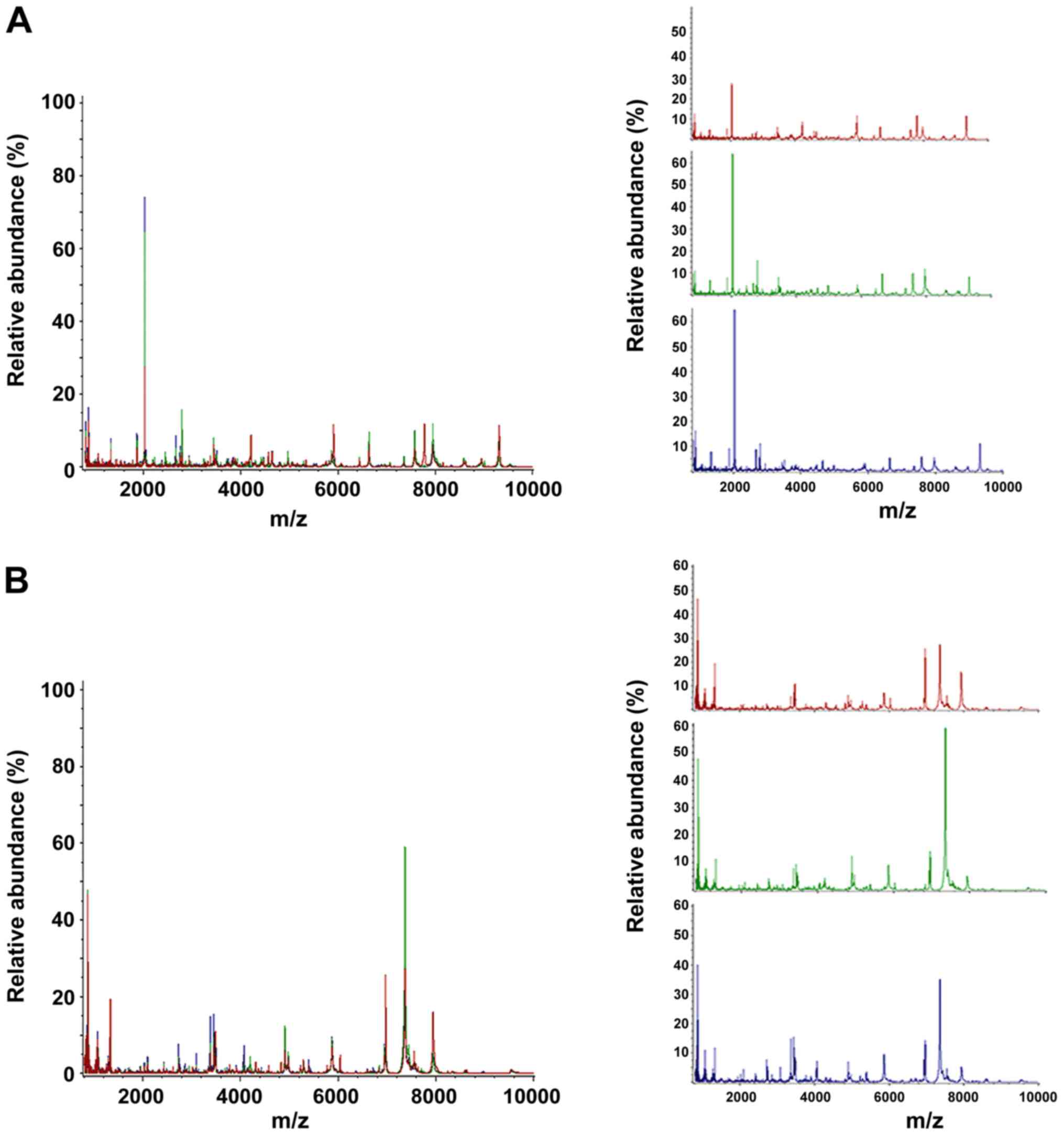
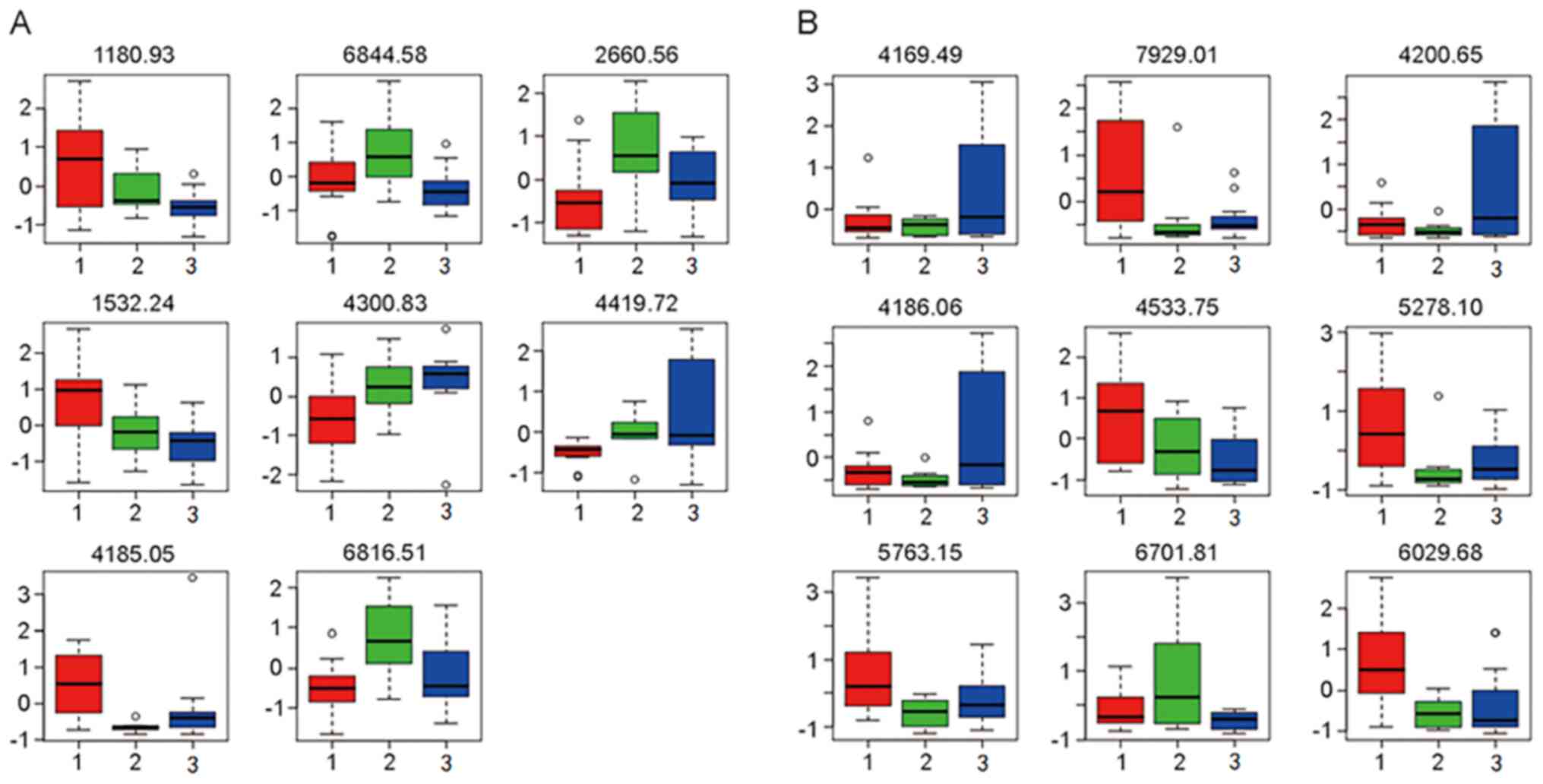
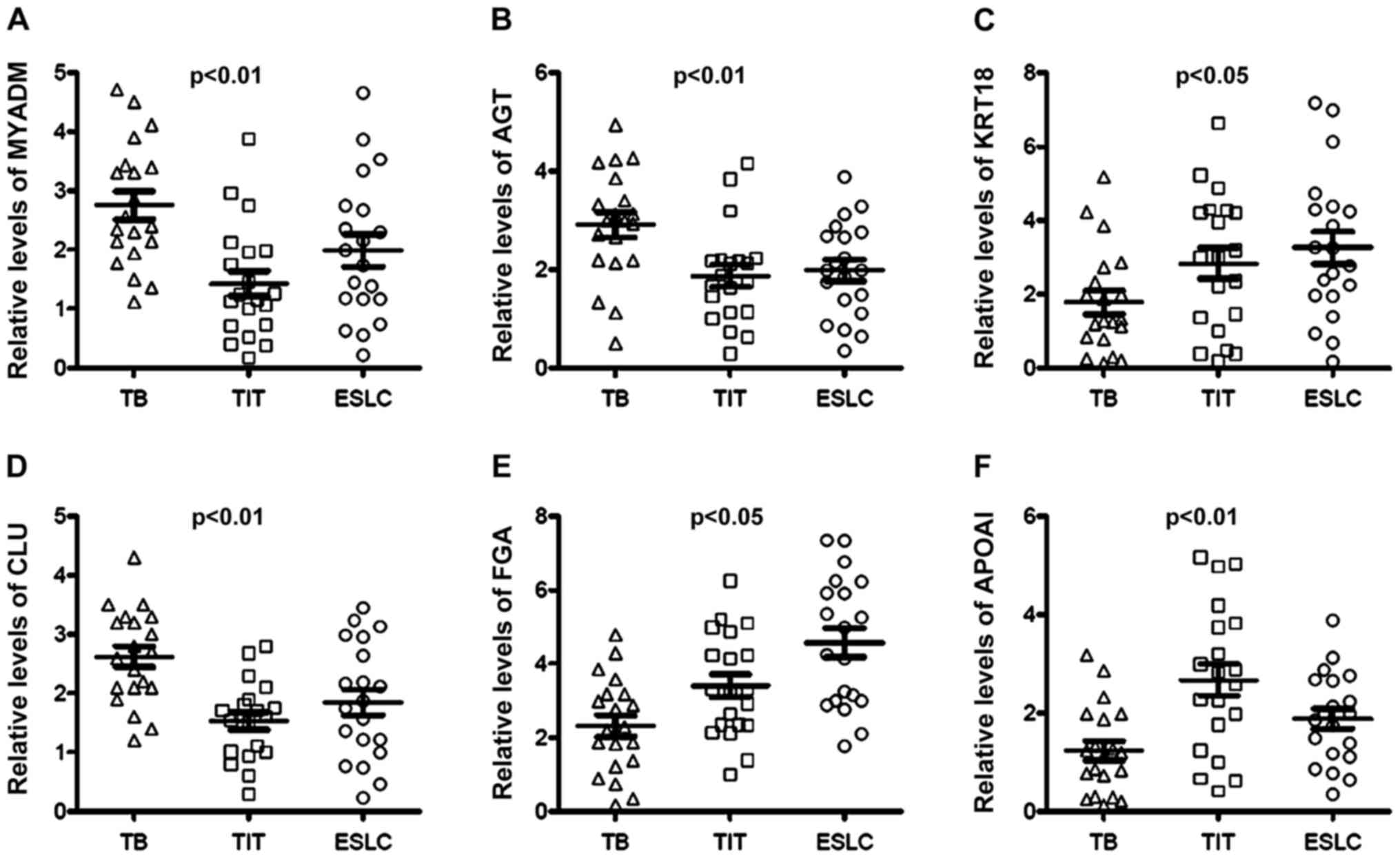
|
1
|
Hirshoren N and Eliashar R: Wound-healing
modulation in upper airway stenosis-Myths and facts. Head Neck.
31:111–126. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siow WT and Lee P: Tracheobronchial
tuberculosis: A clinical review. J Thorac Dis. 9:E71–E77.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nemati A, Safavi E, GhasemiEsfe M, Anaraki
MZ, Firoozbakhsh S, Khalilzadeh O and Anvari M: Fistula formation
between the right and left main bronchus caused by endobronchial
tuberculosis. Am J Med Sci. 343:330–331. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kashyap S, Mohapatra PR and Saini V:
Endobronchial tuberculosis. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci.
45:247–256. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Um SW, Yoon YS, Lee SM, Yim JJ, Yoo CG,
Chung HS, Kim YW, Han SK, Shim YS and Kim DK: Predictors of
persistent airway stenosis in patients with endobronchial
tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 12:57–62. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shahzad T and Irfan M: Endobronchial
tuberculosis-a review. J Thorac Dis. 8:3797–3802. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mondoni M, Repossi A, Carlucci P, Centanni
S and Sotgiu G: Bronchoscopic techniques in the management of
patients with tuberculosis. Int J Infect Dis. 64:27–37.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pathak V, Shepherd RW and Shojaee S:
Tracheobronchial tuberculosis. J Thorac Dis. 8:3818–3825.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
England K, Masini T and Fajardo E:
Detecting tuberculosis: Rapid tools but slow progress. Public
Health Action. 9:80–83. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fan NJ, Gao CF and Wang XL: Tubulin beta
chain, filamin A alpha isoform 1, and cytochrome b-c1 complex
subunit 1 as serological diagnostic biomarkers of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma: A proteomics study. OMICS. 17:215–223.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sobsey CA, Ibrahim S, Richard VR, Gaspar
V, Mitsa G, Lacasse V, Zahedi RP, Batist G and Borchers CH:
Targeted and untargeted proteomics approaches in biomarker
development. Proteomics. 20(e1900029)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Venkatesh A, Gil C, Fuentes M, LaBaer J
and Srivastava S: A Perspective on Proteomics of Infectious
Diseases. Proteomics Clin Appl. 12(e1700139)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dong W, Qiu C, Gong D, Jiang X, Liu W, Liu
W, Zhang L and Zhang W: Proteomics and bioinformatics approaches
for the identification of plasma biomarkers to detect Parkinson's
disease. Exp Ther Med. 18:2833–2842. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Beavis RC and Chait BT: Rapid, sensitive
analysis of protein mixtures by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 87:6873–6877. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Stoeckli M, Farmer TB and Caprioli RM:
Automated mass spectrometry imaging with a matrix-assisted laser
desorption ionization time-of-flight instrument. J Am Soc Mass
Spectrom. 10:67–71. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Peng Y, Zhang Q, Xu C and Shi W: MALDI-TOF
MS for the rapid identification and drug susceptibility testing of
filamentous fungi. Exp Ther Med. 18:4865–4873. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cho YT, Su H, Wu WJ, Wu DC, Hou MF, Kuo CH
and Shiea J: Biomarker Characterization by MALDI-TOF/MS. Adv Clin
Chem. 69:209–254. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Davies HA: The ProteinChip System from
Ciphergen: A new technique for rapid, micro-scale protein biology.
J Mol Med (Berl). 78(B29)2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng BG, Yao JH, Liu QY, Feng XJ, Liu D,
Zhao L, Tu B and Yang F: Comparative serum proteomic analysis of
serum diagnosis proteins of colorectal cancer based on magnetic
bead separation and maldi-tof mass spectrometry. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:6069–6075. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Malys BJ, Piotrowski ML and Owens KG:
Diagnosing and correcting mass accuracy and signal intensity error
due to initial ion position variations in a MALDI TOFMS. J Am Soc
Mass Spectrom. 29:422–434. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cho Y, Park Y, Sim B, Kim J, Lee H, Cho
SN, Kang YA and Lee SG: Identification of serum biomarkers for
active pulmonary tuberculosis using a targeted metabolomics
approach. Sci Rep. 10(3825)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Isa F, Collins S, Lee MH, Decome D, Dorvil
N, Joseph P, Smith L, Salerno S, Wells MT, Fischer S, et al: Mass
spectrometric identification of urinary biomarkers of pulmonary
tuberculosis. EBioMedicine. 31:157–165. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cui W, Yu L, He H, Chu Y, Gao J, Wan B,
Tang L and Zhao S: Cloning of human myeloid-associated
differentiation marker (MYADM) gene whose expression was
up-regulated in NB4 cells induced by all-trans retinoic acid. Mol
Biol Rep. 28:123–138. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Aranda JF, Reglero-Real N, Marcos-Ramiro
B, Ruiz-Sáenz A, Fernández-Martín L, Bernabé-Rubio M, Kremer L,
Ridley AJ, Correas I, Alonso MA, et al: MYADM controls endothelial
barrier function through ERM-dependent regulation of ICAM-1
expression. Mol Biol Cell. 24:483–494. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Aranda JF, Reglero-Real N, Kremer L,
Marcos-Ramiro B, Ruiz-Sáenz A, Calvo M, Enrich C, Correas I, Millán
J and Alonso MA: MYADM regulates Rac1 targeting to ordered
membranes required for cell spreading and migration. Mol Biol Cell.
22:1252–1262. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sun L, Bai Y, Zhao R, Sun T, Cao R, Wang
F, He G, Zhang W, Chen Y, Ye P, et al: Oncological miR-182-3p, a
novel smooth muscle cell phenotype modulator, evidences from model
rats and patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:1386–1397.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Panettieri RA Jr: Airway smooth muscle: An
immunomodulatory cell. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 110
(Suppl):S269–S274. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ozier A, Allard B, Bara I, Girodet PO,
Trian T, Marthan R and Berger P: The pivotal role of airway smooth
muscle in asthma pathophysiology. J Allergy (Cairo).
2011(742710)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kim HJ, Park JS, Heo JS, Moon KY and Park
CS: Plasma apolipoprotein H levels are different between aspirin
induced respiratory diseases and aspirin tolerant asthma. Pulm
Pharmacol Ther. 27:184–189. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Choi JH, Nguyen MP, Lee D, Oh GT and Lee
YM: Hypoxia-induced endothelial progenitor cell function is blunted
in angiotensinogen knockout mice. Mol Cells. 37:487–496.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Ma A, Sun S and Sun Y: Proteomic
analysis of plasma in adult active pulmonary tuberculosis patients
with diabetes mellitus. Clin Lab. 61:1481–1490. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Peix L, Evans IC, Pearce DR, Simpson JK,
Maher TM and McAnulty RJ: Diverse functions of clusterin promote
and protect against the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep.
8(1906)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Habiel DM, Camelo A, Espindola M, Burwell
T, Hanna R, Miranda E, Carruthers A, Bell M, Coelho AL, Liu H, et
al: Divergent roles for clusterin in lung injury and repair. Sci
Rep. 7(15444)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wilson MR and Zoubeidi A: Clusterin as a
therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 21:201–213.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nordestgaard LT, Tybjærg-Hansen A,
Rasmussen KL, Nordestgaard BG and Frikke-Schmidt R: Genetic
variation in clusterin and risk of dementia and ischemic vascular
disease in the general population: Cohort studies and meta-analyses
of 362,338 individuals. BMC Med. 16(39)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Foster EM, Dangla-Valls A, Lovestone S,
Ribe EM and Buckley NJ: Clusterin in Alzheimer's Disease:
Mechanisms, genetics, and lessons from other pathologies. Front
Neurosci. 13(164)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Wang X, Zhao H, Liang B and Du Q:
Clusterin confers resistance to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in
breast cancer cells through NF-kappaB activation and Bcl-2
overexpression. J Chemother. 24:348–357. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tang Y, Liu F, Zheng C, Sun S and Jiang Y:
Knockdown of clusterin sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to
gemcitabine chemotherapy by ERK1/2 inactivation. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 31(73)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Panico F, Rizzi F, Fabbri LM, Bettuzzi S
and Luppi F: Clusterin (CLU) and lung cancer. Adv Cancer Res.
105:63–76. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ma J, Gao W and Gao J: sCLU as prognostic
biomarker and therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. Bioengineered.
10:229–239. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bertacchini J, Mediani L, Beretti F, Guida
M, Ghalali A, Brugnoli F, Bertagnolo V, Petricoin E, Poti F, Arioli
J, et al: Clusterin enhances AKT2-mediated motility of normal and
cancer prostate cells through a PTEN and PHLPP1 circuit. J Cell
Physiol. 234:11188–11199. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Charlton-Menys V and Durrington P:
Apolipoproteins AI and B as therapeutic targets. J Intern Med.
259:462–472. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dong Z, Guo Q, Sun L, Li F, Zhao A, Liu J,
Qu P, Zhu Q, Xiao C, Niu F, et al: Serum lipoprotein and RBC
rigidity index to predict cerebral infarction in patients with
carotid artery stenosis. J Clin Lab Anal. 32(e22356)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Mateos J, Estévez O, González-Fernández Á,
Anibarro L, Pallarés Á, Reljic R, Mussá T, Gomes-Maueia C,
Nguilichane A, Gallardo JM, et al: Serum proteomics of active
tuberculosis patients and contacts reveals unique processes
activated during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Sci
Rep. 10(3844)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Albanna AS, Bachmann K, White D,
Valiquette C and Menzies D: Serum lipids as biomarkers for
therapeutic monitoring of latent tuberculosis infection. Eur Respir
J. 42:547–550. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang C, Wei LL, Shi LY, Pan ZF, Yu XM, Li
TY, Liu CM, Ping ZP, Jiang TT, Chen ZL, et al: Screening and
identification of five serum proteins as novel potential biomarkers
for cured pulmonary tuberculosis. Sci Rep. 5(15615)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang W, Xu H, Shi Y, Nandedkar S, Zhang H,
Gao H, Feroah T, Weihrauch D, Schulte ML, Jones DW, et al: Genetic
deletion of apolipoprotein A-I increases airway
hyperresponsiveness, inflammation, and collagen deposition in the
lung. J Lipid Res. 51:2560–2570. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yao X, Dai C, Fredriksson K, Dagur PK,
McCoy JP, Qu X, Yu ZX, Keeran KJ, Zywicke GJ, Amar MJ, et al: 5A,
an apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, attenuates the induction of
house dust mite-induced asthma. J Immunol. 186:576–583.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kwan R, Looi KS and Omary MB: Absence of
keratins 8 and 18 in rodent epithelial cell lines associates with
keratin gene mutation and DNA methylation: Cell line selective
effects on cell invasion. Exp Cell Res. 335:12–22. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang H, Chen X, Wang J, Guang W, Han W,
Zhang H, Tan X and Gu Y: EGR1 decreases the malignancy of human
non-small cell lung carcinoma by regulating KRT18 expression. Sci
Rep. 4(5416)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wang X, Lao Y, Xu N, Xi Z, Wu M, Wang H,
Li X, Tan H, Sun M and Xu H: Oblongifolin C inhibits metastasis by
up-regulating keratin 18 and tubulins. SciRep.
5(10293)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|