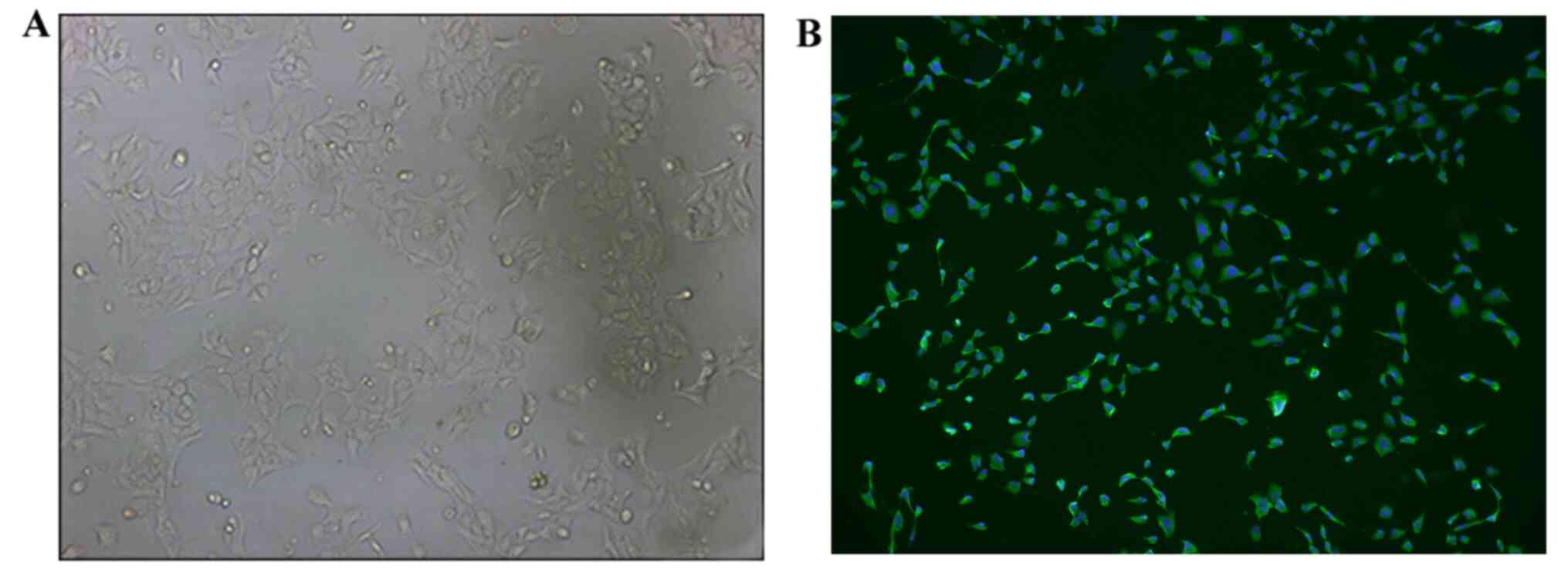
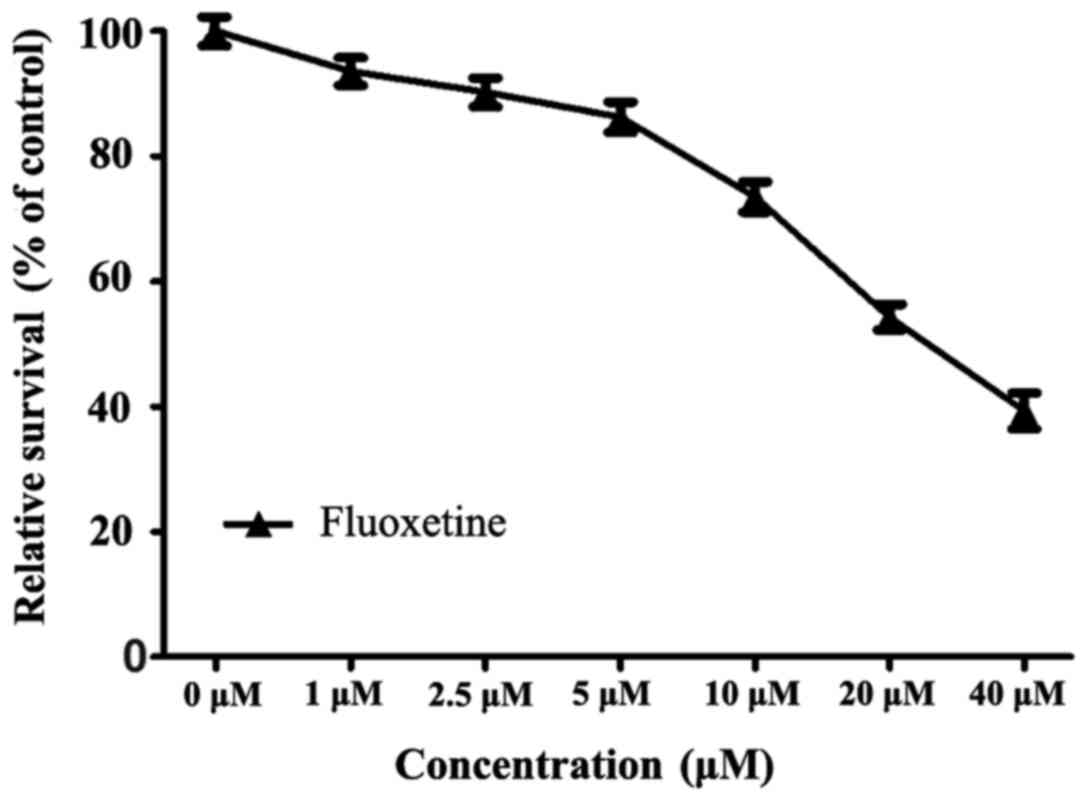
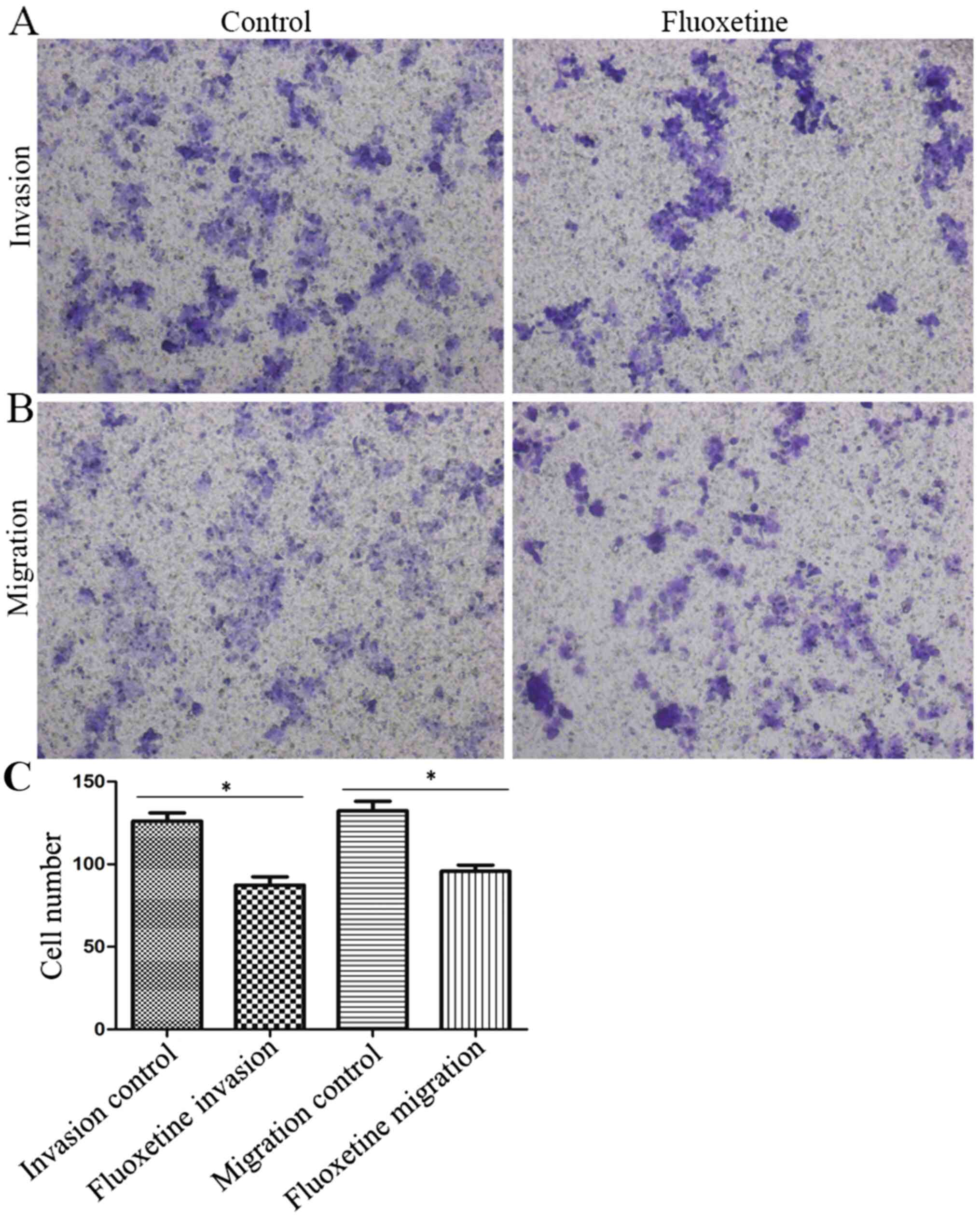
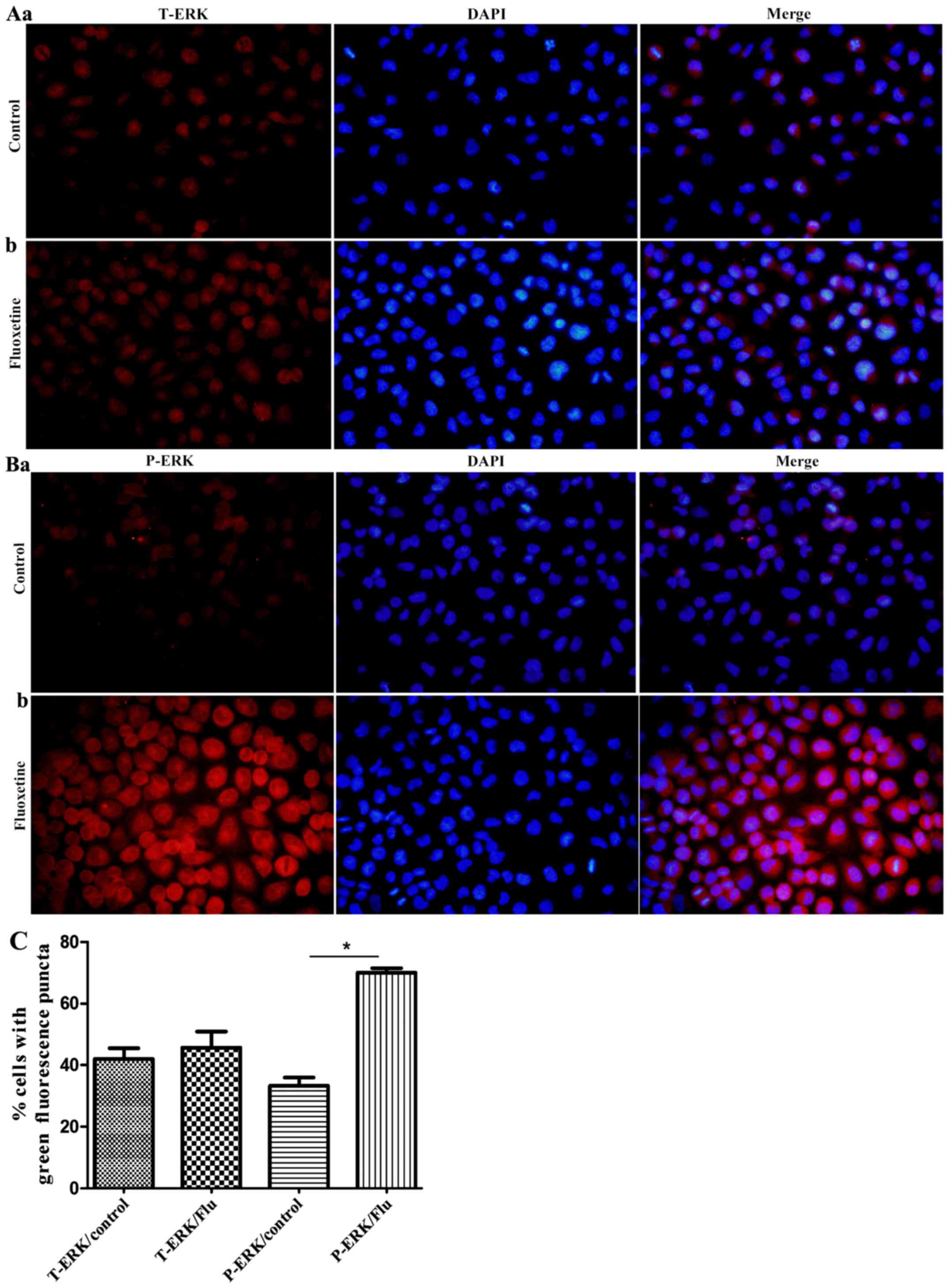
|
1
|
Schiffman RM, Walt JG, Jacobsen G, Doyle
JJ, Lebovics G and Sumner W: Utility assessment among patients with
dry eye disease. Ophthalmology. 110:1412–1419. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Han SB, Hyon JY, Woo SJ, Lee JJ, Kim TH
and Kim KW: Prevalence of dry eye disease in an elderly Korean
population. Arch Ophthalmol. 129:633–638. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lin PY, Cheng CY, Hsu WM, Tsai SY, Lin MW,
Liu JH and Chou P: Association between symptoms and signs of dry
eye among an elderly Chinese population in Taiwan: The shihpai eye
study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:1593–1598. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Management and therapy of dry eye disease.
Report of the management and therapy subcommittee of the
international dry eye WorkShop. Ocul Surf. 5:163–178.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Luo C, Wang F, Qin S, Chen Q and Wang QK:
Coronary artery disease susceptibility gene ADTRP regulates cell
cycle progression, proliferation, and apoptosis by global gene
expression regulation. Physiol Genomics. 48:554–564.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Paul A, Wilson S, Belham CM, Robinson CJ,
Scott PH, Gould GW and Plevin R: Stress-activated protein kinases:
Activation, regulation and function. Cell Signal. 9:403–410.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pflugfelder SC, de Paiva CS, Tong L, Luo
L, Stern ME and Li DQ: Stress-activated protein kinase signaling
pathways in dry eye and ocular surface disease. Ocul Surf. 3 (4
Suppl):S154–S157. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li DQ, Luo L, Chen Z, Kim HS, Song XJ and
Pflugfelder SC: JNK and ERK MAP kinases mediate induction of
IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-8 following hyperosmolar stress in human
limbal epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 82:588–596. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tang CH and Tsai CC: CCL2 increases MMP-9
expression and cell motility in human chondrosarcoma cells via the
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:335–344. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chang F, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Lee JT,
Navolanic PM, Blalock WL, Franklin R and McCubrey JA: Regulation of
cell cycle progression and apoptosis by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway
(Review). Int J Oncol. 22:469–480. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Raison CL, Capuron L and Miller AH:
Cytokines sing the blues: Inflammation and the pathogenesis of
depression. Trends Immunol. 27:24–31. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Luo L, Li DQ, Doshi A, Farley W, Corrales
RM and Pflugfelder SC: Experimental dry eye stimulates production
of inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 and activates MAPK signaling
pathways on the ocular surface. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
45:4293–4301. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dota A, Nishida K, Adachi W, Nakamura T,
Koizumi N, Kawamoto S, Okubo K and Kinoshita S: An expression
profile of activegenes in human conjunctival epithelium. Exp Eye
Res. 72:235–241. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Krishna M and Narang H: The complexity of
mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) made simple. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 65:3525–3544. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dwivedi Y, Rizavi HS, Zhang H, Roberts RC,
Conley RR and Pandey GN: Aberrant extracellular signal-regulated
kinase (ERK)1/2 signalling in suicide brain: Role of ERK kinase 1
(MEK1). Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 12:1337–1354. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim KW, Han SB, Han ER, Woo SJ, Lee JJ,
Yoon JC and Hyon JY: Association between depression and dry eye
disease in an elderly population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
52:7954–7958. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kroemer G: The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and
its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med. 3:614–620.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
De Paiva CS, Corrales RM, Villarreal AL,
Farley WJ, Li DQ, Stern ME and Pflugfelder SC: Corticosteroid and
doxycycline suppress MMP-9 and inflammatory cytokine expression,
MAPK activation in the corneal epithelium in experimental dry eye.
Exp Eye Res. 83:526–535. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|