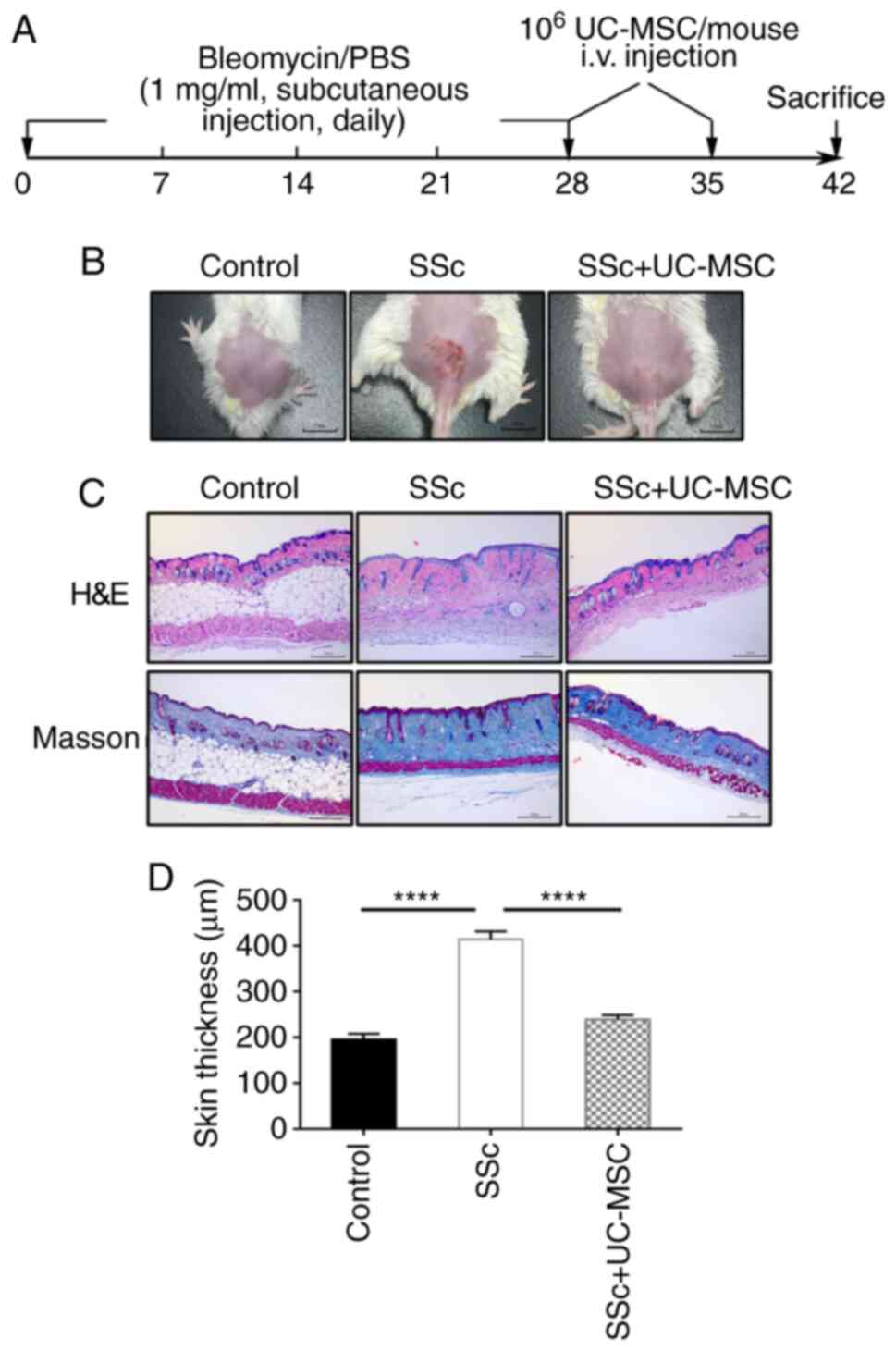
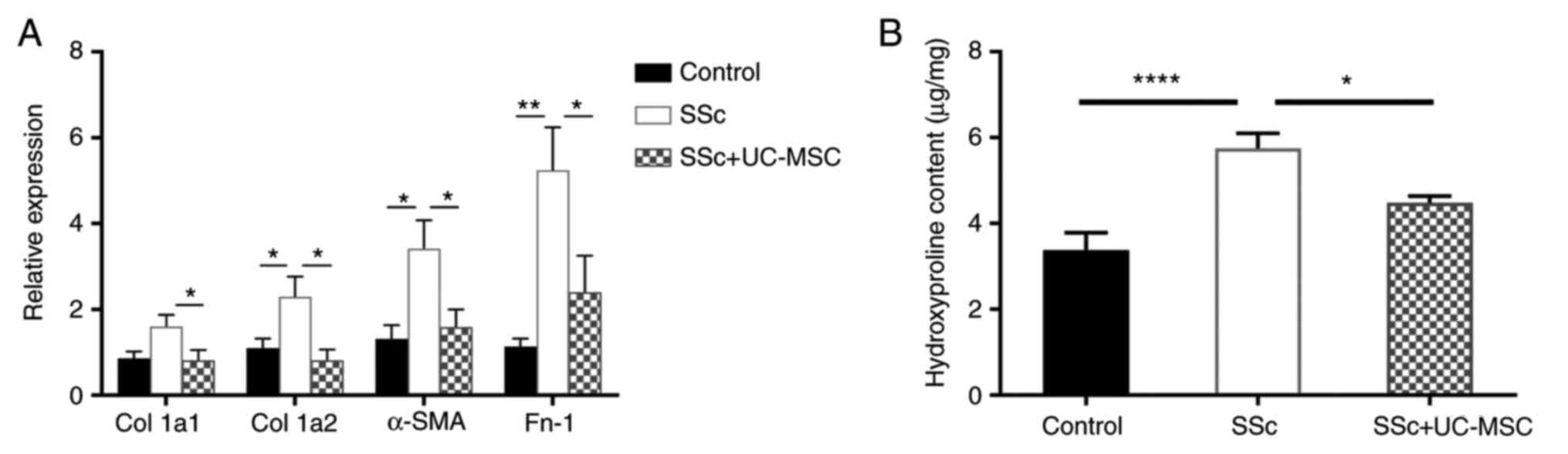
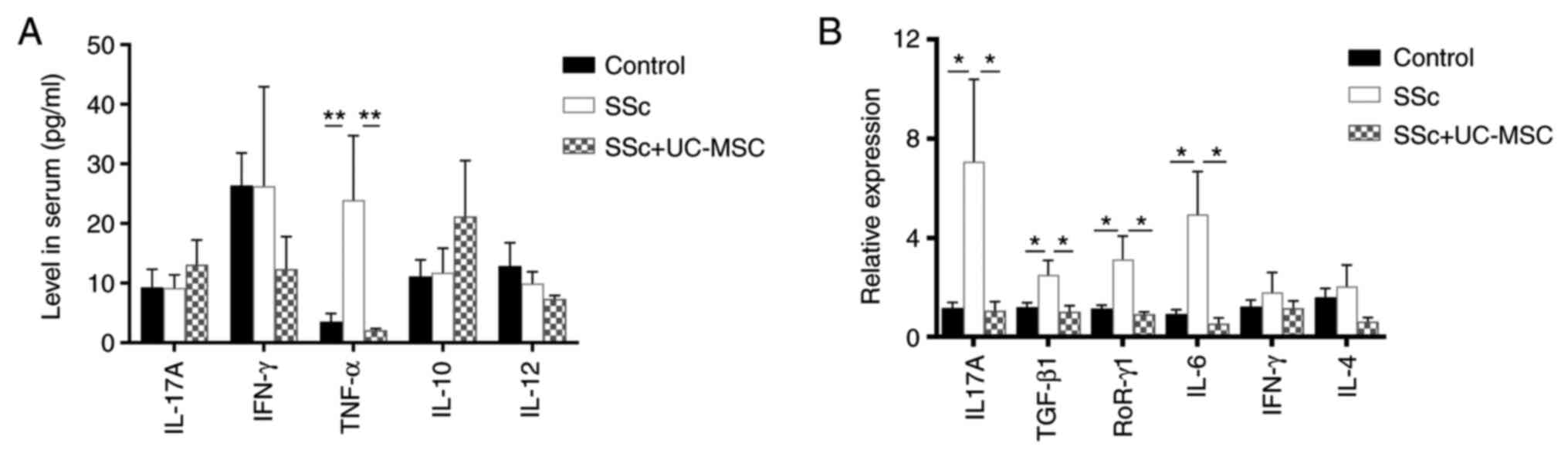
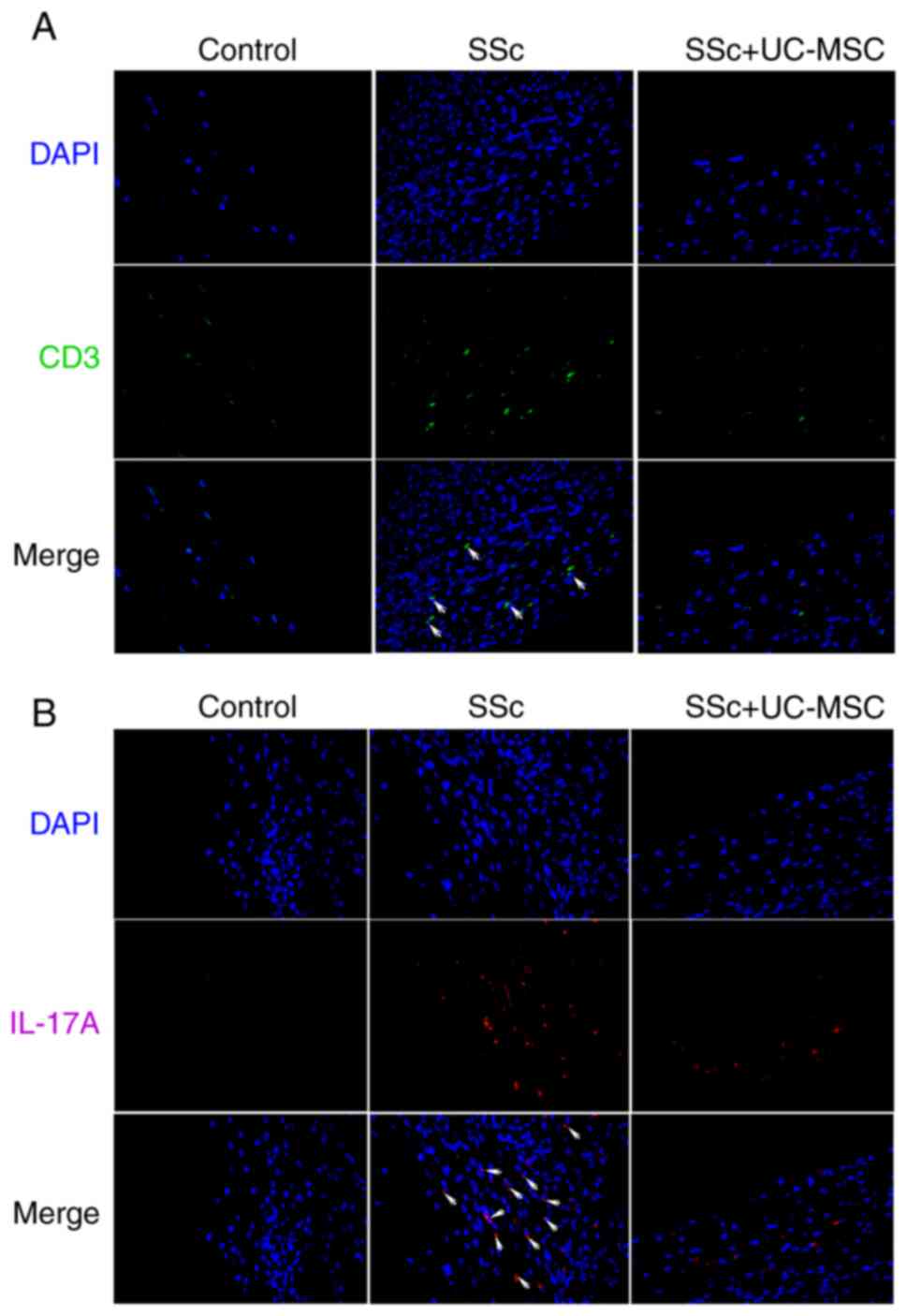
|
1
|
Varga J and Abraham D: Systemic sclerosis:
A prototypic multisystem fibrotic disorder. J Clin Invest.
117:557–567. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chizzolini C, Brembilla NC, Montanari E
and Truchetet ME: Fibrosis and immune dysregulation in systemic
sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 10:276–281. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chifflot H, Fautrel B, Sordet C, Chatelus
E and Sibilia J: Incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis: A
systematic literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 37:223–235.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu M, Wu W, Sun X, Yang J, Xu J, Fu W and
Li M: New insights into CD4(+) T cell abnormalities in systemic
sclerosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 28:31–36. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fujii H, Hasegawa M, Takehara K, Mukaida N
and Sato S: Abnormal expression of intracellular cytokines and
chemokine receptors in peripheral blood T lymphocytes from patients
with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 130:548–556.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wynn TA: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of fibrosis. J Pathol. 214:199–210. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ghosh AK, Yuan W, Mori Y, Chen Sj and
Varga J: Antagonistic regulation of type I collagen gene expression
by interferon-gamma and transforming growth factor-beta.
Integration at the level of p300/CBP transcriptional coactivators.
J Biol Chem. 276:11041–11048. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ulloa L, Doody J and Massagué J:
Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta/SMAD signalling by
the interferon-gamma/STAT pathway. Nature. 397:710–713.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Higashi K, Inagaki Y, Fujimori K, Nakao A,
Kaneko H and Nakatsuka I: Interferon-gamma interferes with
transforming growth factor-beta signaling through direct
interaction of YB-1 with Smad3. J Biol Chem. 278:43470–43479.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Radstake TR, van Bon L, Broen J, Hussiani
A, Hesselstrand R, Wuttge DM, Deng Y, Simms R, Lubberts E and
Lafyatis R: The pronounced Th17 profile in systemic sclerosis (SSc)
together with intracellular expression of TGFbeta and IFNgamma
distinguishes SSc phenotypes. PLoS One. 4(e5903)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rodríguez-Reyna TS, Furuzawa-Carballeda J,
Cabiedes J, Fajardo-Hermosillo LD, Martínez-Reyes C, Díaz-Zamudio M
and Llorente L: Th17 peripheral cells are increased in diffuse
cutaneous systemic sclerosis compared with limited illness: A
cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int. 32:2653–2660. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kataoka H, Yasuda S, Fukaya S, Oku K,
Horita T, Atsumi T and Koike T: Decreased expression of Runx1 and
lowered proportion of
Foxp3+CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells
in systemic sclerosis. Mod Rheumatol. 25:90–95. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mo C, Zeng Z, Deng Q, Ding Y and Xiao R:
Imbalance between T helper 17 and regulatory T cell subsets plays a
significant role in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 108:177–183. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fenoglio D, Battaglia F, Parodi A,
Stringara S, Negrini S, Panico N, Rizzi M, Kalli F, Conteduca G,
Ghio M, et al: Alteration of Th17 and Treg cell subpopulations
co-exist in patients affected with systemic sclerosis. Clin
Immunol. 139:249–257. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yanaba K, Yoshizaki A, Asano Y, Kadono T
and Sato S: Serum interleukin 9 levels are increased in patients
with systemic sclerosis: Association with lower frequency and
severity of pulmonary fibrosis. J Rheumatol. 38:2193–2197.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rubio-Rivas M, Royo C, Simeón CP, Corbella
X and Fonollosa V: Mortality and survival in systemic sclerosis:
Systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum.
44:208–219. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Iudici M, van der Goes MC, Valentini G and
Bijlsma JW: Glucocorticoids in systemic sclerosis: Weighing the
benefits and risks-a systematic review. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 31
(Suppl 76):157–165. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Laar JMV, Farge D, Sont JK, Naraghi K,
Marjanovic Z, Larghero J, Schuerwegh AJ, Marijt EWA, Vonk MC,
Schattenberg AV, et al: Autologous hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation vs intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide in diffuse
cutaneous systemic sclerosis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
311:2490–2498. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Arutyunyan I, Elchaninov A, Makarov A and
Fatkhudinov T: Umbilical cord as prospective source mesenchymal
stem cell-based therapy. Stem Cells Int.
2016(6901286)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sabapathy V, Sundaram B, V M S, Mankuzhy P
and Kumar S: Human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells
plasticity augments scar-free skin wound healing with hair growth.
PLoS One. 9(e93726)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Figueroa FE, Carrión F, Villanueva S and
Khoury M: Mesenchymal stem cell treatment for autoimmune diseases:
A critical review. Biol Res. 45:269–277. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Del Papa N, Quirici N, Soligo D, Scavullo
C, Cortiana M, Borsotti C, Maglione W, Comina DP, Vitali C,
Fraticelli P, et al: Bone marrow endothelial progenitors are
defective in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 54:2605–2615.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Trojanowska M: Cellular and molecular
aspects of vascular dysfunction in systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 6:453–460. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Christopeit M, Schendel M, Föll J, Müller
LP, Keysser G and Behre G: Marked improvement of severe progressive
systemic sclerosis after transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells
from an allogeneic haploidentical-related donor mediated by
ligation of CD137L. Leukemia. 22:1062–1064. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sun LY, Zhang HY, Gu F, Feng XB, Zhao H
and Han ZC: Treatment of refractory systemic sclerosis with human
umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Cell
Res. 18 (S1):12008.
|
|
26
|
Martens TP, See F, Schuster MD,
Sondermeijer HP, Hefti MM, Zannettino A, Gronthos S, Seki T and
Itescu S: Mesenchymal lineage precursor cells induce vascular
network formation in ischemic myocardium. Nat Clin Pract
Cardiovasc. Med 3 (Suppl 1):S18–S22. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Maria AT, Toupet K, Bony C, Pirot N,
Vozenin MC, Petit B, Roger P, Batteux F, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C,
et al: Antifibrotic, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of
mesenchymal stem cells in HOCl-induced systemic sclerosis.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:1013–1025. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhao F, Zhang YF, Liu YG, Zhou JJ, Li ZK,
Wu CG and Qi HW: Therapeutic effects of bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells engraftment on bleomycin-induced lung injury
in rats. Transplant Proc. 40:1700–1705. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Maria AT, Toupet K, Maumus M, Fonteneau G,
Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Guilpain P and Noël D: Human adipose
mesenchymal stem cells as potent anti-fibrosis therapy for systemic
sclerosis. J Autoimmun. 70:31–39. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Luo Y, Xu W, Marion
TN and Liu Y: Successful mesenchymal stem cell treatment of leg
ulcers complicated by Behcet disease: A case report and literature
review. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e0515)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu D, Yang G, Gou Y, Xiao H, Liu W, Liang
H, Zhou J, Huang Z, Zhang Y, Tan Z, et al: Human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells alleviate intestinal barrier injury in rats
with severe acute pancreatitis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 11:3439–3446.
2018.
|
|
32
|
Yamamoto T, Takagawa S, Katayama I,
Yamazaki K, Hamazaki Y, Shinkai H and Nishioka K: Animal model of
sclerotic skin. I: Local injections of bleomycin induce sclerotic
skin mimicking scleroderma. J Invest Dermatol. 112:456–462.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Phan SH: Biology of fibroblasts and
myofibroblasts. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 5:334–337. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shi F, Harman J, Fujiwara K and Sottile J:
Collagen I matrix turnover is regulated by fibronectin
polymerization. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 298:C1265–C1275.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kubow KE, Vukmirovic R, Zhe L, Klotzsch E,
Smith ML, Gourdon D, Luna S and Vogel V: Mechanical forces regulate
the interactions of fibronectin and collagen I in extracellular
matrix. Nat Commun. 6(8026)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ehrlich HP, Allison GM and Leggett M: The
myofibroblast, cadherin, alpha smooth muscle actin and the collagen
effect. Cell Biochem Funct. 24:63–70. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Beşliu AN, Bănică LM, Lonescu R,
Predeţeanu D, Stăvaru C, Marica CM, Chiţonu C, Pistol G, Stefănescu
M and Matache C: Role of cellular immunity in systemic sclerosis
pathogenesis: Update on CD4+T cells population studies. Roum Arch
Microbiol Immunol. 68:5–13. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tolar J, Le Blanc K, Keating A and Blazar
BR: Concise review: Hitting the right spot with mesenchymal stromal
cells. Stem Cells. 28:1446–1455. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ghannam S, Bouffi C, Djouad F, Jorgensen C
and Noël D: Immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells: Mechanisms
and clinical applications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 1(2)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Beyer C, Schett G, Distler O and Distler
JH: Animal models of systemic sclerosis: Prospects and limitations.
Arthritis Rheum. 62:2831–2844. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ishikawa H, Takeda K, Okamoto A, Matsuo S
and Isobe K: Induction of autoimmunity in a bleomycin-induced
murine model of experimental systemic sclerosis: An important role
for CD4+ T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 129:1688–1695. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Avouac J: Mouse model of experimental
dermal fibrosis: The bleomycin-induced dermal fibrosis. Methods Mol
Biol. 1142:91–98. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen JY, Mou XZ, Du XC and Xiang C:
Comparative analysis of biological characteristics of adult
mesenchymal stem cells with different tissue origins. Asian Pac J
Trop Med. 8:739–746. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ankrum JA, Ong JF and Karp JM: Mesenchymal
stem cells: Immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol.
32:252–260. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lim R, Milton P, Murphy SV, Dickinson H,
Chan ST and Jenkin G: Human mesenchymal stem cells reduce lung
injury in immunocompromised mice but not in immunocompetent mice.
Respiration. 85:332–341. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ho JH, Tseng TC, Ma WH, Ong WK, Chen YF,
Chen MH, Lin MW, Hong CY and Lee OK: Multiple intravenous
transplantations of mesenchymal stem cells effectively restore
long-term blood glucose homeostasis by hepatic engraftment and
β-cell differentiation in streptozocin-induced diabetic mice. Cell
Transplant. 21:997–1009. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liu J, Lu X, Lou Y, Cai Y, Cui W, Wang J,
Nie P, Chen L, Li B and Luo P: Xenogeneic transplantation of human
placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviates renal injury and
reduces inflammation in a mouse model of Lupus Nephritis. BioMed
Res Int. 2019(9370919)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hynes K, Bright R, Proudman S, Haynes D,
Gronthos S and Bartold M: Immunomodulatory properties of
mesenchymal stem cell in experimental arthritis in rat and mouse
models: A systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 46:1–19.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Srour N and Thébaud B: Mesenchymal stromal
cells in animal bleomycin pulmonary fibrosis models: A systematic
review. Stem Cells Transl Med. 4:1500–1510. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lin YT, Chern Y, Shen CK, Wen HL, Chang
YC, Li H, Cheng TH and Hsieh-Li HM: Human mesenchymal stem cells
prolong survival and ameliorate motor deficit through trophic
support in Huntington's disease mouse models. PLoS One.
6(e22924)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kendall RT and Feghali-Bostwick CA:
Fibroblasts in fibrosis: Novel roles and mediators. Front
Pharmacol. 5(123)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Mayes MD: Endothelin and endothelin
receptor antagonists in systemic rheumatic disease. Arthritis
Rheum. 48:1190–1199. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kissin EY, Lemaire R, Korn JH and Lafyatis
R: Transforming growth factor beta induces fibroblast fibrillin-1
matrix formation. Arthritis Rheum. 46:3000–3009. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yamamoto T, Takagawa S, Katayama I and
Nishioka K: Anti-sclerotic effect of transforming growth
factor-beta antibody in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced
scleroderma. Clin Immunol. 92:6–13. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Postlethwaite AE, Shigemitsu H and
Kanangat S: Cellular origins of fibroblasts: Possible implications
for organ fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
16:733–738. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Tsuji-Yamada J, Nakazawa M, Minami M and
Sasaki T: Increased frequency of interleukin 4 producing CD4+ and
CD8+ cells in peripheral blood from patients with systemic
sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 28:1252–1258. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sakkas LI, Xu B, Artlett CM, Lu S, Jimenez
SA and Platsoucas CD: Oligoclonal T cell expansion in the skin of
patients with systemic sclerosis. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950).
168:3649–3659. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Jimenez SA and Derk CT: Following the
molecular pathways toward an understanding of the pathogenesis of
systemic sclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 140:37–50. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yuan W, Yufit T, Li L, Mori Y, Chen SJ and
Varga J: Negative modulation of alpha1(I) procollagen gene
expression in human skin fibroblasts: Transcriptional inhibition by
interferon-gamma. J Cell Physiol. 179:97–108. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Okamoto Y, Hasegawa M, Matsushita T,
Hamaguchi Y, Huu DL, Iwakura Y, Fujimoto M and Takehara K:
Potential roles of interleukin-17A in the development of skin
fibrosis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 64:3726–3735. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Lakos G, Melichian D, Wu M and Varga J:
Increased bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis in mice lacking the
Th1-specific transcription factor T-bet. Pathobiology. 73:224–237.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Aliprantis AO, Wang J, Fathman JW, Lemaire
R, Dorfman DM, Lafyatis R and Glimcher LH: Transcription factor
T-bet regulates skin sclerosis through its function in innate
immunity and via IL-13. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:2827–2830.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Tan FK, Zhou X, Mayes MD, Gourh P, Guo X,
Marcum C, Jin L and Arnett FC Jr: Signatures of differentially
regulated interferon gene expression and vasculotrophism in the
peripheral blood cells of systemic sclerosis patients. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 45:694–702. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Singh RP, Hasan S, Sharma S, Nagra S,
Yamaguchi DT, Wong DT, Hahn BH and Hossain A: Th17 cells in
inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 13:1174–1181.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ivanov II, Zhou L and Littman DR:
Transcriptional regulation of Th17 cell differentiation. Semin
Immunol. 19:409–417. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Xing X, Yang J, Yang X, Wei Y, Zhu L, Gao
D and Li M: IL-17A induces endothelial inflammation in systemic
sclerosis via the ERK signaling pathway. PLoS One.
8(e85032)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Murata M, Fujimoto M, Matsushita T,
Hamaguchi Y, Hasegawa M, Takehara K, Komura K and Sato S: Clinical
association of serum interleukin-17 levels in systemic sclerosis:
Is systemic sclerosis a Th17 disease? J Dermatol Sci. 50:240–242.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Yang X, Yang J, Xing X, Wan L and Li M:
Increased frequency of Th17 cells in systemic sclerosis is related
to disease activity and collagen overproduction. Arthritis Res
Ther. 16(R4)2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Nakashima T, Jinnin M, Yamane K, Honda N,
Kajihara I, Makino T, Masuguchi S, Fukushima S, Okamoto Y, Hasegawa
M, et al: Impaired IL-17 signaling pathway contributes to the
increased collagen expression in scleroderma fibroblasts. J Immunol
(Baltimore, Md: 1950). 188:3573–3583. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wang D, Huang S, Yuan X, Liang J, Xu R,
Yao G, Feng X and Sun L: The regulation of the Treg/Th17 balance by
mesenchymal stem cells in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell
Mol Immunol. 14:423–431. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Luz-Crawford P, Noël D, Fernandez X,
Khoury M, Figueroa F, Carrión F, Jorgensen C and Djouad F:
Mesenchymal stem cells repress Th17 molecular program through the
PD-1 pathway. PLoS One. 7(e45272)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Hu Y, Lou B, Wu X, Wu R, Wang H, Gao L, Pi
J and Xu Y: Comparative study on in vitro culture of mouse bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int.
2018(6704583)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Haddad R and Saldanha-Araujo F: Mechanisms
of T-cell immunosuppression by mesenchymal stromal cells: What do
we know so far? BioMed Res Int. 2014(216806)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Shi Y, Hu G, Su J, Li W, Chen Q, Shou P,
Xu C, Chen X, Huang Y, Zhu Z, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells: A new
strategy for immunosuppression and tissue repair. Cell Res.
20:510–518. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Le Blanc K and Mougiakakos D: Multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune system. Nat Rev
Immunol. 12:383–396. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Prockop DJ and Oh JY: Mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells (MSCs): Role as guardians of inflammation. Mol
Ther. 20:14–20. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Usunier B, Benderitter M, Tamarat R and
Chapel A: Management of fibrosis: The mesenchymal stromal cells
breakthrough. Stem Cells Int. 2014(340257)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|