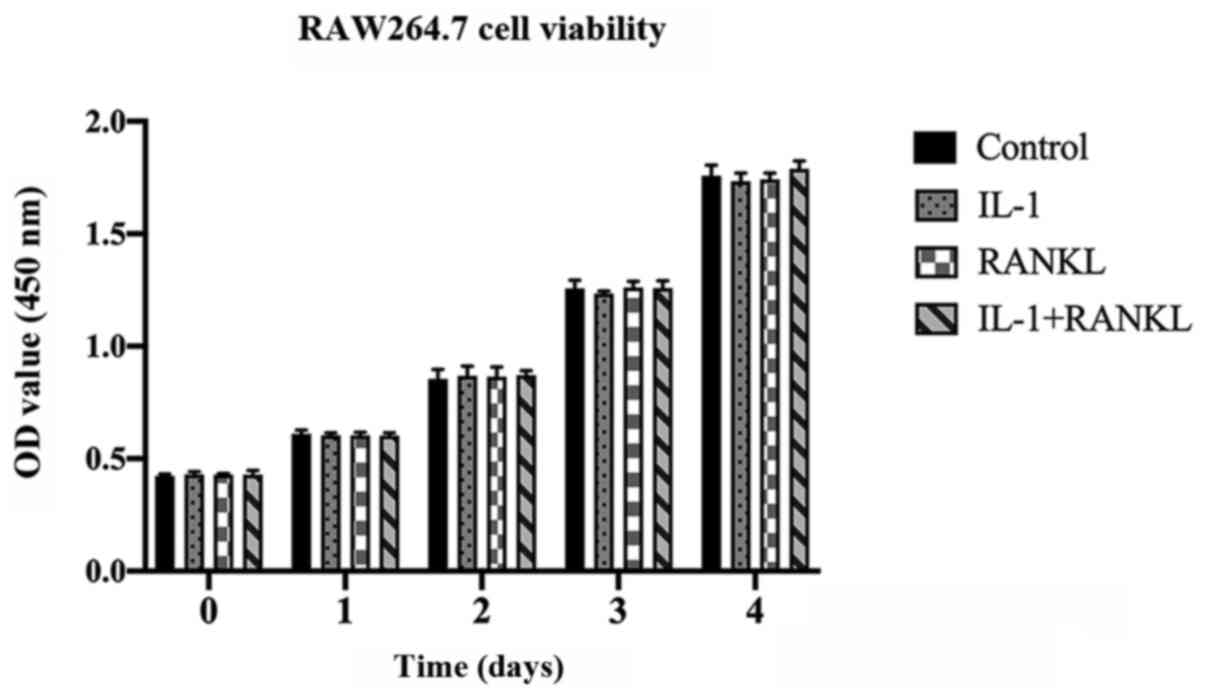
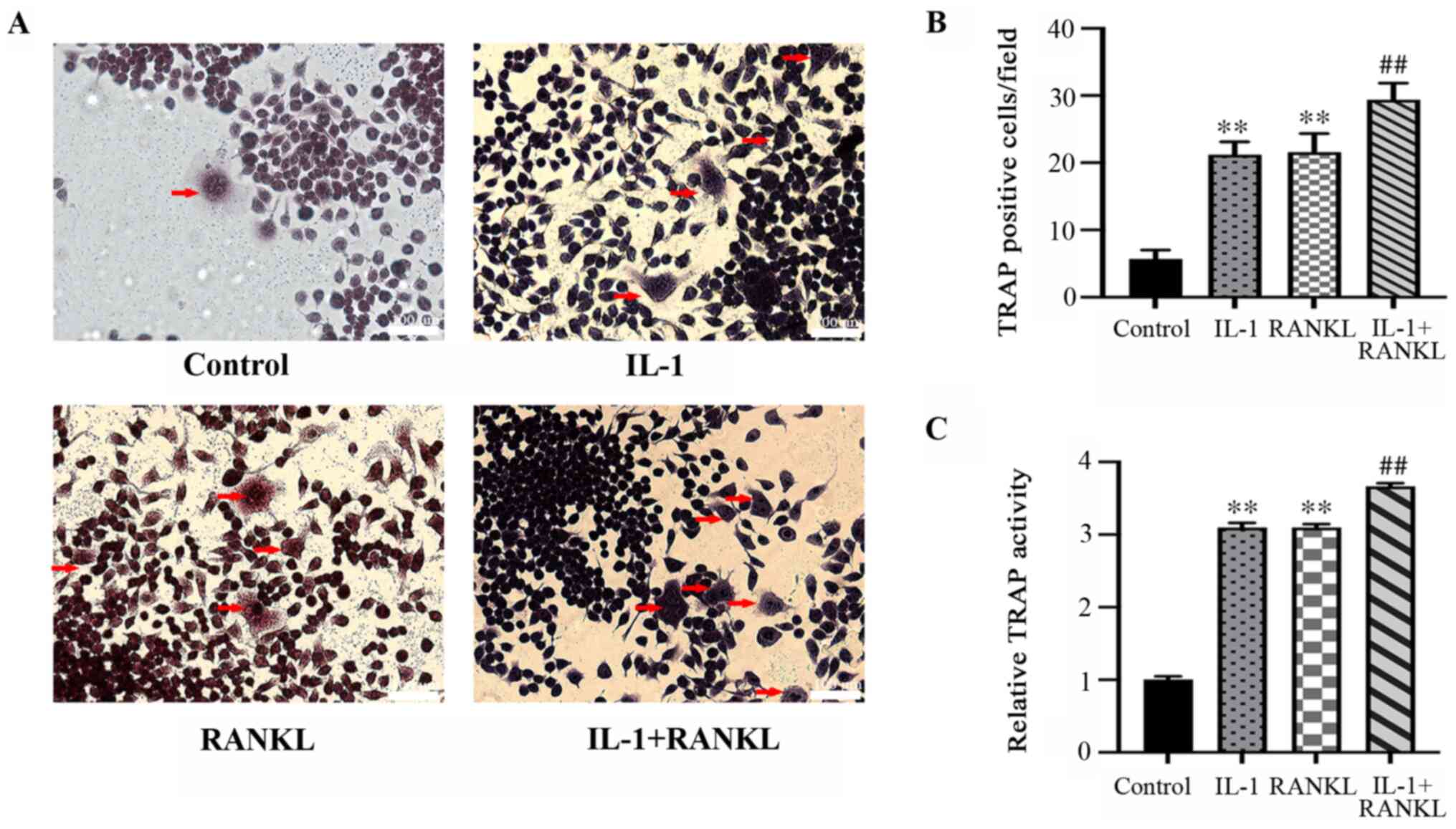
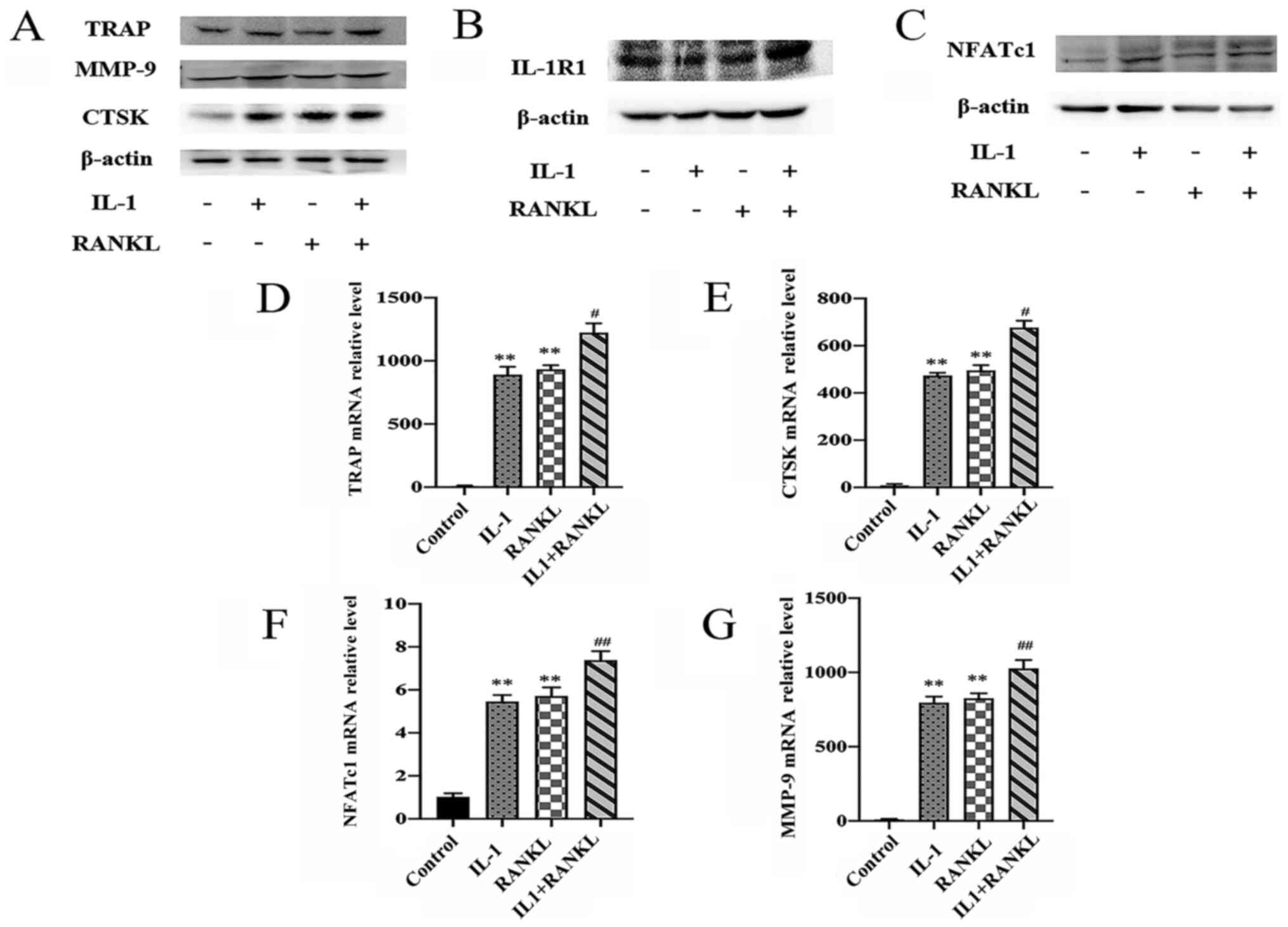
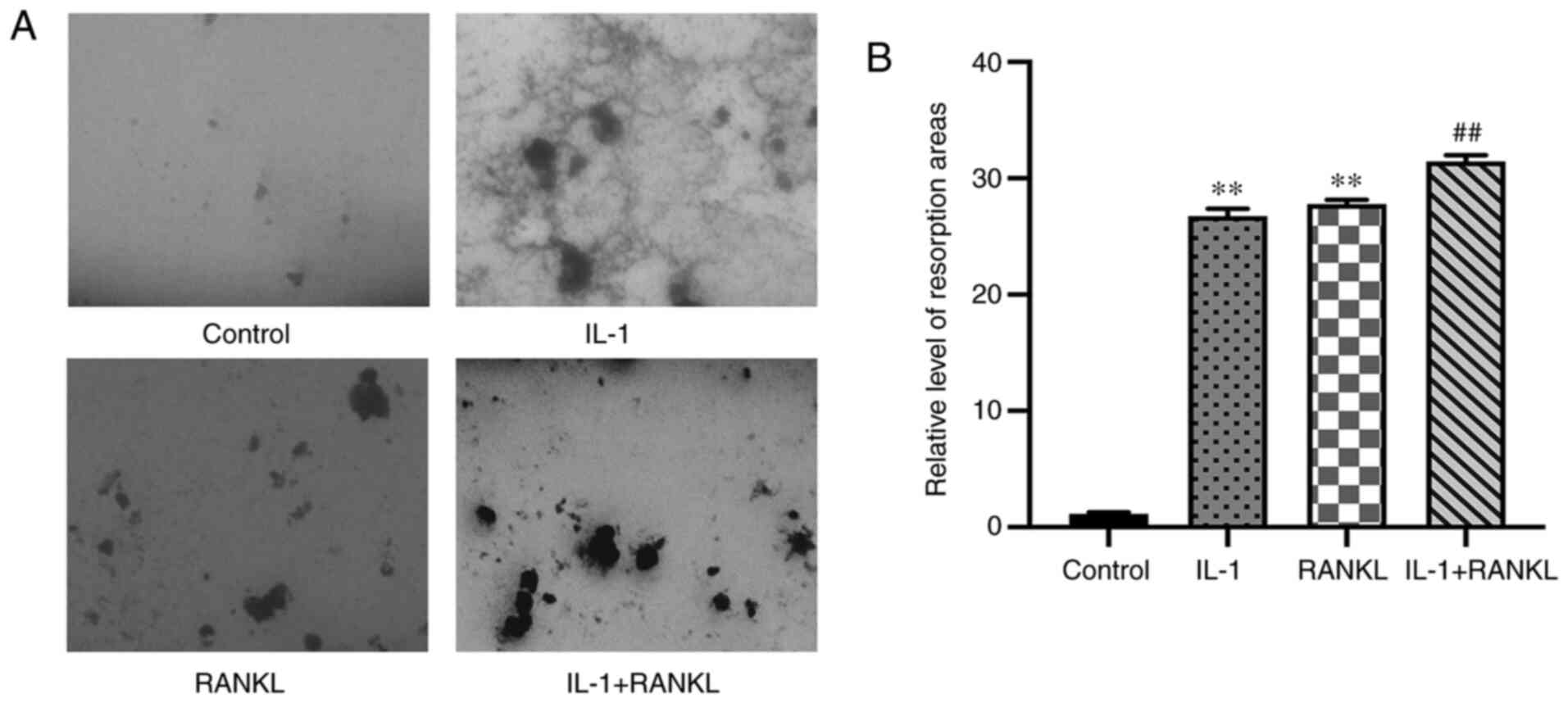
|
1
|
Roodman GD: Mechanisms of bone metastasis.
N Engl J Med. 350:1655–1664. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Brooks PJ, Jang JJ, Silver AS,
Arora PD, Mcculloch CA and Glogauer M: Role of actin filaments in
fusopod formation and osteoclastogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1853:1715–1724. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pi Y, Liang H, Yu Q, Yin Y, Xu H, Lei Y,
Han Z and Tian J: Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field
inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in RAW264.7
cells by scavenging reactive oxygen species. Mol Med Rep.
49:4129–4136. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Park KH, Park B, Yoon DS, Kwon SH, Shin
DM, Lee JW, Lee HG, Shim JH, Park JH and Lee JM: Zinc inhibits
osteoclast differentiation by suppression of
Ca2+-Calcineurin-NFATc1 signaling pathway. Cell Commun
Signal. 11(74)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xu J, Wang C, Han R, Pavlos N, Phan T,
Steer JH, Bakker AJ, Joyce DA and Zheng MH: Evidence of reciprocal
regulation between the high extracellular calcium and RANKL signal
transduction pathways in RAW cell derived osteoclasts. J Cell
Physiol. 202:554–562. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Feng W, Guo J and Li M: RANKL-independent
modulation of osteoclastogenesis. J Oral Biosci. 61:16–21.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kong Y, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, Tan HL, Timms
E, Capparelli C, Morony S, Van G, Itie A, Khoo W, et al: OPGL is a
key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and
lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 397:315–323. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fuller K, Wong B, Fox S, Choi Y and
Chambers TJ: TRANCE is necessary and sufficient for
osteoblast-mediated activation of bone resorption in osteoclasts. J
Exp Med. 188:997–1001. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Takayanagi H: Osteoimmunology: Shared
mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat
Rev Immunol. 7:292–304. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ikebuchi Y, Aoki S, Honma M, Hayashi M,
Sugamori Y, Khan M, Kariya Y, Kato G, Tabata Y, Penninger JM, et
al: Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse
signalling. Nature. 561:195–200. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dinarello CA: The interleuldn-1 family: 10
years of discovery. FASEB J. 8:1314–1325. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang J, Wang J, Liang X, Zhao H, Lu J, Ma
Q, Jing B and Tian F: IL-1β increases the expression of
inflammatory factors in synovial fluid-derived fibroblast-like
synoviocytes via activation of the NF-κB-mediated ERK-STAT1
signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 20:4993–5001. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hanazawa S, Nakada K, Ohmori Y, Miyoshi T,
Amano S and Kitano S: Functional role of interleukin 1 in
periodontal disease: Induction of interleukin 1 production by
Bacteroides gingivalis lipopolysaccharide in peritoneal macrophages
from C3H/HeN and C3H/HeJ mice. Infect Immun. 50:262–270.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lee YM, Fujikado N, Manaka H, Yasuda H and
Iwakura Y: IL-1 plays an important role in the bone metabolism
under physiological conditions. Int Immunol. 22:805–816.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nakamura I and Jimi E: Regulation of
osteoclast differentiation and function by interleukin-1. Vitam
Horm. 74:357–370. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Galli M, Shade Silver A, Lee W,
Song Y, Mei Y, Bachus C, Glogauer M and McCulloch CA: IL1β and TNFα
promote RANKL-dependent adseverin expression and
osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Sci. 131(jcs213967)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kudo O, Fujikawa Y, Itonaga I, Sabokbar A,
Torisu T and Athanasou NA: Proinflammatory cytokine (TNFα/IL-Iα)
induction of human osteoclast formation. J Pathol. 198:220–227.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim JH, Jin HM, Kim K, Song I, Youn BU,
Matsuo K and Kim N: The mechanism of osteoclast differentiation
induced by IL-1. J Immunol. 183:1862–1870. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nakamura I, Kadono Y, Takayanagi H, Jimi
E, Miyazaki T, Oda H, Nakamura K, Tanaka S, Rodan GA and Duong LT:
IL-1 regulates cytoskeletal organization in osteoclasts via TNF
receptor-associated factor 6/c-Src complex. J Immunol.
168:5103–5109. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N: Single-step
method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium
thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem.
162:156–159. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xiaowei W and Seed B: A PCR primer bank
for quantitative gene expression analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
31(e154)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
He JQ, Zhang YS, Chen J, Zheng S, Huang H
and Dong X: Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on the
expression of NFATc1 and CAII in mouse osteoclast-like cells. Aging
Clin Exp Res. 27:13–19. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Guo YQ, Xie CZ, Li XY, Yang J, Yu T, Zhang
RH, Zhang TQ, Saxena D, Snyder M, Wu YJ and Li X: Succinate and its
G-protein-coupled receptor stimulates osteoclastogenesis. Nat
Commun. 8(15621)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu TH, Tsai TY and Pan TM: The
anti-periodontitis effects of ethanol extract prepared using
Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei NTU 101. Nutrients.
10(472)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Takeshita S, Kaji K and Kudo A:
Identification and characterization of the new osteoclast
progenitor with macrophage phenotypes being able to differentiate
into mature osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1477–1488.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ono T and Nakashima T: Recent advances in
osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 149:325–341.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Collin-Osdoby P and Osdoby P:
RANKL-mediated osteoclast formation from murine RAW 264.7 cells.
Methods Mol Biol. 816:187–202. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wei S, Kitaura H, Zhou P, Ross FP and
Teitelbaum SL: IL-1 mediates TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Clin
Invest. 115:282–290. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jimi E, Ikebe T, Takahashi N, Hirata M,
Suda T and Koga T: Interleukin-1 alpha activates an NF-kappaB-like
factor in osteoclast-like cells. J Biol Chem. 271:4605–4608.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Watanabe Y, Namba A, Aida Y, Honda K,
Tanaka H, Suzuki N, Matsumura H and Maeno M: IL-1β suppresses the
formation of osteoclasts by increasing OPG production via an
autocrine mechanism involving celecoxib-related prostaglandins in
chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2009(308596)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lorenzo JA, Naprta A, Rao Y, Alander C,
Glaccum M, Widmer M, Gronowicz G, Kalinowski J and Pilbeam CC: Mice
lacking the type I interleukin1 receptor do not lose bone mass
after ovariectomy. Endocrinology. 139:3022–3025. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee EJ, Kim JL, Gong JH, Park SH and Kang
YH: Inhibition of osteoclast activation by phloretin through
disturbing αvβ3 integrin-c-Src pathway. Biomed Res Int.
2015(680145)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kitazawa R, Kimble RB, Vannice JL, Kung VT
and Pacifici R: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and tumor
necrosis factor binding protein decrease osteoclast formation and
bone resorption in ovariectomized mice. J Clin Invest.
94:2397–2406. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bajayo A, Goshen I, Feldman S, Csernus V,
Iverfeldt K, Shohami E, Yirmiya R and Bab I: Central IL-1 receptor
signaling regulates bone growth and mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:12956–12961. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Vargas SJ, Naprta A, Glaccum M, Lee SK,
Kalinowski J and Lorenzo JA: Interleukin-6 expression and
histomorphometry of bones from mice deficient in receptors for
interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor. J Bone Miner Res.
11:1736–1744. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shaw AT and Gravallese EM: Mediators of
inflammation and bone remodeling in rheumatic disease. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 49:2–10. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Asagiri M, Sato K, Usami T, Ochi S,
Nishina H, Yoshida H, Morita I, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Serfling E and
Takayanagi H: Autoamplification of NFATc1 expression determines its
essential role in bone homeostasis. J Exp Med. 202:1261–1269.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ma T, Miyanishi K, Suen A, Epstein NJ,
Tomita T, Smith RL and Goodman SB: Human interleukin-1-induced
murine osteoclastogenesis is dependent on RANKL, but independent of
TNF-alpha. Cytokine. 26:138–144. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lei Y, Su J, Xu H, Yu Q, Zhao M and Tian
J: Pulsed electromagnetic fields inhibit osteoclast differentiation
in RAW264.7 macrophages via suppression of the protein kinase
B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
18:447–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|