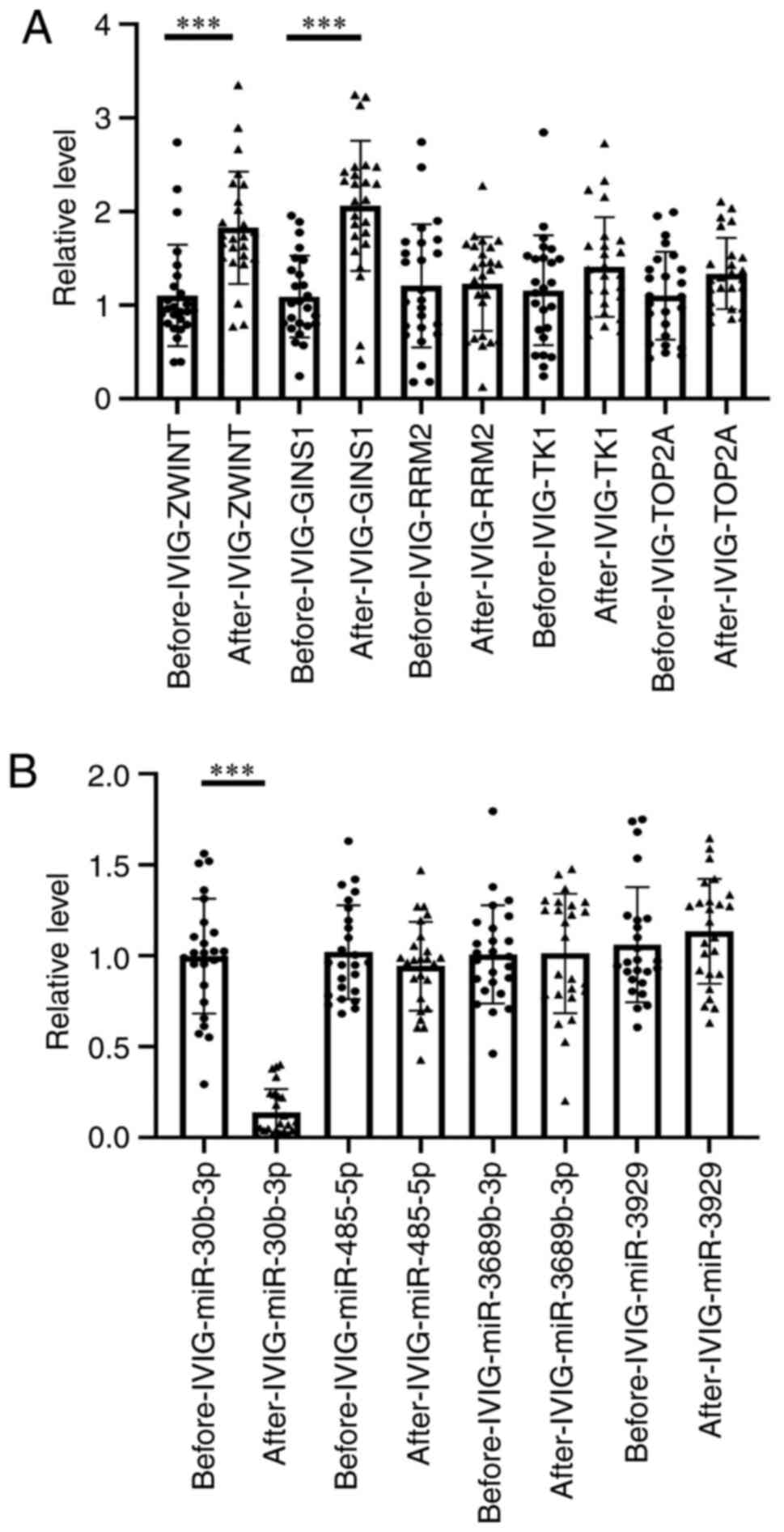
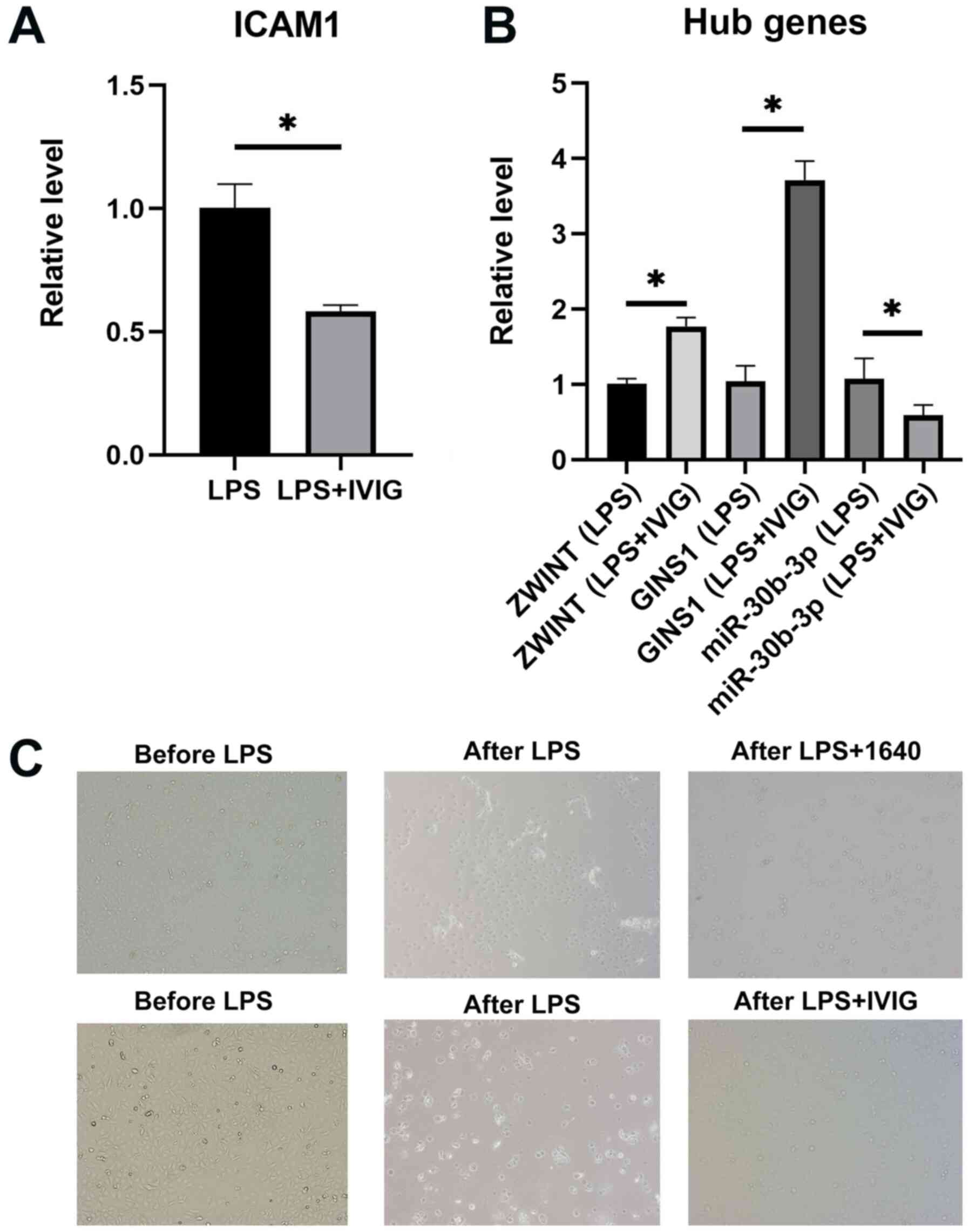
|
1
|
de Graeff N, Groot N, Ozen S, Eleftheriou
D, Avcin T, Bader-Meunier B, Dolezalova P, Feldman BM, Kone-Paut I,
Lahdenne P, et al: European consensus-based recommendations for the
diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease - the SHARE initiative.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 58:672–682. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lo MS and Newburger JW: Role of
intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of Kawasaki disease.
Int J Rheum Dis. 21:64–69. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Furusho K, Kamiya T, Nakano H, Kiyosawa N,
Shinomiya K, Hayashidera T, Tamura T, Hirose O, Manabe Y, Yokoyama
T, et al: High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for Kawasaki disease.
Lancet. 2:1055–1058. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS,
Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, Colan SD, Duffy CE, Fulton DR, Glode
MP, et al: A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as
compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki
syndrome. N Engl J Med. 324:1633–1639. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sosa T, Brower L and Divanovic A:
Diagnosis and Management of Kawasaki Disease. JAMA Pediatr.
173:278–279. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rodriguez MM and Wagner-Weiner L:
Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Pediatric Rheumatology: When to Use
It and What Is the Evidence. Pediatr Ann. 46:e19–e24.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Inagaki M and Yamada K: Inhibitory effects
of high doses of intravenous γ-globulin on platelet interaction
with the vessel wall in Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr Jpn.
33:791–798. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kaneko K, Takahashi M, Yoshimura K, Kitao
T, Yamanouchi S, Kimata T and Tsuji S: Intravenous immunoglobulin
counteracts oxidative stress in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol.
33:1086–1088. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
von Gunten S, Schaub A, Vogel M, Stadler
BM, Miescher S and Simon H-U: Immunologic and functional evidence
for anti-Siglec-9 autoantibodies in intravenous immunoglobulin
preparations. Blood. 108:4255–4259. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lau AC, Duong TT, Ito S and Yeung RS:
Intravenous immunoglobulin and salicylate differentially modulate
pathogenic processes leading to vascular damage in a model of
Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum. 60:2131–2141. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Guo Y, Tian X, Wang X and Xiao Z: Adverse
Effects of Immunoglobulin Therapy. Front Immunol.
9(1299)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang G, Xu S, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wu Y, An
J, Lin J, Yuan Z, Shen L and Si T: Identification of Key Genes and
the Pathophysiology Associated With Major Depressive Disorder
Patients Based on Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Front
Psychiatry. 11(192)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ogihara Y, Ogata S, Nomoto K, Ebato T,
Sato K, Kokubo K, Kobayashi H and Ishii M: Transcriptional
regulation by infliximab therapy in Kawasaki disease patients with
immunoglobulin resistance. Pediatr Res. 76:287–293. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R and Chu G:
Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing
radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:5116–5121.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Smyth GK: Linear models and empirical
bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray
experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 3(e3)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW,
Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, Baker AL, Jackson MA, Takahashi M,
Shah PB, et al: American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever,
Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee of the Council on
Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular and
Stroke Nursing; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia;
and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention: Diagnosis, treatment,
and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A scientific
statement for health professionals from the American Heart
Association. Circulation. 135:e927–e999. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
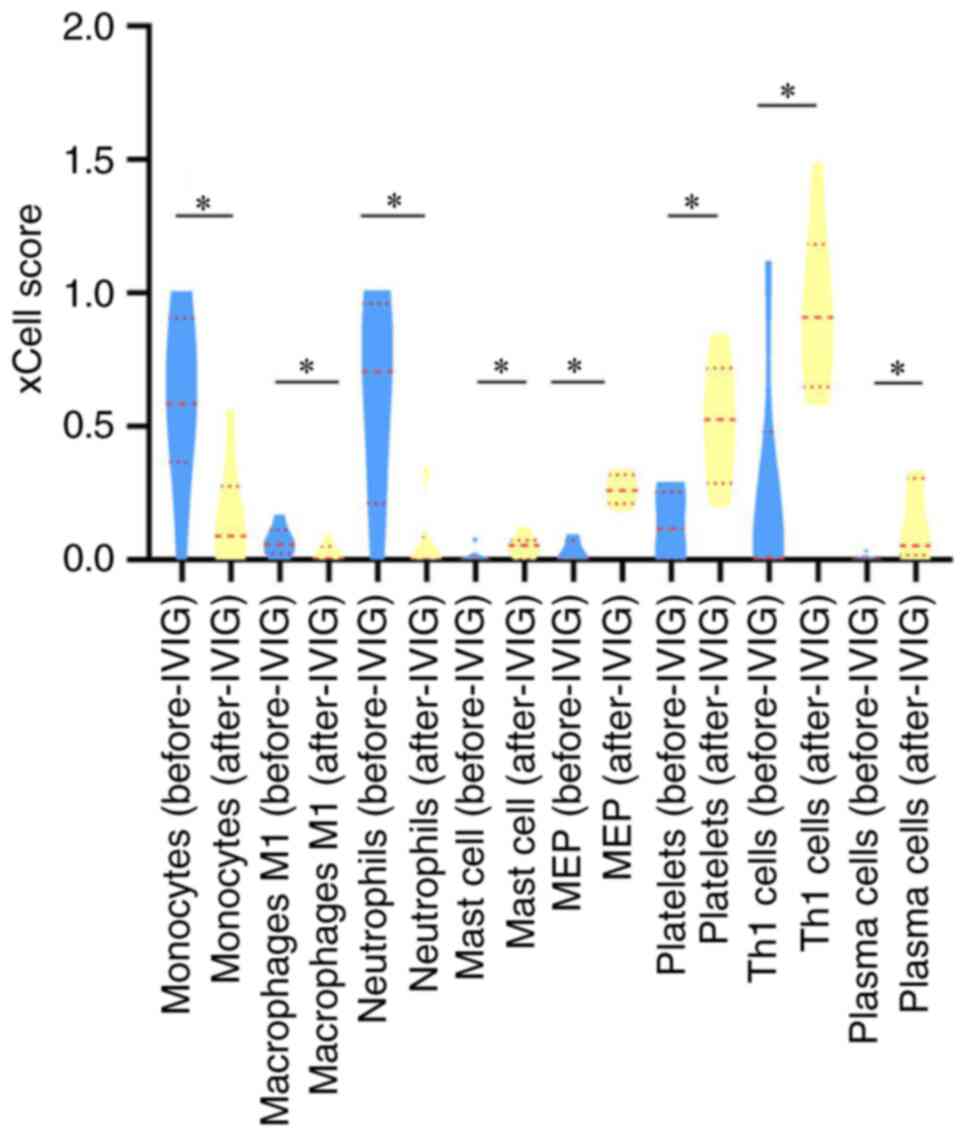
Aran D, Hu Z and Butte AJ: xCell:
Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape.
Genome Biol. 18:220. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
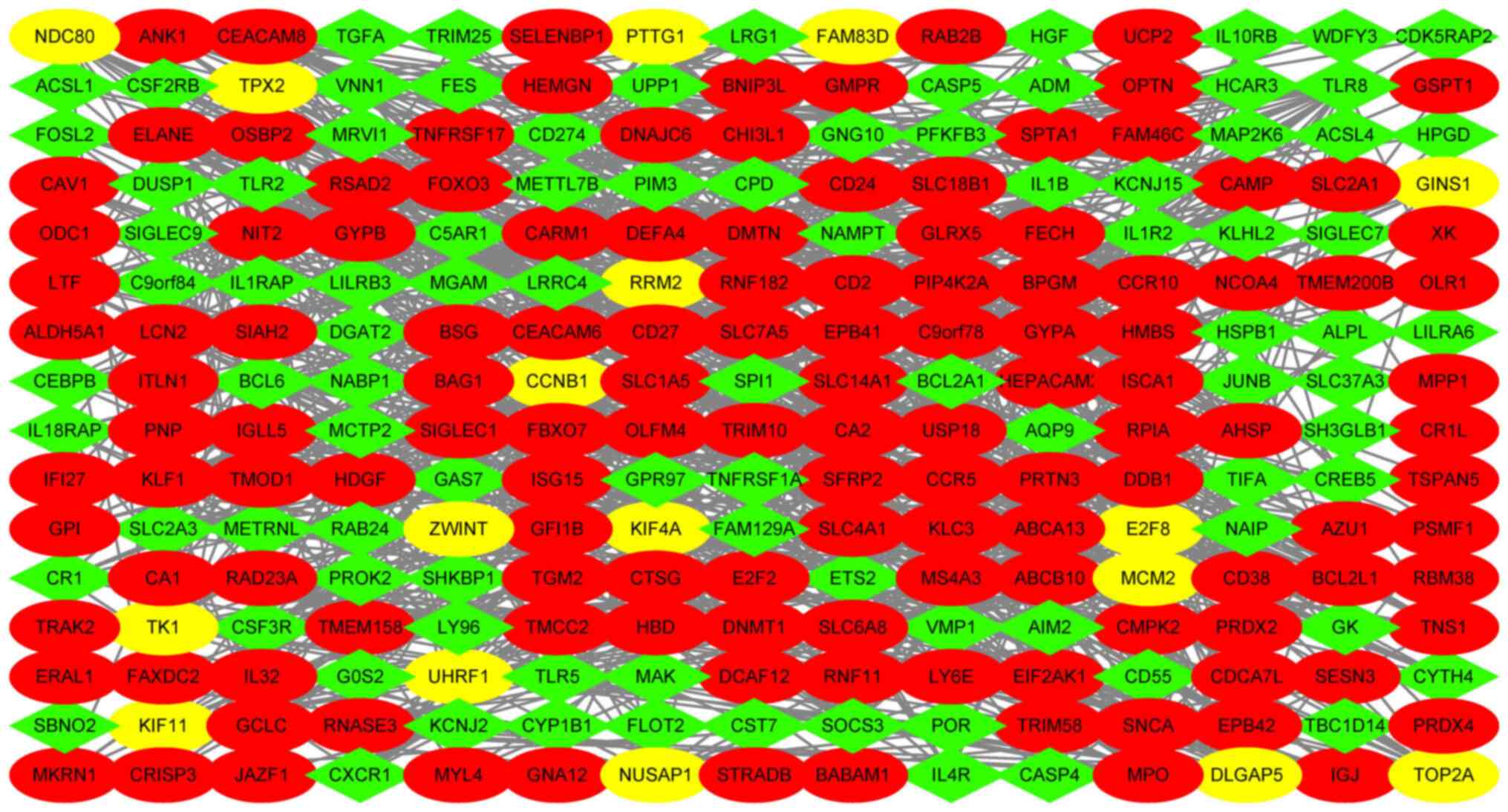
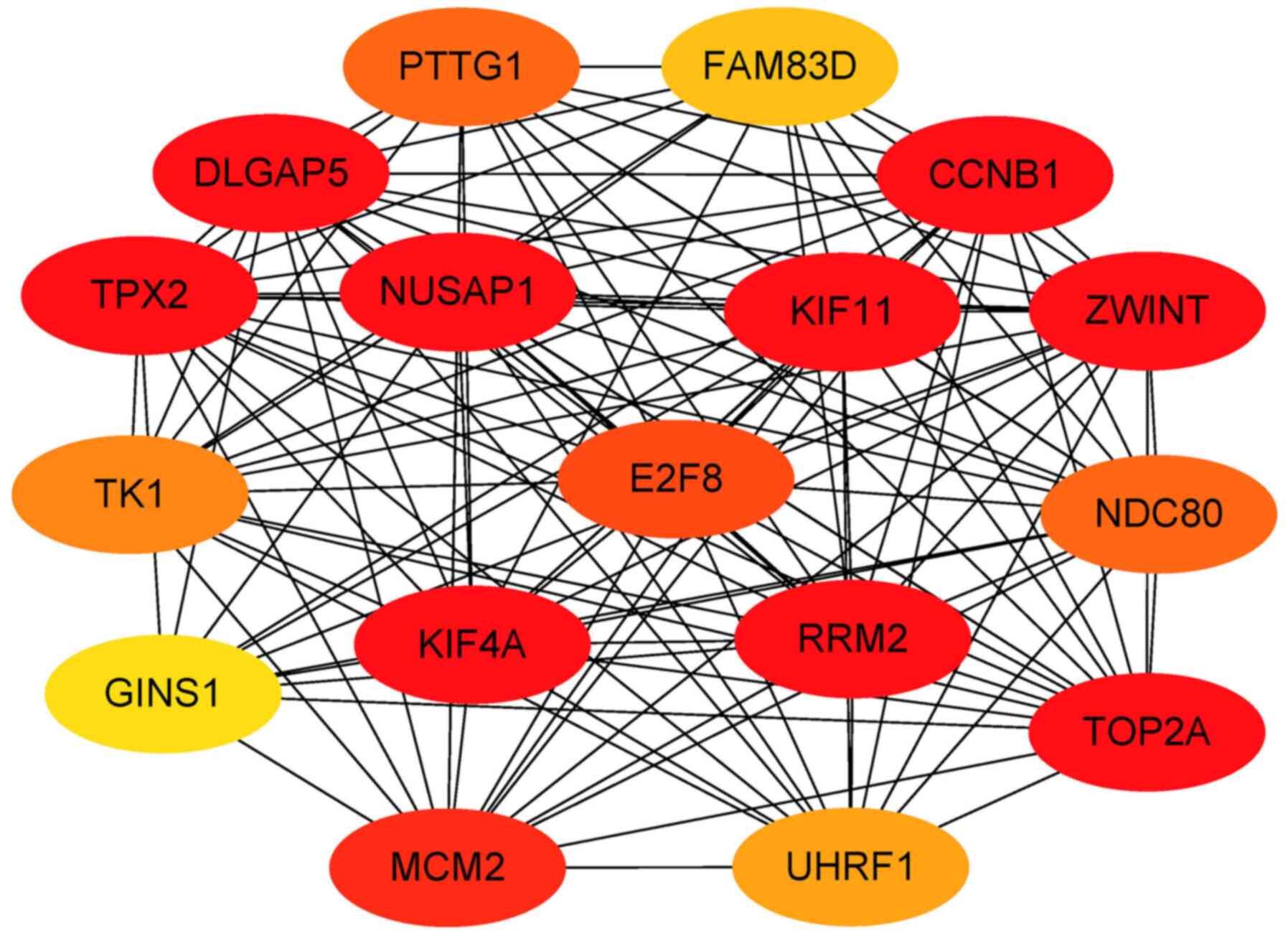
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45D:D362–D368. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4(2)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yi XH, Zhang B, Fu YR and Yi ZJ: STAT1 and
its related molecules as potential biomarkers in Mycobacterium
tuberculosis infection. J Cell Mol Med. 24:2866–2878.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Uthman L, Kuschma M, Römer G, Boomsma M,
Kessler J, Hermanides J, Hollmann MW, Preckel B, Zuurbier CJ and
Weber NC: Novel Anti-inflammatory Effects of Canagliflozin
Involving Hexokinase II in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Human
Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther: Oct 13,
2020 (Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1007/s10557-020-07083-w.
|
|
23
|
Armaroli G, Verweyen E, Pretzer C, Kessel
K, Hirono K, Ichida F, Okabe M, Cabral DA, Foell D, Brown KL, et
al: Monocyte-Derived Interleukin-1β As the Driver of
S100A12-Induced Sterile Inflammatory Activation of Human Coronary
Artery Endothelial Cells: Implications for the Pathogenesis of
Kawasaki Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71:792–804. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Dong Y, Kiuchi MG, Wang J, Li R,
Ling Z, Zhou T, Wang Z, Martinek M, Pürerfellner H, et al: Coronary
artery complication in Kawasaki disease and the importance of early
intervention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr.
170:1156–1163. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shao M-T, Hu Y-Z, Ding H, Wu Q, Pan J-H,
Zhao X-X and Pan Y-L: The overexpression of ZWINT in integrated
bioinformatics analysis forecasts poor prognosis in breast cancer.
Transl Cancer Res. 9:187–193. 2020.
|
|
26
|
Dou Z, Prifti DK, Gui P, Liu X, Elowe S
and Yao X: Recent progress on the localization of the spindle
assembly checkpoint machinery to kinetochores. Cells.
8(278)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Vargas-Rondón N, Villegas VE and
Rondón-Lagos M: The role of chromosomal instability in cancer and
therapeutic responses. Cancers (Basel). 10(4)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu Z, Huang S, Zhang Y, Sun C, Tang Y,
Zhao Q, Zhou Q, Ju W and He X: Bioinformatics analysis on multiple
Gene Expression Omnibus datasets of the hepatitis B virus infection
and its response to the interferon-alpha therapy. BMC Infect Dis.
20(84)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Han N, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Chen R and
Zhang M: ZWINT: A potential therapeutic biomarker in patients with
glioblastoma correlates with cell proliferation and invasion. Oncol
Rep. 43:1831–1844. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jones VG, Mills M, Suarez D, Hogan CA, Yeh
D, Segal JB, Nguyen EL, Barsh GR, Maskatia S and Mathew R: COVID-19
and Kawasaki disease: Novel virus and novel case. Hosp Pediatr.
10:537–540. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rowley AH and Shulman ST: The epidemiology
and pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. Front Pediatr.
6(374)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cottineau J, Kottemann MC, Lach FP, Kang
YH, Vély F, Deenick EK, Lazarov T, Gineau L, Wang Y, Farina A, et
al: Inherited GINS1 deficiency underlies growth retardation along
with neutropenia and NK cell deficiency. J Clin Invest.
127:1991–2006. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tang L, Yu W, Wang Y, Li H and Shen Z:
Anlotinib inhibits synovial sarcoma by targeting GINS1: A novel
downstream target oncogene in progression of synovial sarcoma. Clin
Transl Oncol. 21:1624–1633. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fu Y, Zhou QZ, Zhang XL, Wang ZZ and Wang
P: Identification of Hub Genes Using Co-Expression Network Analysis
in Breast Cancer as a Tool to Predict Different Stages. Med Sci
Monit. 25:8873–8890. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
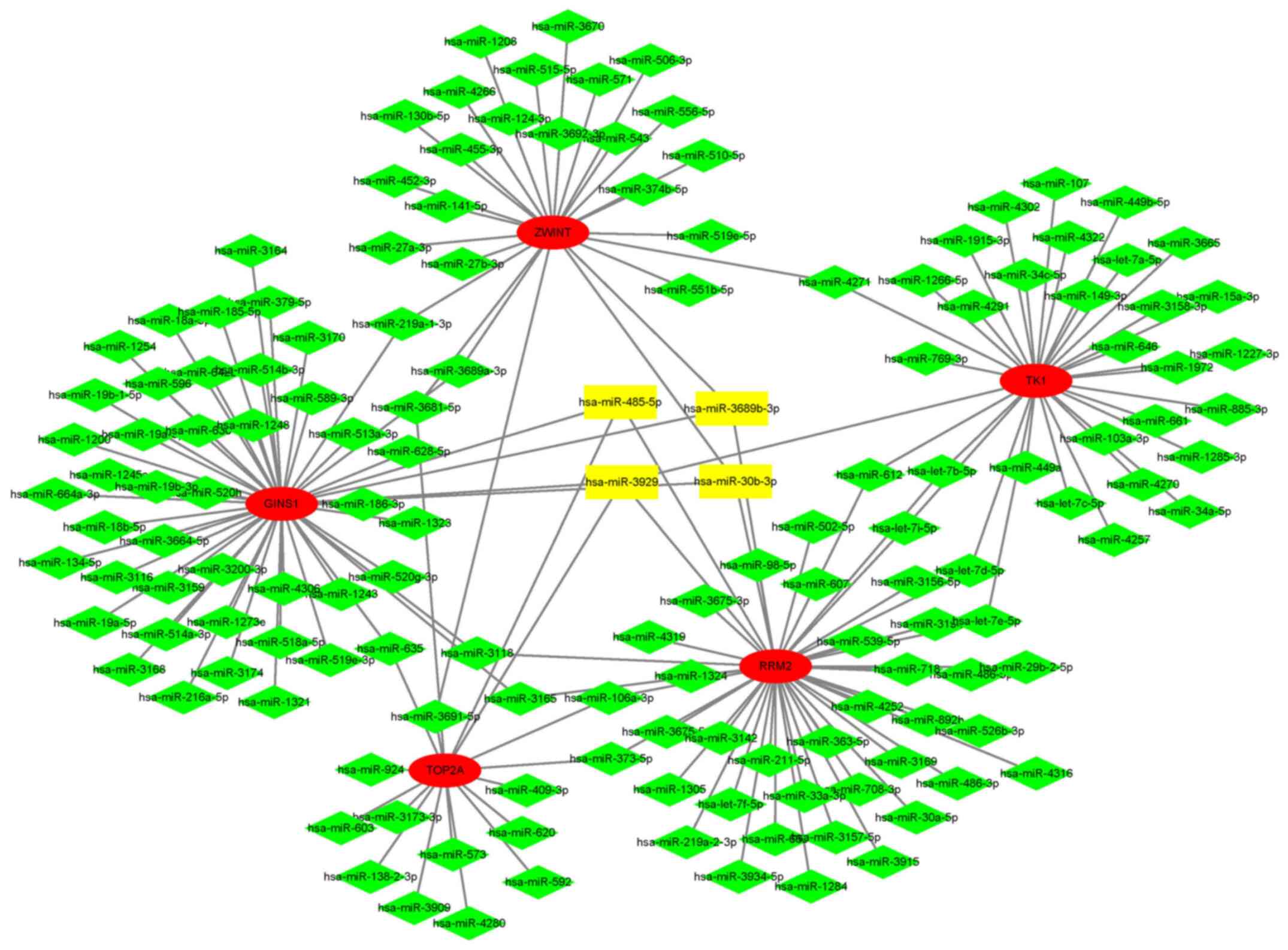
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang X, Huang F, Yang D, Peng T and Lu G:
Identification of miRNA-mRNA Crosstalk in Respiratory Syncytial
Virus- (RSV-) Associated Pediatric Pneumonia through Integrated
miRNAome and Transcriptome Analysis. Mediators Inflamm.
2020(8919534)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jian Y, Xu CH, Li YP, Tang B, Xie SH and
Zeng EM: Down-regulated microRNA-30b-3p inhibits proliferation,
invasion and migration of glioma cells via inactivation of the AKT
signaling pathway by up-regulating RECK. Biosci Rep.
39(BSR20182226)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Zhou J, Wang J, Chen X, Zhu Y and
Chen Y: miR-30b-3p affects the migration and invasion function of
ovarian cancer cells by targeting the CTHRC1 gene. Biol Res.
53(10)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kumar B, Khaleghzadegan S, Mears B, Hatano
K, Kudrolli TA, Chowdhury WH, Yeater DB, Ewing CM, Luo J, Isaacs
WB, et al: Identification of miR-30b-3p and miR-30d-5p as direct
regulators of androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer by
complementary functional microRNA library screening. Oncotarget.
7:72593–72607. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kato K, Sakamoto T and Ito K:
Gamma-globulin inhibits superantigen-induced lymphocyte
proliferation and cytokine production. Allergol Int. 56:439–444.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Andreozzi L, Bracci B, D'Errico F and
Rigante D: A master role for neutrophils in Kawasaki syndrome.
Immunol Lett. 184:112–114. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sun L, Tang Y, Wang Y, Qian G, Yan W, Wang
B, Li X and Lv H: Changes in Profiles of Kawasaki Disease Noted
over Time in Suzhou, China. Cardiology. 141:25–31. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wu G, Yue P, Ma F, Zhang Y, Zheng X and Li
Y: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a biomarker for predicting the
intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Medicine
(Baltimore). 99(e18535)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tsujimoto H, Takeshita S, Nakatani K,
Kawamura Y, Tokutomi T and Sekine I: Delayed apoptosis of
circulating neutrophils in Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol.
126:355–364. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Inamo Y, Harada K, Okuni M, Kimoto K,
Takeuchi S and Sakurabayashi I: Immunoreactive polymorphonuclear
leukocyte elastase in complex with alpha 1-antitrypsin in Kawasaki
disease. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 29:202–205. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Maruyama K, Fukasaka M, Vandenbon A,
Saitoh T, Kawasaki T, Kondo T, Yokoyama KK, Kidoya H, Takakura N,
Standley D, et al: The transcription factor Jdp2 controls bone
homeostasis and antibacterial immunity by regulating osteoclast and
neutrophil differentiation. Immunity. 37:1024–1036. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chang D, Qian C, Li H and Feng H:
Comprehensive analyses of DNA methylation and gene expression
profiles of Kawasaki disease. J Cell Biochem. 120:13001–13011.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sugitani Y, Furuno K, Sueishi K and Hara
T: Macrophages and cytotoxic T cells infiltrate the destructed
mitral tissue in Kawasaki disease. BMJ Case Rep: Feb 22.
2018(bcr2017223584)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Koizumi K, Hoshiai M, Moriguchi T,
Katsumata N, Toda T, Kise H, Hasebe Y, Kono Y, Sunaga Y, Yoshizawa
M, et al: Plasma Exchange Downregulates Activated Monocytes and
Restores Regulatory T Cells in Kawasaki Disease. Ther Apher Dial.
23:92–98. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Han JW, Oh JH, Rhim JW and Lee KY:
Correlation between elevated platelet count and immunoglobulin
levels in the early convalescent stage of Kawasaki disease.
Medicine (Baltimore). 96(e7583)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ikeda K, Yamaguchi K, Tanaka T, Mizuno Y,
Hijikata A, Ohara O, Takada H, Kusuhara K and Hara T: Unique
activation status of peripheral blood mononuclear cells at acute
phase of Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 160:246–255.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Leung DY, Burns JC, Newburger JW and Geha
RS: Reversal of lymphocyte activation in vivo in the Kawasaki
syndrome by intravenous gammaglobulin. J Clin Invest. 79:468–472.
1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ross R and Conti P: COVID-19 induced by
SARS-CoV-2 causes Kawasaki-like disease in children: Role of
pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. J Biol Regul
Homeost Agents. 34:767–773. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|