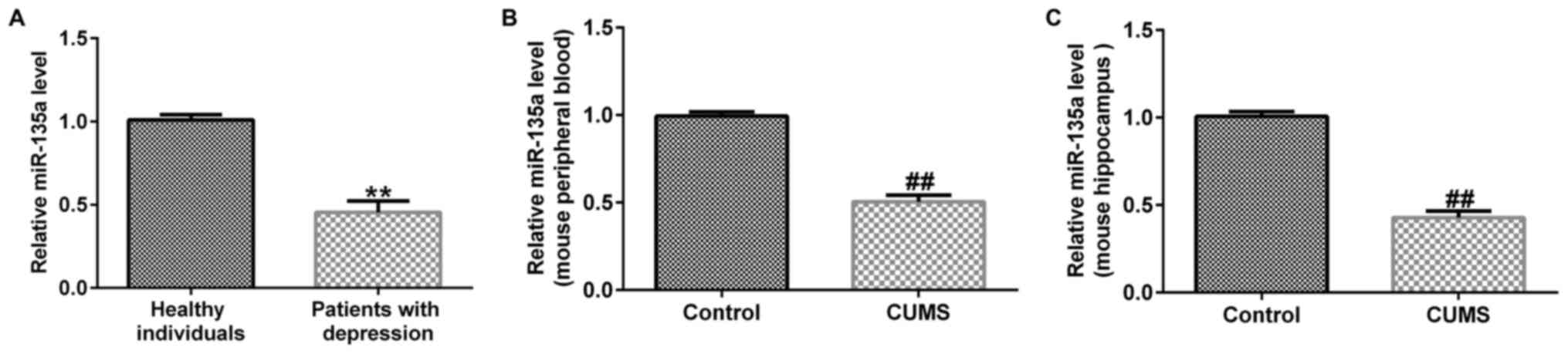
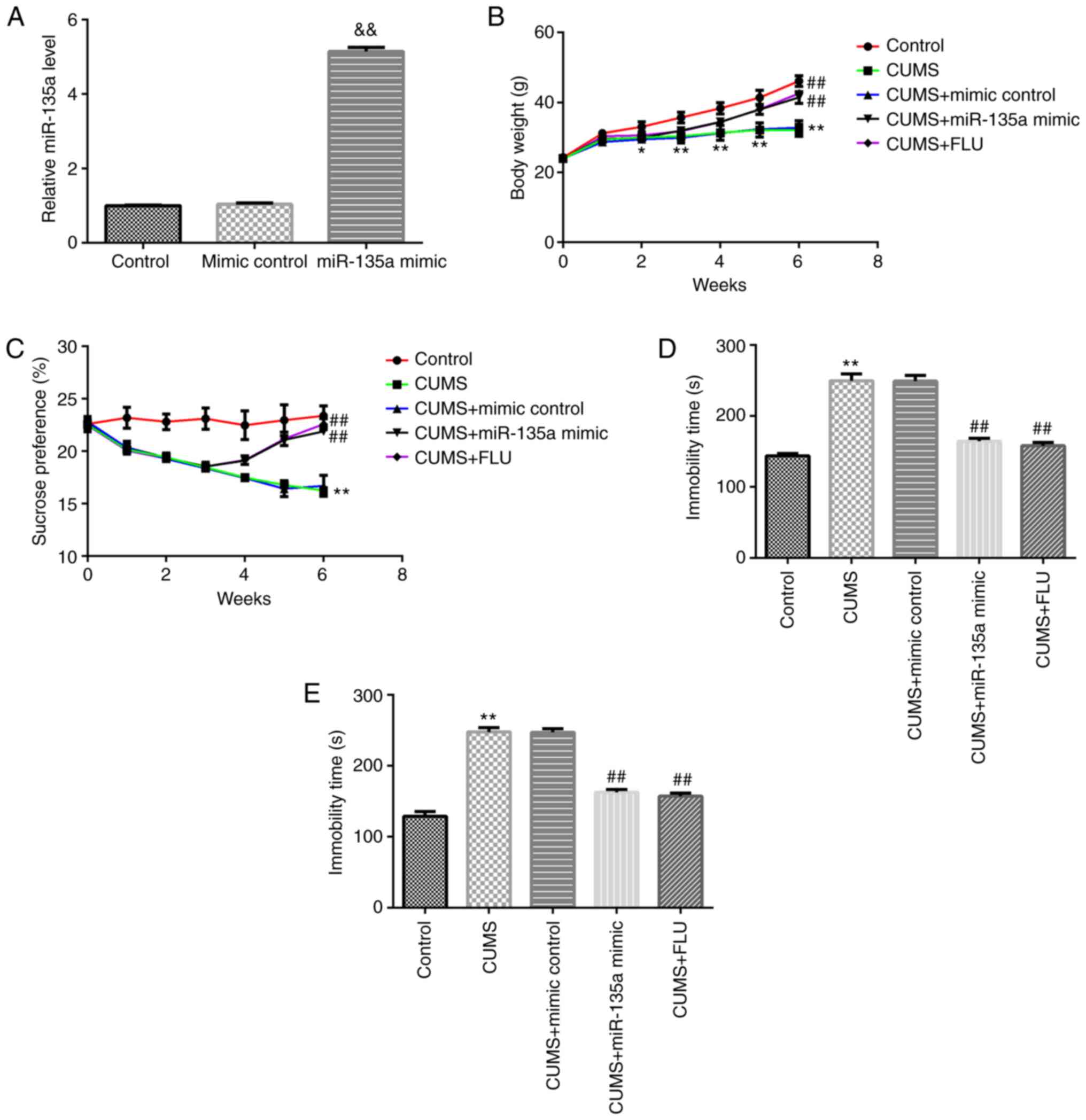
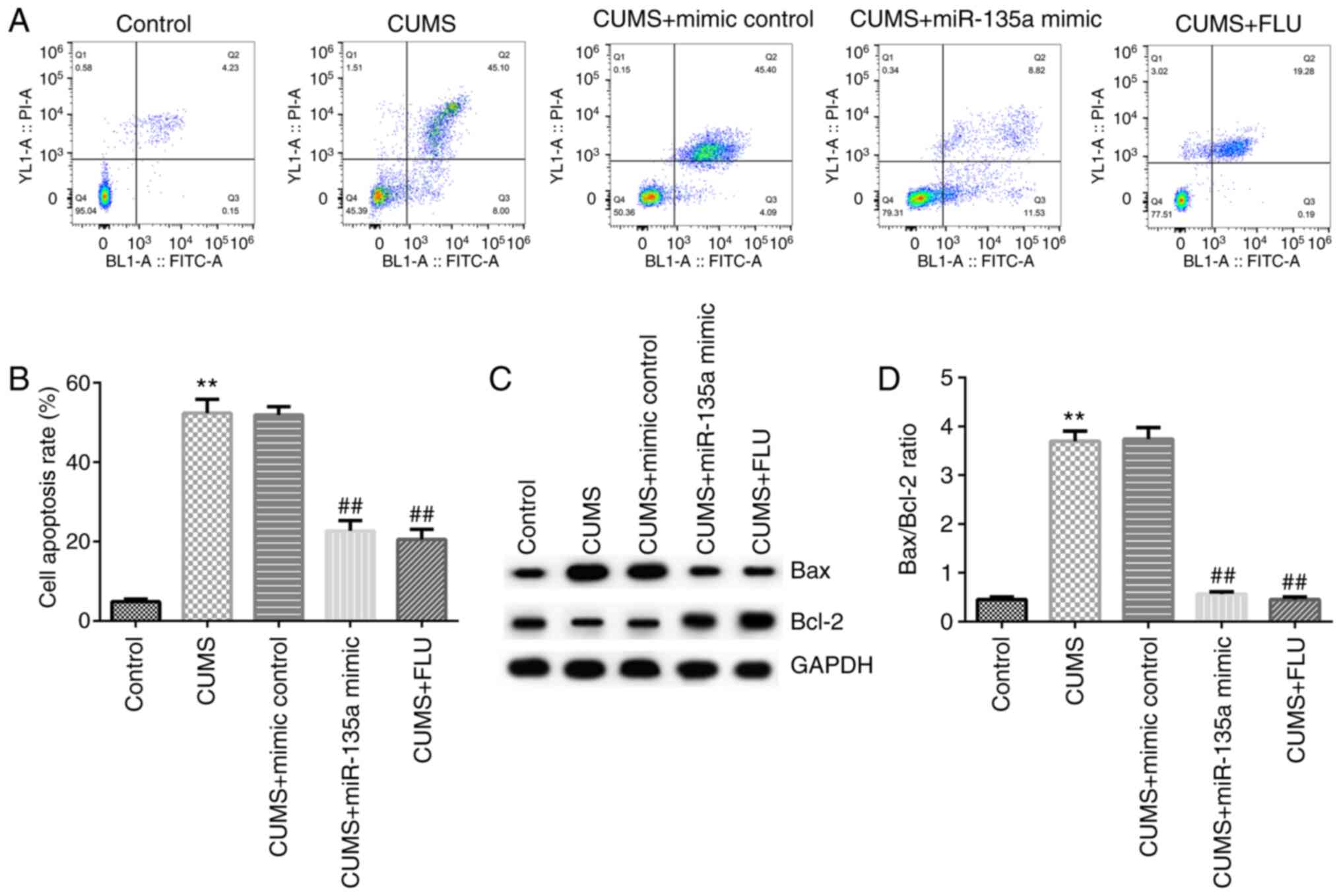
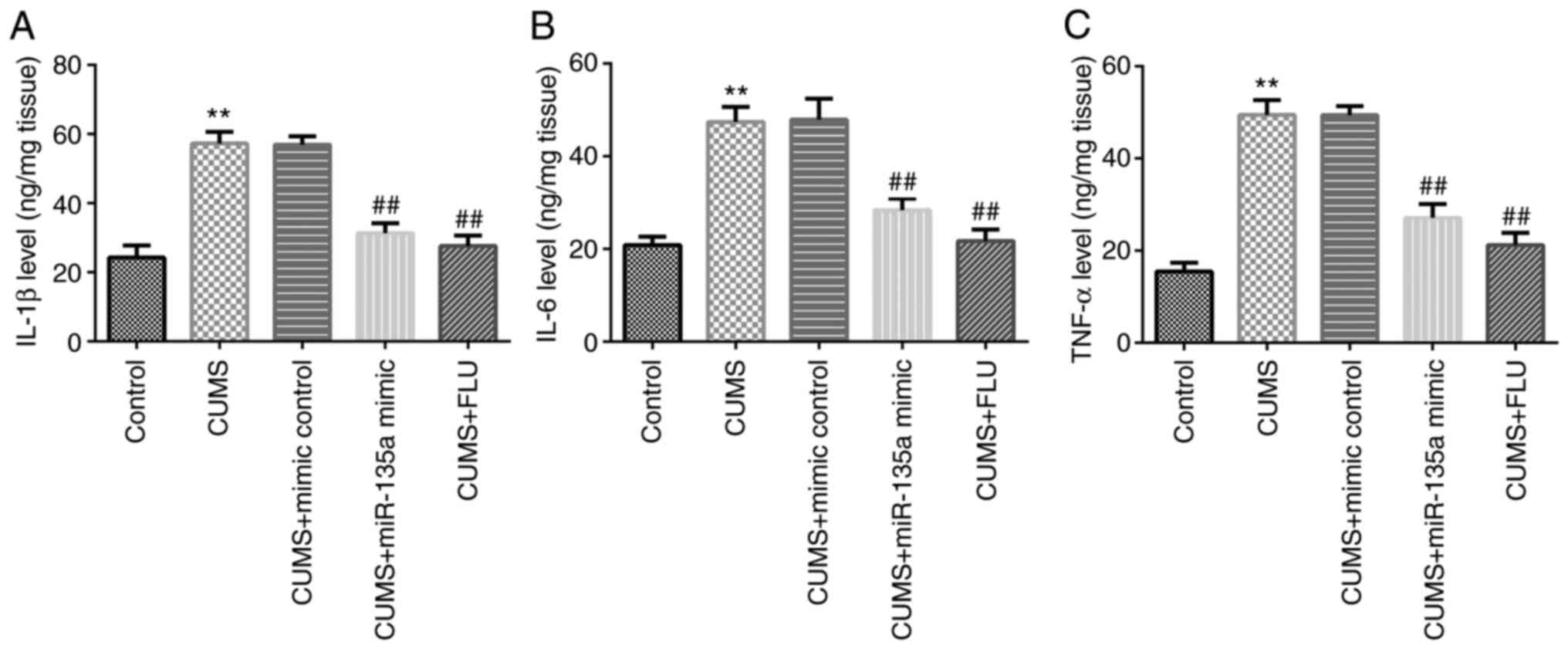
|
1
|
Bortolato B, Carvalho AF, Soczynska JK,
Perini GI and McIntyre RS: The involvement of TNF-α in cognitive
dysfunction associated with major depressive disorder: An
opportunity for domain specific treatments. Curr Neuropharmacol.
13:558–576. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Belmaker RH and Agam G: Major depressive
disorder. N Engl J Med. 358:55–68. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Prokofieva M, Koukia E and Dikeos D:
Mental health nursing in Greece: Nursing diagnoses and
interventions in major depression. Issues Ment Health Nurs.
37:556–562. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chuang YH and Kuo LM: Nurses' confidence
in providing and managing care for older persons with depressive
symptoms or depression in long-term care facilities: A national
survey. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 27:1767–1775. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xie X, Shi Y and Zhang J: Structural
network connectivity impairment and depressive symptoms in cerebral
small vessel disease. J Affect Disord. 220:8–14. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Suzuki H, Matsumoto Y, Ota H, Sugimura K,
Takahashi J, Ito K, Miyata S, Furukawa K, Arai H, Fukumoto Y, et
al: Hippocampal blood flow abnormality associated with depressive
symptoms and cognitive impairment in patients with chronic heart
failure. Circ J. 80:1773–1780. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nabavi SM, Daglia M, Braidy N and Nabavi
SF: Natural products, micronutrients, and nutraceuticals for the
treatment of depression: A short review. Nutr Neurosci. 20:180–194.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Weil-Malherbe H: The biochemistry of
affective disorders. In: Handbook of Neurochemistry. Springer,
Boston, MA, pp371-416, 1972.
|
|
9
|
Lee S, Jeong J, Kwak Y and Park SK:
Depression research: Where are we now? Mol Brain. 3:8–0.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ebmeier KP, Donaghey C and Steele JD:
Recent developments and current controversies in depression.
Lancet. 367:153–167. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Leistedt SJ and Linkowski P: Brain,
networks, depression, and more. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 23:55–62.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kessler RC: The costs of depression.
Psychiatr Clin North Am. 35:1–14. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ota KT and Duman RS: Environmental and
pharmacological modulations of cellular plasticity: Role in the
pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Neurobiol Dis.
57:28–37. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M,
et al: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites
and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mendell J and Olson E: . MicroRNAs in
stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 148:1172–1187.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Maes OC, Chertkow HM, Wang E and Schipper
HM: MicroRNA: Implications for Alzheimer disease and other human
CNS disorders. Curr Genomics. 10:154–168. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kocerha J, Kauppinen S and Wahlestedt C:
MicroRNAs in CNS disorders. Neuromolecular Med. 11:162–172.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zeng YB, Liang XH, Zhang GX, Jiang N,
Zhang T, Huang JY, Zhang L and Zeng XC: miRNA-135a promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by targeting
forkhead box O1. Cancer Cell Int. 16(63)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yao S, Tian C, Ding Y, Ye Q, Gao Y, Yang N
and Li Q: Down-regulation of Krüppel-like factor-4 by
microRNA-135a-5p promotes proliferation and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma by transforming growth factor-β1.
Oncotarget. 7:42566–42578. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ren JW, Li ZJ and Tu C: miR-135
post-transcriptionally regulates FOXO1 expression and promotes cell
proliferation in human malignant melanoma cells. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6356–6366. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu B, Lu X, Zhao Y, Liu C, Huang X, Chen
S, Zhu W, Zhang L and Chen M: MicroRNA-135a induces prostate cancer
cell apoptosis via inhibition of STAT6. Oncol Lett. 17:1889–1895.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gheysarzadeh A, Sadeghifard N, Afraidooni
L, Pooyan F, Mofid MR, Valadbeigi H, Bakhtiari H and Keikhavani S:
Serum-based microRNA biomarkers for major depression: miR-16,
miR-135a, and miR-1202. J Res Med Sci. 23(69)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Deng XY, Li HY, Chen JJ, Li RP, Qu R, Fu Q
and Ma SP: Thymol produces an antidepressant-like effect in a
chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in mice.
Behav Brain Res. 291:12–19. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen YP, Wang C and Xu JP: Chronic
unpredictable mild stress induced depression-like behaviours and
glutamate-glutamine cycling dysfunctions in both blood and brain of
mice. Pharm Biol. 57:280–286. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Duan CM, Zhang JR, Wan TF, Wang Y, Chen HS
and Liu L: SRT2104 attenuates chronic unpredictable mild
stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and imbalance between
microglial M1 and M2 phenotypes in the mice. Behav Brain Res.
378(112296)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lian N, Niu Q, Lei Y, Li X, Li Y and Song
X: miR-221 is involved in depression by regulating Wnt2/CREB/BDNF
axis in hippocampal neurons. Cell Cycle. 17:2745–2755.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Iñiguez SD, Riggs LM, Nieto SJ, Dayrit G,
Zamora NN, Shawhan KL, Cruz B and Warren BL: Social defeat stress
induces a depression-like phenotype in adolescent male c57BL/6
mice. Stress. 17:247–255. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B and Simon P:
The tail suspension test: A new method for screening
antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 85:367–370.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xie B, Lu C, Chen C, Zhou J and Deng Z:
miR-135a alleviates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting
NF-κB/Inflammatory signaling pathway. Mediators Inflamm.
2020(1231243)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ferrúa CP, Giorgi R, da Rosa LC, do Amaral
CC, Ghisleni GC, Pinheiro RT and Nedel F: MicroRNAs expressed in
depression and their associated pathways: A systematic review and a
bioinformatics analysis. J Chem Neuroanat.
100(101650)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Allen L and Dwivedi Y: MicroRNA mediators
of early life stress vulnerability to depression and suicidal
behavior. Mol Psychiatry. 25:308–320. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lou D, Wang J and Wang X: miR-124
ameliorates depressive-like behavior by targeting STAT3 to regulate
microglial activation. Mol Cell Probes. 48(101470)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu B, Tao T, Wang Y, Fang F, Huang Y, Chen
S, Zhu W and Chen M: hsa-miR-135a-1 inhibits prostate cancer cell
growth and migration by targeting EGFR. Tumour Biol.
37:14141–14151. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shi H, Ji Y, Zhang D, Liu Y and Fang P:
miR-135a inhibits migration and invasion and regulates EMT-related
marker genes by targeting KLF8 in lung cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 465:125–130. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yan LH, Chen ZN, Li-Li Chen J, Wei WE, Mo
XW, Qin YZ, Lin Y and Chen JS: miR-135a promotes gastric cancer
progression and resistance to oxaliplatin. Oncotarget.
7:70699–70714. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhou W, Li X, Liu F, Xiao Z, He M, Shen S
and Liu S: miR-135a promotes growth and invasion of colorectal
cancer via metastasis suppressor 1 in vitro. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 44:838–846. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shi HZ, Wang DN, Xu F, Teng JH and Wang
YL: miR-135a inhibits glioma cell proliferation and invasion by
directly targeting FOXO1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:4215–4223.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Henn FA and Vollmayr B: Stress models of
depression: Forming genetically vulnerable strains. Neurosci
Biobehav Rev. 29:799–804. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wan YQ, Feng JG, Li M, Wang MZ, Liu L, Liu
X, Duan XX, Zhang CX and Wang XB: Prefrontal cortex miR-29b-3p
plays a key role in the antidepressant-like effect of ketamine in
rats. Exp Mol Med. 50:1–14. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dey A and Hankey Giblin PA: Insights into
macrophage heterogeneity and cytokineinduced neuroinflammation in
major depressive disorder. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
11(E64)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Iwata M, Ota KT and Duman RS: The
inflammasome: Pathways linking psychological stress, depression,
and systemic illnesses. Brain Behav Immun. 31:105–114.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Rush G, O'Donovan A, Nagle L, Conway C,
McCrohan A, O'Farrelly C, Lucey JV and Malone KM: Alteration of
immune markers in a group of melancholic depressed patients and
their response to electroconvulsive therapy. J Affect Disord.
205:60–68. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Shen Z, Xu Y, Jiang X, Wang Z, Guo Y, Pan
W and Hou J: Avicularin relieves depressive-like behaviors induced
by chronic unpredictable mild stress in mice. Med Sci Monit.
24:1643–3750. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Du XJ and Lu JM: miR-135a represses
oxidative stress and vascular inflammatory events via targeting
toll-like receptor 4 in atherogenesis. J Cell Biochem.
119:6154–6161. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
den Dekker WK, Cheng C, Pasterkamp G and
Duckers HJ: Toll like receptor 4 in atherosclerosis and plaque
destabilization. Atherosclerosis. 209:314–320. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yang L and Gao C: miR-590 inhibits
endothelial cell apoptosis by inactivating the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
in atherosclerosis. Yonsei Med J. 60:298–307. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|