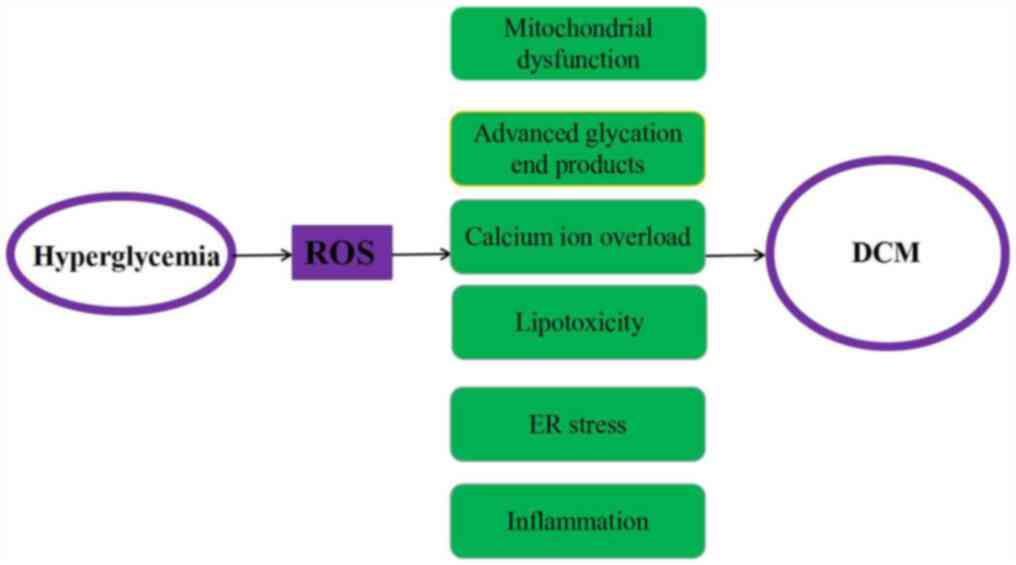
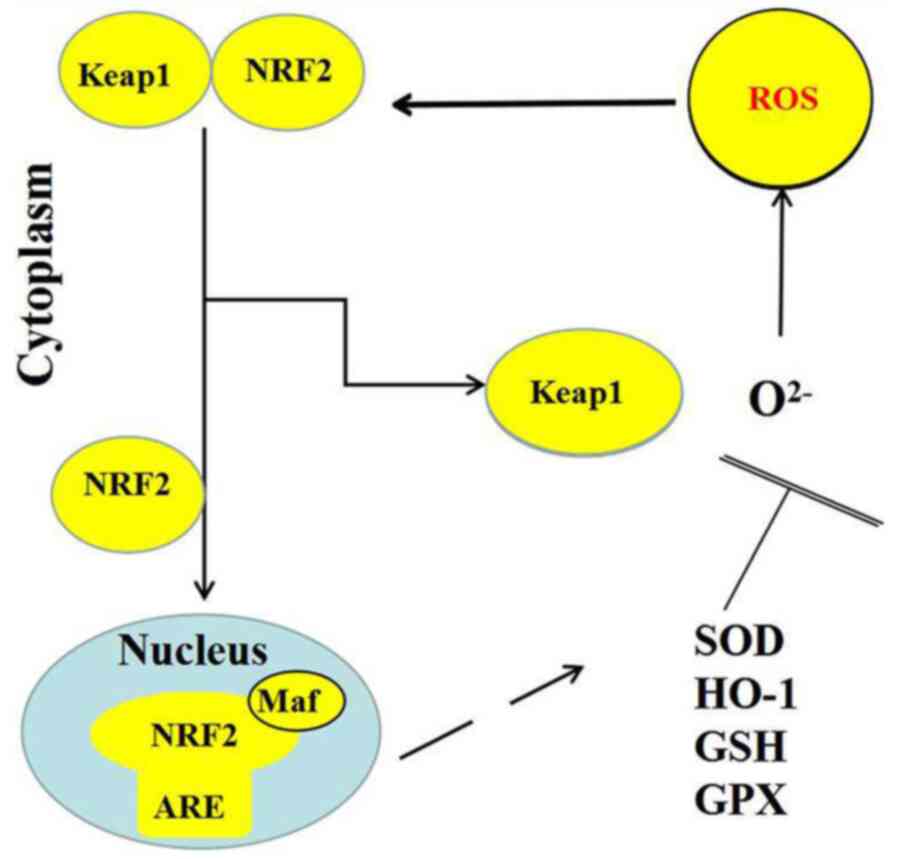
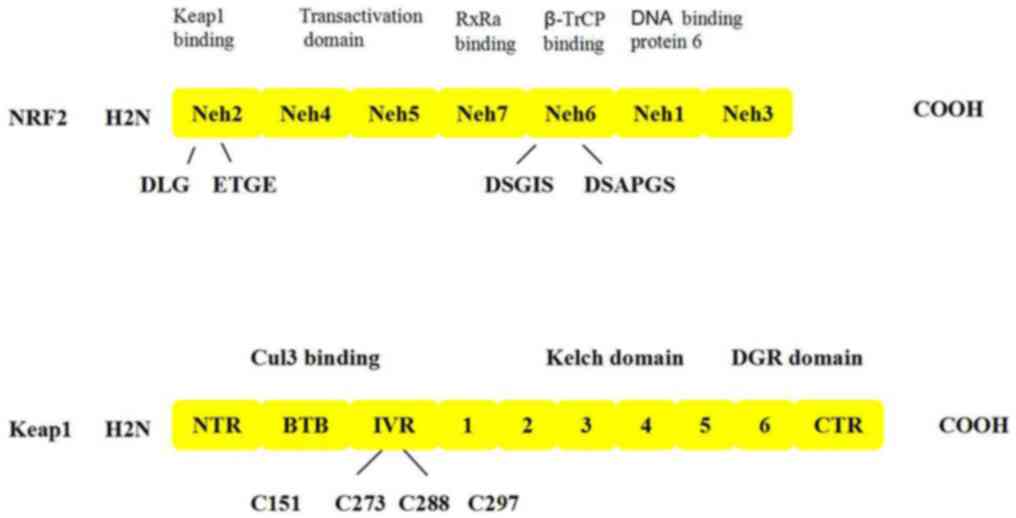
|
1
|
Schrier RW, Abdallah JG, Weinberger HH and
Abraham WT: Therapy of heart failure. Kidney Int. 57:1418–1425.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rafeian-Kopaei M, Setorki M, Doudi M,
Baradaran A and Nasri H: Atherosclerosis: Process, indicators, risk
factors and new hopes. Int J Prev Med. 5:927–946. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Majerczyk M, Choręza P, Mizia-Stec K,
Bożentowicz-Wikarek M, Brzozowska A, Arabzada H, Owczarek AJ,
Szybalska A, Grodzicki T, Więcek A, et al: Plasma level of
retinol-binding protein 4, N-terminal proBNP and renal function in
older patients hospitalized for heart failure. Cardiorenal Med.
8:237–248. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
McGillicuddy FC, Moll HP, Farouk S,
Damrauer SM, Ferran C and Reilly MP: Translational studies of A20
in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Adv Exp Med Biol.
809:83–101. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lindblom R, Ververis K, Tortorella SM and
Karagiannis TC: The early life origin theory in the development of
cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Mol Biol Rep.
42:791–797. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Scolletta S and Biagioli BE: Nergetic
myocardial metabolism and oxidative stress: Let's make them our
friends in the fight against heart failure. Biomed Pharmacother.
64:203–207. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Reczek CR and Chandel NS: ROS-dependent
signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 33C:8–13. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ichihara S: The pathological roles of
environmental and redox stresses in cardiovascular diseases.
Environ Health Prev Med. 18:177–184. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Brahmanaidu P, Sathibabu U and Ganapathy
S: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Molecular mechanisms, detrimental
effects of conventional treatment, and beneficial effects of
natural therapy. Heart Fail Rev. 24:279–299. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chakraborty S and Ain R: Nitric-oxide
synthase trafficking inducer is a pleiotropic regulator of
endothelial cell function and signaling. J Biol Chem.
292:6600–6620. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Balakumar P, Singh AP and Singh M: Rodent
models of heart failure. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 56:1–10.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Furfaro AL, Traverso N, Domenicotti C,
Piras S, Moretta L, Marinari UM, Pronzato MA and Nitti M: The
NRF2/HO-1 axis in cancer cell growth andchemoresistance. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2016(1958174)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Suzuki T and Yamamoto M: Molecular basis
of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Radic Biol Med. 88:93–100.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jay PY, Berul CI, Tanaka M, Ishii M,
Kurachi Y and Izumo S: Cardiac conduction and arrhythmia: Insights
from Nkx2.5 mutations in mouse and humans. Novartis Found Symp.
250:227–238. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Namani A, Li Y, Wang XJ and Tang X:
Modulation of Nrf2 signaling pathway by nuclear receptors:
Implications for cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:1875–1885.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto M, Kensler TW and Motohashi H:
The KEAP1-NRF2 system: A thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for
maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 98:1169–1203.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li W and Kong AN: Molecular mechanisms of
Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol Carcinog. 48:91–104.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nguyen T, Nioi P and Pickett CB: The
Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its
activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 284:13291–13295.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Corradi D, Callegari S, Maestri R, Benussi
S and Alfieri O: Structural remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Nat
Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 5:782–796. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Saracino MR and Lampe JW: Phytochemical
regulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: Implications for cancer
prevention. Nutr Cancer. 59:121–141. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Niture SK, Kaspar JW and Shen J: Nrf2
signaling and cell survival. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 244:37–42.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dhamodharan U, Ponjayanthi B, Sireesh D,
Bhakkiyalakshmi E and Ramkumar KM: Association of single-nucleotide
polymorphisms of the KEAP1 gene with the risk of various human
diseases and its functional impact using in silico analysis.
Pharmacol Res. 137:205–218. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tian W, Rojo de la Vega M, Schmidlin CJ,
Ooi A and Zhang DD: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1)
differentially regulates nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factors
1 and 2 (NRF1 and NRF2). J Biol Chem. 293:2029–2040.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mohan S and Gupta D: Crosstalk of
toll-like receptors signaling and Nrf2 pathway for regulation of
inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:1866–1878. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Niture SK, Khatri R and Jaiswal AK:
Regulation of NRF2-an update. Free Radic Biol Med. 66:36–44.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Katoh Y, Iida K, Kang MI, Kobayashi A,
Mizukami M, Tong KI, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Itoh K and Yamamoto M:
Evolutionary conserved N-terminal domain of Nrf2 is essential for
the Keap1-mediated degradation of the protein by proteasome. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 433:342–350. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Baird L, Llères D, Swift S and
Dinkova-Kostova AT: Regulatory flexibility in the Nrf2-mediated
stress response is conferred by conformational cycling of the
Keap1-Nrf2 protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:15259–15264. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hegedűs K, Nagy P, Gáspári Z and Juhász G:
The putative HORMA domain protein Atg101 dimerizes and is required
for starvation-induced and selective autophagy in
Drosophila. Biomed Res Int. 2014(470482)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Baird L and Dinkova-Kostova AT: The
cytoprotective role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Arch Toxicol.
85:241–272. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao Q, Liu Z and Huang B: PEDF improves
cardiac function in rats subjected to myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ROS generation via
PEDF-R. Int J Mol Med. 41:3243–3252. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sporn MB and Liby KT: NRF2 and cancer: The
good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:564–571. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cameron BD, Sekhar KR, Ofori M and Freeman
ML: The role of Nrf2 in the response to normal tissue radiation
injury. Radiat Res. 190:99–106. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xiang MJ, Namani A, Wu SJ and Wang XL:
Nrf2: Bane or blessing in cancer? J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
140:1251–1259. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lau YS, Ling WC, Murugan D and Mustafa MR:
Boldine ameliorates vascular oxidative stress and endothelial
dysfunction: Therapeutic implication for hypertension and diabetes.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 65:522–531. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gillet FX, Bournaud C, Antonino de Souza
Júnior JD and Grossi-de-Sa MF: Plant-parasitic nematodes: Towards
understanding molecular players in stress responses. Ann Bot.
119:775–789. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lu MC, Ji JA, Jiang ZY and You QD: The
Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic
target: An update. Med Res Rev. 36:924–963. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cheng D, Wu R, Guo Y and Kong AN:
Regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling: The role of epigenetics. Curr
Opin Toxicol. 1:134–138. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chiou YS, Huang Q, Ho CT, Wang YJ and Pan
MH: Directly interact with Keap1 and LPS is involved in the
anti-inflammatory mechanisms of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate in
LPS-induced macrophages and endotoxemia. Free Radic Biol Med.
94:1–16. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Itoh K, Ye P, Matsumiya T, Tanji K and
Ozaki T: Emerging functional cross-talk between the Keap1-Nrf2
system and mitochondria. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 56:91–97.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zenkov NK, Menshchikova EB and Tkachev VO:
Keap1/Nrf2/ARE redox-sensitive signaling system as a
pharmacological target. Biochemistry (Mosc). 78:19–36.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Tu J, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Dai Y, Li N, Yang F,
Zhang Q, Brann DW and Wang R: Cell-permeable peptide targeting the
Nrf2-Keap1 interaction: A potential novel therapy for global
cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. 35:14727–14739. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wakabayashi N, Slocum SL, Skoko JJ, Shin S
and Kensler TW: When NRF2 talks, who's listening? Antioxid Redox
Signal. 13:1649–1663. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons
ML, Chaitman BR and White HD: Task Force for the Universal
Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Third universal definition of
myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 9:620–633. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ostadal B, Drahota Z, Houstek J, Milerova
M, Ostadalova I, Hlavackova M and Kolar F: Developmental and sex
difference in cardiac tolerance to ischemia/reperfusion injury: The
role of mitochondria1. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
97:808–814. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xue M, Momiji H, Rabbani N, Barker G,
Bretschneider T, Shmygol A, Rand DA and Thornalley PJ: Frequency
modulated translocational oscillations of Nrf2 mediate the
antioxidant response element cytoprotective transcriptional
response. Antioxid Redox Signal. 23:613–629. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chai D, Zhang L, Xi S, Cheng Y, Jiang H
and Hu R: Nrf2 activation induced by Sirt1 ameliorates acute lung
injury after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion through NOX4-mediated
gene regulation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:781–792. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Schwarz M, Lossow K, Kopp JF, Schwerdtle T
and Kipp AP: Crosstalk of Nrf2 with the trace elements selenium,
iron, zinc, and copper. Nutrients. 11(2112)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mazzei L, Docherty NG and Manucha W:
Mediators and mechanisms of heat shock protein 70 based
cytoprotection in obstructive nephropathy. Cell Stress Chaperones.
20:893–906. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mann GE, Bonacasa B, Ishii T and Siow RC:
Targeting the redox sensitive Nrf2-Keap1 defense pathway in
cardiovascular disease: Protection afforded by dietary isoflavones.
Curr Opin Pharmacol. 9:139–145. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Xu B, Zhang J, Strom J, Lee S and Chen QM:
Myocardial ischemic reperfusion induces de novo NRF2 protein
translation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1842:1638–1647. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ashrafian H, Czibik G, Bellahcene M,
Aksentijević D, Smith AC, Mitchell SJ, Dodd MS, Kirwan J, Byme JJ,
Ludwiq C, et al: Fumarate is cardioprotective via activation of the
NRF2 antioxidant pathway. Cell Metab. 15:361–371. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Farías JG, Carrasco-Pozo C, Carrasco Loza
R, Sepúlveda N, Álvarez P, Quezada M, Quiñones J, Molina V and
Castillo RL: Polyunsaturated fatty acid induces cardioprotection
against ischemia- reperfusion through the inhibition of NF-kappaB
and induction of NRF2. Exp Biol Med. 242:1104–1114. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bhogal RH, Weston CJ, Velduis S, G D
Leuvenink H, Reynolds GM, Davies S, Nyguet-Thin L, Alfaifi M,
Shepard EL, Boteon Y, et al: The reactive oxygen species-mitophagy
signaling pathway regulates liver endothelial cell survival during
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Liver Transpl. 24:1437–1452.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z: ROS,
mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol.
17:422–427. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Dinkova-Kostova AT and Abramov AY: The
emerging role of NRF2 in mitochondrial function. Free Radic Biol
Med. 88:179–188. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ludtmann MH, Angelova PR, Zhang Y, Abramov
AY and Dinkova-Kostova AT: NRF2 affects the efficiency of
mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Biochem J. 457:415–424.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Glinka YY and Youdim MB: Inhibition of
mitochondrial complexes I and IV by 6-hydroxydopamine. Eur J
Pharmacol. 292:329–332. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Baechler BL, Bloemberg D and Quadrilatero
J: Mitophagy regulates mitochondrial network signaling, oxidative
stress, and apoptosis during myoblast differentiation. Autophagy.
15:1606–1619. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Qiu M, Zhang S, Ke L, Tang H, Zeng X and
Liu J: JS-K enhances chemosensitivity of prostate cancer cells to
Taxol via reactive oxygen species activation. Oncol Lett.
17:757–764. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang Y, Sano M, Shinmura K, Tamaki K,
Katsumata Y, Matsuhashi T, Morizane S, Ito H, Hishiki T, Endo J, et
al: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal protects against cardiac
ischemiareperfusion injury via the NRF2-dependent pathway. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 49:576–586. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Anedda A, López-Bernardo E, Acosta-Iborra
B, Saadeh Suleiman M, Landázuri MO and Cadenas S: The transcription
factor NRF2 promotes survival by enhancing the expression of
uncoupling protein 3 under conditions of oxidative stress. Free
Radic Biol Med. 61C:395–407. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Curfman G: Stem cell therapy for heart
failure: An unfulfilled promise? JAMA. 321:1186–1187.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Chen YL, Fan J, Cao L, Han TL, Zeng M, Xu
Y, Ling Z and Yin Y: Unique mechanistic insights into the
beneficial effects of angiotensin-(1-7) on the prevention of
cardiac fibrosis: A metabolomic analysis of primary cardiac
fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 378:158–170. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Ambrosi N, Guerrieri D, Caro F, Sanchez F,
Haeublein G, Casadei D, Incardona C and Chuluyan E: Alpha lipoic
acid: A therapeutic strategy that tend to limit the action of free
radicals in transplantation. Int J Mol Sci. 19(102)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kageyama S, Saito T, Obata M, Koide RH,
Ichimura Y and Komatsu M: Negative regulation of the Keap1-Nrf2
pathway by a p62/Sqstm1 splicing variant. Mol Cell Biol.
38:e00642–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Erpicum P, Rowart P, Defraigne JO,
Krzesinski JM and Jouret F: What we need to know about
lipid-associated injury in case of renal ischemia-reperfusion. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 315:F1714–F1719. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lee LY, Harberg C, Matkowskyj KA, Cook S,
Roenneburg D, Werner S, Johnson J and Foley DP: Overactivation of
the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2-antioxidant
response element pathway in hepatocytes decreases hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Liver Transpl. 22:91–102.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kaplinsky E: DAPA-HF trial: Dapagliflozin
evolves from a glucose-lowering agent to a therapy for heart
failure. Drugs Context. 9(2019-11-3)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Virani SA, Sharma V, McCann M, Koehler J,
Tsang B and Zieroth S: Prospective evaluation of integrated device
diagnostics for heart failure management: Results of the TRIAGE-HF
study. ESC Heart Fail. 5:809–817. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD,
Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C,
Gomez-Sanchez MA, et al: ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and
treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The task force
for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure
2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in
collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC.
Eur Heart J. 33:1787–1847. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Zhu X, Oseghale AR, Nicole LH, Li B and
Pace BS: Mechanisms of NRF2 activation to mediate fetal hemoglobin
induction and protection against oxidative stress in sickle cell
disease. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 244:171–182. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Rajasekaran NS, Varadharaj S, Khanderao
GD, Davidson CJ, Kannan S, Firpo MA, Zweier JL and Benjamin IJ:
Sustained activation of nuclear erythroid 2-related factor
2/antioxidant response element signaling promotes reductive stress
in the human mutant protein aggregation cardiomyopathy in mice.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:957–971. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Ichikawa T, Li J, Meyer CJ, Janicki JS,
Hannink M and Cui T: Dihydro-CDDO-trifluoroethyl amide (dh404), a
novel Nrf2 activator, suppresses oxidative stress in
cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 4(e8391)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Li J, Zhang C, Xing Y, Janicki JS,
Yamamoto M, Wang XL, Tang DQ and Cui T: Up-regulation of p27(kip1)
contributes to Nrf2-mediated protection against angiotensin
II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 90:315–324.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Burchfield JS, Xie M and Hill JA:
Pathological ventricular remodeling: Mechanisms: Part 1 of 2.
Circulation. 128:388–400. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Takimoto E and Kass DA: Role of oxidative
stress in cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling. Hypertension.
49:241–248. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Guan Y, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Tian H, Li A and
Han X: Effects of PP2A/Nrf2 on experimental diabetes
mellitus-related cardiomyopathy by regulation of autophagy and
apoptosis through ROS dependent pathway. Cell Signal.
62(109339)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Murdoch CE, Zhang M, Cave AC and Shah AM:
NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signalling in cardiac hypertrophy,
remodelling and failure. Cardiovasc Res. 71:208–215.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Shuai W, Kong B, Fu H, Shen C, Jiang X and
Huang H: MD1 Deficiency promotes inflammatory atrial remodelling
induced by high-fat diets. Can J Cardiol. 35:208–216.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Yu C, Lin H, Yang H, Kong SL, Zhang Q and
Lee SW: Progression of systolic abnormalities in patients with
‘isolated’ diastolic heart failure and diastolic dysfunction.
Circulation. 105:1195–1201. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y and
Kang YJ: Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium:
Mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway.
Diabetes. 51:1938–1948. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Fassett J, Xu X, Kwak D, Zhu G, Fassett
EK, Zhang P, Wang H, Maver B, Bache RJ and Chen Y: Adenosine kinase
attenuates cardiomyocyte microtubule stabilization and protects
against pressure overload-induced hypertrophy and LV dysfunction. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 130:49–58. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Hafstad AD, Nabeebaccus AA and Shah AM:
Novel aspects of ROS signalling in heart failure. Basic Res
Cardiol. 108(359)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Gupta S, Das B and Sen S: Cardiac
hypertrophy: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 9:623–652. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Sabri A, Hughie HH and Lucchesi PA:
Regulation of hypertrophic and apoptotic signaling pathways by
reactive oxygen species in cardiac myocytes. Antioxid Redox Signal.
5:731–740. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Zhang X, Xiao Z, Yao J, Zhao G, Fa X and
Niu J: Participation of protein kinase C in the activation of Nrf2
signaling by ischemic preconditioning in the isolated rabbit heart.
Mol Cell Biochem. 372:169–179. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Zhao WY, Zhao TQ, Chen YJ, Ahokas RA and
Sun Y: Oxidative stress mediates cardiac fbrosis by enhancing
transforming growth factor-beta1 in hypertensive rats. Mol Cell
Biochem. 317:43–50. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Yang T, Sun Y, Mao L, Zhang M, Li Q, Zhang
L, Shi Y, Leak RK, Chen J and Zhang F: Brain ischemic
preconditioning protects against ischemic injury and preserves the
blood-brain barrier via oxidative signaling and Nrf2 activation.
Redox Biol. 17:323–337. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC,
Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, Lackland DT, LeFevre ML,
MacKenzie TD, Oqedeqbe O, et al: Evidence-based guideline for the
management of high blood pressure in adults: Report from the panel
members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee. JAMA.
311:507–520. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Hu CM, Chen YH, Chiang MT and Chau LY:
Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiac
hypertrophy in vitro and in vivo. Circulation. 110:309–316.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Mancusi C, Canciello G, Izzo R, Damiano S,
Grimaldi MG, Luca N, Simone G, Trimarco B and Losi MA: Left atrial
dilatation: A target organ damage in young to middle-age
hypertensive patients. The Campania Salute Network. Int J Cardiol.
265:229–233. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Wang ZH, Liu JL, Wu L, Yu Z and Yang HT:
Concentration-dependent wrestling between detrimental and
protective effects of H2O2 during myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death Dis. 5(e1297)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Yao SY, Liu J, Li Y, Wang M, Wang C and
Xue H: Association between plasma microRNA-29a and left ventricular
hypertrophy in patients with hypertension. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan
Bing Za Zhi. 47:215–220. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
95
|
Mitra A, Basak T, Datta K, Naskar S,
Sengupta S and Sarkar S: Role of a-crystallin B as a regulatory
switch in modulating cardiomyocyte apoptosis by mitochondria or
endoplasmic reticulum during cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial
infarction. Cell Death Dis. 4(e582)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Delmar M and Makita N: Cardiac connexins,
mutations and arrhythmias. Curr Opin Cardiol. 27:236–241.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Stout JM, Gousset MU, Drummond HA, Gray W
III, Pruett BE and Stec DE: Sex-specific effects of heme
oxygenase-2 deficiency on renovascular hypertension. J Am Soc
Hypertens. 7:328–335. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Tian C, Gao L, Zimmerman MC and Zucker IH:
Myocardial infarction-induced microRNA-enriched exosomes contribute
to cardiac Nrf2 dysregulation in chronic heart failure. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 314:H928–H939. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Tham YK, Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Weeks KL and
McMullen JR: Pathophysiology of cardiac hypertrophy and heart
failure: Signaling pathways and novel therapeutic targets. Arch
Toxicol. 89:1401–1438. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Yang KC and Dudley JSC: Oxidative stress
and atrial fibrillation: Finding a missing piece to the puzzle.
Circulation. 128:1724–1726. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Barry SP, Davidson SM and Townsend PA:
Molecular regulation of cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 40:2023–2039. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Maulik SK and Kumar S: Oxidative stress
and cardiac hypertrophy: A review. Toxicol Mech Methods.
22:359–366. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Baruteau AE, Probst V and Abriel H:
Inherited progressive cardiac conduction disorders. Curr Opin
Cardiol. 30:33–39. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Chang YJ, Hsiao HJ, Hsia SH, Lin JJ, Hwang
MS, Chung HT, Chen CL, Huang YC and Tsai MH: Analysis of clinical
parameters and echocardiography as predictors of fatal pediatric
myocarditis. PLoS One. 14(e0214087)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Zhao YS, An JR, Yang S, Guan P, Yu FY, Li
W, Li JR, Guo Y, Sun ZM and Ji ES: Hydrogen and oxygen mixture to
improve cardiac dysfunction and myocardial pathological changes
induced by intermittent hypoxia in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(7415212)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Nakamura M and Sadoshima J: Mechanisms of
physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Rev
Cardiol. 15:387–407. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Li J, Ichikawa T, Villacorta L, Janicki
JS, Brower GL, Yamamoto M and Cui T: Nrf2 protects against
maladaptive cardiac responses to hemodynamic stress. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1843–1850. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Nakamura M and Sadoshima J: Cardiomyopathy
in obesity, insulin resistance or diabetes. J Physiol.
598:2977–2993. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Felker GM, Thompson RE, Hare JM, Hruban
RH, Clemetson DE, Howard DL, Baughman K and Kasper EK: Underlying
causes and long-term survival in patients with initially
unexplained cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 342:1077–1184.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Quinaglia T, Oliveira DC, Matos-Souza JR
and Sposito AC: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Factual or factoid? Rev
Assoc Med Bras (1992). 65:61–69. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Cooper LT Jr: Myocarditis. N Engl J Med.
360:1526–1538. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Althunibat OY, Al Hroob AM, Abukhalil MH,
Germoush MO, Bin-Jumah M and Mahmoud AM: Fisetin ameliorates
oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Life Sci. 221:83–92. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Zhao X, Cai A, Peng Z, Liang W, Xi H, Li
P, Chen G, Yu J and Chen L: JS-K induces reactive oxygen
species-dependent anti-cancer effects by targeting mitochondria
respiratory chain complexes in gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
23:2489–2504. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Ansley DM and Wang B: Oxidative stress and
myocardial injury in the diabetic heart. J Pathol. 229:232–241.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Hernández M, Wicz S and Corral RS:
Cardioprotective actions of curcumin on the pathogenic
NFAT/COX-2/prostaglandin E2 pathway induced during Trypanosoma
cruzi infection. Phytomedicine. 23:1392–1400. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Ndisang JF, Lane N, Syed N and Jadhav A:
Up-regulating the heme oxygenase system with hemin improves insulin
sensitivity and glucose metabolism in adult spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Endocrinology. 151:549–560. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Jiménez-Osorio AS, García-Niño WR,
González-Reyes S, Álvarez-Mejía AE, Guerra-León S, Salazar-Segovia
J, Falcón I, Montes de Oca-Solano H, Madero M and Pedraza-Chaverri
J: The effect of dietary supplementation with curcumin on redox
status and Nrf2 activation in patients with nondiabetic or diabetic
proteinuric chronic kidney disease: A pilot study. J Ren Nutr.
26:237–244. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Soundararajan P and Kim JS:
Anti-carcinogenic glucosinolates in cruciferous vegetables and
their antagonistic effects on prevention of cancers. Molecules.
23(2983)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Wang J, Wang S, Wang W, Chen J, Zhang Z,
Zheng Q, Liu Q and Cai L: Protection against diabetic
cardiomyopathy is achieved using a combination of sulforaphane and
zinc in type 1 diabetic OVE26 mice. J Cell Mol Med. 23:6319–6330.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Zhang Z, Wang S, Zhou S, Yan X, Wang Y,
Chen J, Mellen N, Kong M, Gu J, Tan Y, et al: Sulforaphane prevents
the development of cardiomyopathy in type 2 diabetic mice probably
by reversing oxidative stress-induced inhibition of LKB1/AMPK
pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 77:42–52. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Bai Y, Wang X, Zhao S, Ma C, Cui J and
Zheng Y: Sulforaphane protects against cardiovascular disease via
Nrf2 activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015(407580)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Delucchi F, Berni R, Frati C, Cavalli S,
Graiani G, Sala R, Chaponnier C, Gabbiani G, Calani L, Rio DD, et
al: Resveratrol treatment reduces cardiac progenitor cell
dysfunction and prevents morpho-functional ventricular remodeling
in type-1 diabetic rats. PLoS One. 7(e39836)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Sun X, Shan A, Wei Z and Xu B: Intravenous
mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate myocardial
inflammation in the dilated cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 503:2611–2618. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Ge ZD, Lian Q, Mao X and Xia Z: Current
status and challenges of NRF2 as a potential therapeutic target for
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Int Heart J. 60:512–520. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
El-Agamy DS, El-Harbi KM, Khoshhal S,
Ahmed N, Elkablawy MA, Shaaban AA and Abo-Haded HM: Pristimerin
protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and fibrosis
through modulation of Nrf2 and MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways.
Cancer Manag Res. 11:47–61. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Zhou S, Jin J, Bai T, Sachleben LR Jr, Cai
L and Zheng Y: Potential drugs which activate nuclear factor
E2-related factor 2 signaling to prevent diabetic cardiovascular
complications: A focus on fumaric acid esters. Life Sci. 134:56–62.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Saidu NE, Noé G, Cerles O, Cabel L,
Kavian-Tessler N, Chouzenoux S, Bahuaud M, Chéreau C, Nicco C,
Leroy K, et al: Dimethyl fumarate controls the NRF2/DJ-1 axis in
cancer cells: Therapeutic applications. Mol Cancer Ther.
16:529–539. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Brennan MS, Patel H, Allaire N, Thai A,
Cullen P, Rvan S, Lukashev M, Bista P, Huang R, Rhodes KJ and
Scannevin RH: Pharmacodynamics of dimethyl fumarate are tissue
specific and involve Nrf2-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 24:1058–1071. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Bomprezzi R: Dimethyl fumarate in the
treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: An overview.
Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 8:20–30. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Ganeshpurkar A and Saluja AK: The
pharmacological potential of rutin. Saudi Pharm J. 25:149–164.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Moore PK, Griffiths RJ and Lofts FJ: The
effect of some flavone drugs on the conversion of prostacyclin to
6-oxoprostaglandin E1. Biochem Pharmacol. 32:2813–2817.
1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Gao HC, Zhu K, Gao HM, Miao CS, Zhang LN,
Liu W and Xin H: Role of tissue transglutaminase in the
pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy and the intervention effect
of rutin. Exp Ther Med. 9:1103–1108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Sayed AS, Xia K, Salma U, Yang T and Peng
J: Diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic role of circulating miRNAs
in cardiovascular diseases. Heart Lung Circ. 23:503–510.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Chen S, Puthanveetil P, Feng B, Matkovich
SJ, Dorn GW II and Chakrabarti S: Cardiac miR-133a overexpression
prevents early cardiac fibrosis in diabetes. J Cell Mol Med.
18:415–421. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Chen K, Ma Y, Wu S, Zhuang Y, Liu X, Lv L
and Zhang G: Construction and analysis of a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA
network based on competitive endogenous RNA reveals functional
lncRNAs in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Med Rep. 20:1393–1403.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Lin M and Mao ZJ: lncRNA-mRNA competing
endogenous RNA network in IR-hepG2 cells ameliorated by APBBR
decreasing ROS levels: A systematic analysis. PeerJ.
8(e8604)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Dludla PV, Nkambule BB, Dias SC and
Johnson R: Cardioprotective potential of N-acetyl cysteine against
hyperglycaemia-induced oxidative damage: A protocol for a
systematic review. Syst Rev. 6(96)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Mansueto G, Benincasa G, Della Mura N,
Nicoletti GF and Napoli C: Epigenetic-sensitive liquid biomarkers
and personalised therapy in advanced heart failure: A focus on
cell-free DNA and microRNAs. J Clin Pathol. 73:535–543.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Zhang X, Dong S, Jia Q, Zhang A, Li Y, Zhu
Y, Lv S and Zhang J: The microRNA in ventricular remodeling: The
miR-30 family. Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20190788)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Raut SK, Singh GB, Rastogi B, Saikia UN,
Mittal A, Dogra N, Singh S, Prasad R and Khullar M: miR-30c and
miR-181a synergistically modulate p53-p21 pathway in diabetes
induced cardiac hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem. 417:191–203.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Li M, Chen X, Chen L, Chen K, Zhou J and
Song J: MiR-1-3p that correlates with left ventricular function of
HCM can serve as a potential target and differentiate HCM from DCM.
J Transl Med. 16(161)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|