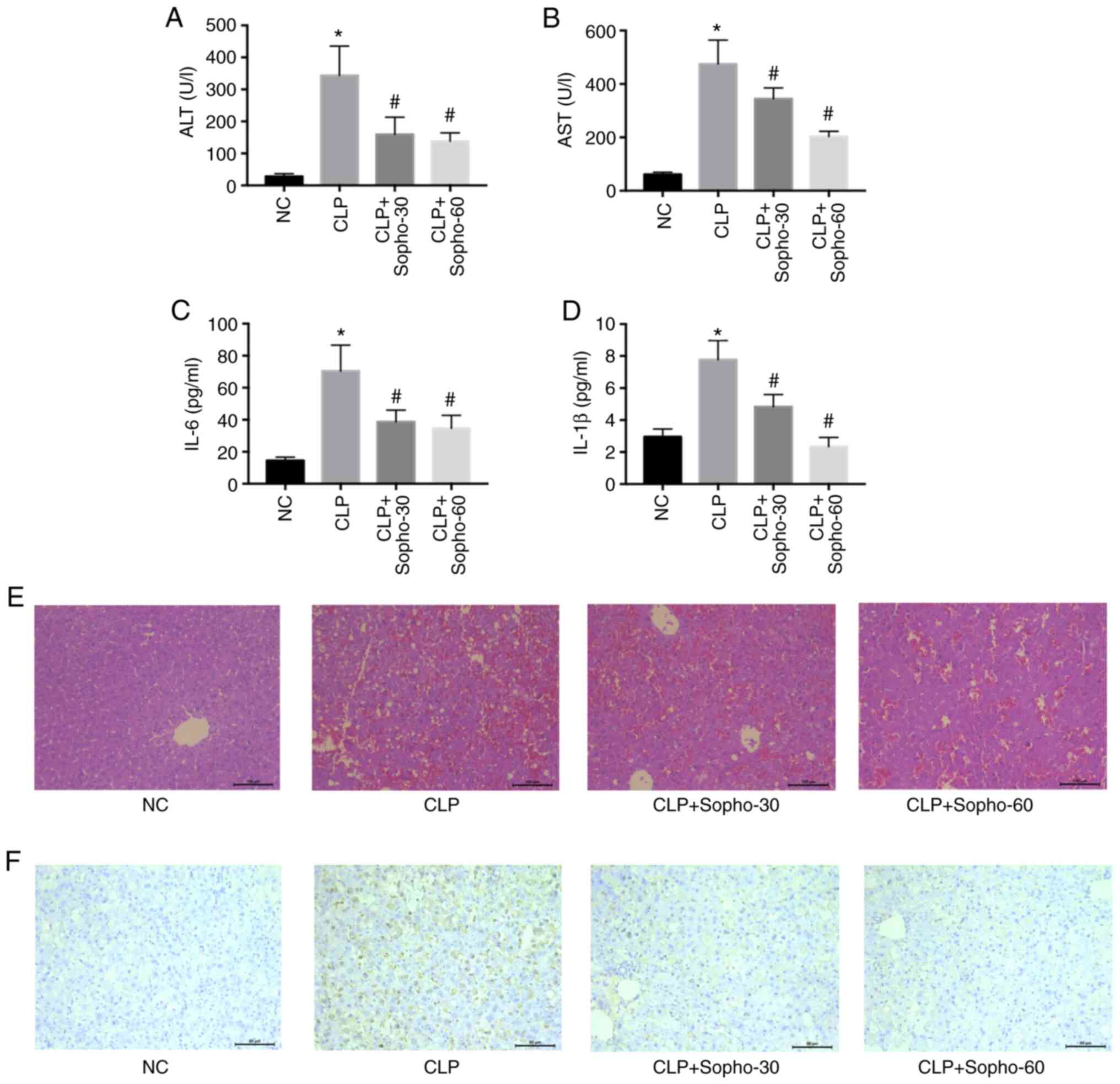
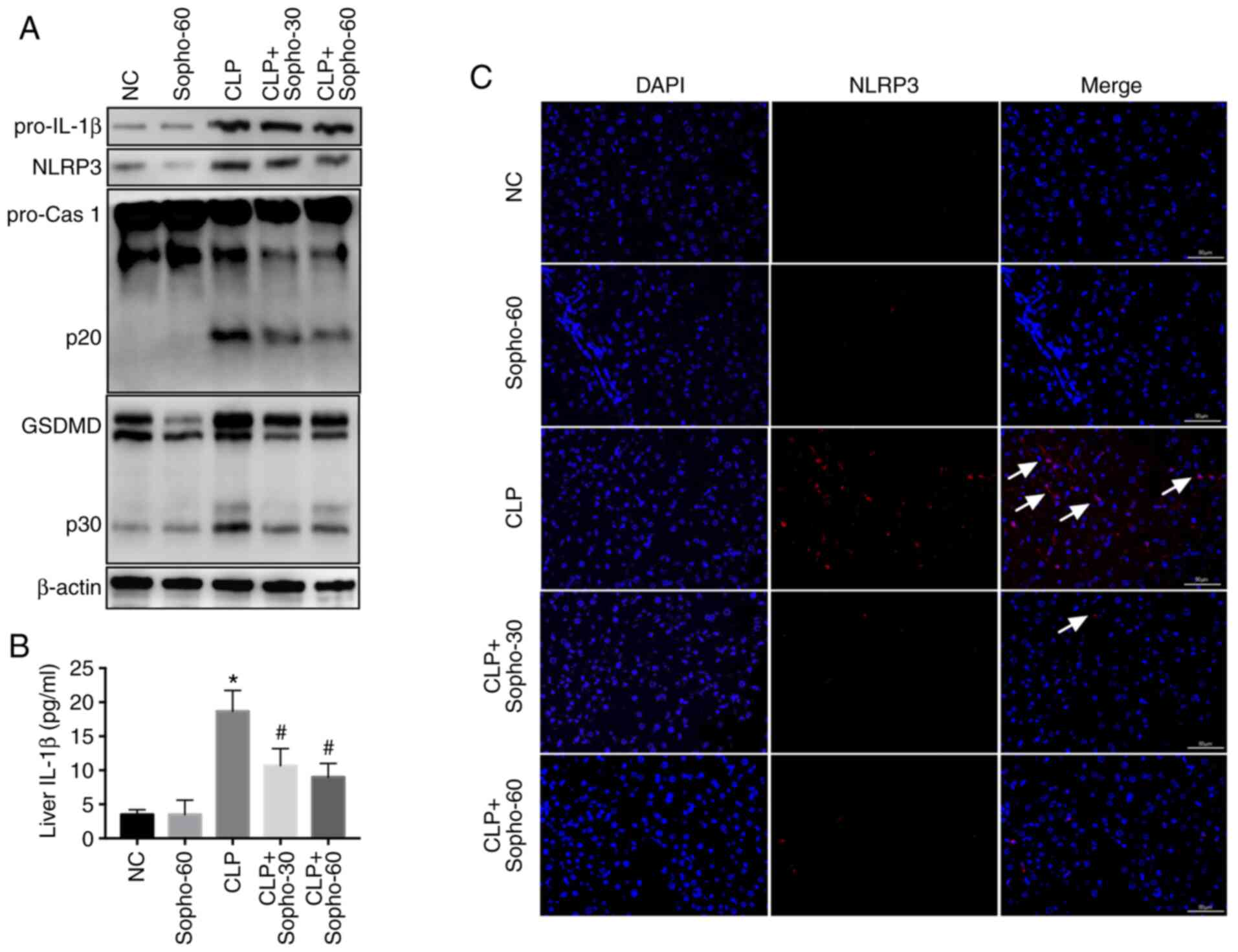
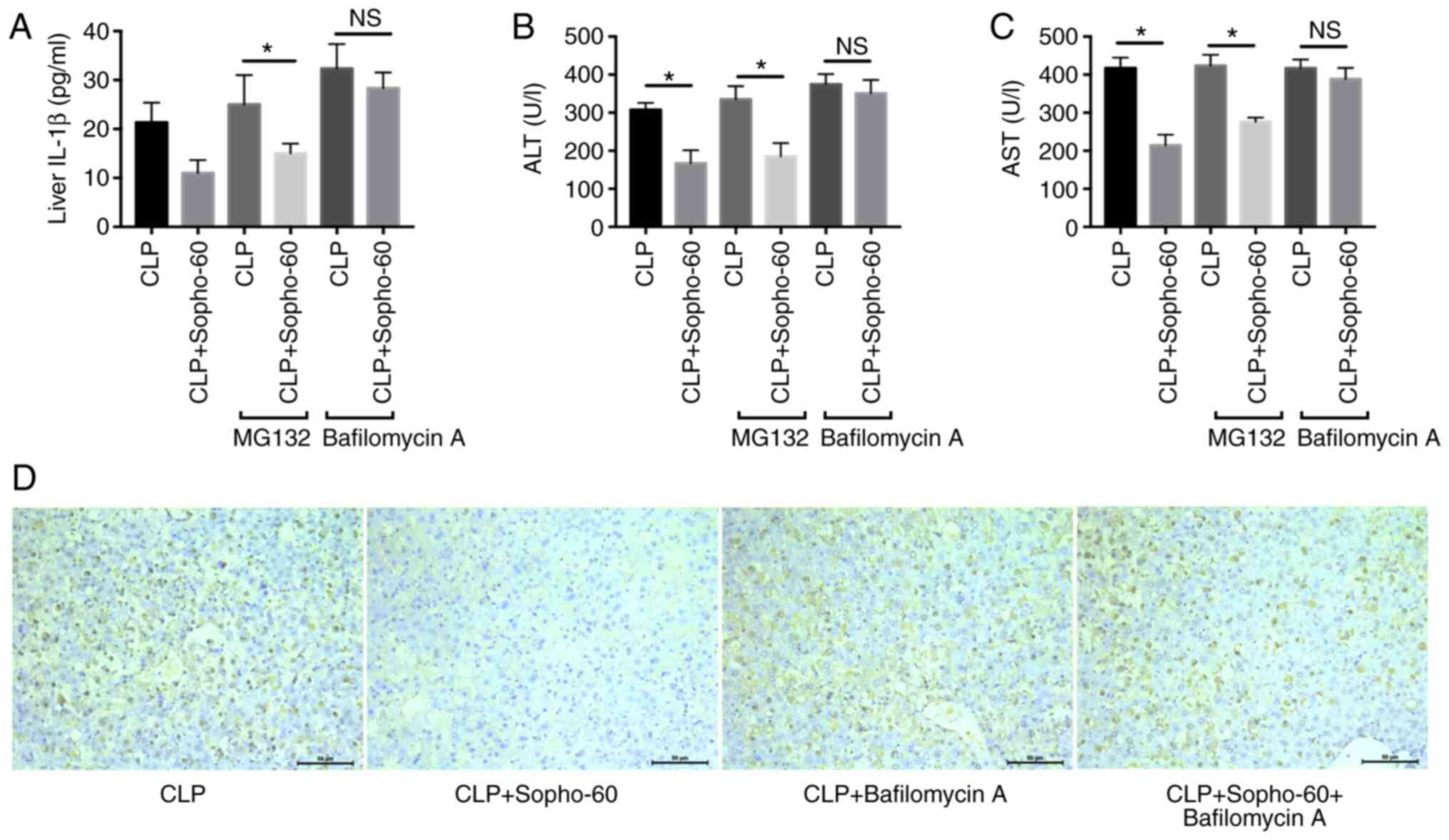
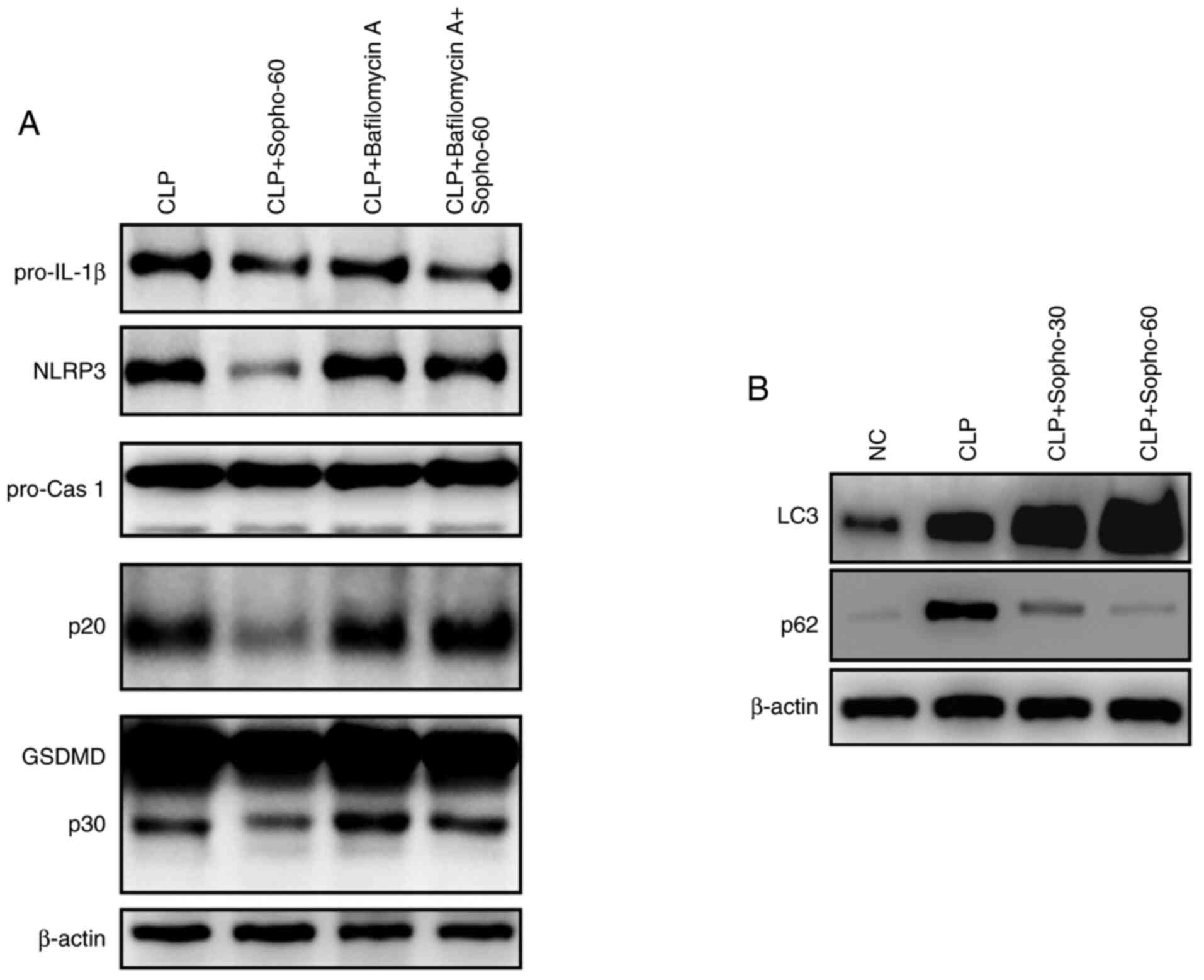
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Hari
MS, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD,
Coopersmith CM, et al: The Third International Consensus
Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). Jama.
315:801–810. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Strnad P, Tacke F, Koch A and Trautwein C:
Liver-guardian, modifier and target of sepsis. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:55–66. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yan J and Li S and Li S: The role of the
liver in sepsis. Int Rev Immunol. 33:498–510. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Savio LEB, de Andrade Mello P, Figliuolo
VR, de Avelar Almeida TF, Santana PT, Oliveira SDS, Silva CLM,
Feldbrügge L, Csizmadia E, Minshall RD, et al: CD39 limits P2X7
receptor inflammatory signaling and attenuates sepsis-induced liver
injury. J Hepatol. 67:716–726. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Alhusaini A, Faddaa L, Ali HM, Hassan I,
El Orabi NF and Bassiouni Y: Amelioration of the protein expression
of Cox2, NFκB, and STAT-3 by some antioxidants in the liver of
sodium fluoride-intoxicated rats. Dose-Response.
16(1559325818800153)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Geng Y, Ma Q, Liu YN, Peng N, Yuan FF, Li
XG, Li M, Wu YS, Li BL, Song WB, et al: Heatstroke induces liver
injury via IL-1β and HMGB1-induced pyroptosis. J Hepatol.
63:622–633. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lebeaupin C, Proics E, de Bieville CH,
Rousseau D, Bonnafous S, Patouraux S, Adam G, Lavallard VJ, Rovere
C, Le Thuc O, et al: ER stress induces NLRP3 inflammasome
activation and hepatocyte death. Cell Death Dis. 6:e1879.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li W, Li Y, Siraj S, Jin H, Fan Y, Yang X,
Huang X, Wang X, Wang J, Liu L, et al: FUN14 domain-containing
1-mediated mitophagy suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by inhibition
of inflammasome activation in mice. Hepatology. 69:604–621.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Han CY, Rho HS, Kim A, Kim TH, Jang K, Jun
DW, Kim JW, Kim B and Kim SG: FXR inhibits endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatocytes and ameliorates
liver injury. Cell Rep. 24:2985–2999. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li X, Wang M, Hong H, Luo C, Liu Z and
Yang R: Sophocarpine attenuates murine lupus nephritis via
inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and NF- κB activation. Immunol Res.
66:521–527. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Luan J, Chen W, Fan J, Nan Y,
Wang Y, Liang Y, Meng G and Ju D: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles
induced hepatotoxicity via NLRP3 inflammasome activation and
caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis. Nanoscale. 10:9141–9152.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang CS, Kim JJ, Kim TS, Lee PY, Kim SY,
Lee HM, Shin DM, Nguyen LT, Lee MS, Jin HS, et al: Small
heterodimer partner interacts with NLRP3 and negatively regulates
activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nature Commun.
6(6115)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jiang Z, Meng Y, Bo L, Wang C, Bian J and
Deng X: Sophocarpine attenuates LPS-induced liver injury and
improves survival of mice through suppressing oxidative stress,
inflammation, and apoptosis. Mediators Inflamm.
2018(5871431)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sang XX, Wang RL, Zhang CE, Liu SJ, Shen
HH, Guo YM, Zhang YM, Niu M, Wang JB, Bai ZF and Xiao XH:
Sophocarpine protects mice from ConA-induced hepatitis via
inhibition of the IFN-Gamma/STAT1 pathway. Front Pharmacol.
8(140)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhu L and Zhu L: Sophocarpine suppress
inflammatory response in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and in
mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Eur Cytokine Netw.
28:120–126. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jiang Z, Bo L, Meng Y, Wang C, Chen T,
Wang C, Yu X and Deng X: Overexpression of homeodomain-interacting
protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) attenuates sepsis-mediated liver injury by
restoring autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 9(847)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Harhouri K, Navarro C, Depetris D, Mattei
MG, Nissan X, Cau P, De Sandre-Giovannoli A and Lévy N:
MG132-induced progerin clearance is mediated by autophagy
activation and splicing regulation. EMBO Mol Med. 9:1294–1313.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Roustan A, Perrin J, Berthelot-Ricou A,
Lopez E, Botta A and Courbiere B: Evaluating methods of mouse
euthanasia on the oocyte quality: Cervical dislocation versus
isoflurane inhalation. Lab Anim. 46:167–169. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gehrke N, Hövelmeyer N, Waisman A, Straub
BK, Weinmann-Menke J, Wörns MA, Galle PR and Schattenberg JM:
Hepatocyte-specific deletion of IL1-RI attenuates liver injury by
blocking IL-1 driven autoinflammation. J Hepatol. 68:986–995.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang Y, Chen X, Guo G, Guo W, Ma Q and
Yuan J: Sophocarpine inhibits the growth of gastric cancer cells
via autophagy and apoptosis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
24:616–627. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu M, Jiang Z, Wang C, Li N, Bo L, Zha Y,
Bian J, Zhang Y and Deng X: Acetate attenuates inflammasome
activation through GPR43-mediated Ca2+-dependent NLRP3
ubiquitination. Exp Mol Med. 51(1)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Woolbright BL and Jaeschke H: Role of the
inflammasome in acetaminophen-induced liver injury and acute liver
failure. J Hepatol. 66:836–848. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Luan J and Ju D: Inflammasome: A
double-edged sword in liver diseases. Front Immunol.
9(2201)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Alegre F, Pelegrin P and Feldstein AE:
Inflammasomes in liver fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 37:119–127.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zheng T, Yang X, Li W, Chen L, Wu Dan,
Bian F, Xing S and Jin S: Salidroside attenuates high-fat
diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via AMPK-dependent
TXNIP/NLRP3 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018(8597897)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai Tao, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, O'Rourke K,
Anderson K, Warming S, Cuellar T, Haley B, Roose-Girma M, Phung QT,
et al: Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical
inflammasome signalling. Nature. 526:666–671. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|