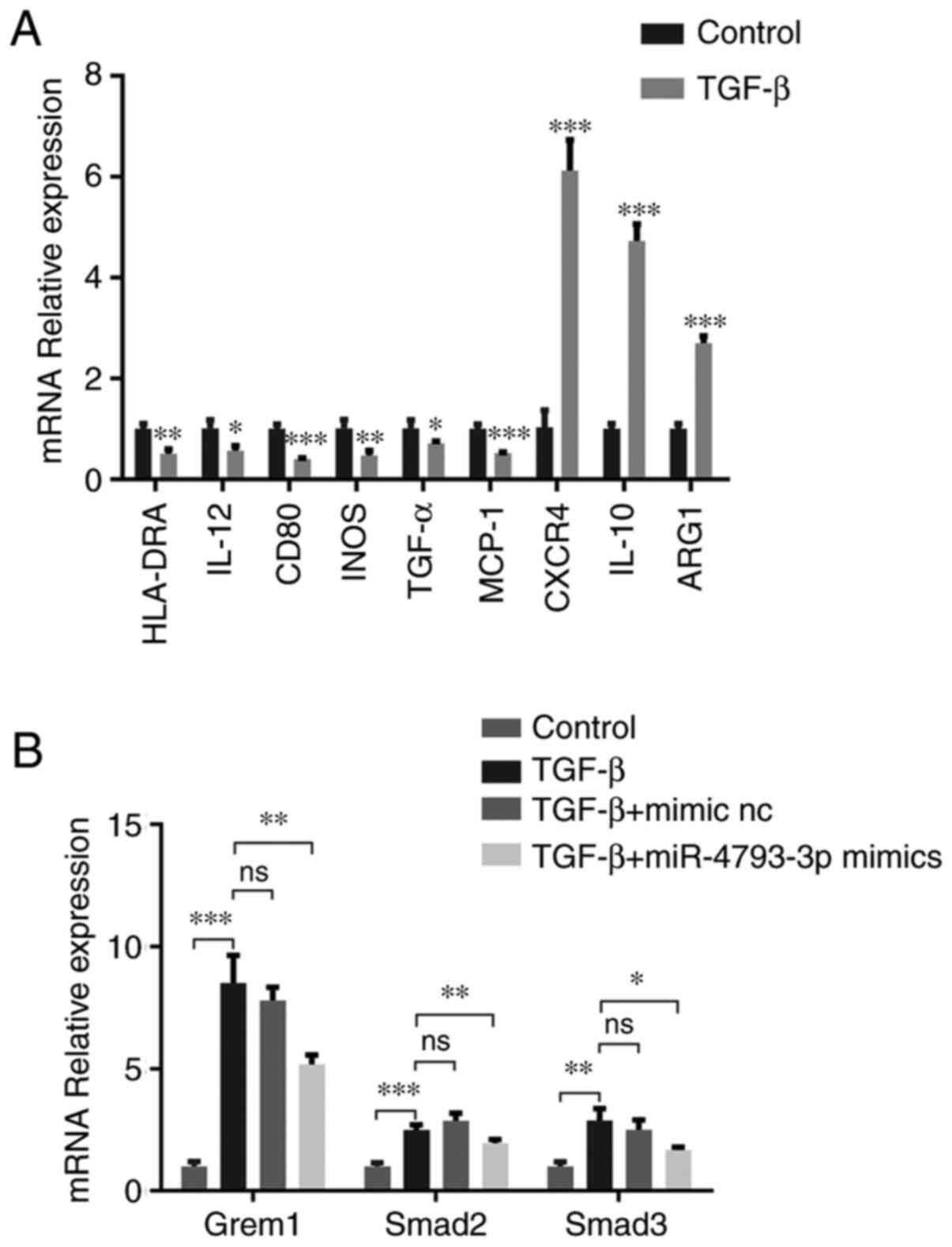
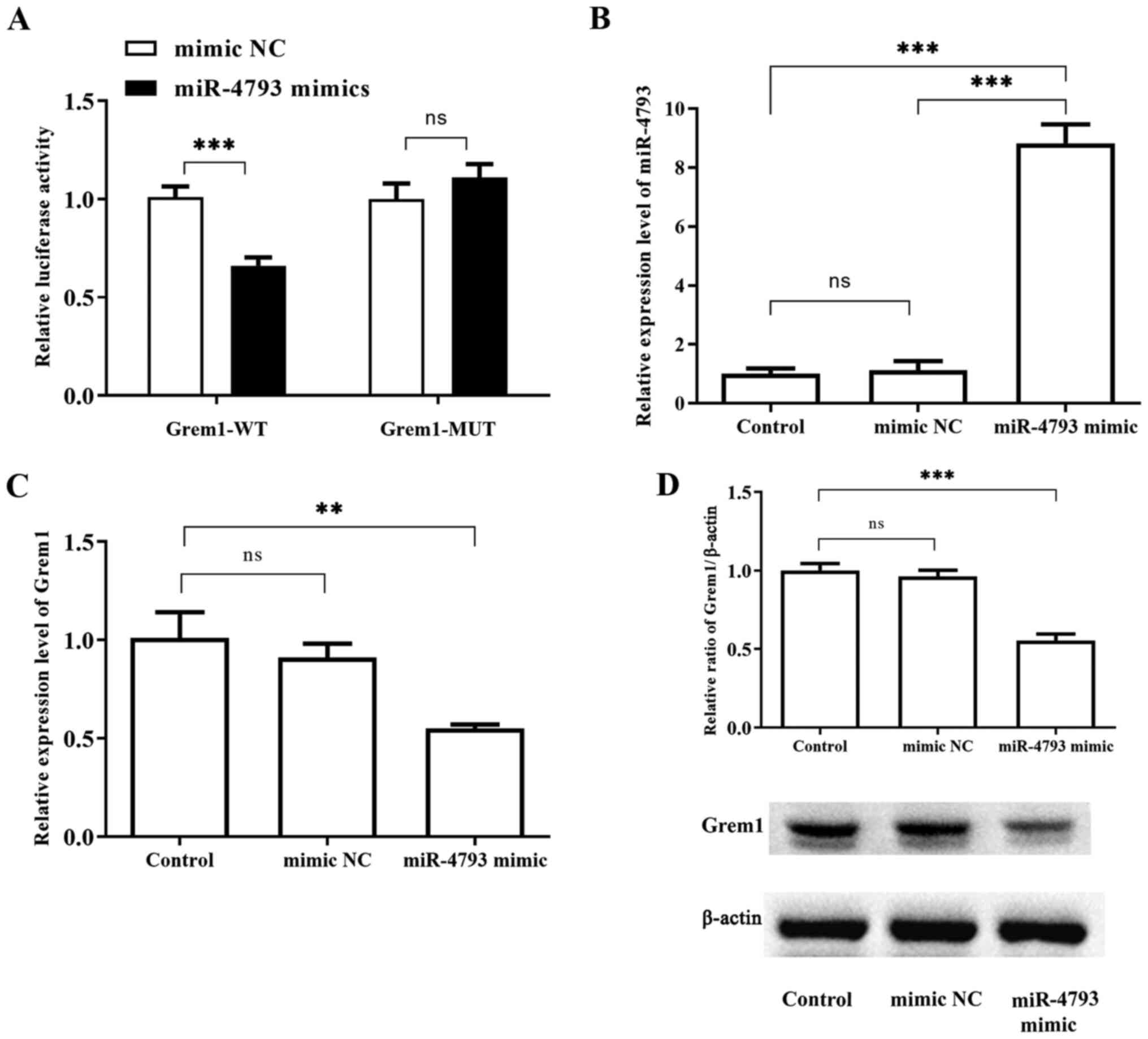
|
1
|
Guidelines WHO; Approved by the Guidelines
Review Committee: In: Guidelines for the Prevention, Care and
Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. World
Health Organization Copyright © World Health Organization 2015.,
Geneva2015.
|
|
2
|
Lesmana LA, Leung NWY, Mahachai V, Phiet
PH, Suh DJ, Yao G and Zhuang H: Hepatitis B: Overview of the burden
of disease in the Asia-Pacific region. Liver Int. 26 (S2):3–10.
2006.
|
|
3
|
Lin X, Robinson NJ, Thursz M, Rosenberg
DM, Weild A, Pimenta JM and Hall AJ: Chronic hepatitis B virus
infection in the Asia-Pacific region and Africa: Review of disease
progression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:833–843. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guan R and Lui HF: Treatment of hepatitis
B in decompensated liver cirrhosis. Int J Hepatol.
2011(918017)2011.urihttps://doi.org/10.4061/2011/918017simplehttps://doi.org/10.4061/2011/918017.
|
|
5
|
Peng CY, Chien RN and Liaw YF: Hepatitis B
virus-related decompensated liver cirrhosis: Benefits of antiviral
therapy. J Hepatol. 57:442–450. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bajaj JS, O'Leary JG, Wong F, Reddy KR and
Kamath PS: Bacterial infections in end-stage liver disease: Current
challenges and future directions. Gut. 61:1219–1225.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jalan R, Fernandez J, Wiest R, Schnabl B,
Moreau R, Angeli P, Stadlbauer V, Gustot T, Bernardi M, Canton R,
et al: Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: A position statement
based on the EASL Special Conference 2013. J Hepatol. 60:1310–1324.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Arvaniti V, D'Amico G, Fede G, Manousou P,
Tsochatzis E, Pleguezuelo M and Burroughs AK: Infections in
patients with cirrhosis increase mortality four-fold and should be
used in determining prognosis. Gastroenterology. 139:1246–1256,
e1245. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dueck A, Ziegler C, Eichner A, Berezikov E
and Meister G: microRNAs associated with the different human
Argonaute proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:9850–9862.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Loosen SH, Schueller F, Trautwein C, Roy S
and Roderburg C: Role of circulating microRNAs in liver diseases.
World J Hepatol. 9:586–594. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Starkey Lewis PJ, Dear J, Platt V, Simpson
KJ, Craig DG, Antoine DJ, French NS, Dhaun N, Webb DJ, Costello EM,
et al: Circulating microRNAs as potential markers of human
drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 54:1767–1776.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
DiStefano JK and Gerhard GS: Circulating
microRNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:161–163. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Migita K, Komori A, Kozuru H, Jiuchi Y,
Nakamura M, Yasunami M, Furukawa H, Abiru S, Yamasaki K, Nagaoka S,
et al: Circulating microRNA profiles in patients with type-1
autoimmune hepatitis. PLoS One. 10(e0136908)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Das K, Garnica O and Dhandayuthapani S:
Modulation of Host miRNAs by intracellular bacterial pathogens.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 6(79)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhou X, Li X and Wu M: miRNAs reshape
immunity and inflammatory responses in bacterial infection. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 3(14)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ma C, Li Y, Li M, Deng G, Wu X, Zeng J,
Hao X, Wang X, Liu J, Cho WC, et al: microRNA-124 negatively
regulates TLR signaling in alveolar macrophages in response to
mycobacterial infection. Mol Immunol. 62:150–158. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Schulte LN, Eulalio A, Mollenkopf HJ,
Reinhardt R and Vogel J: Analysis of the host microRNA response to
Salmonella uncovers the control of major cytokines by the let-7
family. EMBO J. 30:1977–1989. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lutz P, M Haimid M, Pohlmann A, Lehmann J,
Jansen C, Schierwagen R, Klein S, Strassburg CP, Spengler U and
Trebicka J: MicroRNA-155 is upregulated in ascites in patients with
spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Sci Rep. 7(40556)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan
HL, Chen CJ, Chen DS, Chen HL, Chen PJ, Chien RN, et al:
Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of
hepatitis B: A 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 10:1–98. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shiha G, Sarin SK, Ibrahim AE, Omata M,
Kumar A, Lesmana LA, Leung N, Tozun N, Hamid S, Jafri W, et al:
Jury of the APASL Consensus Development Meeting 29 January 2008 on
Liver Fibrosis With Without Hepatitis B or C: Liver fibrosis:
Consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the
Study of the Liver (APASL). Hepatol Int. 3:323–333. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Åstrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
eLife 42015.
|
|
24
|
Liu W and Wang X: Prediction of functional
microRNA targets by integrative modeling of microRNA binding and
target expression data. 20: 18, 2019.
|
|
25
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shalova IN, Lim JY, Chittezhath M,
Zinkernagel AS, Beasley F, Hernández-Jiménez E, Toledano V,
Cubillos-Zapata C, Rapisarda A, Chen J, et al: Human monocytes
undergo functional re-programming during sepsis mediated by
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Immunity. 42:484–498. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Atri C, Guerfali FZ and Laouini D: Role of
human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 19(1801)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang F, Wang H, Wang X, Jiang G, Liu H,
Zhang G, Wang H, Fang R, Bu X, Cai S, et al: TGF-β induces M2-like
macrophage polarization via SNAIL-mediated suppression of a
pro-inflammatory phenotype. Oncotarget. 7:52294–52306.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Song X, Xie S, Lu K and Wang C:
Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental asthma by inducing
polarization of alveolar macrophages. Inflammation. 38:485–492.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Saha B, Kodys K, Szabo G and Hepatitis C:
Hepatitis C virus-induced monocyte differentiation into polarized
M2 macrophages promotes stellate cell activation via TGF-β. Cell
Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:302–316.e8. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
ischer P, Grigoras C, Bugariu A,
Nicoara-Farcau O, Stefanescu H, Benea A, Hadade A, Margarit S,
Sparchez Z, Tantau M, Ionescu D and Procopet B: Are presepsin and
resistin better markers for bacterial infection in patients with
decompensated liver cirrhosis? Dig Liver Dis. 51:1685–1691.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Johnston CJ, Smyth DJ, Dresser DW and
Maizels RM: TGF-β in tolerance, development and regulation of
immunity. Cell Immunol. 299:14–22. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Marcoe JP, Lim JR, Schaubert KL,
Fodil-Cornu N, Matka M, McCubbrey AL, Farr AR, Vidal SM and Laouar
Y: TGF-β is responsible for NK cell immaturity during ontogeny and
increased susceptibility to infection during mouse infancy. Nat
Immunol. 13:843–850. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Meadows SK, Eriksson M, Barber A and
Sentman CL: Human NK cell IFN-gamma production is regulated by
endogenous TGF-beta. Int Immunopharmacol. 6:1020–1028.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dong C: TH17 cells in development: An
updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming.
Nat Rev Immunol. 8:337–348. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee YS, Park JS, Jung SM, Kim SD, Kim JH,
Lee JY, Jung KC, Mamura M, Lee S, Kim SJ, et al: Inhibition of
lethal inflammatory responses through the targeting of
membrane-associated Toll-like receptor 4 signaling complexes with a
Smad6-derived peptide. EMBO Mol Med. 7:577–592. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Park BS and Lee JO: Recognition of
lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Exp Mol Med.
45(e66)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Choi KC, Lee YS, Lim S, Choi HK, Lee CH,
Lee EK, Hong S, Kim IH, Kim SJ and Park SH: Smad6 negatively
regulates interleukin 1-receptor-Toll-like receptor signaling
through direct interaction with the adaptor Pellino-1. Nat Immunol.
7:1057–1065. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ng PC, Chan KY, Leung KT, Tam YH, Ma TP,
Lam HS, Cheung HM, Lee KH, To KF and Li K: Comparative MiRNA
Expressional profiles and molecular networks in human small bowel
tissues of necrotizing enterocolitis and spontaneous intestinal
perforation. PLoS One. 10(e0135737)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Staloch D, Gao X, Liu K, Xu M, Feng X,
Aronson JF, Falzon M, Greeley GH, Rastellini C, Chao C, et al:
Gremlin is a key pro-fibrogenic factor in chronic pancreatitis. J
Mol Med (Berl). 93:1085–1093. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Miao H, Wang N, Shi LX, Wang Z and Song
WB: Overexpression of mircoRNA-137 inhibits cervical cancer cell
invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
suppressing the TGF-β/smad pathway via binding to GREM1. Cancer
Cell Int. 19(147)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mori T, Takahashi K, Naito M, Kodama T,
Hakamata H, Sakai M, Miyazaki A, Horiuchi S and Ando M: Endocytic
pathway of scavenger receptors via trans-Golgi system in bovine
alveolar macrophages. Lab Invest. 71:409–416. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu Z, Xu L, Li W, Jin X, Song X, Chen X,
Zhu J, Zhou S, Li Y, Zhang W, et al: Innate scavenger receptor-A
regulates adaptive T helper cell responses to pathogen infection.
Nat Commun. 8(16035)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Thomas CA, Li Y, Kodama T, Suzuki H,
Silverstein SC and El Khoury J: Protection from lethal
gram-positive infection by macrophage scavenger receptor-dependent
phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 191:147–156. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Arredouani MS, Yang Z, Imrich A, Ning Y,
Qin G and Kobzik L: The macrophage scavenger receptor SR-AI/II and
lung defense against pneumococci and particles. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 35:474–478. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang J, Nikrad MP, Travanty EA, Zhou B,
Phang T, Gao B, Alford T, Ito Y, Nahreini P, Hartshorn K, et al:
Innate immune response of human alveolar macrophages during
influenza A infection. PLoS One. 7(e29879)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|