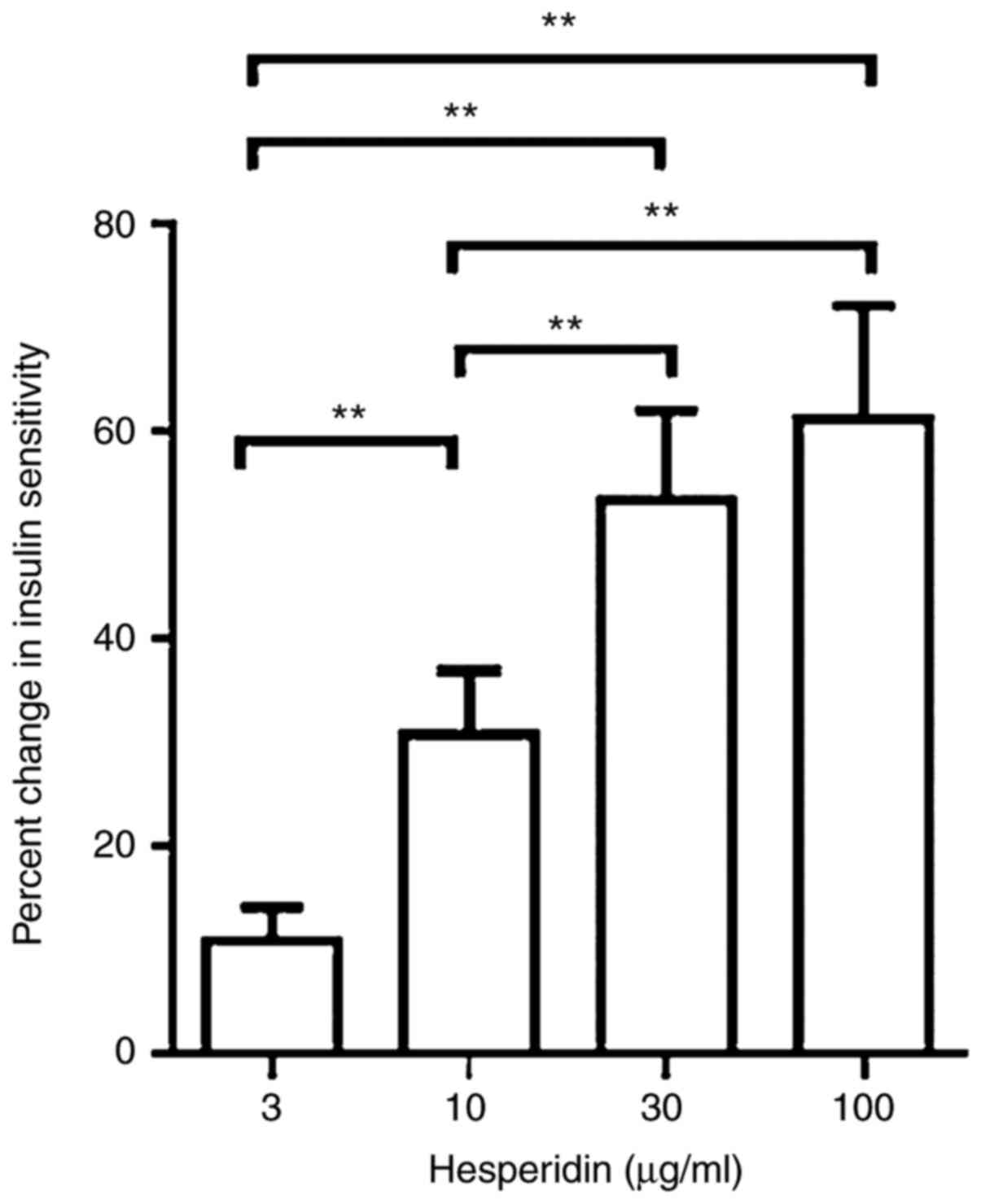
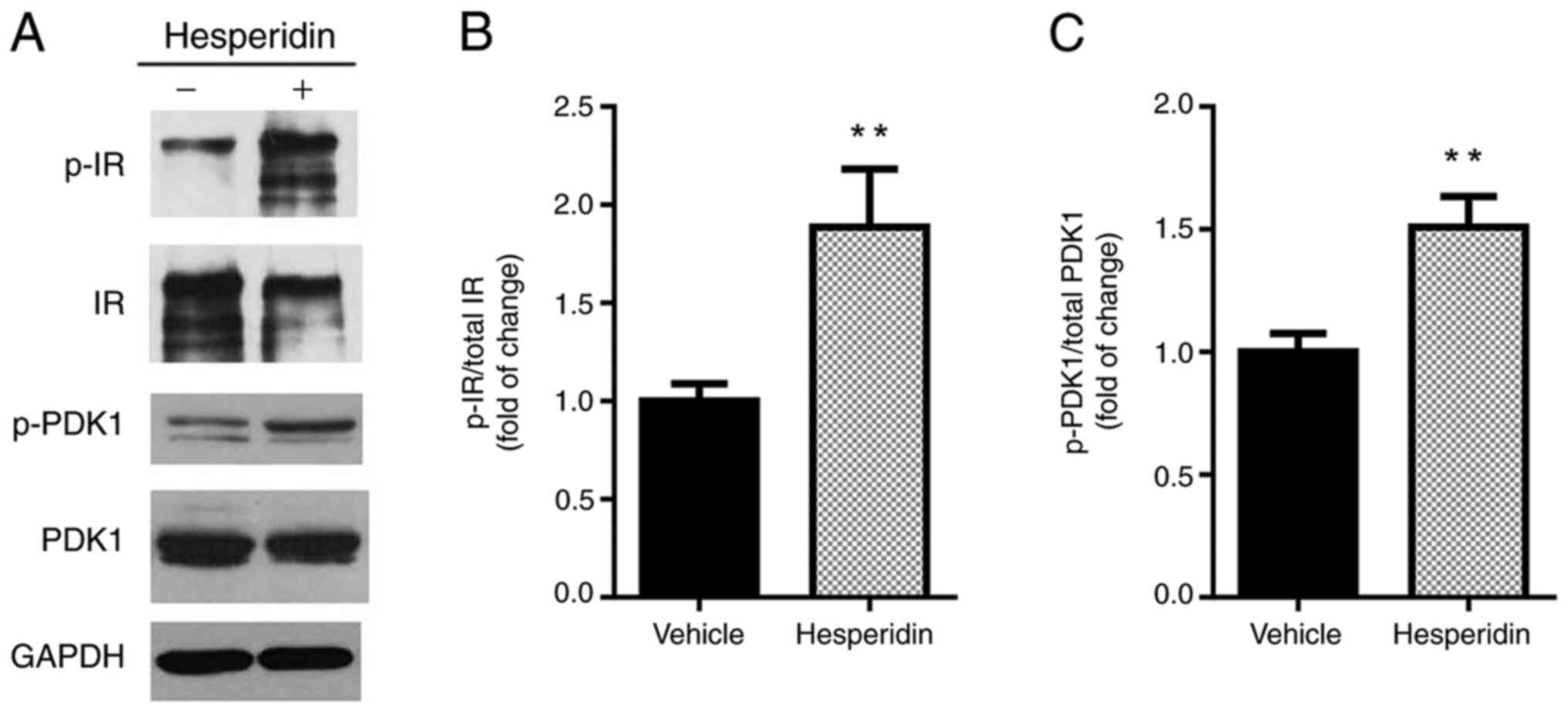
|
1
|
Elizabeth MM, Alarcon-Aguilar J F, Clara
OC, Escobar-Villanueva and Carmen M: Pancreatic β-cells and
type 2 diabetes development. Curr Diabetes Rev. 13:108–121.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
American Diabetes Association. 2.
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 40 (Suppl
1):S11–S24. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T,
Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, et al: 2010 China Noncommunicable
Disease Surveillance Group: Prevalence and control of diabetes in
Chinese adults. JAMA. 310:948–959. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang SH, Dou KF and Song WJ: Prevalence of
diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:2425–2426;
author reply 2426. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, Huang Z, Zhang D,
Deng Q, Li Y, Zhao Z, Qin X, Jin D, et al: Prevalence and ethnic
pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA.
317:2515–2523. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang L, Shao J, Bian Y, Wu H, Shi L, Zeng
L, Li W and Dong J: Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among
inland residents in China (2000-2014): A meta-analysis. J Diabetes
Investig. 7:845–852. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y,
Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N,
et al: The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin
resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med.
7:941–946. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
DeFronzo RA and Ferrannini E: Insulin
resistance A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity,
hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular
disease. Diabetes Care. 14:173–194. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Leto D and Saltiel AR: Regulation of
glucose transport by insulin: Traffic control of GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:383–396. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pollak M: The insulin and insulin-like
growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: An update. Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:159–169. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang H, Tan C, Wang H, Xue S and Wang M:
Study on the history of Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat
diabetes. Eur J Integr Med. 2:41–46. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Calixto JB: Efficacy, safety, quality
control, marketing and regulatory guidelines for herbal medicines
(phytotherapeutic agents). Braz J Med Biol Res. 33:179–189.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Valli G and Giardina EG: Benefits, adverse
effects and drug interactions of herbal therapies with
cardiovascular effects. J Am Coll Cardiol. 39:1083–1095.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ong KC and Khoo HE: Insulinomimetic
effects of myricetin on lipogenesis and glucose transport in rat
adipocytes but not glucose transport translocation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 51:423–429. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hsu FL, Liu IM, Kuo DH, Chen WC, Su HC and
Cheng JT: Antihyperglycemic effect of puerarin in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Nat Prod. 66:788–792.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Choi JS, Yokozawa T and Oura H:
Improvement of hyperglycemia and hyperlipemia in
streptozotocin-diabetic rats by a methanolic extract of Prunus
davidiana stems and its main component, prunin. Planta Med.
57:208–211. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shisheva A and Shechter Y: Quercetin
selectively inhibits insulin receptor function in vitro and the
bioresponses of insulin and insulinomimetic agents in rat
adipocytes. Biochemistry. 31:8059–8063. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Garg A, Garg S, Zaneveld LJ and Singla AK:
Chemistry and pharmacology of the Citrus bioflavonoid hesperidin.
Phytother Res. 15:655–669. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jung UJ, Lee MK, Jeong KS and Choi MS: The
hypoglycemic effects of hesperidin and naringin are partly mediated
by hepatic glucose-regulating enzymes in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. J
Nutr. 134:2499–2503. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Akiyama S, Katsumata S, Suzuki K, Nakaya
Y, Ishimi Y and Uehara M: Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of
hesperidin and cyclodextrin-clathrated hesperetin in Goto-Kakizaki
rats with type 2 diabetes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 73:2779–2782.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ahmed OM, Mahmoud AM, Abdelmoneim A and
Ashour MB: Antidiabetic effects of hesperidin and naringin in type
2 diabetic rats. Diabetol Croat. 41:53–67. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shi X, Liao S, Mi H, Guo C, Qi D, Li F,
Zhang C and Yang Z: Hesperidin prevents retinal and plasma
abnormalities in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Molecules.
17:12868–12881. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu X, Motoshima H, Mahadev K, Stalker TJ,
Scalia R and Goldstein BJ: Involvement of AMP-activated protein
kinase in glucose uptake stimulated by the globular domain of
adiponectin in primary rat adipocytes. Diabetes. 52:1355–1363.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA):
Technical standards for testing and assessment of health food.
CFDA, 2003.
|
|
25
|
Davidson AL and Arion WJ: Factors
underlying significant underestimations of glucokinase activity in
crude liver extracts: Physiological implications of higher cellular
activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 253:156–167. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Alegre M, Ciudad CJ, Fillat C and
Guinovart JJ: Determination of glucose-6-phosphatase activity using
the glucose dehydrogenase-coupled reaction. Anal Biochem.
173:185–189. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bentle LA and Lardy HA: Interaction of
anions and divalent metal ions with phosphoenolpyruvate
carboxykinase. J Biol Chem. 251:2916–2921. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nordlie RC and Foster JD: A retrospective
review of the roles of multifunctional glucose-6-phosphatase in
blood glucose homeostasis: Genesis of the tuning/retuning
hypothesis. Life Sci. 87:339–349. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Li X, Xie C, Luo X, Bao Y, Wu B, Hu
Y, Zhong Z, Liu C and Li M: Prevention effects and possible
molecular mechanism of mulberry leaf extract and its formulation on
rats with insulin-insensitivity. PLoS One.
11(e0152728)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Dong H, Wang M and Zhang J:
Quercetin isolated from Toona sinensis leaves attenuates
hyperglycemia and protects hepatocytes in
high-carbohydrate/high-fat diet and alloxan induced experimental
diabetic mice. J Diabetes Res. 2016(8492780)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wallace TM, Levy JC and Matthews DR: Use
and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 27:1487–1495.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Geloneze B, Vasques AC, Stabe CF, Pareja
JC, Rosado LE, Queiroz EC and Tambascia MA: BRAMS Investigators.
HOMA1-IR and HOMA2-IR indexes in identifying insulin resistance and
metabolic syndrome: Brazilian Metabolic Syndrome Study (BRAMS). Arq
Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 53:281–287. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wei W and Wu XM: Li: Experimental
Methodology of Pharmacology. 4th edition. People's Medical
Publishing House, Beijing, 2010 (In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
DeFronzo RA: Lilly lecture 1987. The
triumvirate: Beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for
NIDDM. Diabetes. 37:667–687. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Reaven GM: Pathophysiology of insulin
resistance in human disease. Physiol Rev. 75:473–486.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Iynedjian PB, Gjinovci A and Renold AE:
Stimulation by insulin of glucokinase gene transcription in liver
of diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 263:740–744. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Massillon D, Chen W, Barzilai N,
Prus-Wertheimer D, Hawkins M, Liu R, Taub R and Rossetti L: Carbon
flux via the pentose phosphate pathway regulates the hepatic
expression of the glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate
carboxykinase genes in conscious rats. J Biol Chem. 273:228–234.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lochhead PA, Salt IP, Walker KS, Hardie DG
and Sutherland C: 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside mimics
the effects of insulin on the expression of the 2 key gluconeogenic
genes PEPCK and glucose-6-phosphatase. Diabetes. 49:896–903.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Al-Quraishy S, Dkhil MA and Abdel Moneim
AE: Anti-hyperglycemic activity of selenium nanoparticles in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Nanomedicine.
10:6741–6756. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Govers R: Cellular regulation of glucose
uptake by glucose transporter GLUT4. Adv Clin Chem. 66:173–240.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Natali A and Ferrannini E: Effects of
metformin and thiazolidinediones on suppression of hepatic glucose
production and stimulation of glucose uptake in type 2 diabetes: A
systematic review. Diabetologia. 49:434–441. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dhanya R, Arun KB, Nisha VM, Syama HP,
Nisha P, Santhosh Kumar TR and Jayamurthy P: Preconditioning L6
muscle cells with naringin ameliorates oxidative stress and
increases glucose uptake. PLoS One. 10(e0132429)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zygmunt K, Faubert B, MacNeil J and Tsiani
E: Naringenin, a citrus flavonoid, increases muscle cell glucose
uptake via AMPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:178–183.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yang Y, Wolfram J, Boom K, Fang X, Shen H
and Ferrari M: Hesperetin impairs glucose uptake and inhibits
proliferation of breast cancer cells. Cell Biochem Funct.
31:374–379. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ganugapati J, Baldwa A and Lalani S:
Molecular docking studies of banana flower flavonoids as insulin
receptor tyrosine kinase activators as a cure for diabetes
mellitus. Bioinformation. 8:216–220. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cohen P, Alessi DR and Cross DAE: PDK1,
one of the missing links in insulin signal transduction? FEBS Lett.
410:3–10. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|