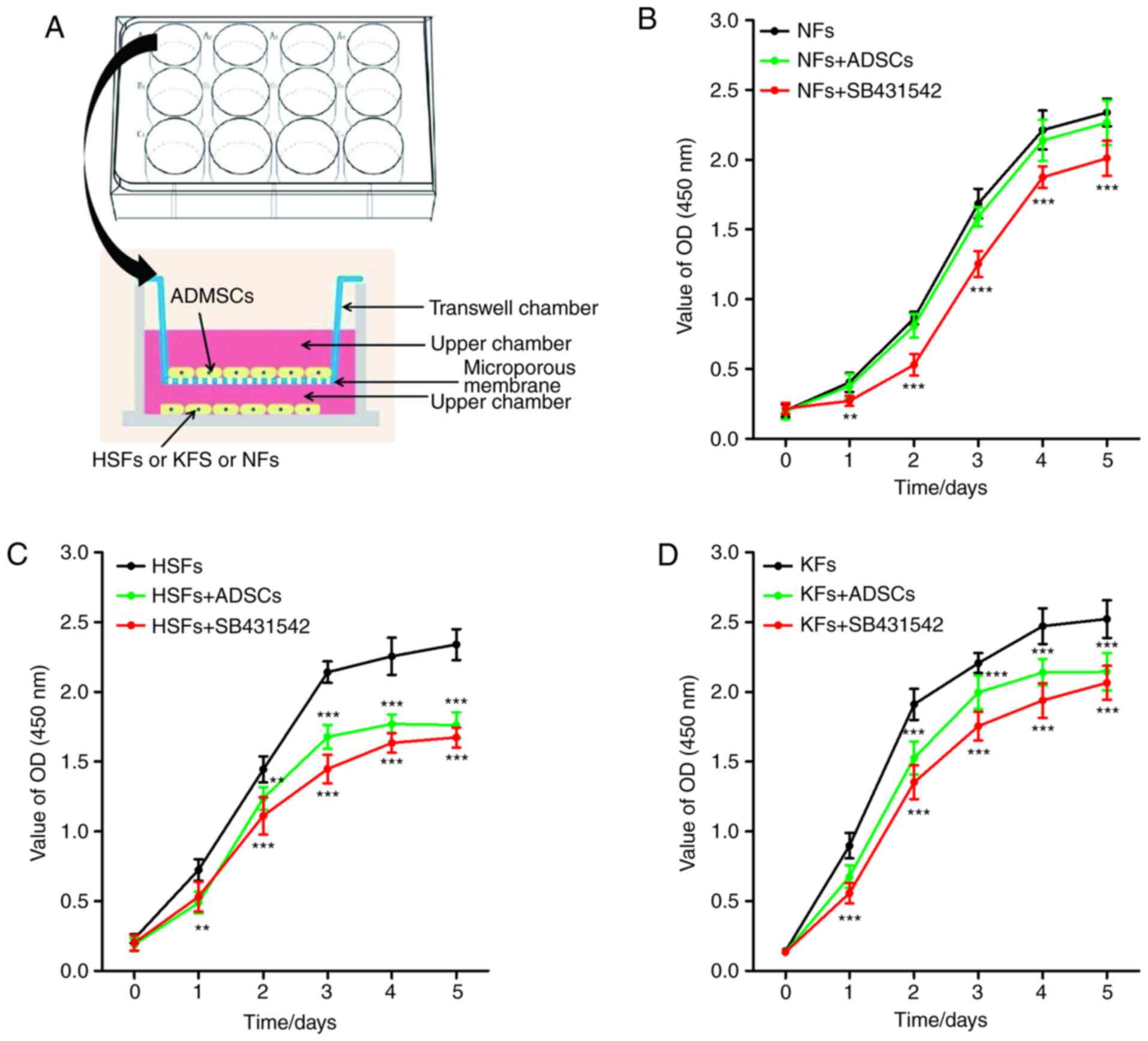
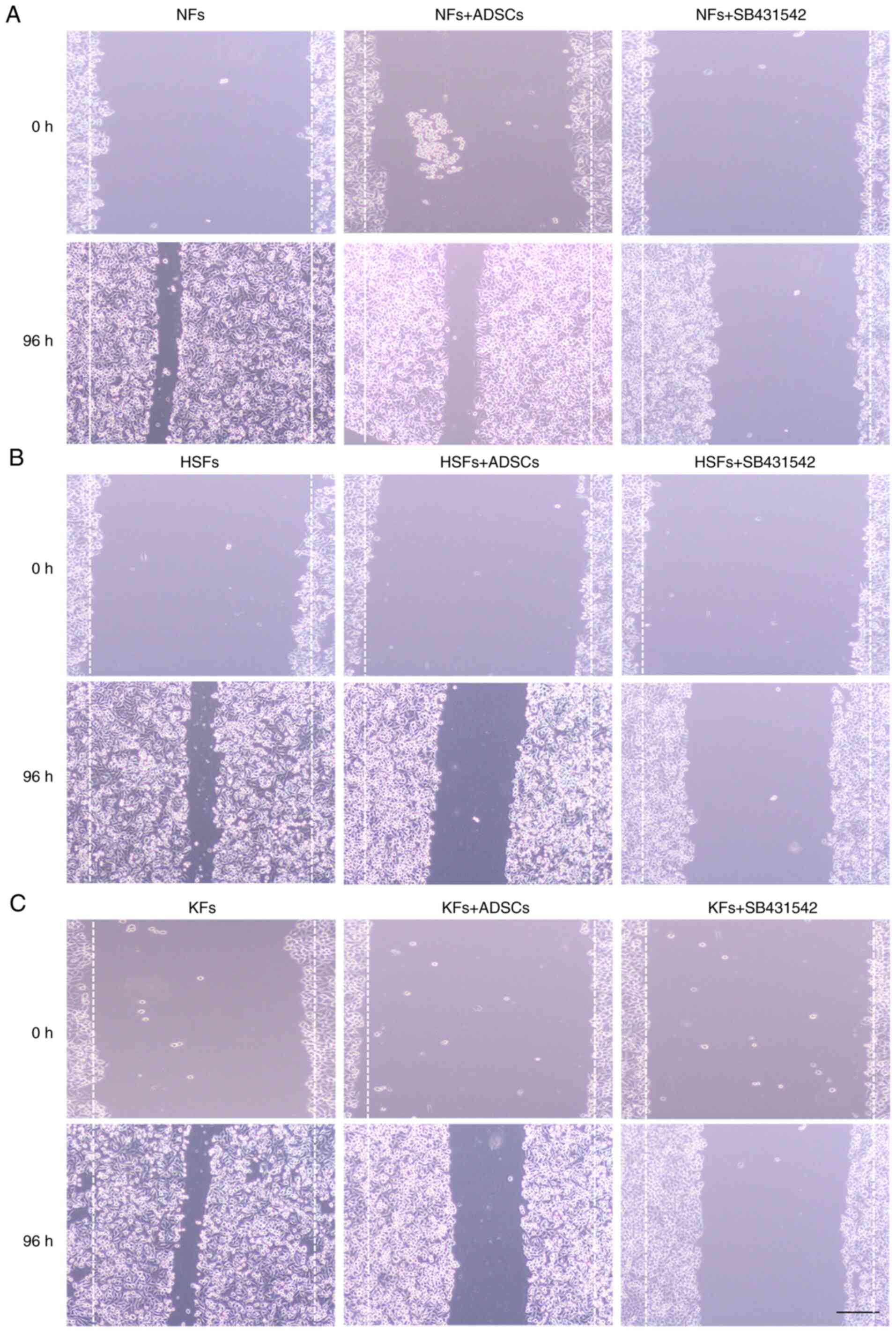
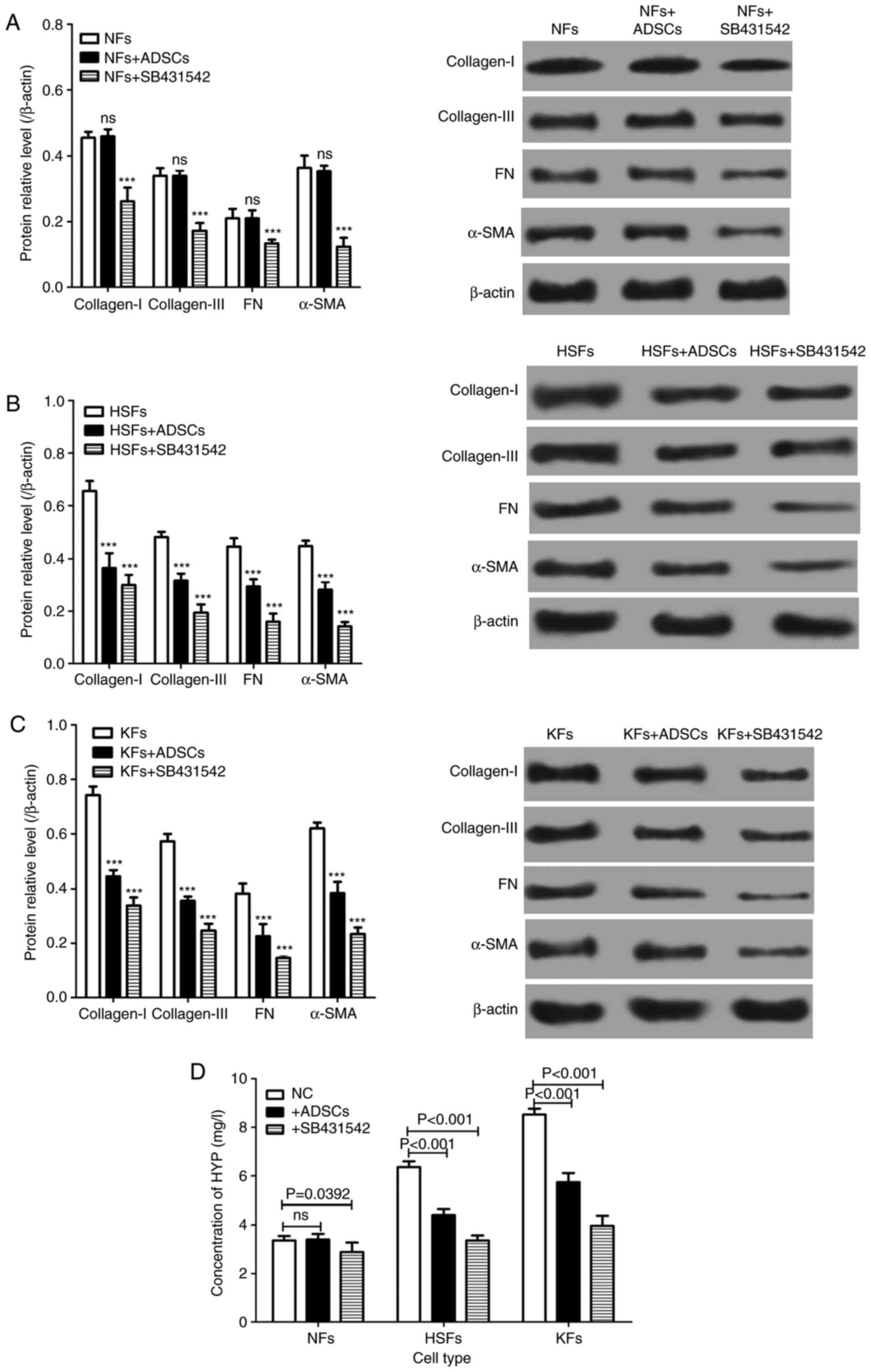
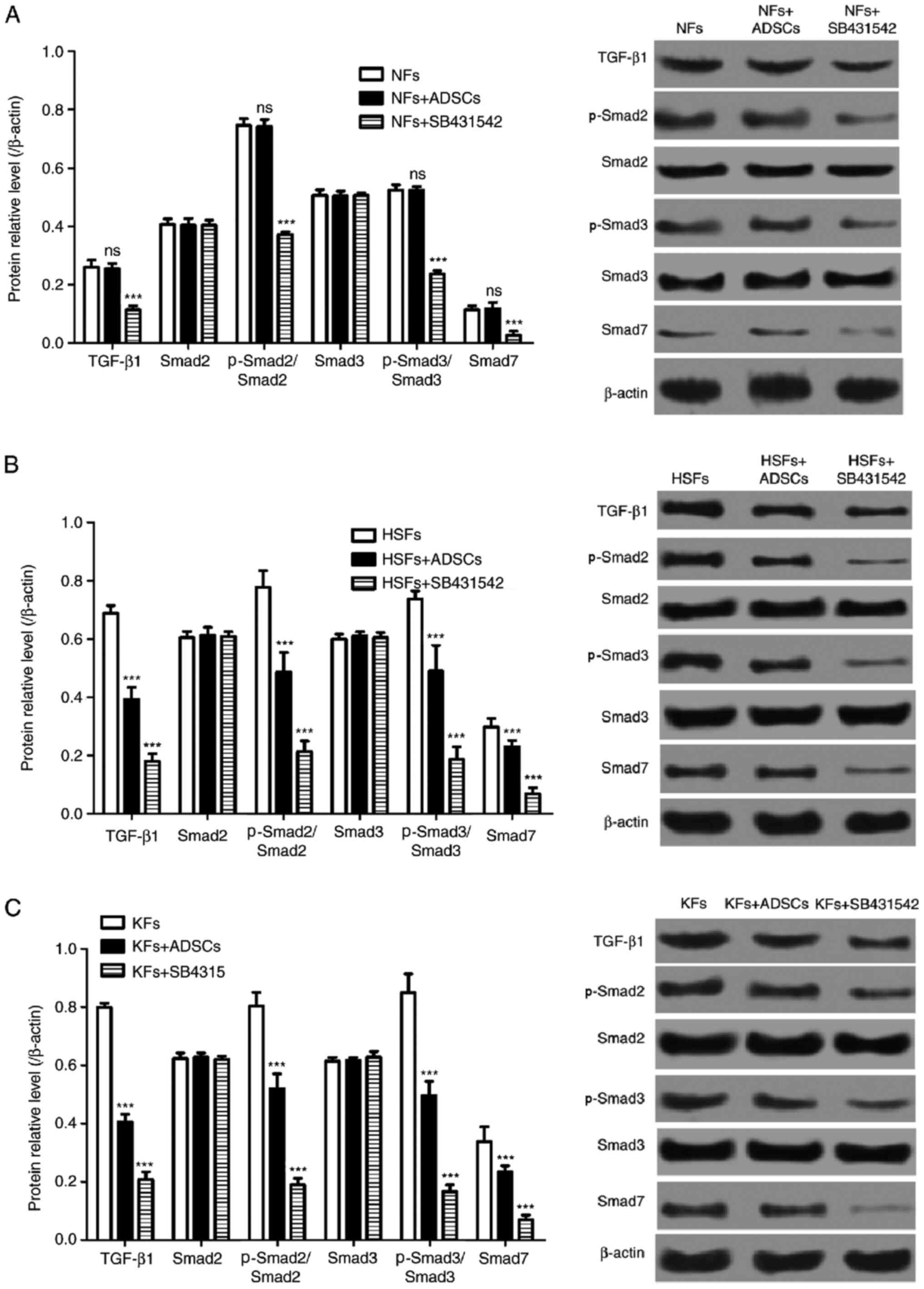
|
1
|
Fearmonti RM, Bond JE, Erdmann D, Levin
LS, Pizzo SV and Levinson H: The modified patient and observer scar
assessment scale: A novel approach to defining pathologic and
nonpathologic scarring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 129:242–247.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bock O, Schmid-Ott G, Malewski P and
Mrowietz U: Quality of life of patients with keloid and
hypertrophic scarring. Arch Dermatol Res. 297:433–438.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rohrer TE and Gold M: Introduction to
special issue on hypertrophic scars and keloids. Dermatol Surg. 43
(Suppl 1):S1–S2. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Seifert O and Mrowietz U: Keloid scarring:
Bench and bedside. Arch Dermatol Res. 301:259–272. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T,
Ruzicka T and Jeschke MG: Hypertrophic Scarring and Keloids:
Pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies. Mol
Med. 17:113–125. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nakajima H, Uchida K, Guerrero AR,
Watanabe S, Sugita D, Takeura N, Yoshida A, Long G, Wright KT and
Johnson WE: Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells promotes an
alternative pathway of macrophage activation and functional
recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 29:1614–1625.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Schurgers E, Kelchtermans H, Mitera T,
Geboes L and Matthys P: Discrepancy between the in vitro and in
vivo effects of murine mesenchymal stem cells on T-cell
proliferation and collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
12(R31)2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kim WS, Park BS, Kim HK, Park JS, Kim KJ,
Choi JS, Chung SJ, Kim DD and Sung JH: Evidence supporting
antioxidant action of adipose-derived stem cells: Protection of
human dermal fibroblasts from oxidative stress. J Dermatol Sci.
49:133–142. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hiwatashi N, Bing R, Kraja I and Branski
RC: Mesenchymal stem cells have antifibrotic effects on
transforming growth factor-β1-stimulated vocal fold fibroblasts.
Laryngoscope. 127:E35–E41. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Smith AN, Willis E, Chan VT, Muffley LA,
Isik FF, Gibran NS and Hocking AM: Mesenchymal stem cells induce
dermal fibroblast responses to injury. Exp Cell Res. 316:48–54.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Harvestine JN, Orbay H, Chen JY, Sahar DE
and Leach JK: Cell-secreted extracellular matrix, independent of
cell source, promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human
stromal vascular fraction. J Mater Chem B. 6:4104–4115.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Antoniou KM, Papadaki HA, Soufla G,
Kastrinaki MC, Damianaki A, Koutala H, Spandidos DA and Siafakas
NM: Investigation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM MSCs)
involvement in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Respir Med.
104:1535–1542. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang D, Sun S, Wang Z, Zhu P, Yang Z and
Zhang B: Stromal cell-derived factor-1 receptor
CXCR4-overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerate
wound healing by migrating into skin injury areas. Cell Reprogram.
15:206–215. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yuben M, Daniel A, Ursula M, Samuel CS,
Jorge T, Sivakami I, Richard B and Alan T: Human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells reduce fibrosis of bleomycin-induced lung
injury. Am J Pathol. 175:303–313. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee MJ, Jung J, Na KH, Moon JS, Lee HJ,
Kim JH, Kim GI, Kwon SW, Hwang SG and Kim GJ: Anti-fibrotic effect
of chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells isolated from
human placenta in a rat model of CCl(4)-injured liver: Potential
application to the treatment of hepatic diseases. J Cell Biochem.
111:1453–1463. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bunnell BA: Adipose-derived stem cells.
Methods Mol Biol. 5:59–67. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Ma T, Sun J, Zhao Z, Lei W, Chen Y, Wang
X, Yang J and Shen Z: A brief review: Adipose-derived stem cells
and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 8(124)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yang D, Wang W, Li L, Peng Y, Chen P,
Huang H, Guo Y, Xia X, Wang Y and Wang H: The relative contribution
of paracine effect versus direct differentiation on adipose-derived
stem cell transplantation mediated cardiac repair. PLoS One.
8(e59020)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim WS, Park BS, Sung JH, Yang JM, Park
SB, Kwak SJ and Park JS: Wound healing effect of adipose-derived
stem cells: A critical role of secretory factors on human dermal
fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 48:15–24. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee SH, Lee JH and Cho KH: Effects of
human adipose-derived stem cells on cutaneous wound healing in nude
mice. Ann Dermatol. 23:150–155. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Maharlooei MK, Bagheri M, Solhjou Z,
Jahromi BM, Akrami M, Rohani L, Monabati A, Noorafshan A and Omrani
GR: Adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cell (AD-MSC) promotes
skin wound healing in diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
93:228–234. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gao W, Qiao X, Ma S and Cui L:
Adipose-derived stem cells accelerate neovascularization in
ischaemic diabetic skin flap via expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α. J Cell Mol Med. 15:2575–2585. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bock O, Yu H, Zitron S, Bayat A, Ferguson
MWJ and Mrowietz U: Studies of transforming growth factors beta 1-3
and their receptors I and II in fibroblast of keloids and
hypertrophic scars. Acta Derm Venereol. 85:216–220. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wong VW, You F, Januszyk M, Gurtner GC and
Kuang AA: Transcriptional profiling of rapamycin-treated
fibroblasts from hypertrophic and keloid scars. Ann Plast Surg.
72:711–719. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tao J, Zhang J, Ling Y, Mccall CE and Liu
TF: Mitochondrial sirtuin 4 resolves immune tolerance in monocytes
by rebalancing glycolysis and glucose oxidation homeostasis. Front
Immunol. 9(419)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
O'Leary R, Wood EJ and Guillou PJ:
Pathological scarring: Strategic interventions. Eur J Surg.
168:523–534. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sarrazy V, Billet F, Micallef L, Coulomb B
and Desmoulière A: Mechanisms of pathological scarring: Role of
myofibroblasts and current developments. Wound Repair Regen. 19
(Suppl 1):S10–S15. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wagner JA: Therapy of pathological scars.
J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 11:1139–1157. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu YL, Liu WH, Sun J, Hou TJ, Liu YM, Liu
HR, Luo YH, Zhao NN, Tang Y and Deng FM: Mesenchymal stem
cell-mediated suppression of hypertrophic scarring is p53 dependent
in a rabbit ear model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 5(136)2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang Q, Liu LN, Yong Q, Deng JC and Cao
WG: Intralesional injection of adipose-derived stem cells reduces
hypertrophic scarring in a rabbit ear model. Stem Cell Res Ther.
6(145)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jia SS, Li WY, Liu X and Li LY:
Transforming growth factor-β1 induces differentiation of bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblasts via
production of reactive oxygen species. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi
Xue Ban. 47:737–742. 2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Lichtman MK, Otero-Vinas M and Falanga V:
Transforming growth factors β (TGF-β) isoforms in wound healing and
fibrosis. Wound Repair Regen. 24:215–222. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Stagg J: Immune regulation by mesenchymal
stem cells: Two sides to the coin. Tissue Antigens. 69:1–9.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Park JE, Seo YK, Yoon HH, Kim CW, Park JK
and Jeon S: Electromagnetic fields induce neural differentiation of
human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells via ROS mediated
EGFR activation. Neurochem Int. 62:418–424. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Manieri NA, Mack MR, Himmelrich MD,
Worthley DL, Hanson EM, Lars E, Wang TC and Stappenbeck TS:
Mucosally transplanted mesenchymal stem cells stimulate intestinal
healing by promoting angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 125:3606–3618.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zuk P, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell
J, Katz A, Benhaim P, Lorenz H and Hedrick M: Multilineage cells
from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies.
Tissue Eng. 7:211–228. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA,
Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P and Hedrick
MH: Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol
Biol Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bayesgenis A, Soler-Botija C, Farré J,
Sepúlveda P, Raya A, Roura S, Prat-Vidal C, Gálvez-Montón C,
Montero JA and Büscher D: Human progenitor cells derived from
cardiac adipose tissue ameliorate myocardial infarction in rodents.
J Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:771–780. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Cao Y, Sun Z, Liao L, Meng Y, Han Q and
Zhao RC: Human adipose tissue-derived stem cells differentiate into
endothelial cells in vitro and improve postnatal neovascularization
in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 332:370–379. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yoshihiko K, Kobler JB, Herrera VLM and
Zeitels SM: Perspectives on adipose-derived stem/stromal cells as
potential treatment for scarred vocal folds: Opportunity and
challenges. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:175–181. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yun IS, Jeon YR, Lee WJ, Lee JW, Rah DK,
Tark KC and Lew DH: Effect of human adipose derived stem cells on
scar formation and remodeling in a pig model: A pilot study.
Dermatol Surg. 38:1678–1688. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Spiekman M, Przybyt E, Plantinga JA, Gibbs
S, van der Lei B and Harmsen MC: Adipose tissue-derived stromal
cells inhibit TGF-β1-induced differentiation of human dermal
fibroblasts and keloid scar-derived fibroblasts in a paracrine
fashion. Plast Reconstr Surg. 134:699–712. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zonari A, Martins TM, Paula AC, Boeloni
JN, Novikoff S, Marques AP, Correlo VM, Reis RL and Goes AM:
Polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate structures loaded with
adipose stem cells promote skin healing with reduced scarring. Acta
Biomater. 17:170–181. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Dong W, Wang J, Cai J and Wang Z:
Human omental adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned
medium alters the proteomic profile of epithelial ovarian cancer
cell lines in vitro. Onco Targets Ther. 10:1655–1663.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ivanova-Todorova E, Bochev I, Dimitrov R,
Belemezova K, Mourdjeva M, Kyurkchiev S, Kinov P, Altankova I and
Kyurkchiev D: Conditioned medium from adipose tissue-derived
mesenchymal stem cells induces CD4+FOXP3+
cells and increases IL-10 secretion. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012(295167)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pardali E, Sanchez-Duffhues G,
Gomez-Puerto MC and Dijke PT: TGF-β-induced endothelial-mesenchymal
transition in fibrotic diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
18(2157)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yichiang H, Chen MJ, Yu YM, Shunyao K and
Chang CC: Suppression of TGF-β1/SMAD pathway and extracellular
matrix production in primary keloid fibroblasts by curcuminoids:
Its potential therapeutic use in the chemoprevention of keloid.
Arch Dermatol Res. 302:717–724. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Emami A, Halim AS, Salahshifar I, Yussof
SJ, Khoo TL and Kannan TP: Association of TGFβ1 and SMAD4 variants
in the etiology of keloid scar in the Malay population. Arch
Dermatol Res. 304:541–547. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Jung H, Kim HH, Lee DH, Hwang YS, Yang HC
and Park JC: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 in adipose derived
stem cells conditioned medium is a dominant paracrine mediator
determines hyaluronic acid and collagen expression profile.
Cytotechnology. 63:57–66. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Shah M, Foreman DM and Ferguson MW:
Neutralisation of TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 or exogenous addition
of TGF-beta 3 to cutaneous rat wounds reduces scarring. J Cell Sci.
108:985–1002. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pohlers D, Brenmoehl J, Löffler I, Müller
CK, Leipner C, Schultze-Mosgau S, Stallmach A, Kinne RW and Wolf G:
TGF-β and fibrosis in different organs-molecular pathway imprints.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:746–756. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|