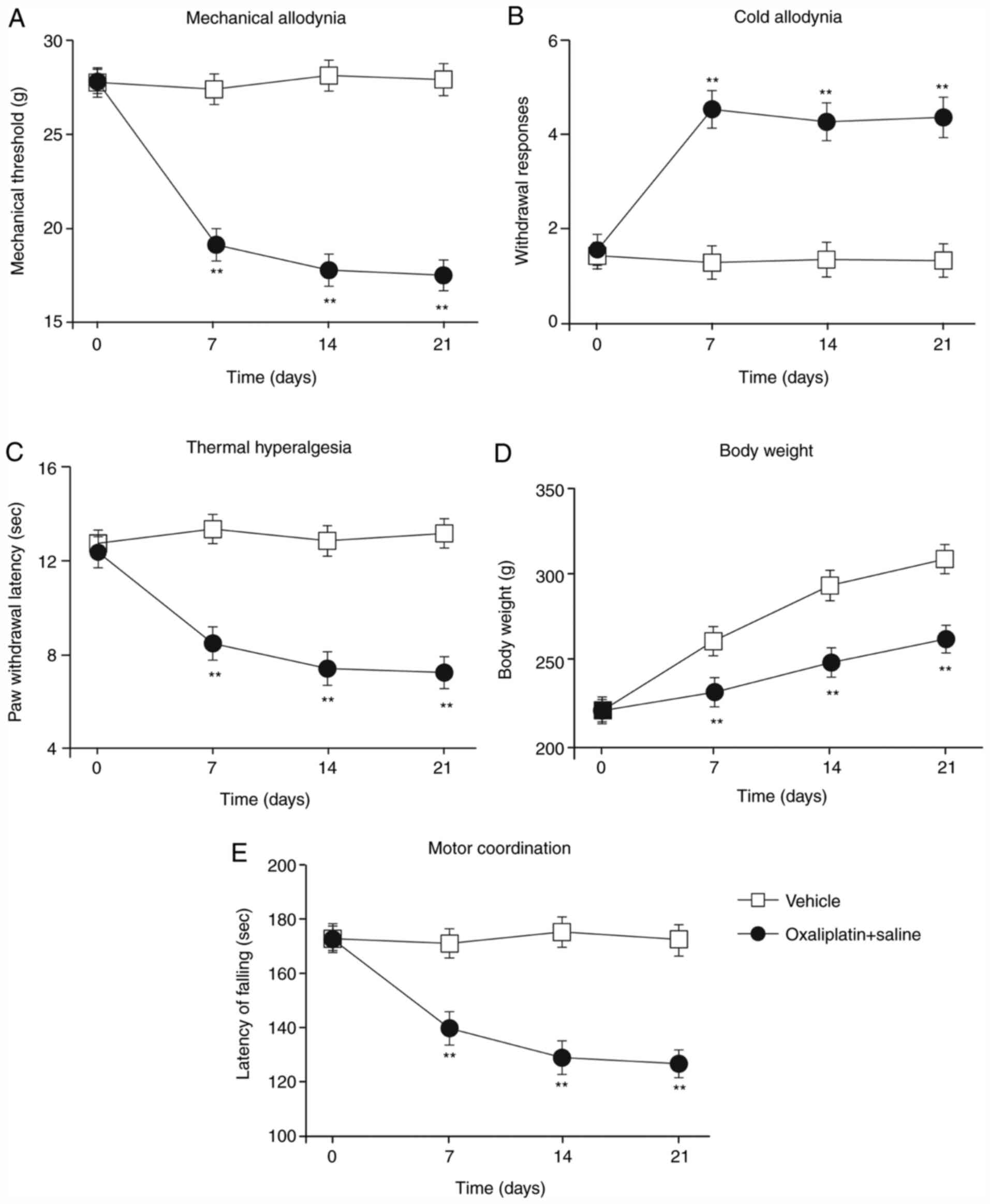
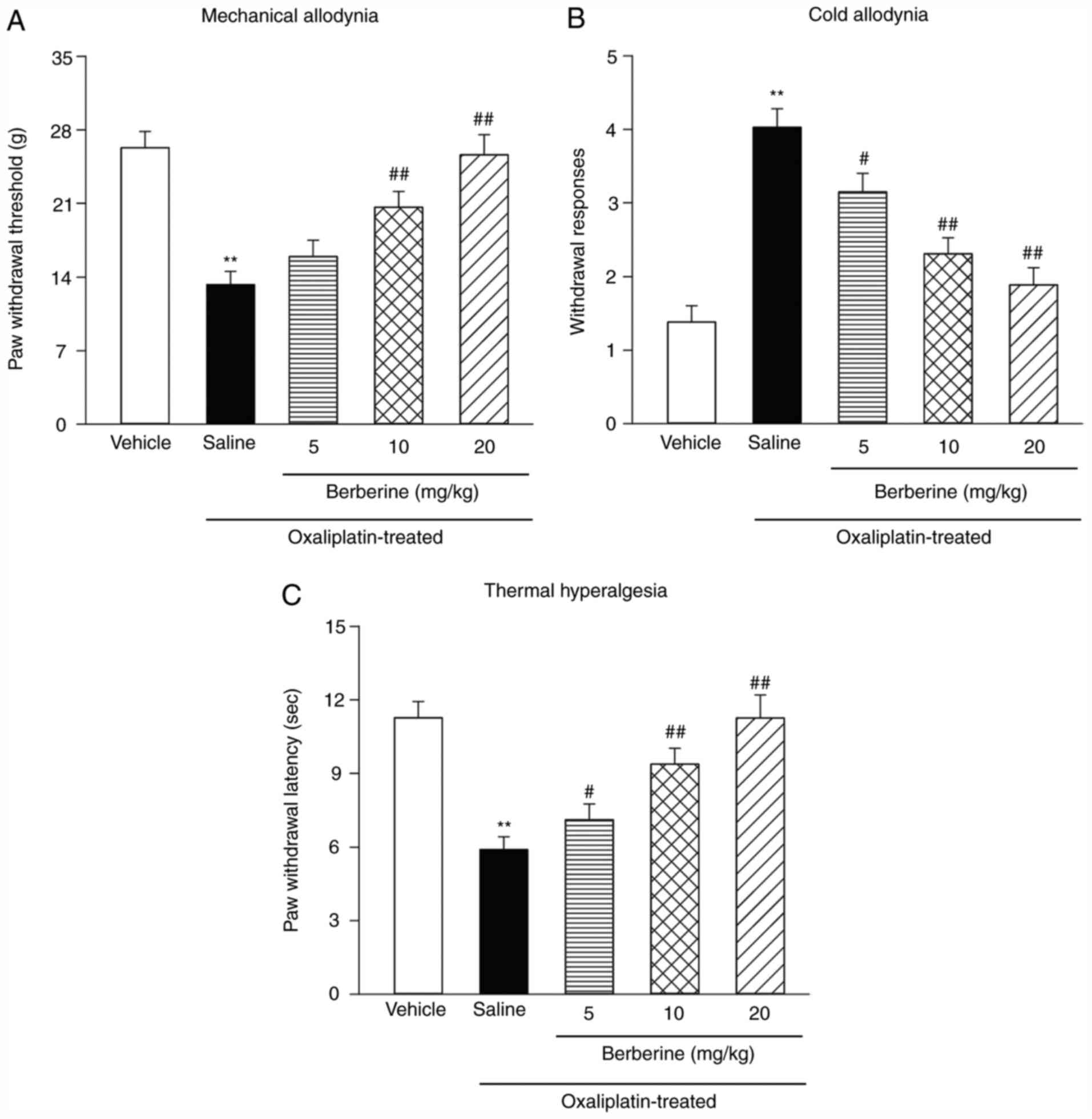
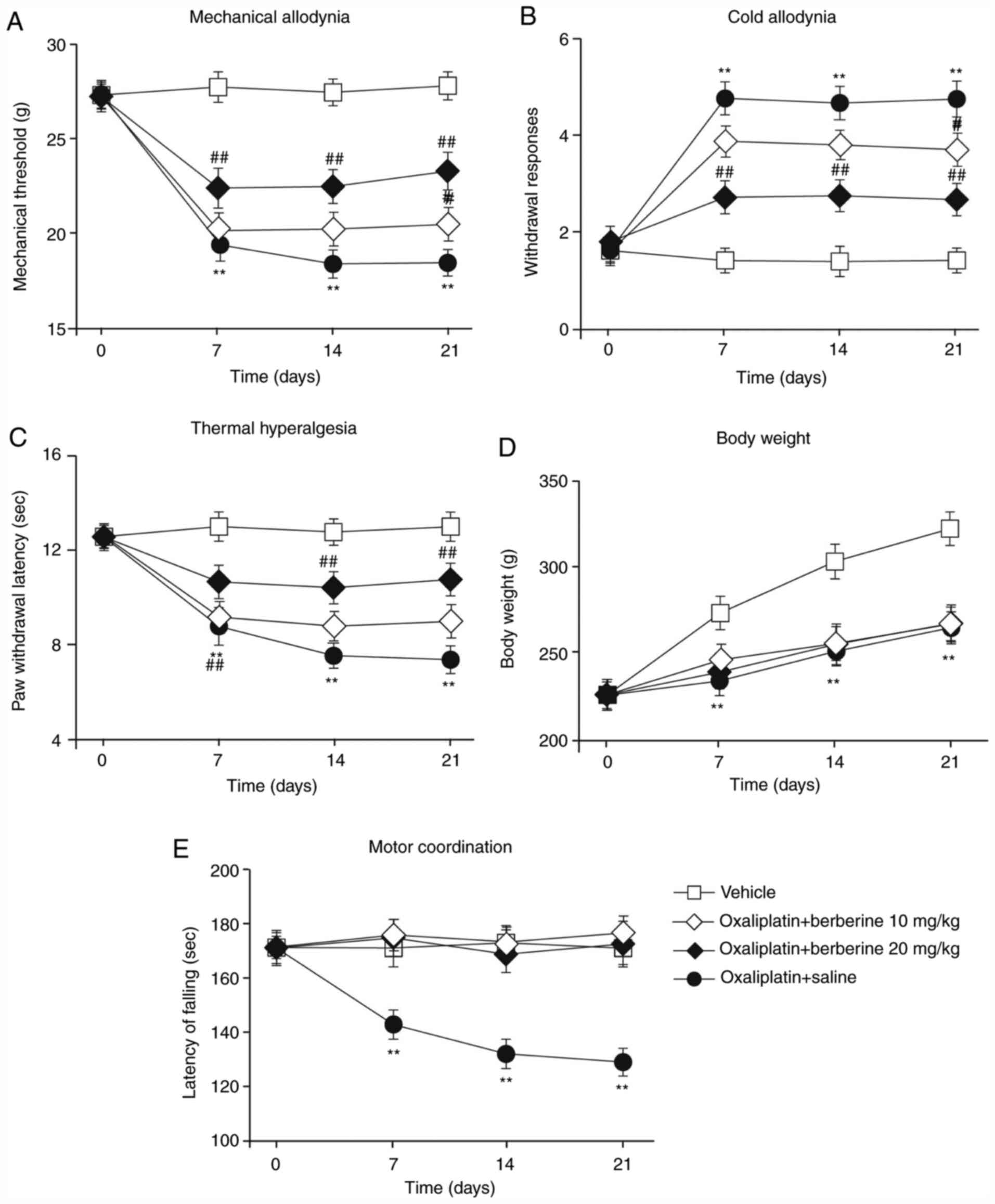
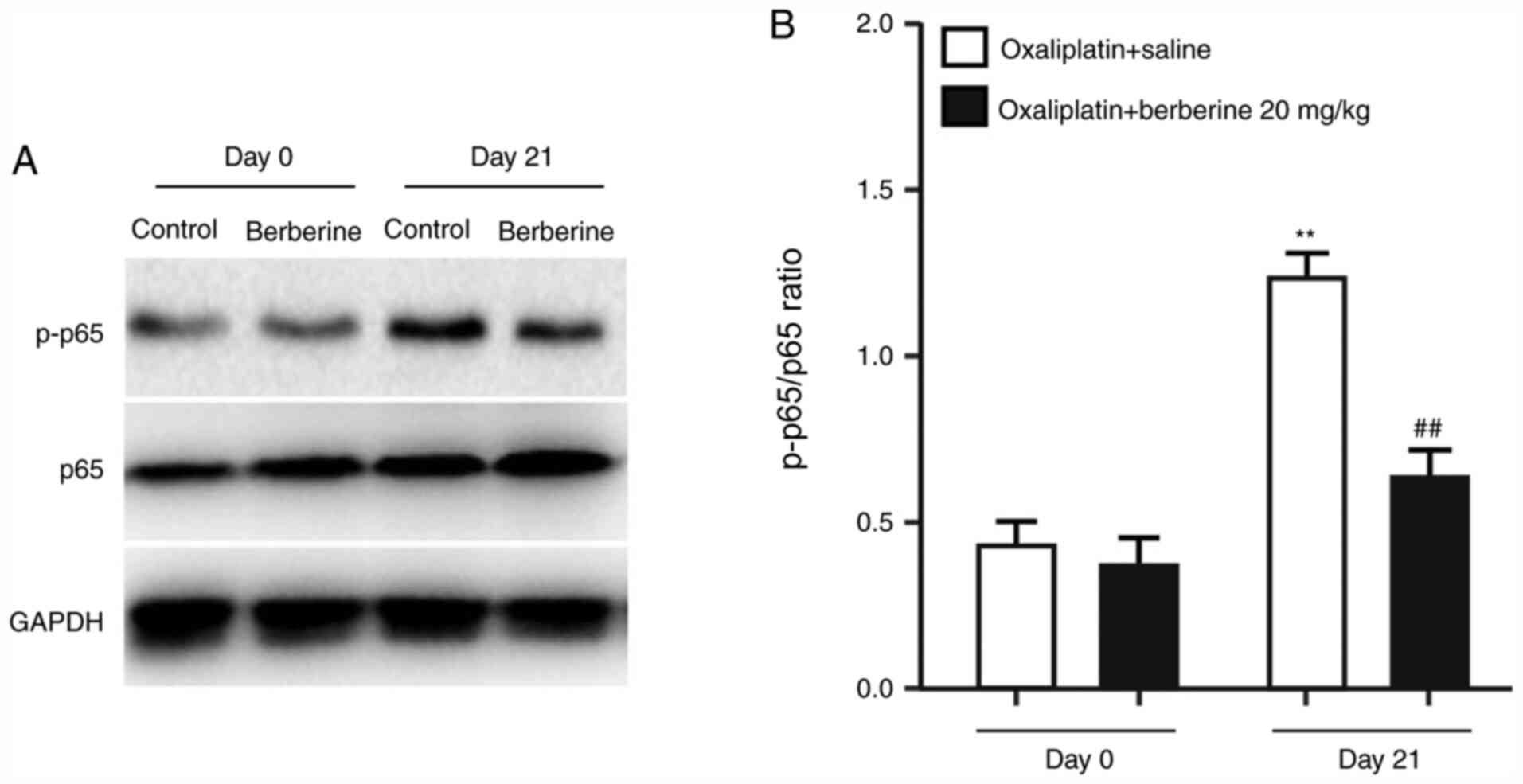
|
1
|
Park SB, Goldstein D, Krishnan AV, Lin CS,
Friedlander ML, Cassidy J, Koltzenburg M and Kiernan MC:
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: A critical analysis.
CA Cancer J Clin. 63:419–437. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Argyriou AA, Bruna J, Marmiroli P and
Cavaletti G: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (CIPN):
An update. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 82:51–77. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L,
Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan
P, Bridgewater J, et al: Multicenter International Study of
Oxaliplatin/5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in the Adjuvant Treatment of
Colon Cancer (MOSAIC) Investigators: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2343–2351. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cersosimo RJ: Oxaliplatin-associated
neuropathy: A review. Ann Pharmacother. 39:128–135. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Farquhar-Smith P: Chemotherapy-induced
neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 5:1–7.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Brewer JR, Morrison G, Dolan ME and
Fleming GF: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Current
status and progress. Gynecol Oncol. 140:176–183. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vallabhapurapu S and Karin M: Regulation
and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune
system. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:693–733. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Meffert MK, Chang JM, Wiltgen BJ, Fanselow
MS and Baltimore D: NF-kappa B functions in synaptic signaling and
behavior. Nat Neurosci. 6:1072–1078. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kaltschmidt B and Kaltschmidt C: NF-kappaB
in the nervous system. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1(a001271)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wan F, Anderson DE, Barnitz RA, Snow A,
Bidere N, Zheng L, Hegde V, Lam LT, Staudt LM, Levens D, et al:
Ribosomal protein S3: A KH domain subunit in NF-kappaB complexes
that mediates selective gene regulation. Cell. 131:927–939.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao LX, Jiang BC, Wu XB, Cao DL and Gao
YJ: Ligustilide attenuates inflammatory pain via inhibition of
NFκB-mediated chemokines production in spinal astrocytes. Eur J
Neurosci. 39:1391–1402. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chu LW, Chen JY, Wu PC and Wu BN:
Atorvastatin prevents neuroinflammation in chronic constriction
injury rats through nuclear NFκB downregulation in the dorsal root
ganglion and spinal cord. ACS Chem Neurosci. 6:889–898.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Huang ZZ, Li D, Ou-Yang HD, Liu CC, Liu
XG, Ma C, Wei JY, Liu Y and Xin WJ: Cerebrospinal fluid oxaliplatin
contributes to the acute pain induced by systemic administration of
oxaliplatin. Anesthesiology. 124:1109–1121. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fu ES, Zhang YP, Sagen J, Candiotti KA,
Morton PD, Liebl DJ, Bethea JR and Brambilla R: Transgenic
inhibition of glial NF-kappaB reduces pain behavior and
inflammation after peripheral nerve injury. Pain. 148:509–518.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fu ES, Zhang YP, Sagen J, Yang ZQ and
Bethea JR: Transgenic glial nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition
decreases formalin pain in mice. Neuroreport. 18:713–717.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nong X, Lan Y and Picroside II: Picroside
II Attenuates CCI-induced neuropathic pain in rats by inhibiting
spinal reactive astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation through the
NF-κB pathway. Neurochem Res. 43:1058–1066. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tao W, Luo X, Cui B, Liang D, Wang C, Duan
Y, Li X, Zhou S, Zhao M, Li Y, et al: Practice of traditional
Chinese medicine for psycho-behavioral intervention improves
quality of life in cancer patients: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 6:39725–39739. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yuan QL, Guo TM, Liu L, Sun F and Zhang
YG: Traditional Chinese medicine for neck pain and low back pain: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One.
10(e0117146)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li Q, Yue N, Liu SB, Wang ZF, Mi WL, Jiang
JW, Wu GC, Yu J, Wang YQ, et al: Effects of chronic
electroacupuncture on depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in
rats with chronic neuropathic pain. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2014(158987)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen C, Lu M, Pan Q, Fichna J, Zheng L,
Wang K, Yu Z, Li Y, Li K, Song A, et al: Berberine improves
intestinal motility and visceral pain in the mouse models mimicking
diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) symptoms in
an opioid-receptor dependent manner. PLoS One.
10(e0145556)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen C, Tao C, Liu Z, Lu M, Pan Q, Zheng
L, Li Q, Song Z and Fichna J: A randomized clinical Trial of
berberine hydrochloride in patients with diarrhea-predominant
irritable bowel syndrome. Phytother Res. 29:1822–1827.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tan W, Li Y, Chen M and Wang Y: Berberine
hydrochloride: Anticancer activity and nanoparticulate delivery
system. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:1773–1777. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kim SO and Kim HJ: Berberine ameliorates
cold and mechanical allodynia in a rat model of diabetic
neuropathy. J Med Food. 16:511–517. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Han AM, Heo H and Kwon YK: Berberine
promotes axonal regeneration in injured nerves of the peripheral
nervous system. J Med Food. 15:413–417. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Rezaee R, Monemi A, SadeghiBonjar MA and
Hashemzaei M: Berberine alleviates paclitaxel-induced neuropathy. J
Pharmacopuncture. 22:90–94. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sisignano M, Baron R, Scholich K and
Geisslinger G: Mechanism-based treatment for chemotherapy-induced
peripheral neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Neurol. 10:694–707.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Majithia N, Loprinzi CL and Smith TJ: New
practical approaches to chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain:
Prevention, assessment, and treatment. Oncology (Williston Park).
30:1020–1029. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu M, Gao L and Zhang N: Berberine
reduces neuroglia activation and inflammation in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
33(2058738419866379)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ghosh S and Karin M: Missing pieces in the
NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 109 (Suppl 1):S81–S96. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Vermeulen L, De Wilde G, Notebaert S,
Vanden Berghe W and Haegeman G: Regulation of the transcriptional
activity of the nuclear factor-kappaB p65 subunit. Biochem
Pharmacol. 64:963–970. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lu L, Hu J, Wu Q, An Y, Cui W, Wang J and
Ye Z: Berberine prevents human nucleus pulposus cells from IL 1β
induced extracellular matrix degradation and apoptosis by
inhibiting the NF κB pathway. Int J Mol Med. 43:1679–1686.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yoon SY and Oh J: Neuropathic cancer pain:
Prevalence, pathophysiology, and management. Korean J Intern Med
(Korean Assoc Intern Med). 33:1058–1069. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Carozzi VA, Canta A and Chiorazzi A:
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: What do we know about
mechanisms? Neurosci Lett. 596:90–107. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ahmed AS, Berg S, Alkass K, Druid H, Hart
DA, Svensson CI and Kosek E: NF-κB-associated pain-related
neuropeptide expression in patients with degenerative disc disease.
Int J Mol Sci. 20(20)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shih RH, Wang CY and Yang CM: NF-kappaB
signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: A mini review.
Front Mol Neurosci. 8(77)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|