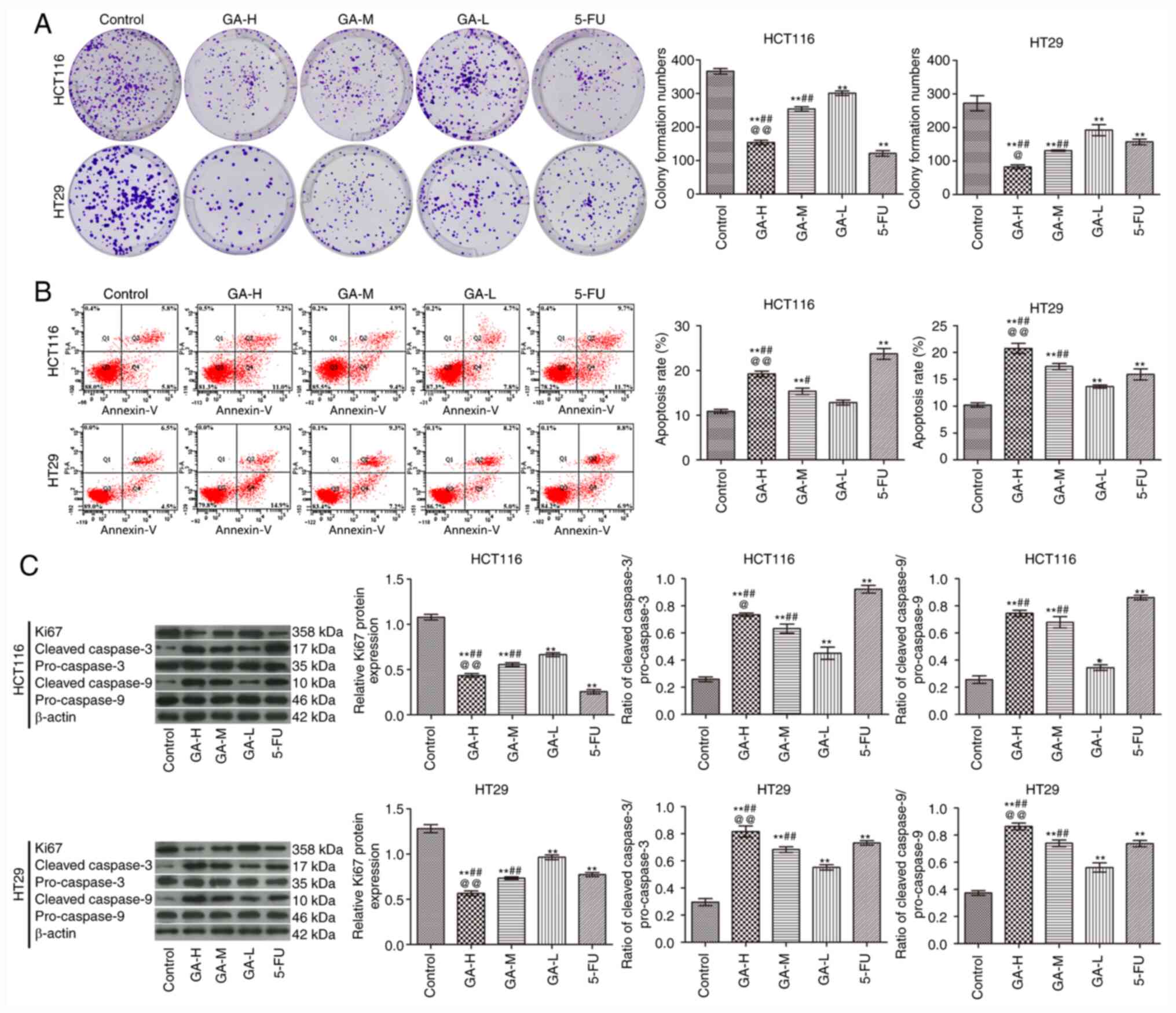
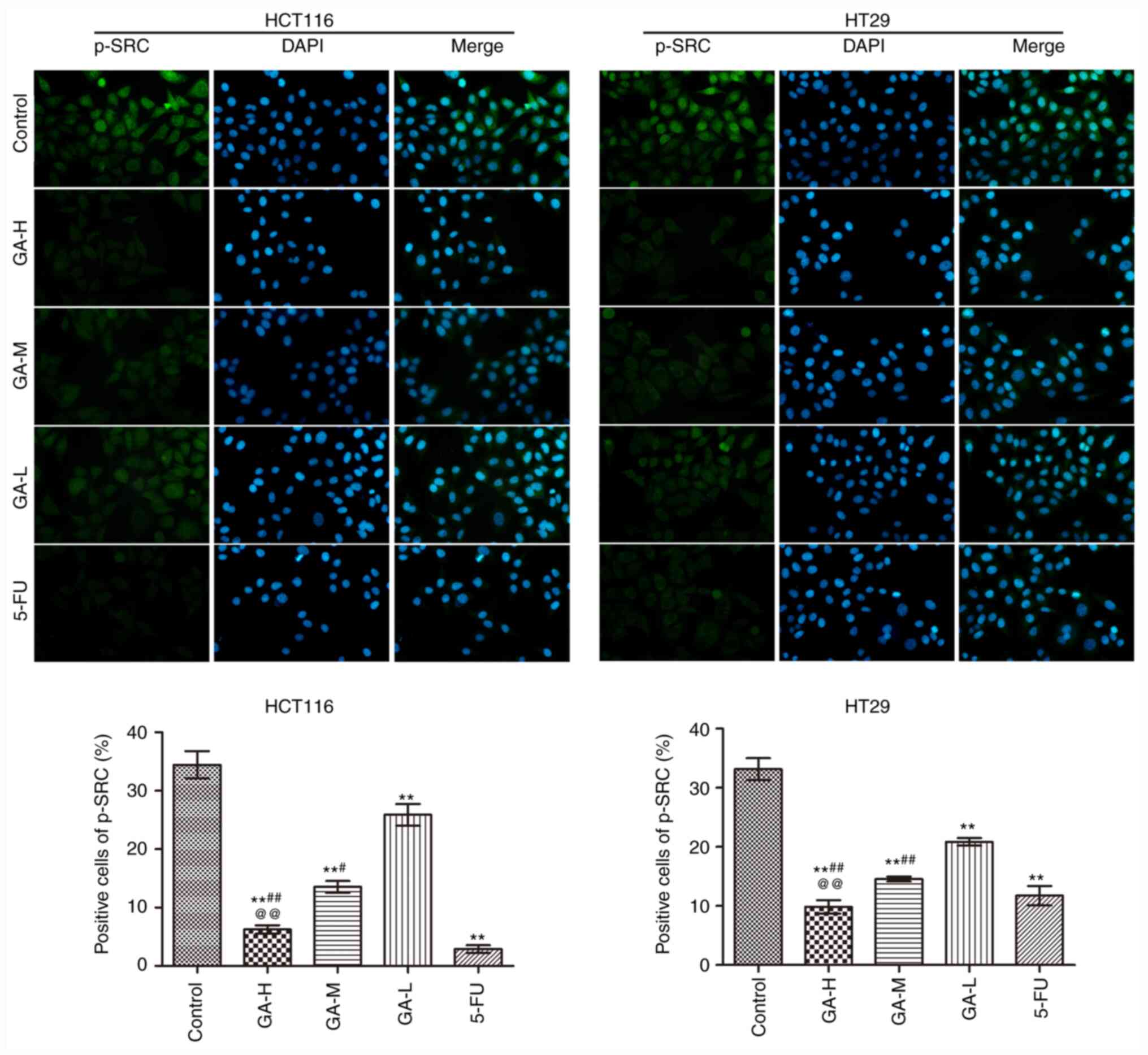
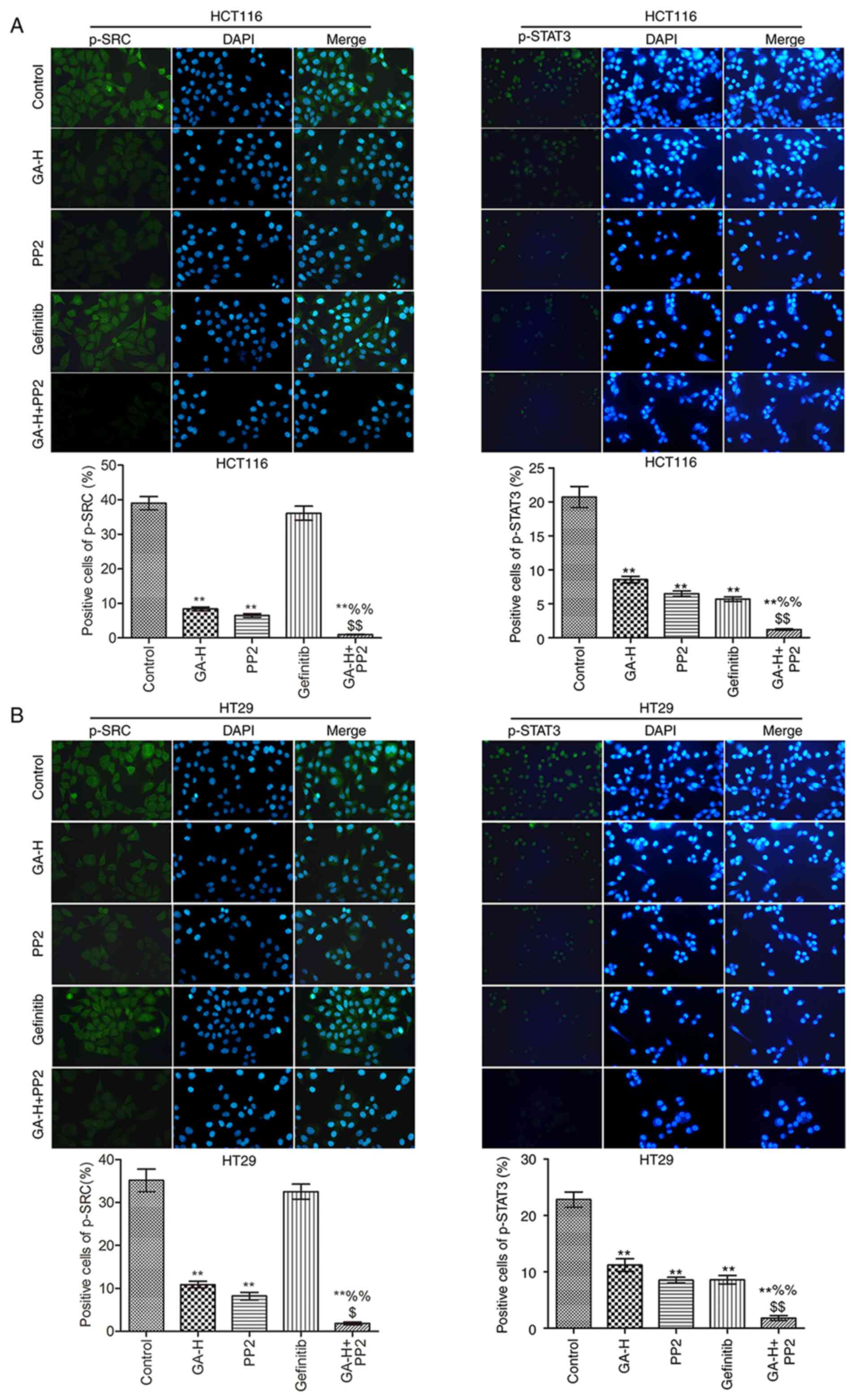
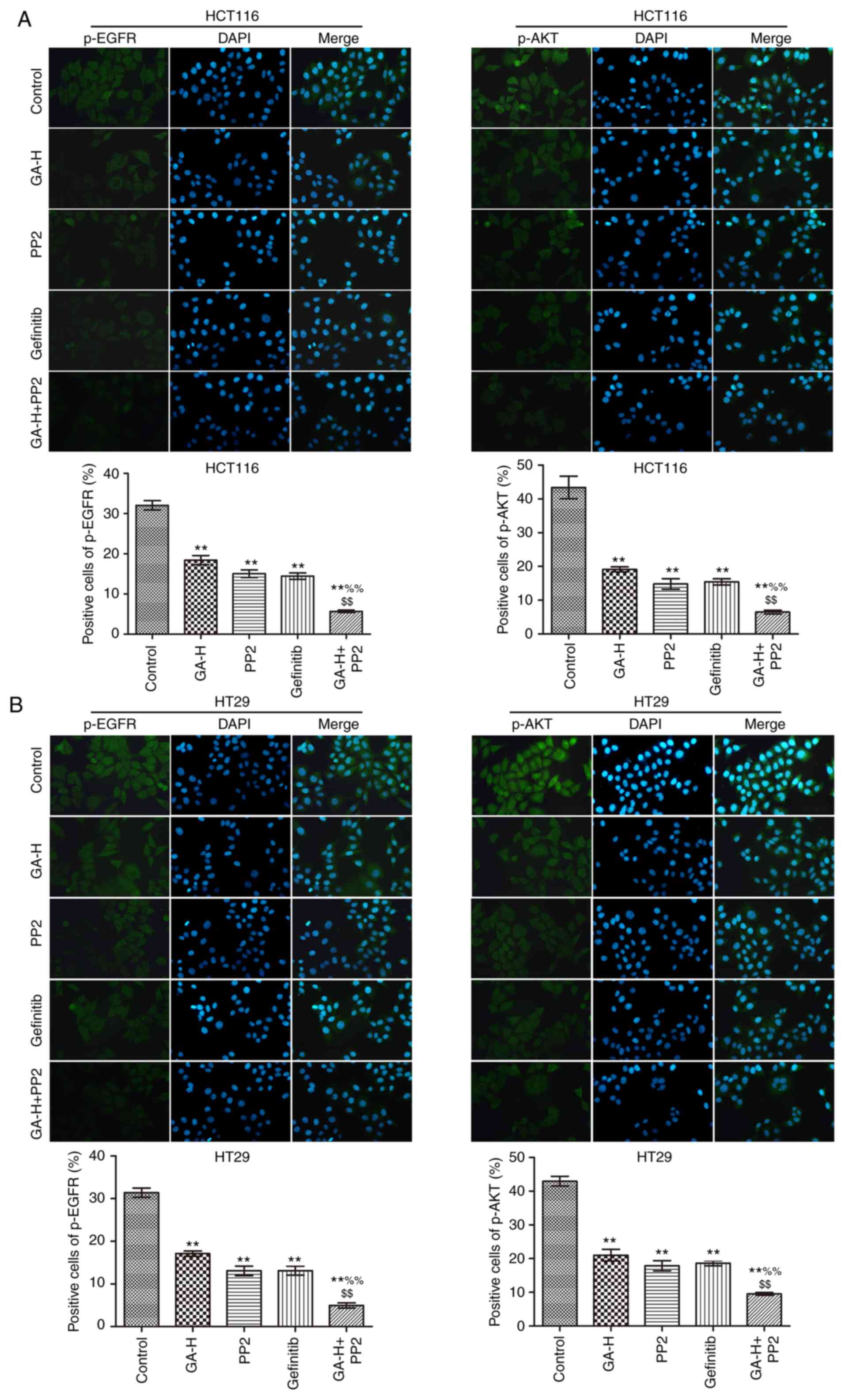
|
1
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Favoriti P, Carbone G, Greco M, Pirozzi F,
Pirozzi RE and Corcione F: Worldwide burden of colorectal cancer: A
review. Updates Surg. 68:7–11. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Giftson JS, Jayanthi S and Nalini N:
Chemopreventive efficacy of gallic acid, an antioxidant and
anticarcinogenic polyphenol, against 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine induced
rat colon carcinogenesis. Invest New Drugs. 28:251–259.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Carole M, Livine D, Daniel K, Järvinen JR,
Annelise L and Muller CD: Impact of procyanidins from different
berries on caspase 8 activation in colon cancer. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015(154164)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Grothey A and Venook AP: Optimizing
adjuvant therapy for localized colon cancer and treatment selection
in advanced colorectal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 16:611–615.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
No authors listed: Adjuvant chemotherapy
with oxaliplatin, in combination with fluorouracil plus leucovorin
prolongs disease-free survival, but causes more adverse event
cancer Abstracted from: Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, et
al. Multicenter international study of
oxaliplatin/5-fluorouracil/leucovorin in the adjuvant treatment of
colon cancer (MOSAIC) investigators. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med
350, 2343-2351, 2004. Cancer Treat Rev 30, 711-713, 2004.
|
|
7
|
Schmoll HJ, Tabernero J, Maroun J, de
Braud F, Price T, Van Cutsem E, Hill M, Hoersch S, Rittweger K and
Haller DG: Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with
fluorouracil/folinic acid as adjuvant therapy for stage III colon
cancer: Final results of the NO16968 randomized controlled phase
III trial. J Clin Oncol. 33:3733–3740. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu X, Jiang J, Chan R, Ji Y, Lu J, Liao
YP, Okene M, Lin J, Lin P, Chang CH, et al: Improved efficacy and
reduced toxicity using a custom-designed irinotecan-delivering
silicasome for orthotopic colon cancer. ACS Nano. 13:38–53.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Deng S, Shanmugam MK, Kumar AP, Yap CT,
Sethi G and Bishayee A: Targeting autophagy using natural compounds
for cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer. 125:1228–1246.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yaffe PB, Power Coombs MR, Doucette CD,
Walsh M and Hoskin DW: Piperine, an alkaloid from black pepper,
inhibits growth of human colon cancer cells via G1 arrest and
apoptosis triggered by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Carcinog.
54:1070–1085. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Venancio VP, Cipriano PA, Kim H, Antunes
LM, Talcott ST and Mertens-Talcott SU: Cocoplum (Chrysobalanus
icaco L.) anthocyanins exert anti-inflammatory activity in
human colon cancer and non-malignant colon cells. Food Funct.
8:307–314. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kubow S, Iskandar MM, Melgar-Bermudez E,
Sleno L, Sabally K, Azadi B, How E, Prakash S, Burgos G and Felde
TZ: Effects of simulated human gastrointestinal digestion of two
purple-fleshed potato cultivars on anthocyanin composition and
cytotoxicity in colonic cancer and non-tumorigenic cells.
Nutrients. 9(953)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mazewski C, Liang K and de Mejia EG:
Inhibitory potential of anthocyanin-rich purple and red corn
extracts on human colorectal cancer cell proliferation in vitro. J
Funct Foods. 34:254–265. 2017.
|
|
14
|
Niemetz R and Gross GG: Enzymology of
gallotannin and ellagitannin biosynthesis. Phytochemistry.
66:2001–2011. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kroes BH, van den Berg AJ, Quarles van
Ufford HC, van Dijk H and Labadie RP: Anti-inflammatory activity of
gallic acid. Planta Med. 58:499–504. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Choi HJ, Song JH, Bhatt LR and Baek SH:
Anti-human rhinovirus activity of gallic acid possessing
antioxidant capacity. Phytother Res. 24:1292–1296. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
You BR and Park WH: Gallic acid-induced
lung cancer cell death is related to glutathione depletion as well
as reactive oxygen species increase. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1356–1362. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun GL and Wang D: Gallic acid from
terminalia chebula inhibited the growth of esophageal carcinoma
cells by suppressing the Hippo signal pathway. Iran J Basic Med
Sci. 23:1401–1408. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee HL, Lin CS, Kao SH and Chou MC: Gallic
acid induces G1 phase arrest and apoptosis of triple-negative
breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 via p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase/p21/p27 axis. Anticancer Drugs. 28:1150–1156.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, Tsutsumi S,
Takeuchi T and Kuwano H: Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA enhances
the effect of 5-FU-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Ann
Surg Oncol. 16:761–771. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kundu J, Choi BY, Jeong CH, Kundu JK and
Chun KS: Thymoquinone induces apoptosis in human colon cancer
HCT116 cells through inactivation of STAT3 by blocking JAK2- and
Src-mediated phosphorylation of EGF receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncol
Rep. 32:821–828. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Agelaki S, Spiliotaki M, Markomanolaki H,
Kallergi G, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V and Stournaras C: Caveolin-1
regulates EGFR signaling in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and enhances
gefitinib-induced tumor cell inhibition. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:1470–1477. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li ZJ, Liu M, Dawuti G, Dou Q, Ma Y, Liu
HG and Aibai S: Antifungal activity of gallic acid in vitro and in
vivo. Phytother Res. 31:1039–1045. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lou L, Yu Z, Wang Y, Wang S and Zhao Y:
c-Src inhibitor selectively inhibits triple-negative breast cancer
overexpressed vimentin in vitro and in vivo. Cancer. 109:1648–1659.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bruzzese F, Di Gennaro E, Avallone A, Pepe
S, Arra C, Caraglia M, Tagliaferri P and Budillon A: Synergistic
antitumor activity of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor gefitinib and IFN-alpha in head and neck cancer
cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 12:617–625.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang T, Ma L, Wu P, Li W, Li T, Gu R, Dan
X, Li Z, Fan X and Xiao Z: Gallic acid has anticancer activity and
enhances the anticancer effects of cisplatin in non-small cell lung
cancer A549 cells via the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
41:1779–1788. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Phan AN, Hua TN, Kim MK, Vo VT, Choi JW,
Kim HW, Rho JK, Kim KW and Jeong Y: Gallic acid inhibition of
Src-Stat3 signaling overcomes acquired resistance to EGF receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:54702–54713. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liao CC, Chen SC, Huang HP and Wang CJ:
Gallic acid inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation and
migration via regulating fatty acid synthase (FAS). J Food Drug
Anal. 26:620–627. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang H, Wu J, Zhang J, Yang Z, Jin W, Li
Y, Jin L, Yin L, Liu H and Wang Z: Integrated bioinformatics
analysis of key genes involved in progress of colon cancer. Mol
Genet Genomic Med. 7(e00588)2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen J, Elfiky A, Han M, Chen C and Saif
MW: The role of Src in colon cancer and its therapeutic
implications. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 13:5–13. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W,
Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S,
Holmgren E, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2335–2342. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xie G, Peng Z and Raufman JP: Src-mediated
aryl hydrocarbon and epidermal growth factor receptor cross talk
stimulates colon cancer cell proliferation. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302:G1006–G1015. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Atmaca A, Werner D, Pauligk C, Steinmetz
K, Wirtz R, Altmannsberger HM, Jäger E and Al-Batran SE: The
prognostic impact of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients
with metastatic gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 12(524)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nam B, Rho JK, Shin DM and Son J: Gallic
acid induces apoptosis in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancers
by accelerating EGFR turnover. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 26:4571–4575.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liu ZM and Huang HS: As2O3-induced
c-Src/EGFR/ERK signaling is via Sp1 binding sites to stimulate
p21WAF1/CIP1 expression in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells.
Cell Signal. 18:244–255. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sen B, Saigal B, Parikh N, Gallick G and
Johnson FM: Sustained Src inhibition results in signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation and cancer cell
survival via altered Janus-activated kinase-STAT3 binding. Cancer
Res. 69:1958–1965. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen YJ, Lin KN, Jhang LM, Huang CH, Lee
YC and Chang LS: Gallic acid abolishes the
EGFR/Src/Akt/Erk-mediated expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9
in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact. 252:131–140.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|