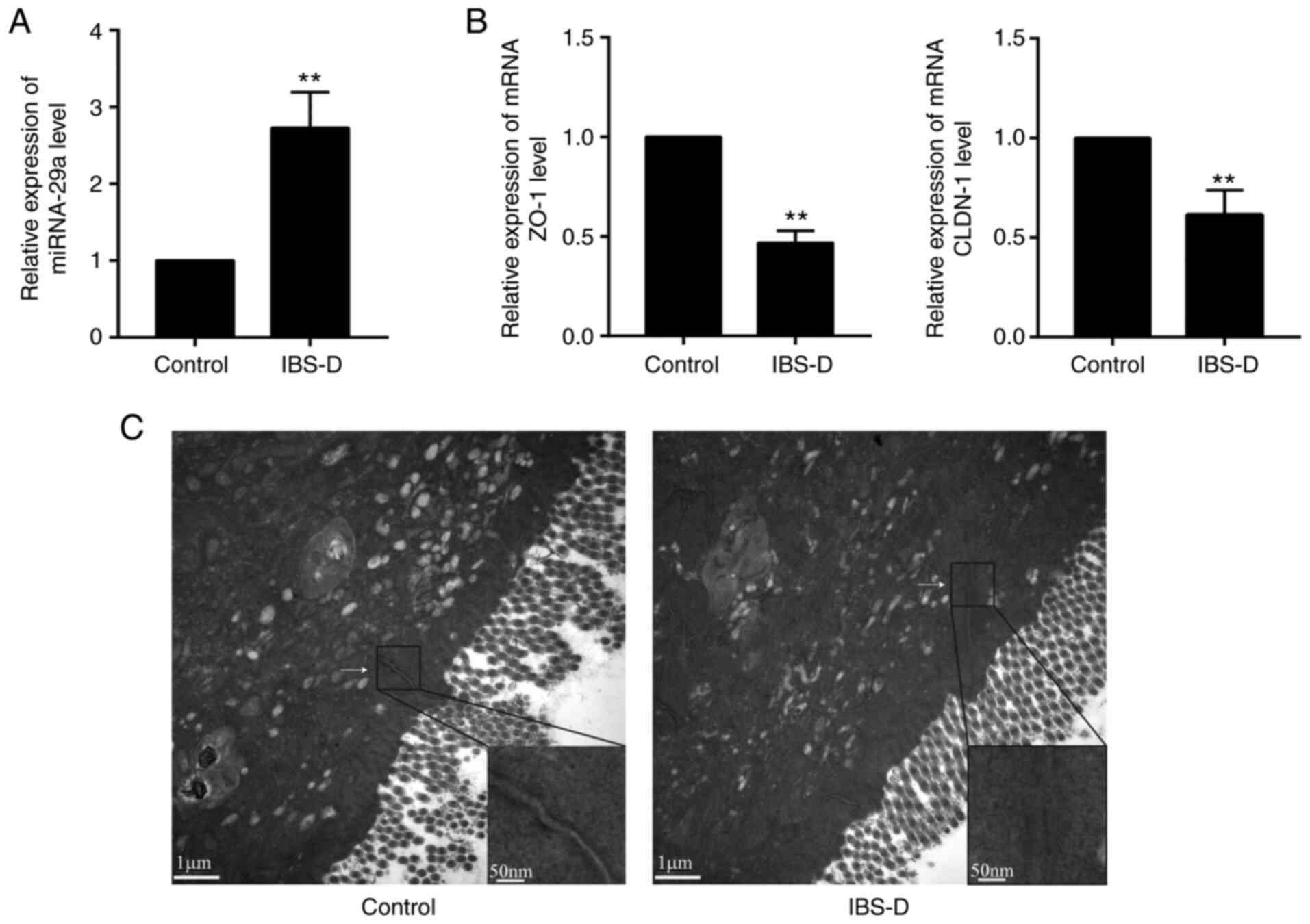
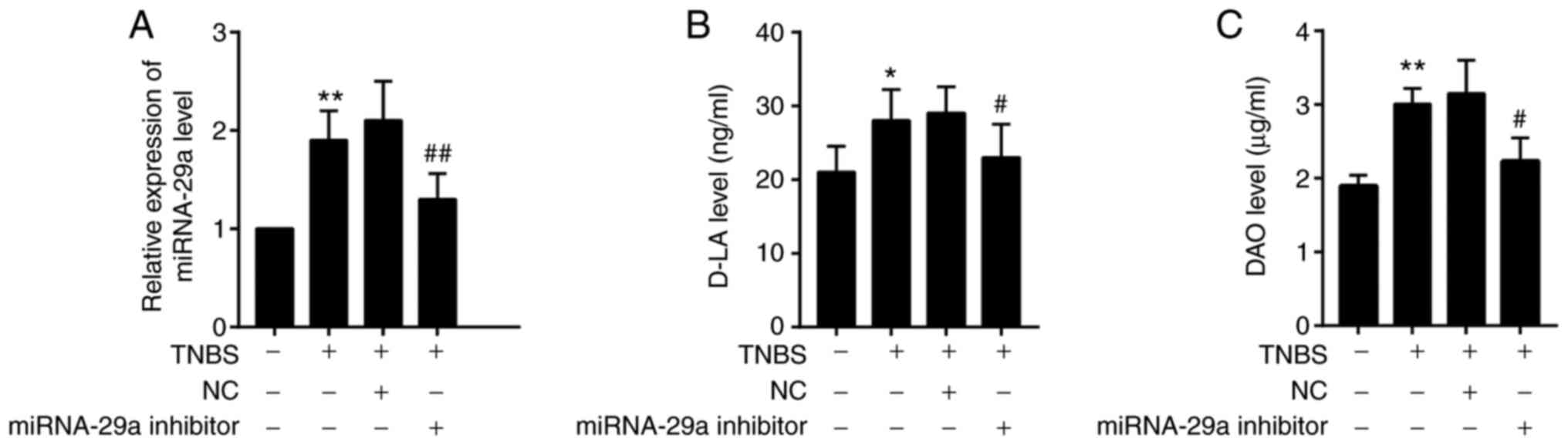
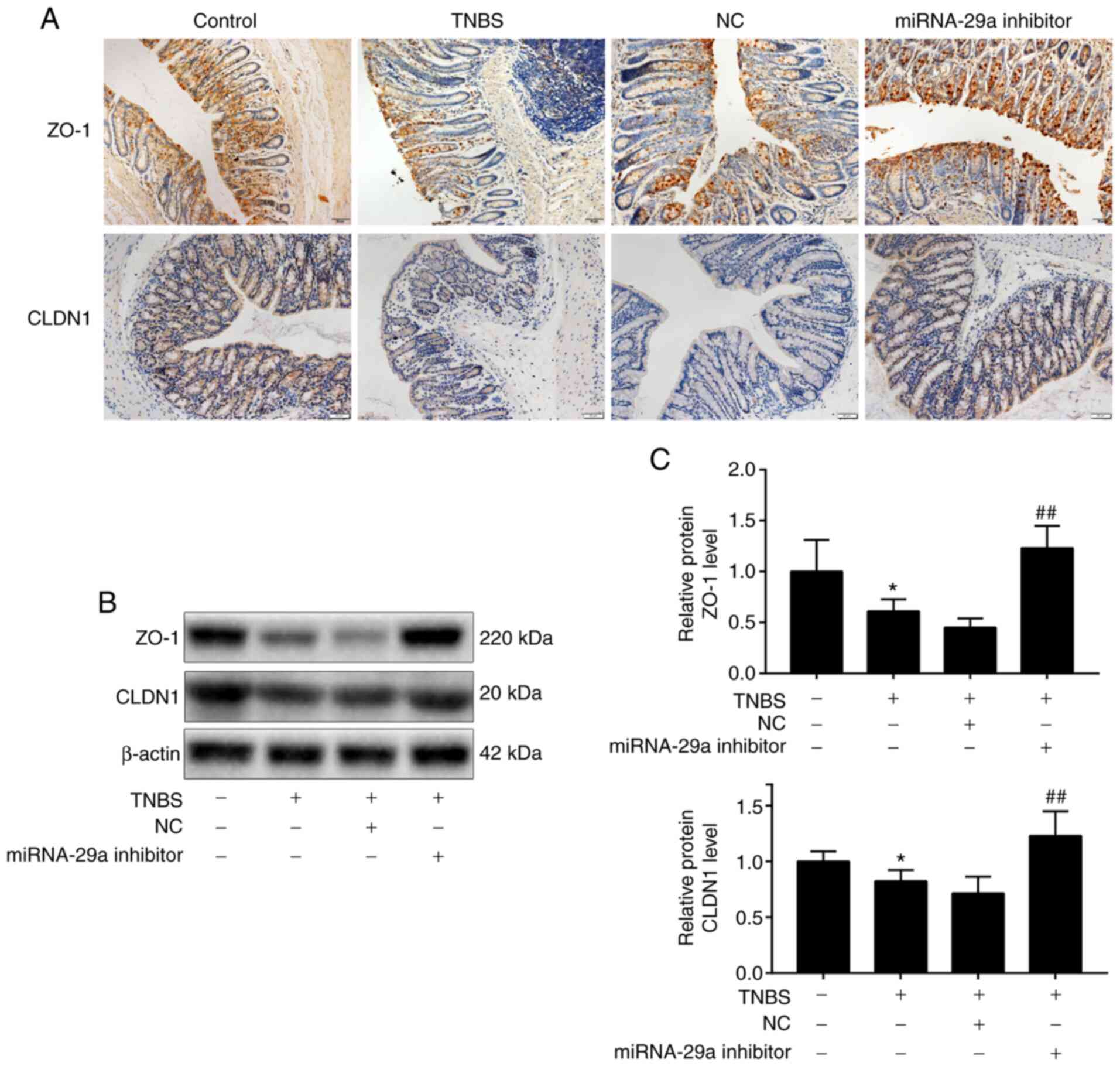
|
1
|
Piche T, Barbara G, Aubert P, Bruley des
Varannes S, Dainese R, Nano JL, Cremon C, Stanghellini V, De
Giorgio R, Galmiche JP, et al: Impaired intestinal barrier
integrity in the colon of patients with irritable bowel syndrome:
Involvement of soluble mediators. Gut. 58:196–201. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Martínez C, Lobo B, Pigrau M, Ramos L,
González-Castro AM, Alonso C, Guilarte M, Guilá M, de Torres I,
Azpiroz F, et al: Diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome:
An organic disorder with structural abnormalities in the jejunal
epithelial barrier. Gut. 62:1160–1168. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Matricon J, Meleine M, Gelot A, Piche T,
Dapoigny M, Muller E and Ardid D: Review article: Associations
between immune activation, intestinal permeability and the
irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 36:1009–1031.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Martínez C, González-Castro A, Vicario M
and Santos J: Cellular and molecular basis of intestinal barrier
dysfunction in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Liver. 6:305–315.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Camilleri M, Lasch K and Zhou W: Irritable
bowel syndrome: Methods, mechanisms, and pathophysiology. The
confluence of increased permeability, inflammation, and pain in
irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
303:G775–G785. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bertiaux-Vandaële N, Youmba SB, Belmonte
L, Lecleire S, Antonietti M, Gourcerol G, Leroi AM, Déchelotte P,
Ménard JF, Ducrotté P, et al: The expression and the cellular
distribution of the tight junction proteins are altered in
irritable bowel syndrome patients with differences according to the
disease subtype. Am J Gastroenterol. 106:2165–2173. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bjorkman DJ and Popp JW: Mucosal Barrier
Defects in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Who Left the Door Open? Am J
Gastroenterol. 101:864–865. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xu XJ, Zhang YL, Liu L, Pan L and Yao SK:
Increased expression of nerve growth factor correlates with
visceral hypersensitivity and impaired gut barrier function in
diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: A preliminary
explorative study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 45:100–114.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Martínez C, Rodiño-Janeiro BK, Lobo B,
Stanifer ML, Klaus B, Granzow M, González-Castro AM, Salvo-Romero
E, Alonso-Cotoner C, Pigrau M, et al: miR-16 and miR-125b are
involved in barrier function dysregulation through the modulation
of claudin-2 and cingulin expression in the jejunum in IBS with
diarrhoea. Gut. 66:1537–1538. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou Q, Souba WW, Croce CM and Verne GN:
MicroRNA-29a regulates intestinal membrane permeability in patients
with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 59:775–784. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wilcz-Villega E, McClean S and O'Sullivan
M: Reduced E-cadherin expression is associated with abdominal pain
and symptom duration in a study of alternating and diarrhea
predominant IBS. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 26:316–325.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Drossman DA: Functional Gastrointestinal
Disorders: History, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features and Rome IV.
Gastroenterology. 150:1262–1279. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Liu W, Peng QX, Peng JL, Yu LZ and
Hu JL: Protective effect of huoxiang zhengqi oral liquid on
intestinal mucosal mechanical barrier of rats with postinfectious
irritable bowel syndrome induced by acetic acid. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2014(218383)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Du C, Peng L, Kou G, Wang P, Lu L and Li
Y: Assessment of Serum sTREM-1 as a Marker of Subclinical
Inflammation in Diarrhea-Predominant Patients with Irritable Bowel
Syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 63:1182–1191. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chao G, Wang Y, Ye F and Zhang S:
Regulation of Colonic Mucosal MicroRNA Expression via Multiple
Targets in Visceral Hypersensitivity Rats by Tongxieyaofang. Yonsei
Med J. 59:945–950. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Raju D, Ilango K, Chitra V and Ashish K:
Evaluation of Anti-ulcer activity of methanolic extract of
Terminalia chebula fruits in experimental rats. J Pharm Sci Res.
1:101–107. 2009.
|
|
20
|
van Herck H, Baumans V, Brandt CJWM, Hesp
APM, Sturkenboom JH, van Lith HA, van Tintelen G and Beynen AC:
Orbital sinus blood sampling in rats as performed by different
animal technicians: The influence of technique and expertise. Lab
Anim. 32:377–386. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
van Herck H, Baumans V, de Boer SF, van
der Gugten J, van Woerkom AB and Beynen AC: Endocrine stress
response in rats subjected to singular orbital puncture while under
diethyl-ether anaesthesia. Lab Anim. 25:325–329. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liao XJ, Mao WM, Wang Q, Yang GG, Wu WJ
and Shao SX: MicroRNA-24 inhibits serotonin reuptake transporter
expression and aggravates irritable bowel syndrome. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 469:288–293. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Deng Y, Zhou X, Xiang X, Ou Y and He J:
Effect of miRNA-19a on gastrointestinal motility in rats with
functional dyspepsia. Exp Ther Med. 15:4875–4879. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Viswambharan V, Thanseem I, Vasu MM,
Poovathinal SA and Anitha A: miRNAs as biomarkers of
neurodegenerative disorders. Biomarkers Med. 11:151–167.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Issler O and Chen A: Determining the role
of microRNAs in psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci.
16:201–212. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hou Q, Huang Y, Zhu S, Li P, Chen X, Hou Z
and Liu F: miR-144 Increases Intestinal Permeability in IBS-D Rats
by Targeting OCLN and ZO1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:2256–2268.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wohlfarth C, Schmitteckert S, Härtle JD,
Houghton LA, Dweep H, Fortea M, Assadi G, Braun A, Mederer T, et
al: miR-16 and miR-103 impact 5-HT4 receptor signalling
and correlate with symptom profile in irritable bowel syndrome. Sci
Rep. 7(14680)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kapeller J, Houghton LA, Mönnikes H,
Walstab J, Möller D, Bönisch H, Burwinkel B, Autschbach F, Funke B,
Lasitschka F, et al: First evidence for an association of a
functional variant in the microRNA-510 target site of the serotonin
receptor-type 3E gene with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel
syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 17:2967–2977. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Duan N and Duan S: MiR-29a Inhibits
Glioma Tumorigenesis through a Negative Feedback Loop of TRAF4/Akt
Signaling. BioMed Res Int. 2018(2461363)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liang C, Shi S, Meng Q, Liang D, Hua J,
Qin Y, Zhang B, Xu J, Ni Q and Yu X: MiR-29a, targeting caveolin 2
expression, is responsible for limitation of pancreatic cancer
metastasis in patients with normal level of serum CA125. Int J
Cancer. 143:2919–2931. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang YH, Yang YL and Wang FS: The Role of
miR-29a in the Regulation, Function, and Signaling of Liver
Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 19(1889)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou Q, Costinean S, Croce CM, Brasier AR,
Merwat S, Larson SA, Basra S and Verne GN: MicroRNA 29 targets
nuclear factor-κB-repressing factor and Claudin 1 to increase
intestinal permeability. Gastroenterology. 148:158–169.e8.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xue H, Zhang G, Geurts AM, Usa K, Jensen
DM, Liu Y, Widlansky ME and Liang M: Tissue-specific effects of
targeted mutation of Mir29b1 in rats. EBioMedicine. 35:260–269.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lin X, Zhou X, Liu D, Yun L, Zhang L, Chen
X, Chai Q and Li L: MicroRNA-29 regulates high-glucose-induced
apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelial cells through PTEN.
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 52:419–426. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pope JL, Bhat AA, Sharma A, Ahmad R,
Krishnan M, Washington MK, Beauchamp RD, Singh AB and Dhawan P:
Claudin-1 regulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis through the
modulation of Notch-signalling. Gut. 63:622–634. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hadj-Rabia S, Baala L, Vabres P,
Hamel-Teillac D, Jacquemin E, Fabre M, Lyonnet S, De Prost Y,
Munnich A, Hadchouel M, et al: Claudin-1 gene mutations in neonatal
sclerosing cholangitis associated with ichthyosis: A tight junction
disease. Gastroenterology. 127:1386–1390. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Masahiko I, Mikio F, Kazumasa M and Koji
K: Mitinori Saitou and Tsukita AS: Direct Binding of Three Tight
Junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH
Termini of Claudins. J Cell Biol. 147:1351–1363. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang N, Han Q, Wang G, Ma WP, Wang J, Wu
WX, Guo Y, Liu L, Jiang XY, Xie XL, et al: Resveratrol Protects
Oxidative Stress-Induced Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction
by Upregulating Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression. Dig Dis Sci.
61:2522–2534. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu DR, Xu XJ and Yao SK: Increased
intestinal mucosal leptin levels in patients with
diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. World J
Gastroenterol. 24:46–57. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|