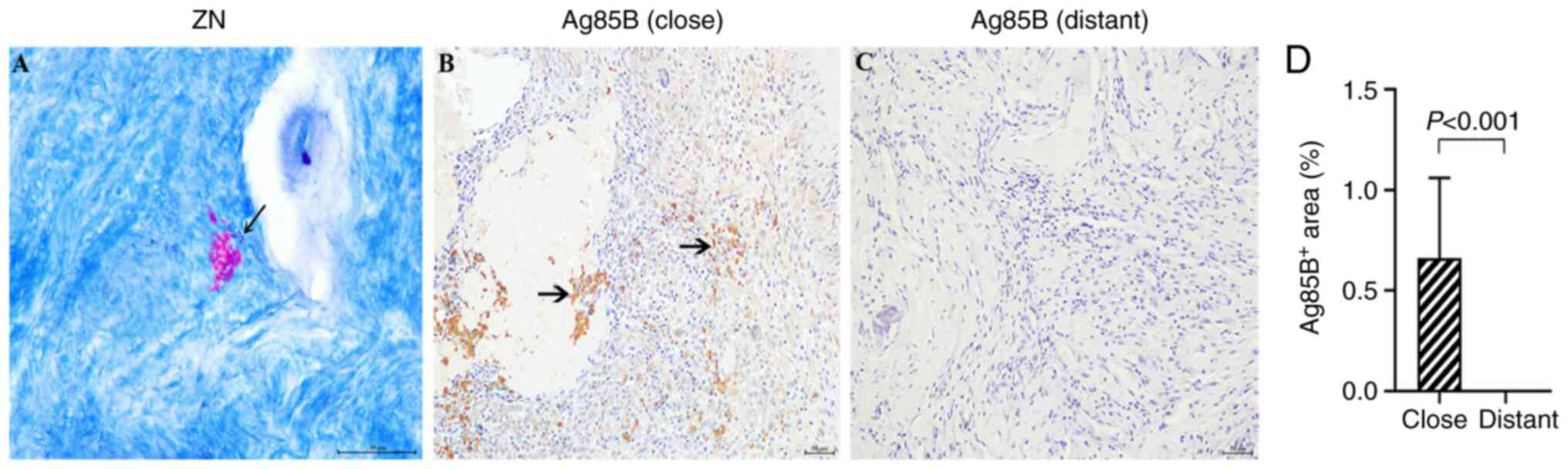
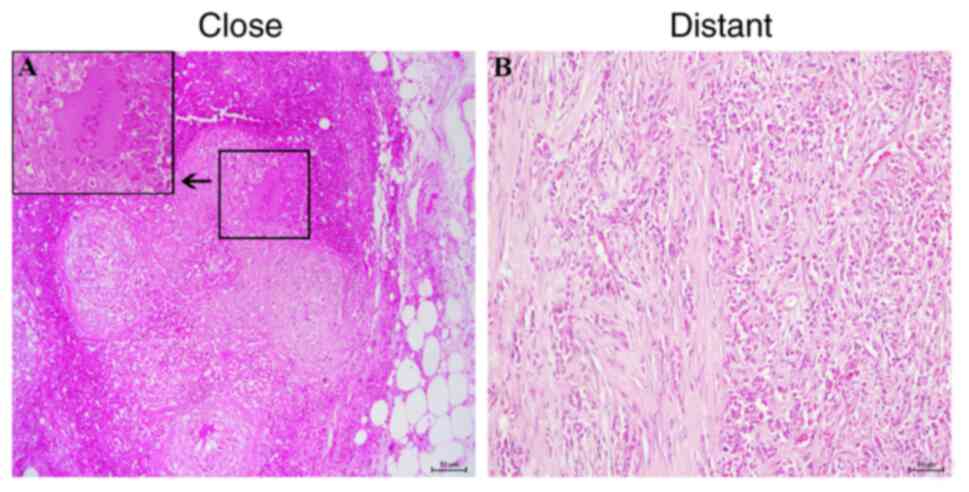
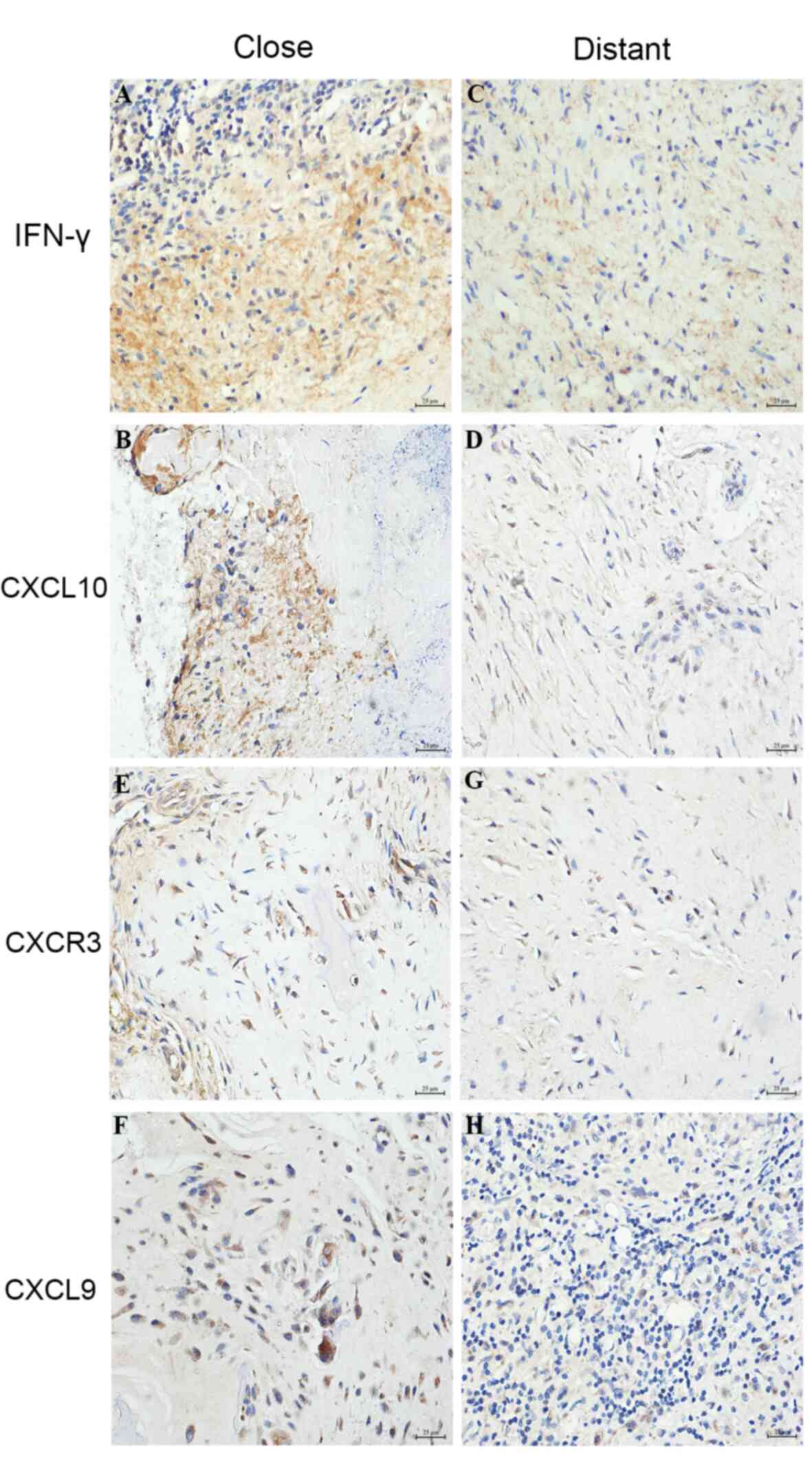
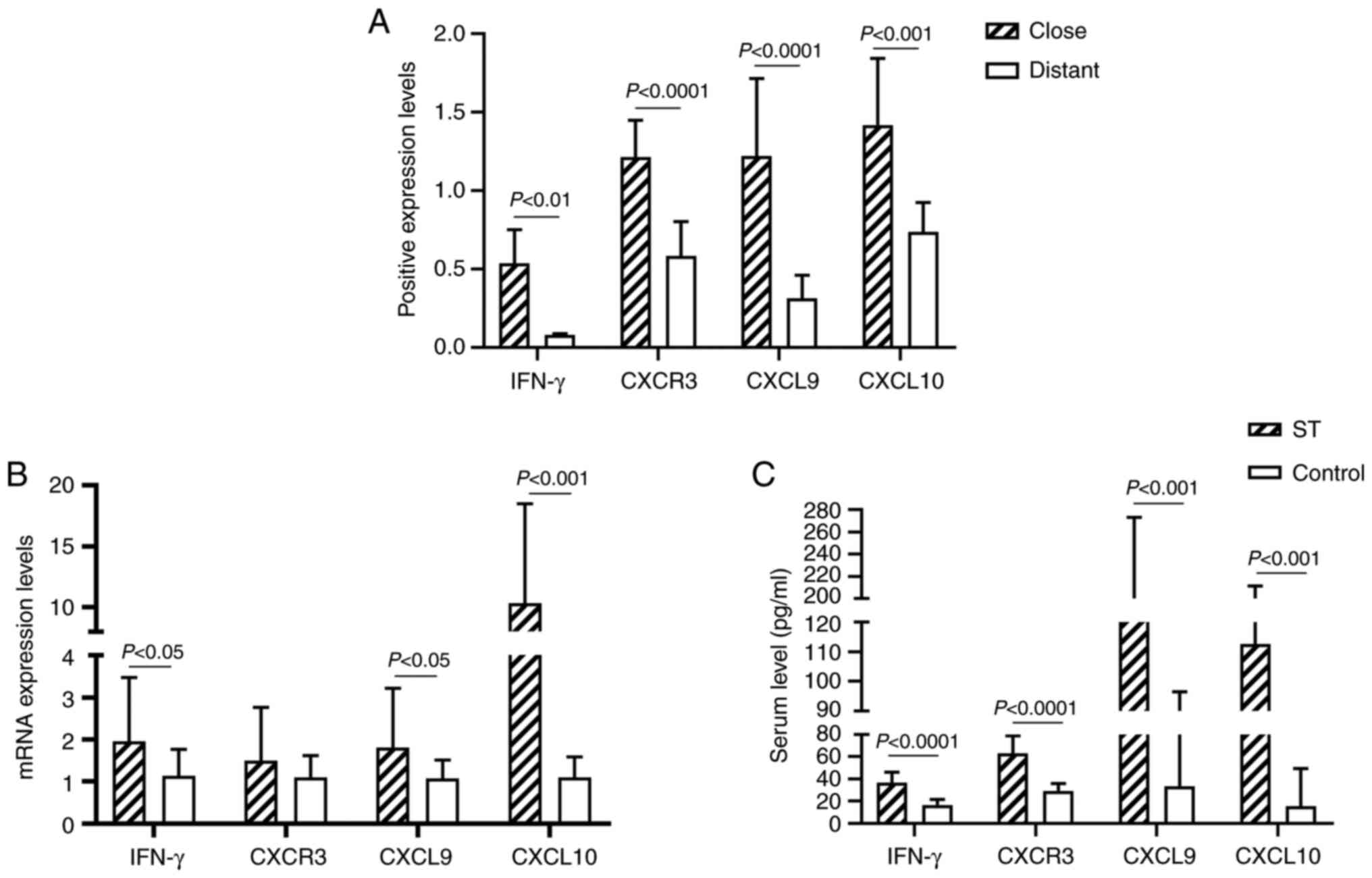
|
1
|
López-Ramos JE, Macías-Segura N,
Cuevas-Cordoba B, Araujo-Garcia Z, Bastián Y, Castañeda-Delgado JE,
Lara-Ramirez EE, Gándara-Jasso B, Serrano CJ, Salinas E and
Enciso-Moreno JA: Improvement in the diagnosis of tuberculosis
combining Mycobacterium tuberculosis immunodominant peptides
and serum host biomarkers. Arch Med Res. 49:147–153.e1.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Schutz C, Barr D, Andrade BB, Shey M, Ward
A, Janssen S, Burton R, Wilkinson KA, Sossen B, Fukutani KF, et al:
Clinical, microbiologic, and immunologic determinants of mortality
in hospitalized patients with HIV-associated tuberculosis: A
prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 16(e1002840)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhu R, Yang C, Chen Z, Bai
Y, Li M and Zhai X: Trends of spinal tuberculosis research
(1994-2015): A bibliometric study. Medicine (Baltimore).
95(e4923)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Patel R, Gannamani V, Shay E and Alcid D:
Spinal tuberculosis and cold abscess without known primary disease:
Case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Infect Dis.
2016(1780153)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yang J, Kong W, Xv N, Huang X and Chen X:
Correlation between the tuberculin skin test and T-SPOT. TB in
patients with suspected tuberculosis infection: A pilot study. Exp
Ther Med. 18:2250–2254. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Doan TN, Eisen DP, Rose MT, Slack A,
Stearnes G and McBryde ES: Interferon-gamma release assay for the
diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: A latent-class
analysis. PLoS One. 12(e0188631)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kufareva I, Gustavsson M, Zheng Y,
Stephens BS and Handel TM: What do structures tell us about
chemokine receptor function and antagonism? Annu Rev Biophys.
46:175–198. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Palomino DC and Marti LC: Chemokines and
immunity. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 13:469–473. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Portuguese).
|
|
9
|
Zhang J, Chen J, Guan GW, Zhang T, Lu FM
and Chen XM: Expression and clinical significance of chemokine
CXCL10 and its receptor CXCR3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Beijing
Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 51:402–408. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Alanio C, Barreira da Silva R, Michonneau
D, Bousso P, Ingersoll MA and Albert ML: CXCR3/CXCL10 axis shapes
tissue distribution of memory phenotype CD8+ T cells in
nonimmunized mice. J Immunol. 200:139–146. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chung W, Jung Y, Lee K, Park J, Sheen S
and Park K: CXCR3 ligands in pleural fluid as markers for the
diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis.
21:1300–1306. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lisi L, Ciotti GM, Braun D, Kalinin S,
Currò D, Dello Russo C, Coli A, Mangiola A, Anile C, Feinstein DL
and Navarra P: Expression of iNOS, CD163 and ARG-1 taken as M1 and
M2 markers of microglial polarization in human glioblastoma and the
surrounding normal parenchyma. Neurosci Lett. 645:106–112.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Tian F, Shan J, Gao J, Li B, Lv J,
Zhou X, Cai X, Wen H and Ma X: Kupffer cells: Important participant
of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
10(8)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nagashima H, Tanishima S and Tanida A:
Diagnosis and management of spinal infections. J Orthop Sci.
23:8–13. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chhawra S, Jain R, Aggarawal R and Pandey
A: A rare case of radius head epiphyseal aneurysmal bone cyst with
predisposing factor as trauma tuberculosis of elbow apart from
genetic. J Orthop Case Rep. 9:23–27. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ma J, Lv Z, Wang J and Lu J: Relationship
between IL-10 gene polymorphism and spinal tuberculosis. Med Sci
Monit. 25:4901–4906. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Farber JM: A macrophage mRNA selectively
induced by gamma-interferon encodes a member of the platelet factor
4 family of cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:5238–5242.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sahmoudi K, Abbassi H, Bouklata N, El
Alami MN, Sadak A, Burant C, Henry Boom W, El Aouad R, Canaday DH
and Seghrouchni F: Immune activation and regulatory T cells in
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected lymph nodes. BMC
Immunol. 19(33)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Matsuzaki G, Yamasaki M, Tamura T and
Umemura M: Dispensable role of chemokine receptors in migration of
mycobacterial antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells into
Mycobacterium-infected lung. Immunobiology. 224:440–448.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Oghumu S, Varikuti S, Stock JC, Volpedo G,
Saljoughian N, Terrazas CA and Satoskar AR: Cutting edge: CXCR3
escapes X chromosome inactivation in T cells during infection:
Potential implications for sex differences in immune responses. J
Immunol. 203:789–794. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meyer M, Hensbergen PJ, van der
Raaij-Helmer EM, Brandacher G, Margreiter R, Heufler C, Koch F,
Narumi S, Werner ER, Colvin R, et al: Cross reactivity of three T
cell attracting murine chemokines stimulating the CXC chemokine
receptor CXCR3 and their induction in cultured cells and during
allograft rejection. Eur J Immunol. 31:2521–2527. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Luster AD, Unkeless JC and Ravetch JV:
Gamma-interferon transcriptionally regulates an early-response gene
containing homology to pIatelet proteins. Nature. 315:672–676.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Manngo PM, Gutschmidt A, Snyders CI,
Mutavhatsindi H, Manyelo CM, Makhoba NS, Ahlers P, Hiemstra A,
Stanley K, McAnda S, et al: Prospective evaluation of host
biomarkers other than interferon gamma in QuantiFERON Plus
supernatants as candidates for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in
symptomatic individuals. J Infect. 79:228–235. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Palucci I, Battah B, Salustri A, De Maio
F, Petrone L, Ciccosanti F, Sali M, Bondet V, Duffy D, Fimia GM, et
al: IP-10 contributes to the inhibition of mycobacterial growth in
an ex vivo whole blood assay. Int J Med Microbiol. 309:299–306.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|