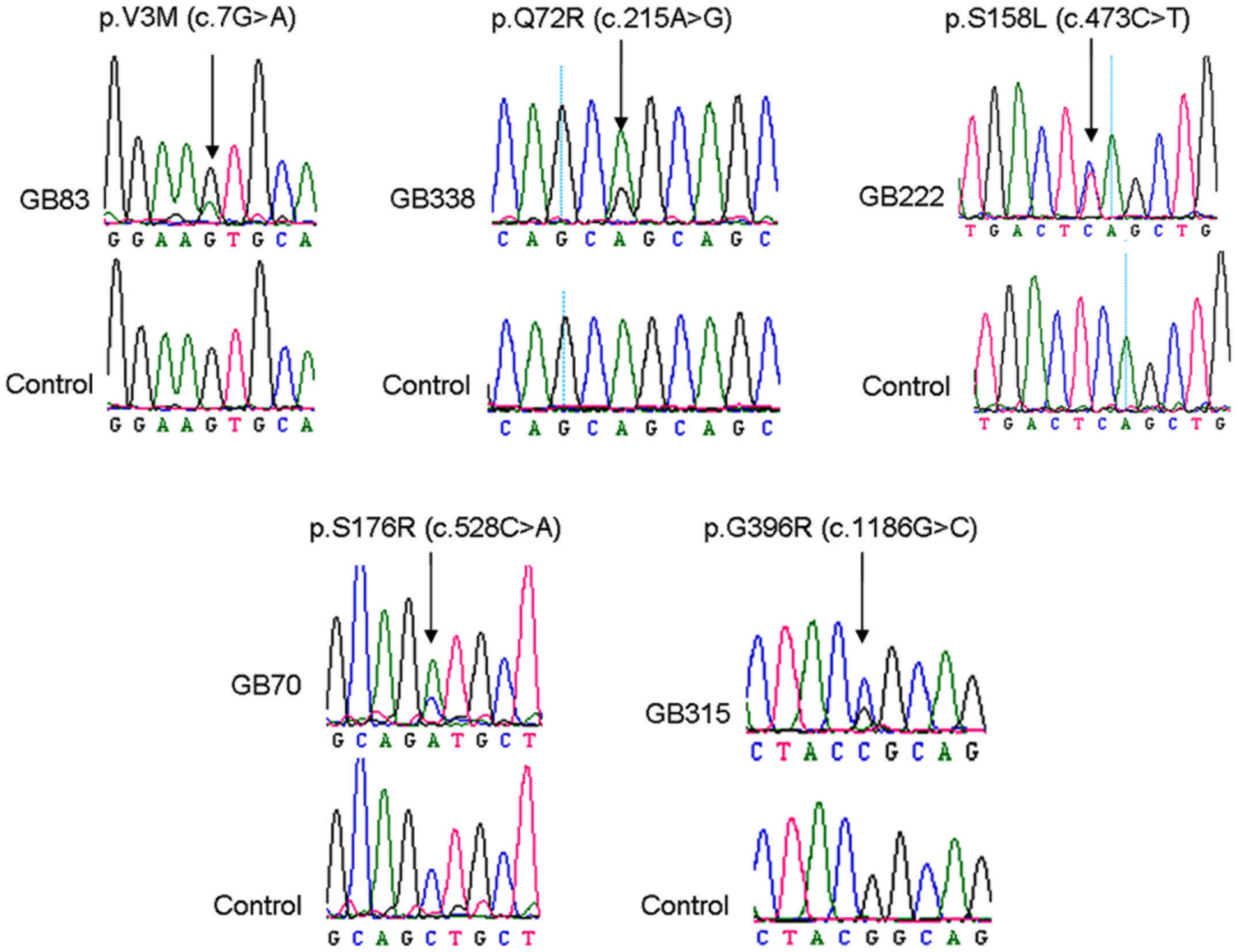
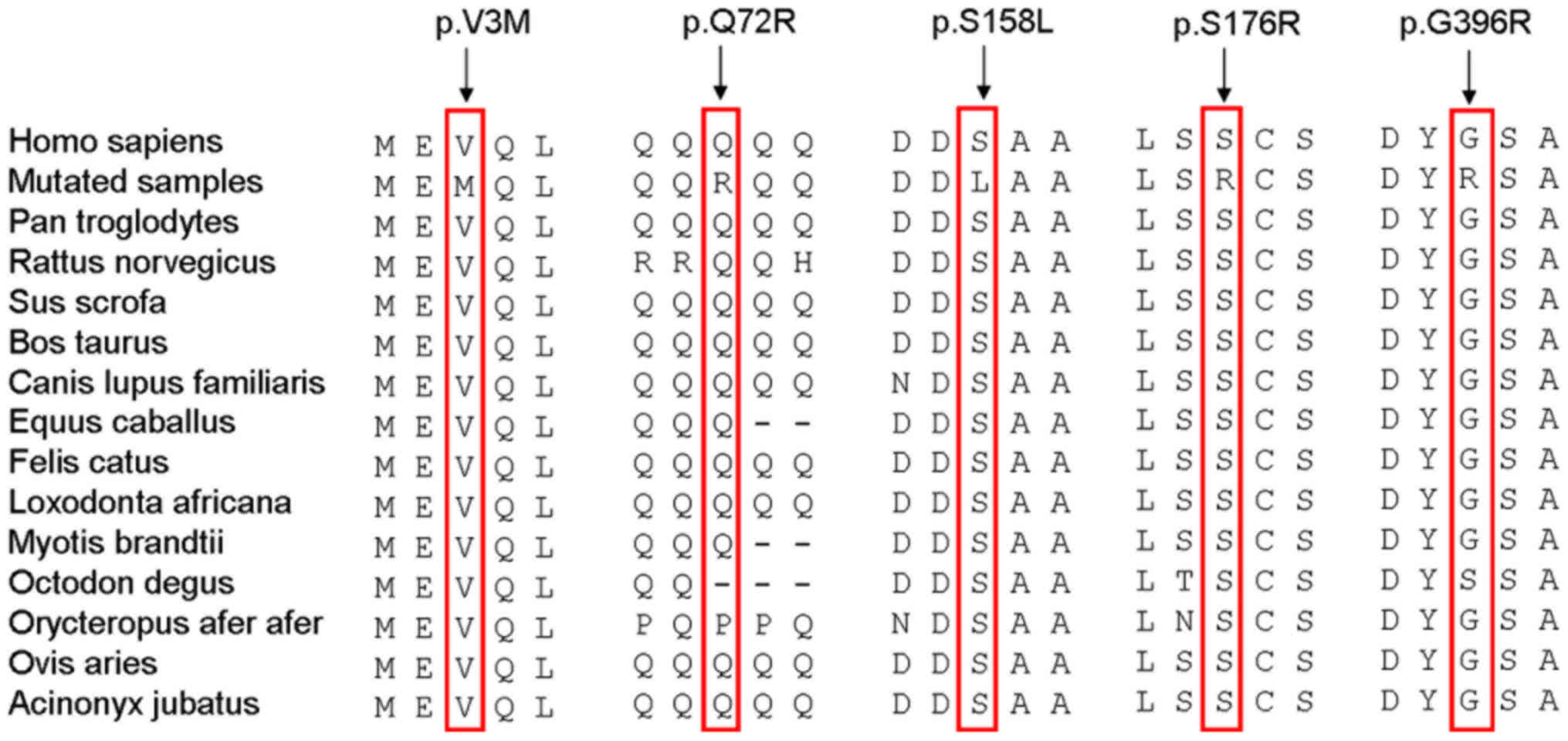
|
1
|
Teede H, Deeks A and Moran L: Polycystic
ovary syndrome: A complex condition with psychological,
reproductive and metabolic manifestations that impacts on health
across the lifespan. BMC Med. 8(41)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Azziz R, Carmina E, Chen Z, Dunaif A,
Laven JS, Legro RS, Lizneva D, Natterson-Horowtiz B, Teede HJ and
Yildiz BO: Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2(16057)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Azziz R, Carmina E, Dewailly D,
Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Escobar-Morreale HF, Futterweit W, Janssen
OE, Legro RS, Norman RJ, Taylor AE, et al: Androgen Excess Society:
Positions statement: Criteria for defining polycystic ovary
syndrome as a predominantly hyperandrogenic syndrome: An Androgen
Excess Society guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91:4237–4245.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chang WY, Knochenhauer ES, Bartolucci AA
and Azziz R: Phenotypic spectrum of polycystic ovary syndrome:
Clinical and biochemical characterization of the three major
clinical subgroups. Fertil Steril. 83:1717–1723. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Livadas S, Pappas C, Karachalios A,
Marinakis E, Tolia N, Drakou M, Kaldrymides P, Panidis D and
Diamanti-Kandarakis E: Prevalence and impact of hyperandrogenemia
in 1,218 women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrine.
47:631–638. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Owens LA, Kristensen SG, Lerner A,
Christopoulos G, Lavery S, Hanyaloglu AC, Hardy K, Yding Andersen C
and Franks S: Gene expression in granulosa cells from small antral
follicles from women with or without polycystic ovaries. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 104:6182–6192. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Younas K, Quintela M, Thomas S,
Garcia-Parra J, Blake L, Whiteland H, Bunkheila A, Francis LW,
Margarit L, Gonzalez D, et al: Delayed endometrial decidualisation
in polycystic ovary syndrome; the role of AR-MAGEA11. J Mol Med
(Berl). 97:1315–1327. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xu G, Wang Q, Zhang AD, Liu JD, Feng JW
and Chen YL: Effect of electroacupuncture at different acupoints on
steroid hormones and ovarian androgen receptor expression in
polycystic ovary syndrome rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 43:543–549.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li X, Pishdari B, Cui P, Hu M, Yang HP,
Guo YR, Jiang HY, Feng Y, Billig H and Shao R: Regulation of
androgen receptor expression alters AMPK phosphorylation in the
endometrium: In vivo and in vitro studies in women with polycystic
ovary syndrome. Int J Biol Sci. 11:1376–1389. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Caldwell AS, Edwards MC, Desai R, Jimenez
M, Gilchrist RB, Handelsman DJ and Walters KA: Neuroendocrine
androgen action is a key extraovarian mediator in the development
of polycystic ovary syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:E3334–E3343. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rajender S, Carlus SJ, Bansal SK, Negi MP,
Sadasivam N, Sadasivam MN and Thangaraj K: Androgen receptor CAG
repeats length polymorphism and the risk of polycystic ovarian
syndrome (PCOS). PLoS One. 8(e75709)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Peng CY, Xie HJ, Guo ZF, Nie YL, Chen J,
Zhou JM and Yin J: The association between androgen receptor gene
CAG polymorphism and polycystic ovary syndrome: A case-control
study and meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet. 31:1211–1219.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Schüring AN, Welp A, Gromoll J, Zitzmann
M, Sonntag B, Nieschlag E, Greb RR and Kiesel L: Role of the CAG
repeat polymorphism of the androgen receptor gene in polycystic
ovary syndrome (PCOS). Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 120:73–79.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ibáñez L, Ong KK, Mongan N, Jääskeläinen
J, Marcos MV, Hughes IA, De Zegher F and Dunger DB: Androgen
receptor gene CAG repeat polymorphism in the development of ovarian
hyperandrogenism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88:3333–3338.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim JJ, Choung SH, Choi YM, Yoon SH, Kim
SH and Moon SY: Androgen receptor gene CAG repeat polymorphism in
women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 90:2318–2323.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xia Y, Che Y, Zhang X, Zhang C, Cao Y,
Wang W, Xu P, Wu X, Yi L, Gao Q, et al: Polymorphic CAG repeat in
the androgen receptor gene in polycystic ovary syndrome patients.
Mol Med Rep. 5:1330–1334. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Möhlig M, Jürgens A, Spranger J, Hoffmann
K, Weickert MO, Schlösser HW, Schill T, Brabant G, Schüring A,
Pfeiffer AF, et al: The androgen receptor CAG repeat modifies the
impact of testosterone on insulin resistance in women with
polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 155:127–130.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hu DG, Hickey TE, Irvine C, Wijayakumara
DD, Lu L, Tilley WD, Selth LA and Mackenzie PI: Identification of
androgen receptor splice variant transcripts in breast cancer cell
lines and human tissues. Horm Cancer. 5:61–71. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang F, Pan J, Liu Y, Meng Q, Lv P, Qu F,
Ding GL, Klausen C, Leung PC, Chan HC, et al: Alternative splicing
of the androgen receptor in polycystic ovary syndrome. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:4743–4748. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Walters KA and Handelsman DJ: Androgen
receptor splice variants and polycystic ovary syndrome: Cause or
effect? Asian J Androl. 18:442–443. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wadosky KM and Koochekpour S: Androgen
receptor splice variants and prostate cancer: From bench to
bedside. Oncotarget. 8:18550–18576. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hickey TE, Irvine CM, Dvinge H, Tarulli
GA, Hanson AR, Ryan NK, Pickering MA, Birrell SN, Hu DG, Mackenzie
PI, et al: Expression of androgen receptor splice variants in
clinical breast cancers. Oncotarget. 6:44728–44744. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nam H, Kim CH, Cha MY, Kim JM, Kang BM and
Yoo HW: Polycystic ovary syndrome woman with heterozygous androgen
receptor gene mutation who gave birth to a child with androgen
insensitivity syndrome. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 58:179–182.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS
Consensus Workshop Group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic
criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary
syndrome. Fertil Steril. 81:19–25. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hatch R, Rosenfield RL, Kim MH and Tredway
D: Hirsutism: Implications, etiology, and management. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 140:815–830. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Balen AH, Laven JS, Tan SL and Dewailly D:
Ultrasound assessment of the polycystic ovary: International
consensus definitions. Hum Reprod Update. 9:505–514.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu J, Zou Y, Luo Y, Guo JB, Liu FY, Zhou
JY, Zhang ZY, Wan L and Huang OP: Prevalence and clinical
significance of mediator complex subunit 12 mutations in 362 Han
Chinese samples with uterine leiomyoma. Oncol Lett. 14:47–54.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li GX, Jiao XH and Cheng XB: Correlations
between blood uric acid and the incidence and progression of type 2
diabetes nephropathy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:506–511.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L,
Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS and Sunyaev SR: A
method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat
Methods. 7:248–249. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Schwarz JM, Cooper DN, Schuelke M and
Seelow D: MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the
deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods. 11:361–362. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kumar S, Stecher G and Tamura K: MEGA7:
Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger
datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 33:1870–1874. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Walters KA, Rodriguez Paris V, Aflatounian
A and Handelsman DJ: Androgens and ovarian function: translation
from basic discovery research to clinical impact. J Endocrinol.
242:R23–R50. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Walters KA and Handelsman DJ: Role of
androgens in the ovary. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 465:36–47.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Baculescu N: The role of androgen receptor
activity mediated by the CAG repeat polymorphism in the
pathogenesis of PCOS. J Med Life. 6:18–25. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lim JJ, Lima PDA, Salehi R, Lee DR and
Tsang BK: Regulation of androgen receptor signaling by
ubiquitination during folliculogenesis and its possible
dysregulation in polycystic ovarian syndrome. Sci Rep.
7(10272)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|