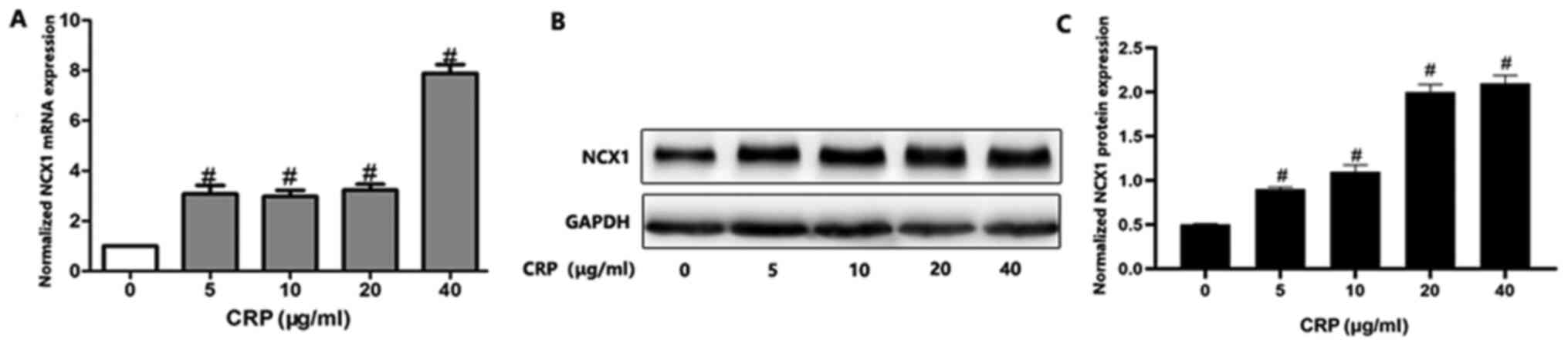
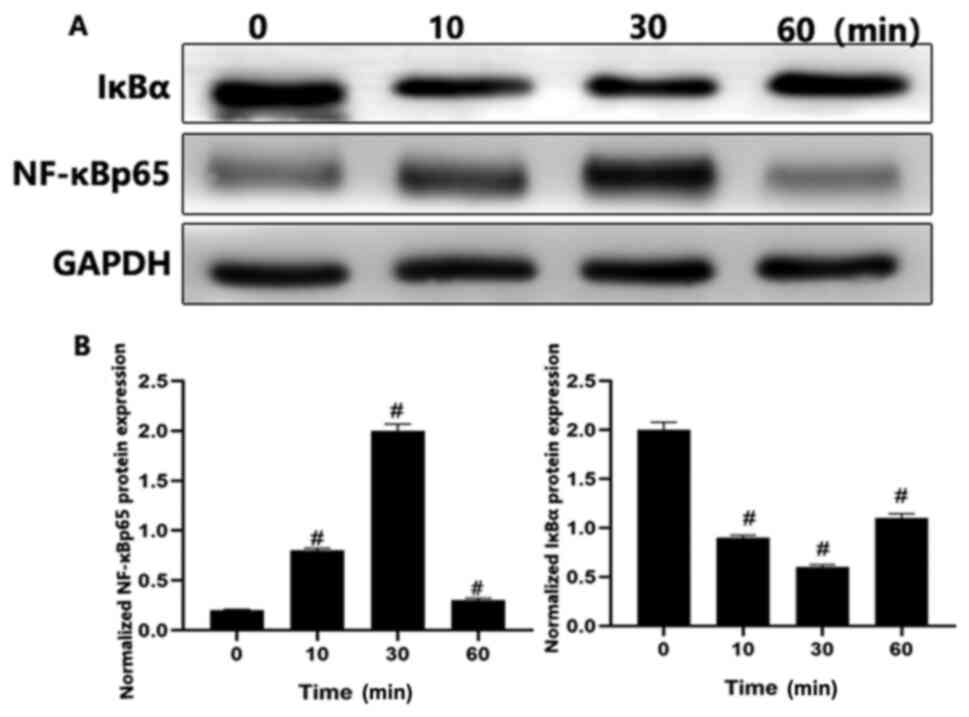
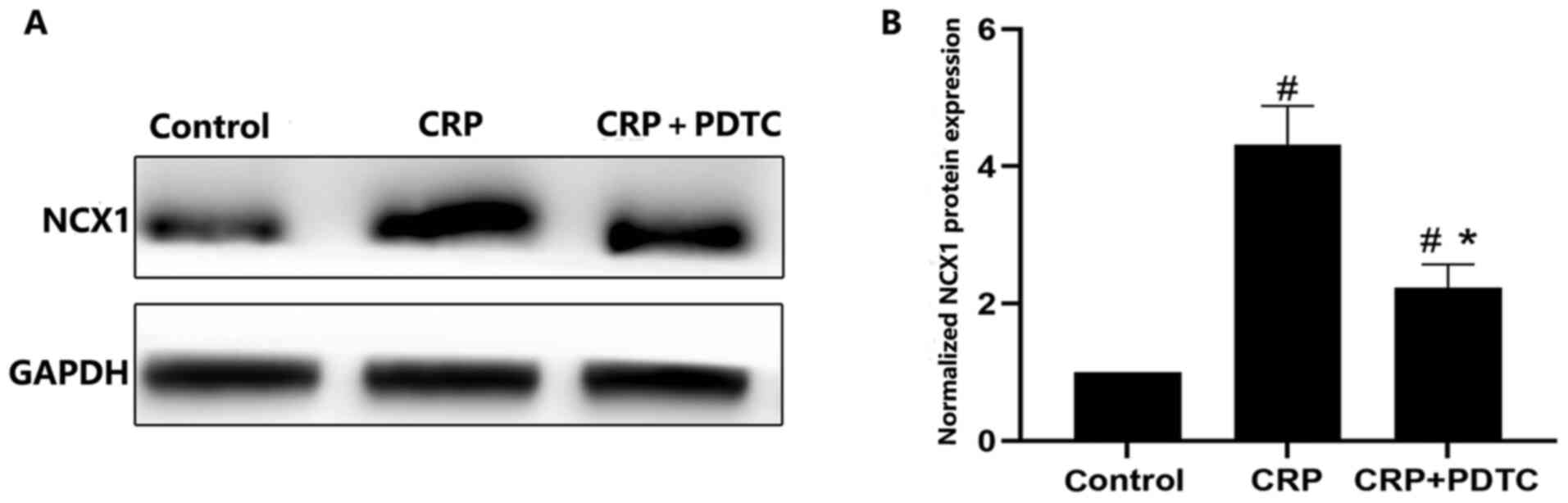
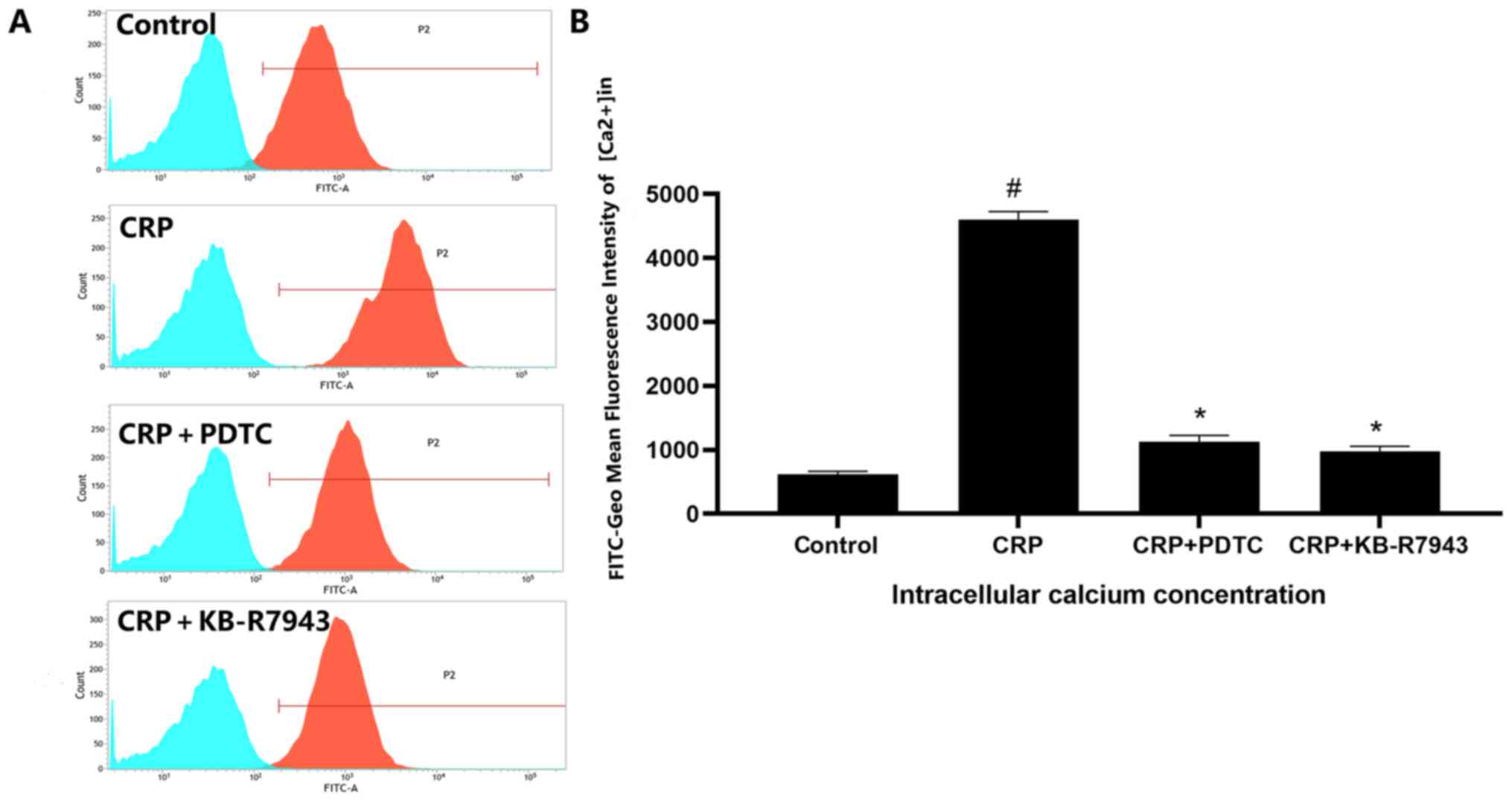
|
1
|
Li Y, Zhong X, Cheng G, Zhao C, Zhang L,
Hong Y, Wan Q, He R and Wang Z: Hs-CRP and all-cause,
cardiovascular, and cancer mortality risk: A meta-analysis.
Atherosclerosis. 259:75–82. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ghazizadeh H, Rezaei M, Avan A, Fazilati
M, Pasdar A, Tavallaie S, Kazemi E, Seyedi SMR, Ferns GA,
Azimi-Nezhad M and Ghayour-Mobarhan M: Association between serum
cell adhesion molecules with hs-CRP, uric acid and VEGF genetic
polymorphisms in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Mol Biol Rep.
47:867–875. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Han K, Lu Q, Zhu WJ, Wang TZ, Du Y and Bai
L: Correlations of degree of coronary artery stenosis with blood
lipid, CRP, Hcy, GGT, SCD36 and fibrinogen levels in elderly
patients with coronary heart disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:9582–9589. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Amorim S, Campelo M, Moura B, Martins E,
Rodrigues J, Barroso I, Faria M, Guimaraes T, Macedo F,
Silva-Cardoso J and Maciel MJ: The role of biomarkers in dilated
cardiomyopathy: Assessment of clinical severity and reverse
remodeling. Rev Port Cardiol. 36:709–716. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Portuguese).
|
|
5
|
Buckley DI, Fu R, Freeman M, Rogers K and
Helfand M: C-reactive protein as a risk factor for coronary heart
disease: A systematic review and meta-analyses for the U.S.
preventive services task force. Ann Intern Med. 151:483–495.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lee Y, Park HC, Shin JH, Lim YH, Shin J
and Park JK: Single and persistent elevation of C-reactive protein
levels and the risk of atrial fibrillation in a general population:
The ansan-ansung cohort of the Korean genome and epidemiology
study. Int J Cardiol. 277:240–246. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kazumi T, Kawaguchi A, Hirano T and
Yoshino G: C-reactive protein in young, apparently healthy men:
Associations with serum leptin, QTc interval, and high-density
lipoprotein-cholesterol. Metabolism. 52:1113–1116. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hodzic E, Drakovac A and Begic E: Troponin
and CRP as indicators of possible ventricular arrhythmias in
myocardial infarction of the anterior and inferior walls of the
heart. Mater Sociomed. 30:185–188. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li C, Jia L, Wang Z, Niu L and An X: The
efficacy of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of pediatric
arrhythmia and its effects on serum IL-6 and hs-CRP. Exp Ther Med.
14:3563–3568. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nagai T, Anzai T, Kaneko H, Anzai A, Mano
Y, Nagatomo Y, Kohsaka S, Maekawa Y, Kawamura A, Yoshikawa T and
Ogawa S: Impact of systemic acidosis on the development of
malignant ventricular arrhythmias after reperfusion therapy for
ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Circ J. 74:1808–1814.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wu KC, Gerstenblith G, Guallar E, Marine
JE, Dalal D, Cheng A, Marbán E, Lima JA, Tomaselli GF and Weiss RG:
Combined cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and C-reactive protein
levels identify a cohort at low risk for defibrillator firings and
death. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 5:178–186. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Saxon LA, Bristow MR, Boehmer J, Krueger
S, Kass DA, De Marco T, Carson P, DiCarlo L, Feldman AM, Galle E
and Ecklund F: Predictors of sudden cardiac death and appropriate
shock in the comparison of medical therapy, pacing, and
defibrillation in heart failure (COMPANION) trial. Circulation.
114:2766–2772. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Theuns DA, Smith T, Szili-Torok T,
Muskens-Heemskerk A, Janse P and Jordaens L: Prognostic role of
high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and B-type natriuretic peptide
in implantable cardioverter-defibrillator patients. Pacing Clin
Electrophysiol. 35:275–282. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Streitner F, Kuschyk J, Veltmann C, Ratay
D, Schoene N, Streitner I, Brueckmann M, Schumacher B, Borggrefe M
and Wolpert C: Role of proinflammatory markers and NT-proBNP in
patients with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and an
electrical storm. Cytokine. 47:166–172. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Vianello E, Dozio E, Barassi A, Sammarco
G, Tacchini L, Marrocco-Trischitta MM, Trimarchi S and Corsi
Romanelli MM: A pilot observational study on magnesium and calcium
imbalance in elderly patients with acute aortic dissection. Immun
Ageing. 14(1)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shattock MJ, Ottolia M, Bers DM, Blaustein
MP, Boguslavskyi A, Bossuyt J, Bridge JH, Chen-Izu Y, Clancy CE,
Edwards A, et al: Na+/Ca2+ exchange and
Na+/K+-ATPase in the heart. J Physiol.
593:1361–1382. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hamilton S and Terentyev D: Proarrhythmic
remodeling of calcium homeostasis in cardiac disease; implications
for diabetes and obesity. Front Physiol. 9(1517)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ma HJ, Li Q, Ma HJ, Guan Y, Shi M, Yang J,
Li DP and Zhang Y: Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia
ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced calcium overload in heart
via Na/Ca2+ exchanger in developing rats. Cell Physiol Biochem.
34:313–324. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health, NIH
publication no. 85-23, revised 1996.
|
|
20
|
Battiprolu PK, Hojayev B, Jiang N, Wang
ZV, Luo X, Iglewski M, Shelton JM, Gerard RD, Rothermel BA,
Gillette TG, et al: Metabolic stress-induced activation of FoxO1
triggers diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice. J Clin Invest.
122:1109–1118. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Simpson P and Savion S: Differentiation of
rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating
nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and
chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 50:101–116.
1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lokuta A, Kirby MS, Gaa ST, Lederer WJ and
Rogers TB: On establishing primary cultures of neonatal rat
ventricular myocytes for analysis over long periods. J Cardiovasc
Electrophysiol. 5:50–62. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xie Y, Mai JT, Wang F, Lin YQ, Yuan WL,
Luo NS, Fang MC, Wang JF and Chen YX: Effects of C-reactive protein
on K(+) channel interaction protein 2 in cardiomyocytes. Am J
Transl Res. 7:922–931. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li M, Ye J, Zhao G, Hong G, Hu X, Cao K,
Wu Y and Lu Z: Gas6 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α
expression and apoptosis in H9C2 cells through NF-κB and MAPK
inhibition via the Axl/PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. 44:982–994.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Martin TP, McCluskey C, Cunningham MR,
Beattie J, Paul A and Currie S: CaMKIIδ interacts directly with
IKKβ and modulates NF-κB signalling in adult cardiac fibroblasts.
Cell Signal. 51:166–175. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
McElnea EM, Quill B, Docherty NG, Irnaten
M, Siah WF, Clark AF, O'Brien CJ and Wallace DM: Oxidative stress,
mitochondrial dysfunction and calcium overload in human lamina
cribrosa cells from glaucoma donors. Mol Vis. 17:1182–1191.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen JB, Yang R, Pappano A and Liang BT:
Cardiac P2X purinergic receptors as a new pathway for increasing
Na+ entry in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 307:H1469–H1477. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xie Y, Gu ZJ, Wu MX, Huang TC, Ou JS, Ni
HS, Lin MH, Yuan WL, Wang JF and Chen YX: Disruption of calcium
homeostasis by cardiac-specific over-expression of PPAR-γ in mice:
A role in ventricular arrhythmia. Life Sci. 167:12–21.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
LaRocca TJ, Fabris F, Chen J, Benhayon D,
Zhang S, McCollum L, Schecter AD, Cheung JY, Sobie EA, Hajjar RJ
and Lebeche D: Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-1 protects
against systolic failure in the Akitains2 model of diabetic
cardiomyopathy via a CXCR4/NF-κB pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 303:H353–H367. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Balasubramaniam SL, Gopalakrishnapillai A,
Gangadharan V, Duncan RL and Barwe SP: Sodium-calcium exchanger 1
regulates epithelial cell migration via calcium-dependent
extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling. J Biol Chem.
290:12463–12473. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kobayashi Y, Tanno K, Ueno A, Fukamizu S,
Murata H, Watanabe N, Sasaki T, Yamamoto T, Takayama M and Nagao K:
In-hospital electrical storm in acute myocardial
infarction-clinical background and mechanism of the electrical
instability. Circ J. 83:91–100. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Nortamo S, Ukkola O, Lepojärvi S, Kenttä
T, Kiviniemi A, Junttila J, Huikuri H and Perkiömäki J: Association
of sST2 and hs-CRP levels with new-onset atrial fibrillation in
coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiol. 248:173–178.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hamilton S and Terentyev D: Altered
intracellular calcium homeostasis and arrhythmogenesis in the aged
heart. Int J Mol Sci. 20(2386)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Davlouros PA, Gkizas V, Vogiatzi C,
Giannopoulos G, Alexopoulos D and Deftereos S: Calcium homeostasis
and kinetics in heart failure. Med Chem. 12:151–161.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kim JJ, Němec J, Papp R, Strongin R,
Abramson JJ and Salama G: Bradycardia alters Ca(2+) dynamics
enhancing dispersion of repolarization and arrhythmia risk. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H848–H860. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Song J, Gao E, Wang J, Zhang XQ, Chan TO,
Koch WJ, Shang X, Joseph JI, Peterson BZ, Feldman AM and Cheung JY:
Constitutive overexpression of phosphomimetic phospholemman S68E
mutant results in arrhythmias, early mortality, and heart failure:
Potential involvement of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302:H770–H781. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Javidanpour S, Dianat M, Badavi M and Mard
SA: The inhibitory effect of rosmarinic acid on overexpression of
NCX1 and stretch-induced arrhythmias after acute myocardial
infarction in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 102:884–893.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jordan MC, Henderson SA, Han T, Fishbein
MC, Philipson KD and Roos KP: Myocardial function with reduced
expression of the sodium-calcium exchanger. J Card Fail.
16:786–796. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Murthy A, Workman SW, Jiang M, Hu J, Sifa
I, Bernas T, Tang W, Deschenes I and Tseng GN: Dynamic
palmitoylation regulates trafficking of K channel interacting
protein 2 (KChIP2) across multiple subcellular compartments in
cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 135:1–9. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Yuen J and Kang S: Sleep duration,
C-reactive protein and risk of incident coronary heart
disease-results from the Framingham offspring study. Nutr Metab
Cardiovasc Dis. 24:600–605. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Anzai T: Inflammatory mechanisms of
cardiovascular remodeling. Circ J. 82:629–635. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ujihara Y, Iwasaki K, Takatsu S, Hashimoto
K, Naruse K, Mohri S and Katanosaka Y: Induced NCX1 overexpression
attenuates pressure overload-induced pathological cardiac
remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 111:348–361. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|