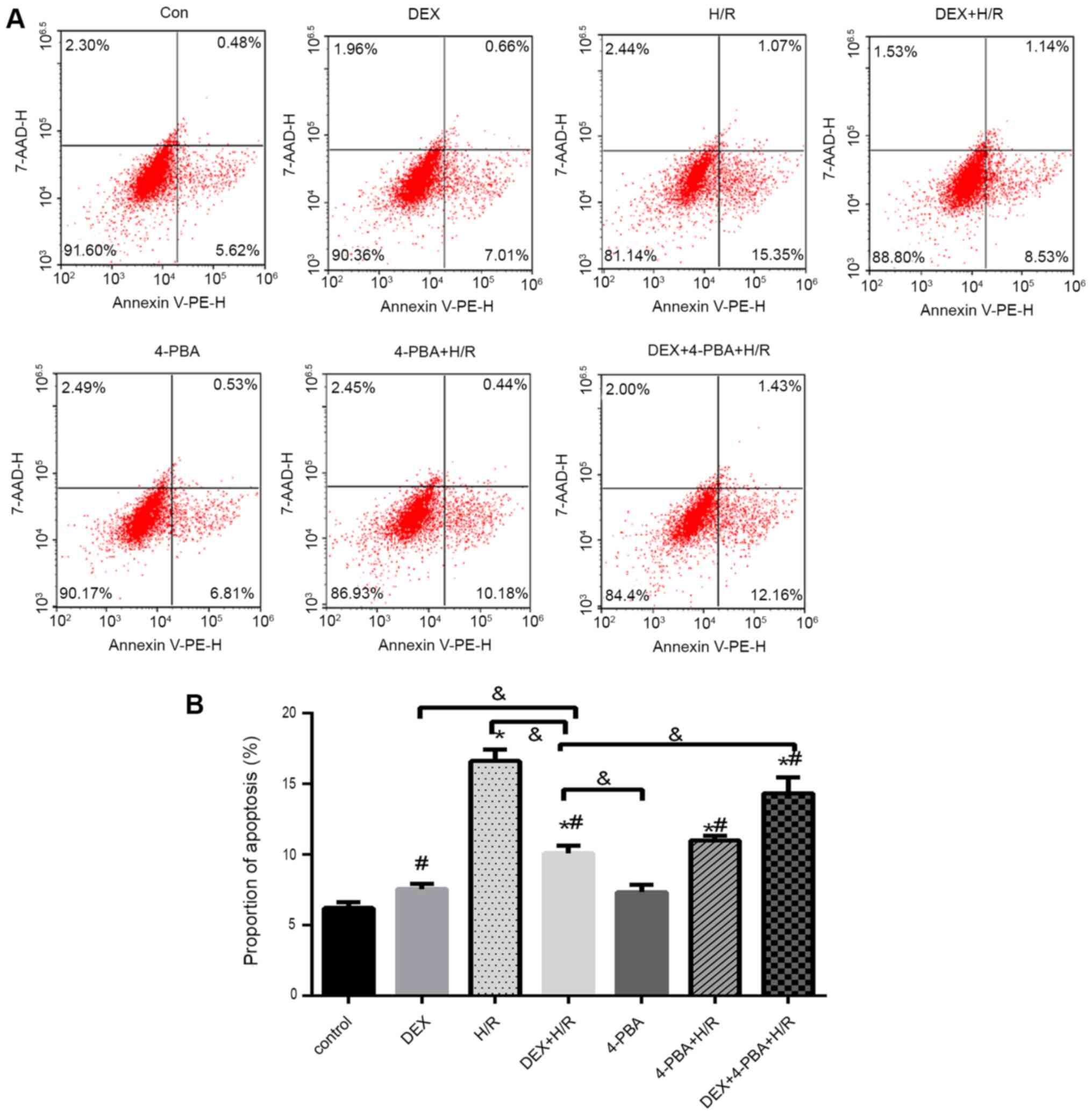
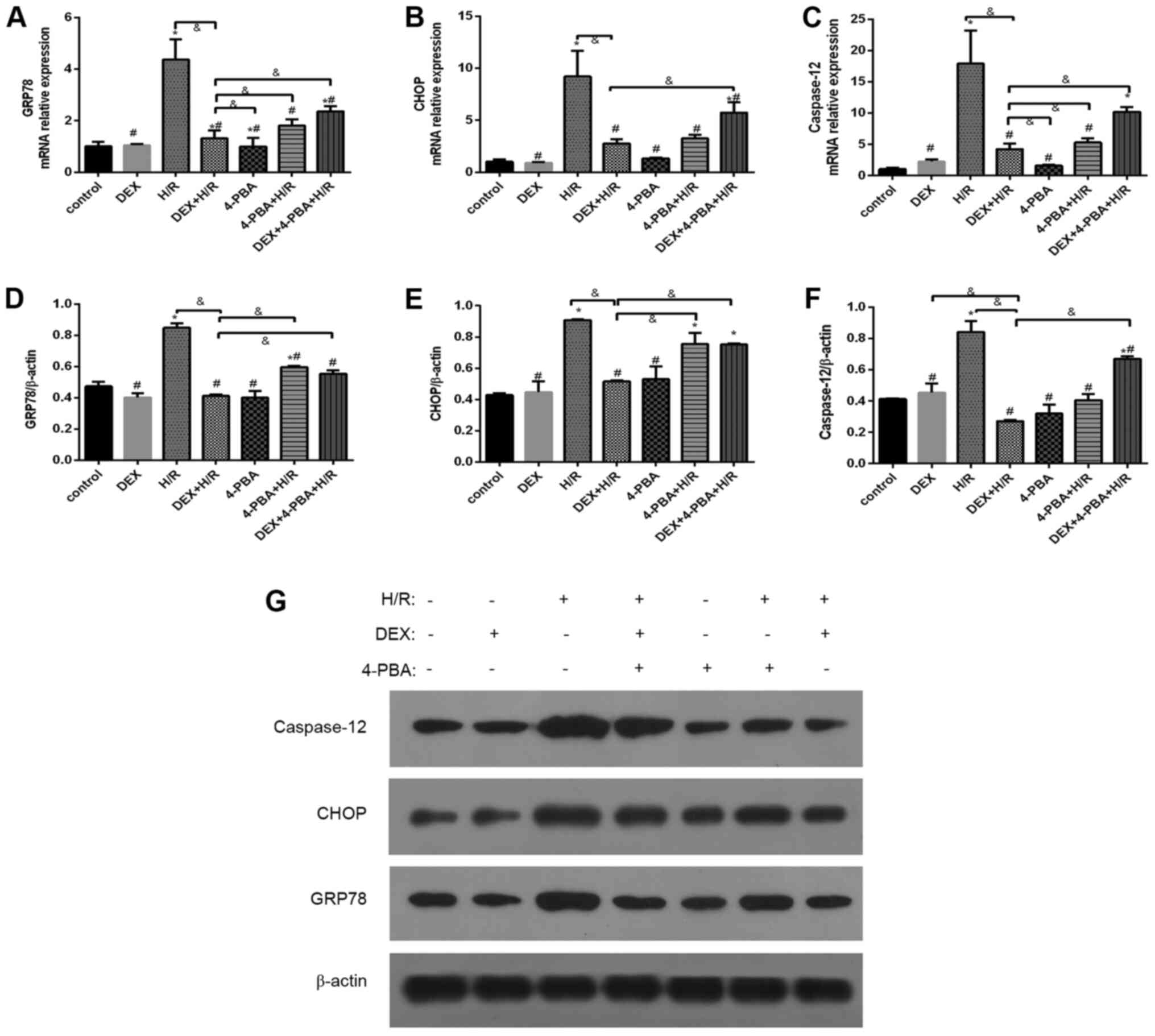
|
1
|
Bunte S, Behmenburg F, Majewski N,
Stroethoff M, Raupach A, Mathes A, Heinen A, Hollmann MW and Huhn
R: Characteristics of dexmedetomidine postconditioning in the field
of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Anesth Analg. 130:90–98.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li L, Li X, Zhang Z, Liu L, Zhou Y and Liu
F: Protective mechanism and clinical application of hydrogen in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pak J Biol Sci. 23:103–112.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xi J, Li QQ, Li BQ and Li N: miR-155
inhibition represents a potential valuable regulator in mitigating
myocardial hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through targeting BAG5 and
MAPK/JNK signaling. Mol Med Rep. 21:1011–1020. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li J, Zhou W, Chen W, Wang H, Zhang Y and
Yu T: Mechanism of the hypoxia inducible factor 1/hypoxic response
element pathway in rat myocardial ischemia/diazoxide
post-conditioning. Mol Med Rep. 21:1527–1536. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kitazume-Taneike R, Taneike M, Omiya S,
Misaka T, Nishida K, Yamaguchi O, Akira S, Shattock MJ, Sakata Y
and Otsu K: Ablation of Toll-like receptor 9 attenuates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
515:442–447. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li J, Zhao Y, Zhou N, Li L and Li K:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
in diabetes mellitus by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. J
Diabetes Res. 2019(7869318)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Heusch G and Gersh BJ: The pathophysiology
of acute myocardial infarction and strategies of protection beyond
reperfusion: A continual challenge. Eur Heart J. 38:774–784.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Heusch G: Cardioprotection research must
leave its comfort zone. Eur Heart J. 39:3393–3395. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Heusch G: Critical issues for the
translation of cardioprotection. Circ Res. 120:1477–1486.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu H, Ye M, Yang J and Ding J: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: A possible role in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 208:65–66.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li W, Li W, Leng Y, Xiong Y and Xia Z:
Ferroptosis is involved in diabetes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress. DNA Cell Biol.
39:210–225. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gao J, Guo Y, Liu Y, Yan J, Zhou J, An X
and Su P: Protective effect of FBXL10 in myocardial ischemia
reperfusion injury via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Respir Med. 161(105852)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Guo C, Zhang J, Zhang P, Si A, Zhang Z,
Zhao L, Lv F and Zhao G: Ginkgolide B ameliorates myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury in rats via inhibiting endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:767–774. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Yuan B, Cheng B, Liu Y, Zhang B,
Wang X, Lin X, Yang B and Gong G: Crocin alleviates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress via
regulation of miR-34a/Sirt1/Nrf2 pathway. Shock. 51:123–130.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hou X, Fu M, Cheng B, Kang Y and Xie D:
Galanthamine improves myocardial ischemia-reperfusion-induced
cardiac dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress-related
apoptosis, and myocardial fibrosis by suppressing AMPK/Nrf2 pathway
in rats. Ann Transl Med. 7(634)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang BF, Jiang H, Chen J, Guo X, Li Y, Hu
Q and Yang S: Nobiletin ameliorates myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated apoptosis through regulation of the PI3K/AKT
signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 73:98–107. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gao JM, Meng XW, Zhang J, Chen WR, Xia F,
Peng K and Ji FH: Dexmedetomidine protects cardiomyocytes against
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by suppressing TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB
signaling. Biomed Res Int. 2017(1674613)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Davidson SM, Ferdinandy P, Andreadou I,
Bøtker HE, Heusch G, Ibáñez B, Ovize M, Schulz R, Yellon DM,
Hausenloy DJ, et al: Multitarget strategies to reduce myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: JACC review topic of the week. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 73:89–99. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kong Q, Wu X, Qiu Z, Huang Q, Xia Z and
Song X: Protective effect of dexmedetomidine on acute lung injury
via the upregulation of tumour necrosis factor-α-induced
protein-8-like 2 in septic mice. Inflammation. 43:833–846.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Liu M, Yang Y, Cao J and Mi W:
Dexmedetomidine exerts a protective effect on ischemia-reperfusion
injury after hepatectomy: A prospective, randomized, controlled
study. J Clin Anesth. 61(109631)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xiong J, Quan J, Qin C, Wang X, Dong Q and
Zhang B: Dexmedetomidine exerts brain-protective effects under
cardiopulmonary bypass through inhibiting the janus kinase 2/signal
transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathway. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 40:116–124. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gong J, Zhang R, Shen L, Xie Y and Li X:
The brain protective effect of dexmedetomidine during surgery for
paediatric patients with congenital heart disease. J Int Med Res.
47:1677–1684. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Oh JE, Jun JH, Hwang HJ, Shin EJ, Oh YJ
and Choi YS: Dexmedetomidine restores autophagy and cardiac
dysfunction in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus.
Acta Diabetol. 56:105–114. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
He L, Hao S, Wang Y, Yang W, Liu L, Chen H
and Qian J: Dexmedetomidine preconditioning attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts with endothelial
dysfunction. Biomed Pharmacother. 114(108837)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Riquelme JA, Westermeier F, Hall AR,
Vicencio JM, Pedrozo Z, Ibacache M, Fuenzalida B, Sobrevia L,
Davidson SM, Yellon DM, et al: Dexmedetomidine protects the heart
against ischemia-reperfusion injury by an endothelial eNOS/NO
dependent mechanism. Pharmacol Res. 103:318–327. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu Y, Wang S, Wang Z, Ding M, Li X, Guo
J, Han G and Zhao P: Dexmedetomidine alleviated endoplasmic
reticulum stress via inducing ER-phagy in the spinal cord of
neuropathic pain model. Front Neurosci. 14(90)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chai Y, Zhu K, Li C, Wang X, Shen J, Yong
F and Jia H: Dexmedetomidine alleviates cisplatin-induced acute
kidney injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
apoptosis via the α2AR/PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep. 21:1597–1605.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun D, Wang J, Liu X, Fan Y, Yang M and
Zhang J: Dexmedetomidine attenuates endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis and improves neuronal function after
traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Res.
1732(146682)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhao L, Zhai M, Yang X, Guo H, Cao Y, Wang
D, Li P and Liu C: Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuronal injury after
spinal cord ischaemia-reperfusion injury by targeting the
CNPY2-endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling. J Cell Mol Med.
23:8173–8183. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu C, Fu Q, Mu R, Wang F, Zhou C, Zhang
L, Yu B, Zhang Y, Fang T and Tian F: Dexmedetomidine alleviates
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic
reticulum stress dependent apoptosis through the
PERK-CHOP-Caspase-11 pathway. Brain Res. 1701:246–254.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Yang Y, Xiong W, Zhou R, Song N,
Liu L and Qian J: Dexmedetomidine protects H9C2 against
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through miR-208b-3p/Med13/Wnt
signaling pathway axis. Biomed Pharmacother.
125(110001)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yuan M, Meng XW, Ma J, Liu H, Song SY,
Chen QC, Liu HY, Zhang J, Song N, Ji FH and Peng K: Dexmedetomidine
protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes against oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reoxygenation-induced intracellular calcium overload
and apoptosis through regulating FKBP12.6/RyR2 signaling. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 13:3137–3149. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cung TT, Morel O, Cayla G, Rioufol G,
Garcia-Dorado D, Angoulvant D, Bonnefoy-Cudraz E, Guérin P, Elbaz
M, Delarche N, et al: Cyclosporine before PCI in patients with
acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 373:1021–1031.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rossello X and Yellon DM:
Cardioprotection: The disconnect between bench and bedside.
Circulation. 134:574–575. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen T and Vunjak-Novakovic G: In vitro
models of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Regen Eng Transl Med.
4:142–153. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
He X, Li S, Liu B, Susperreguy S, Formoso
K, Yao J, Kang J, Shi A, Birnbaumer L and Liao Y: Major
contribution of the 3/6/7 class of TRPC channels to myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion and cellular hypoxia/reoxygenation injuries.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E4582–E4591. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xie M, Kong Y, Tan W, May H, Battiprolu
PK, Pedrozo Z, Wang ZV, Morales C, Luo X, Cho G, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibition blunts ischemia/reperfusion injury by
inducing cardiomyocyte autophagy. Circulation. 129:1139–1151.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Oh JG, Kho C, Hajjar RJ and Ishikawa K:
Experimental models of cardiac physiology and pathology. Heart Fail
Rev. 24:601–615. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kuznetsov AV, Javadov S, Sickinger S,
Frotschnig S and Grimm M: H9c2 and HL-1 cells demonstrate distinct
features of energy metabolism, mitochondrial function and
sensitivity to hypoxia-reoxygenation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1853:276–284. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lecour S, Bøtker HE, Condorelli G,
Davidson SM, Garcia-Dorado D, Engel FB, Ferdinandy P, Heusch G,
Madonna R, Ovize M, et al: ESC working group cellular biology of
the heart: Position paper: Improving the preclinical assessment of
novel cardioprotective therapies. Cardiovasc Res. 104:399–411.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
He S, Wang X, Zhong Y, Tang L, Zhang Y,
Ling Y, Tan Z, Yang P and Chen A: Hesperetin post-treatment
prevents rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in
vitro via activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 91:1106–1112. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yang YF, Peng K, Liu H, Meng XW, Zhang JJ
and Ji FH: Dexmedetomidine preconditioning for myocardial
protection in ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats by
downregulation of the high mobility group box 1-toll-like receptor
4-nuclear factor κB signalling pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
44:353–361. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Peng K, Qiu Y, Li J, Zhang ZC and Ji FH:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in primary
neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Exp Ther Med. 14:689–695.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang R, Yang M, Wang M, Liu X, Xu H, Xu X,
Sun G and Sun X: Total saponins of aralia elata (Miq) seem
alleviate calcium homeostasis imbalance and endoplasmic reticulum
stress-related apoptosis induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:28–40. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bi X, Zhang G, Wang X, Nguyen C, May HI,
Li X, Al-Hashimi AA, Austin RC, Gillette TG, Fu G, et al:
Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone GRP78 protects heart from
ischemia/reperfusion injury through Akt activation. Circ Res.
122:1545–1554. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li H, Chen H, Li R, Xin J, Wu S, Lan J,
Xue K, Li X, Zuo C, Jiang W and Zhu L: Cucurbitacin I induces
cancer cell death through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway.
J Cell Biochem, Sep 11, 2018 (Online ahead of print).
|
|
48
|
Huang ZH, Zhang SX, Wang C, Zhao R, Qiao
J, Bai WQ, Lu JF, Lu XQ and Zhang HH: Downregulated long non-coding
RNA FOXD3-AS1 promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
apoptosis by inhibiting RCN1 via let-7e-5p in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 319(C455)2020.
|
|
49
|
Chen J, Chen J, Cheng Y, Fu Y, Zhao H,
Tang M, Zhao H, Lin N, Shi X, Lei Y, et al: Mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes protect beta cells against hypoxia-induced
apoptosis via miR-21 by alleviating ER stress and inhibiting p38
MAPK phosphorylation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11(97)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|