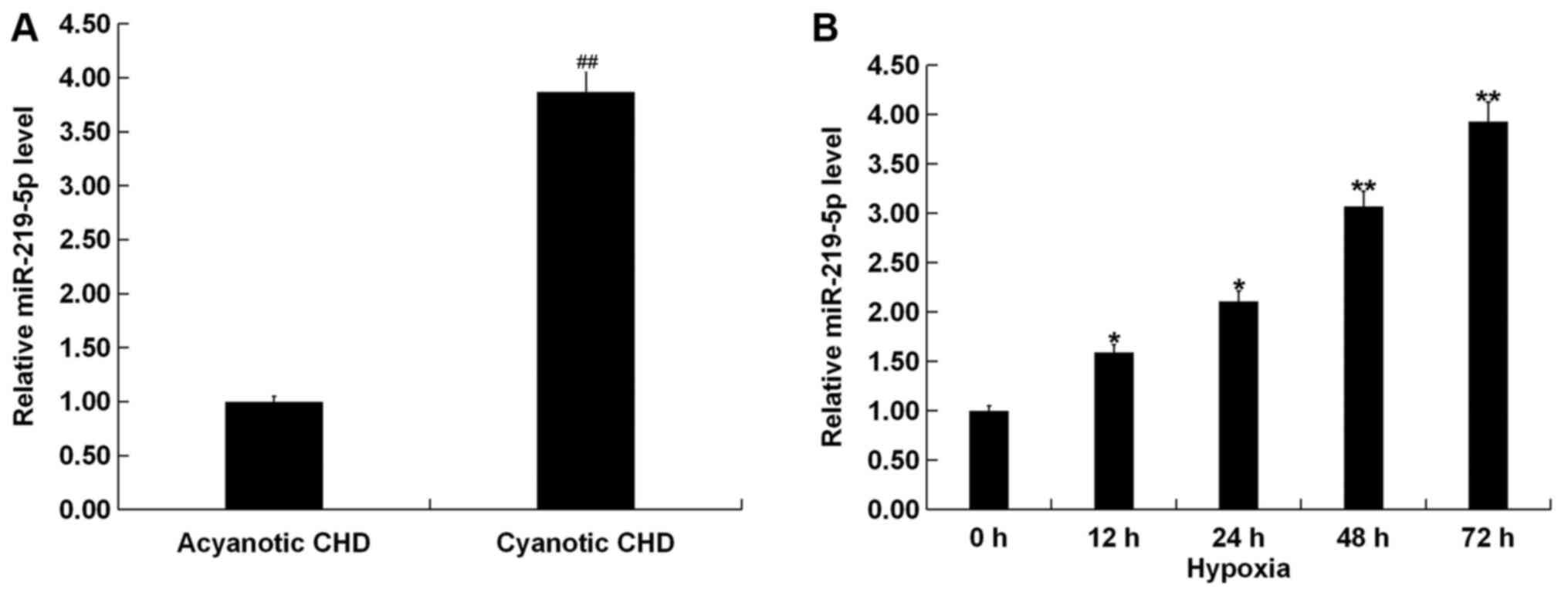
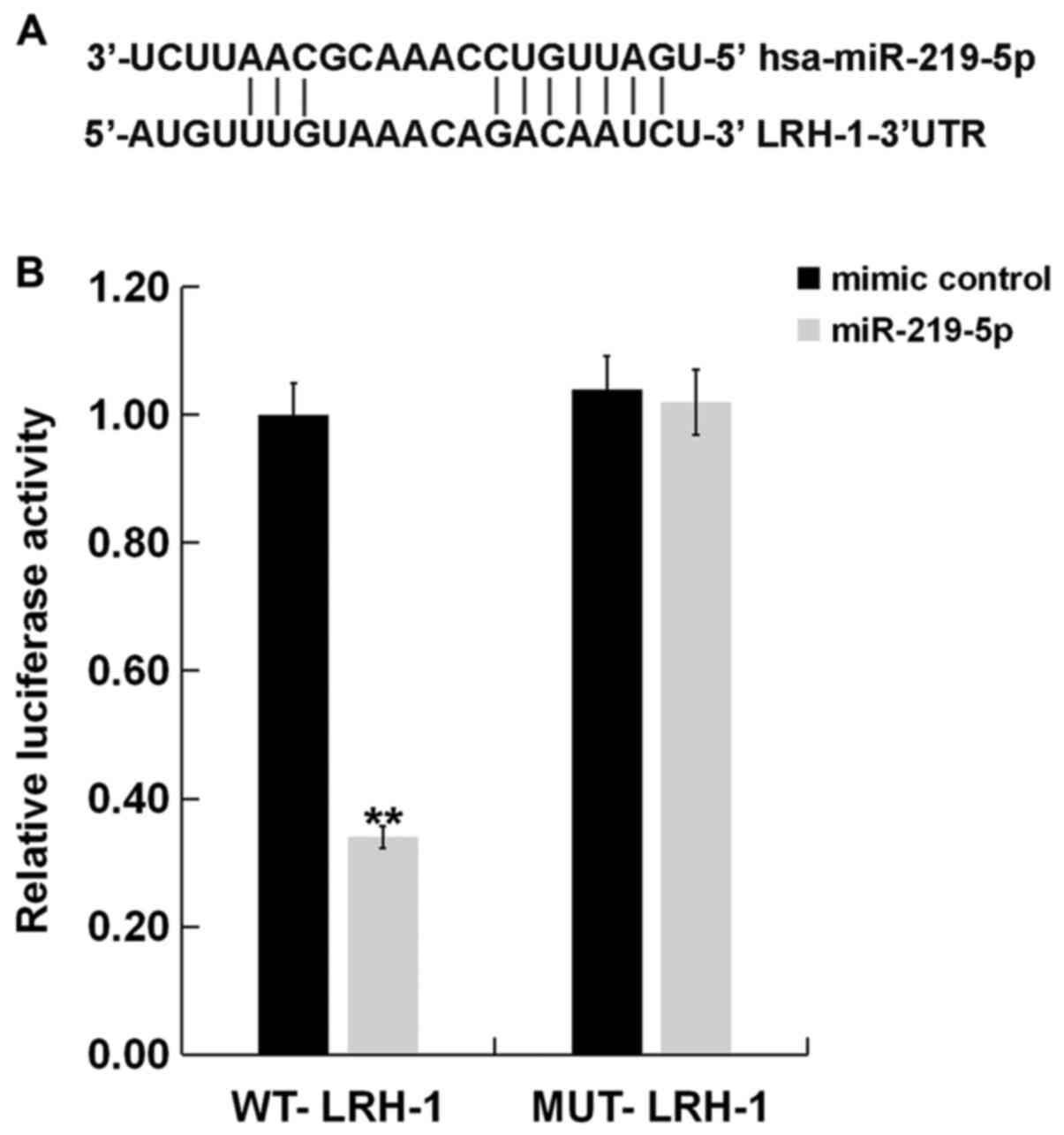
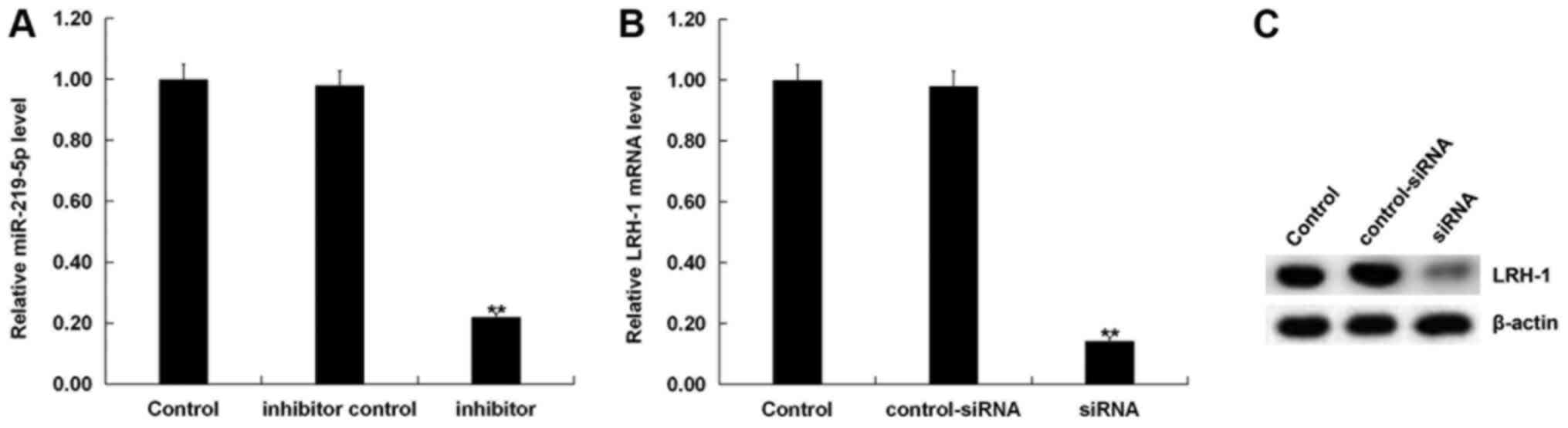
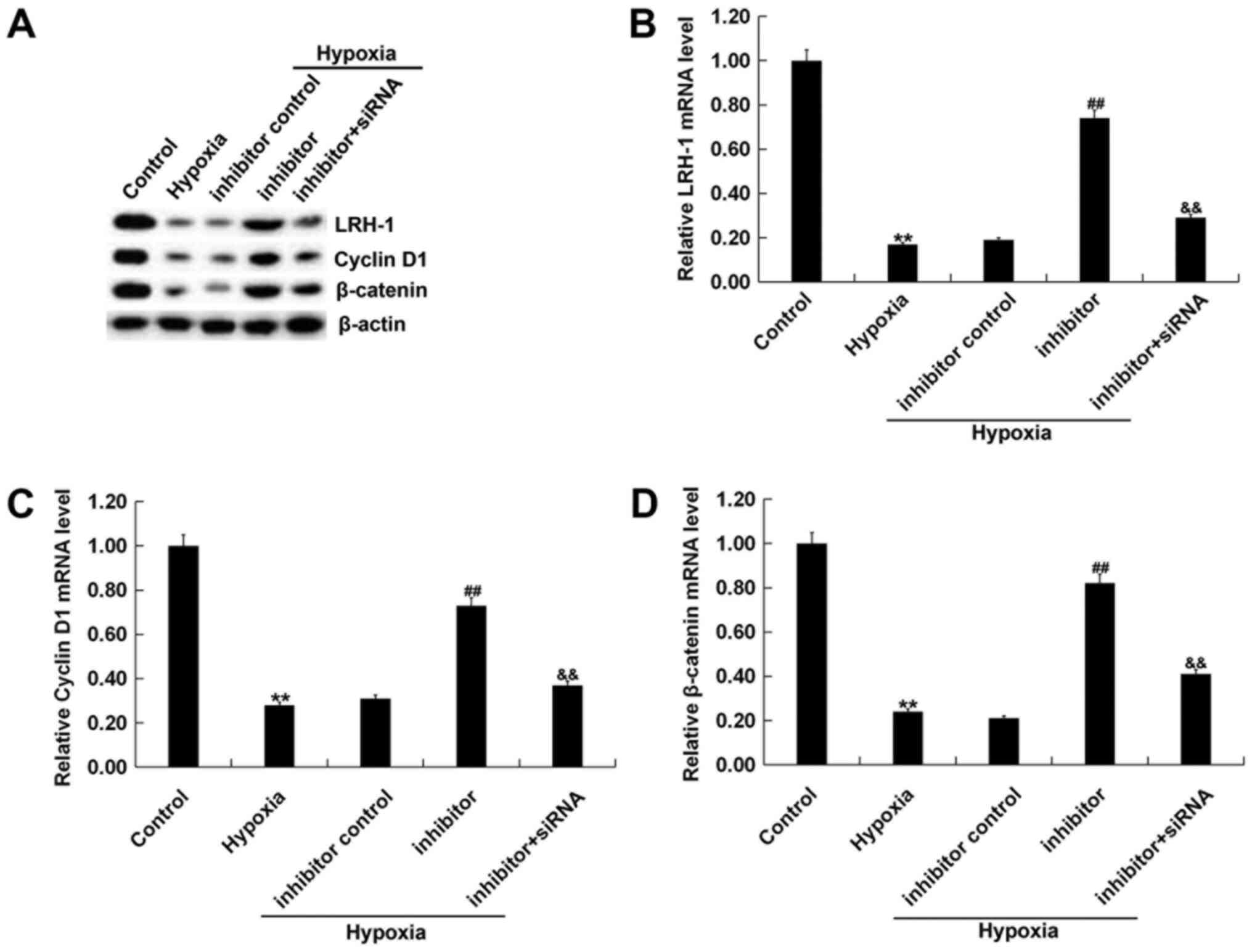
|
1
|
Cassidy AR, White MT, DeMaso DR, Newburger
JW and Bellinger DC: Executive function in children and adolescents
with critical cyanotic congenital heart disease. J Int Neuropsychol
Soc. 21:34–49. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hoffman JI and Kaplan S: The incidence of
congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 39:1890–1900.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Haseba S, Sakakima H, Nakao S, Ohira M,
Yanagi S, Imoto Y, Yoshida A and Shimodozono M: Early postoperative
physical therapy for improving short-term gross motor outcome in
infants with cyanotic and acyanotic congenital heart disease.
Disabil Rehabil. 40:1694–1701. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cordina RL and Celermajer DS: Chronic
cyanosis and vascular function: Implications for patients with
cyanotic congenital heart disease. Cardiol Young. 20:242–253.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang L, Tian D, Hu J, Xing H, Sun M, Wang
J, Jian Q and Yang H: miRNA-145 regulates the development of
congenital heart disease through targeting FXN. Pediatr Cardiol.
37:629–636. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Peng B and Han Y: miR-182
alleviates the development of cyanotic congenital heart disease by
suppressing HES1. Eur J Pharmacol. 836:18–24. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cheng J, Deng R, Zhang P, Wu C, Wu K, Shi
L, Liu X, Bai J, Deng M, Shuai X, et al: miR-219-5p plays a tumor
suppressive role in colon cancer by targeting oncogene Sall4. Oncol
Rep. 34:1923–1932. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jiang Y, Yin L, Jing H and Zhang H:
MicroRNA-219-5p exerts tumor suppressor function by targeting ROBO1
in glioblastoma. Tumour Biol. 36:8943–8951. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fayard E, Auwerx J and Schoonjans K:
LRH-1: An orphan nuclear receptor involved in development,
metabolism and steroidogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 14:250–260.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang ZN, Bassett M and Rainey WE: Liver
receptor homologue-1 is expressed in the adrenal and can regulate
transcription of 11 beta-hydroxylase. J Mol Endocrinol. 27:255–258.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Grgurevic N, Tobet S and Majdic G:
Widespread expression of liver receptor homolog 1 in mouse brain.
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 26:541–547. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu C, Feng J, Li L, Wu Y, Xie H, Yin Y, Ye
J and Li Z: Liver receptor homologue 1, a novel prognostic marker
in colon cancer patients. Oncol Lett. 16:2833–2838. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bianco S, Jangal M, Garneau D and Gévry N:
LRH-1 controls proliferation in breast tumor cells by regulating
CDKN1A gene expression. Oncogene. 34:4509–4518. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xiao L, Wang Y, Xu K, Hu H, Xu Z, Wu D,
Wang Z, You W, Ng CF, Yu S, et al: Nuclear receptor LRH-1 functions
to promote castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer via its
promotion of intratumoral androgen biosynthesis. Cancer Res.
78:2205–2218. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jian Z, Li JB, Ma RY, Chen L, Zhong QJ,
Wang XF, Wang W, Hong Y and Xiao YB: Increase of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor (MIF) expression in cardiomyocytes
during chronic hypoxia. Clin Chim Acta. 405:132–138.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Piccoli M, Conforti E, Varrica A, Ghiroldi
A, Cirillo F, Resmini G, Pluchinotta F, Tettamanti G, Giamberti A,
Frigiola A, et al: NEU3 sialidase role in activating HIF-1α in
response to chronic hypoxia in cyanotic congenital heart patients.
Int J Cardiol. 230:6–13. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gong L, Xu H, Chang H, Tong Y, Zhang T and
Guo G: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA MEG3 protects H9c2 cells
from hypoxia-induced injury by targeting microRNA-183. J Cell
Biochem. 119:1429–1440. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Park M, Youn B, Zheng XL, Wu D, Xu A and
Sweeney G: Globular adiponectin, acting via AdipoR1/APPL1, protects
H9c2 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis. PLoS One.
6(e19143)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hao P, Cao X, Zhu Z, Gao C, Chen Y and Qi
D: Effects of miR-181a targeting XIAP gene on apoptosis of
cardiomyocytes induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation and its mechanism.
J Cell Biochem: Nov 28, 2018 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
22
|
Ma J, Zhang J, Wang Y, Long K, Wang X, Jin
L, Tang Q, Zhu L, Tang G, Li X, et al: miR-532-5p alleviates
hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting PDCD4. Gene.
675:36–43. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li J, Li L and Shen Y: Protective role of
microRNA-219-5p inhibitor against spinal cord injury via liver
receptor homolog-1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway regulation. Exp
Ther Med. 15:3563–3569. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang J, Sheng YY, Wei JW, Gao XM, Zhu Y,
Jia HL, Dong QZ and Qin LX: MicroRNA-219-5p promotes tumor growth
and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating cadherin
1. BioMed Res Int. 2018(4793971)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tang Q and Ran H: MicroRNA-219-5p inhibits
wound healing by targeting TMEM98 in keratinocytes under normoxia
and hypoxia condition. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:6205–6211.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby
C, Brennan T, Wendling O, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Thomas W, Auwerx J,
et al: Synergy between LRH-1 and beta-catenin induces G1
cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 15:499–509.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fodde R and Brabletz T: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:150–158. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhao Y, Wang C, Wang C, Hong X, Miao J,
Liao Y, Zhou L and Liu Y: An essential role for Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in mediating hypertensive heart disease. Sci Rep.
8(8996)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun X, Pang L, Shi M, Huang J and Wang Y:
HIF2α induces cardiomyogenesis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mouse
embryonic stem cells. J Transl Med. 13(88)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|