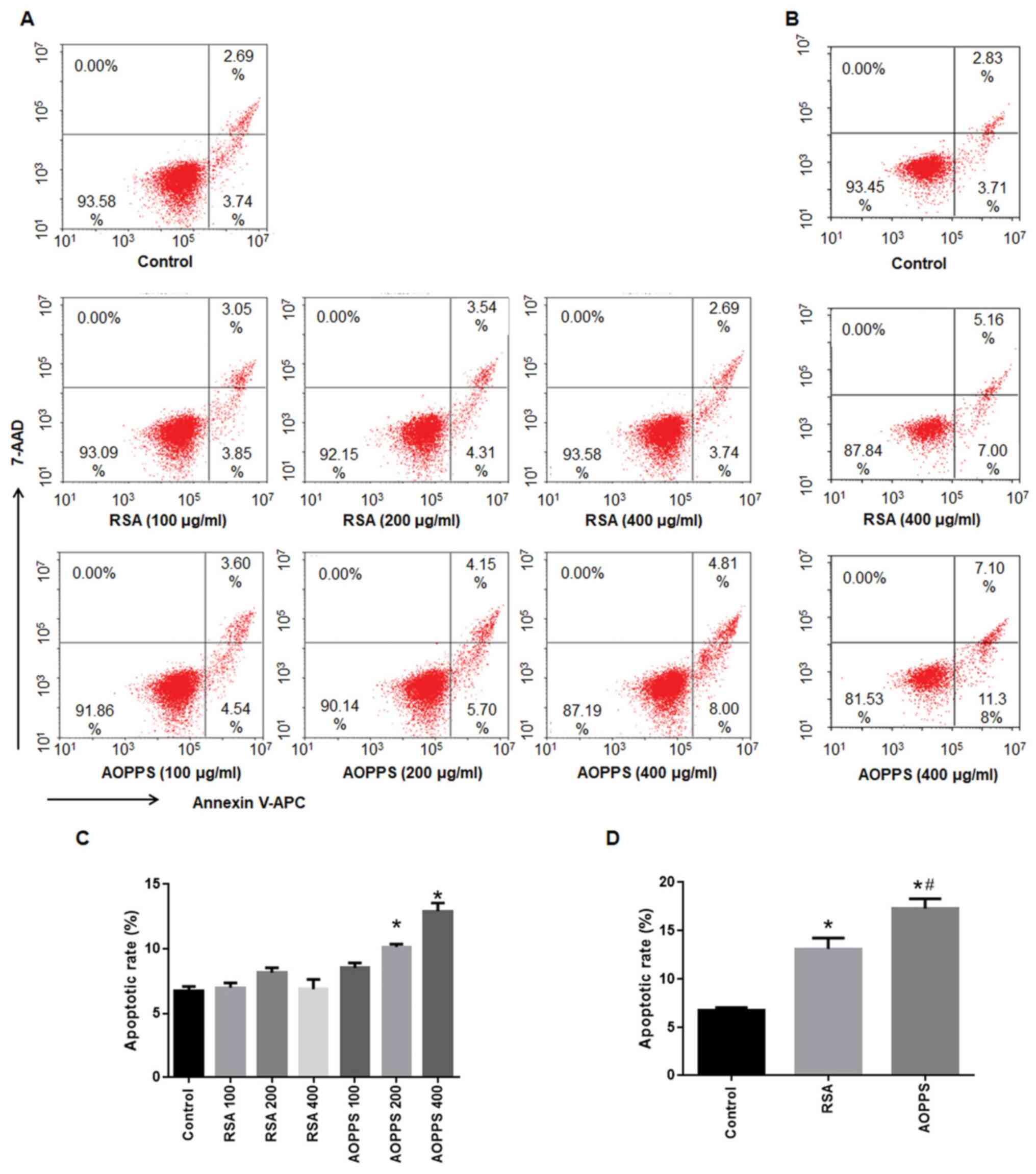
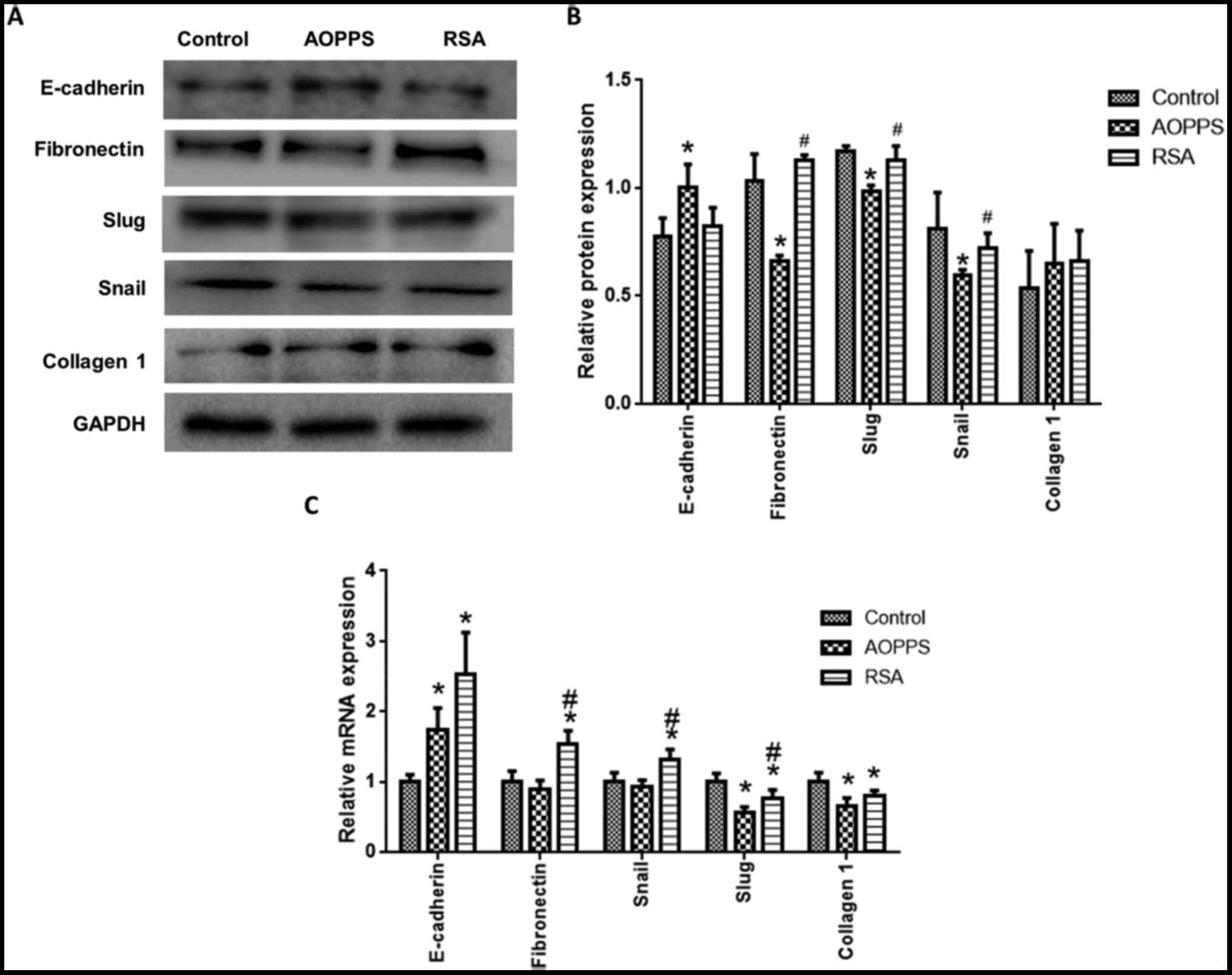
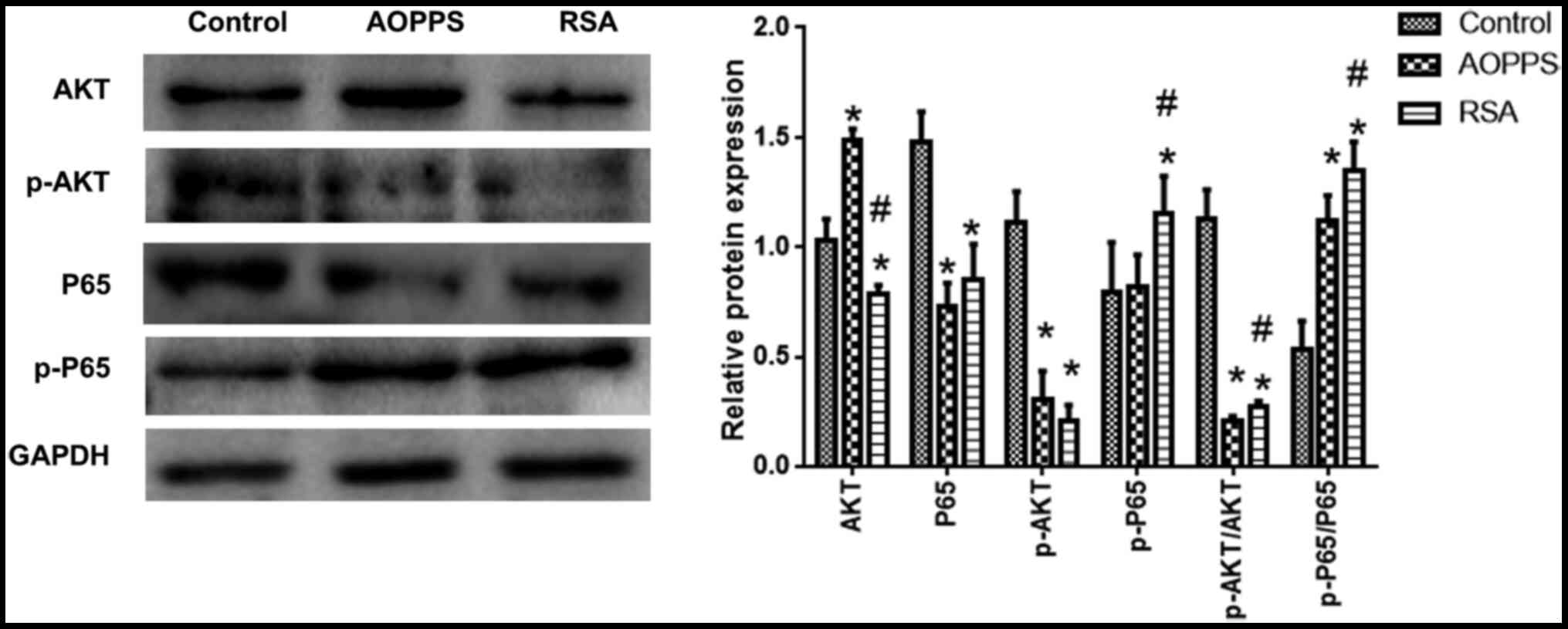
|
1
|
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M,
Capeillère-Blandin C, Nguyen-Khoa T, Nguyen AT, Zingraff J, Jungers
P and Descamps-Latscha B: Advanced oxidation protein products as a
novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia. Kidney Int.
49:1304–1313. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wu Q, Zhong ZM, Pan Y, Zeng JH, Zheng S,
Zhu SY and Chen JT: Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel
marker of oxidative stress in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Med Sci
Monit. 21:2428–2432. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Witko-Sarsat V, Gausson V, Nguyen AT,
Touam M, Drüeke T, Santangelo F and Descamps-Latscha B:
AOPP-induced activation of human neutrophil and monocyte oxidative
metabolism: A potential target for N-acetylcysteine treatment in
dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 64:82–91. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M, Nguyen Khoa
T, Capeillère-Blandin C, Nguyen AT, Canteloup S, Dayer JM, Jungers
P, Drüeke T and Descamps-Latscha B: Advanced oxidation protein
products as novel mediators of inflammation and monocyte activation
in chronic renal failure. J Immunol. 161:2524–2532. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaneda H, Taguchi J, Ogasawara K, Aizawa T
and Ohno M: Increased level of advanced oxidation protein products
in patients with coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis.
162:221–225. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhou LL, Cao W, Xie C, Tian J, Zhou Z,
Zhou Q, Zhu P, Li A, Liu Y, Miyata T, et al: The receptor of
advanced glycation end products plays a central role in advanced
oxidation protein products-induced podocyte apoptosis. Kidney Int.
82:759–770. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu Z, Yao X, Jiang W, Li W, Zhu S, Liao
C, Zou L, Ding R and Chen J: Advanced oxidation protein products
induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB
signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord
injury. J Neuroinflammation. 17(90)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Derkacz A, Olczyk P and Komosinska-Vassev
K: Diagnostic markers for nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases.
Dis Markers. 2018(7451946)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Krzystek-Korpacka M, Neubauer K, Berdowska
I, Boehm D, Zielinski B, Petryszyn P, Terlecki G, Paradowski L and
Gamian A: Enhanced formation of advanced oxidation protein products
in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 14:794–802. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Balmus IM, Ciobica A, Trifan A and Stanciu
C: The implications of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapies
in inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical aspects and animal models.
Saudi J Gastroenterol. 22:3–17. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gunther C, Neumann H, Neurath MF and
Becker C: Apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis: Cell death
regulation in the intestinal epithelium. Gut. 62:1062–1071.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Witko-Sarsat V, Nguyen-Khoa T, Jungers P,
Drueke TB and Descamps-Latscha B: Advanced oxidation protein
products as a novel molecular basis of oxidative stress in uraemia.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 14 (Suppl 1):S76–S78. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Marsche G, Frank S, Hrzenjak A, Holzer M,
Dirnberger S, Wadsack C, Scharnagl H, Stojakovic T, Heinemann A and
Oettl K: Plasma-advanced oxidation protein products are potent
high-density lipoprotein receptor antagonists in vivo. Circ Res.
104:750–757. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhu G, Li J, He L, Wang X and Hong X:
MPTP-induced changes in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory
are prevented by memantine through the BDNF-TrkB pathway. Br J
Pharmacol. 172:2354–2368. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sun S, Xie F, Zhang Q, Cui Z, Cheng X,
Zhong F, He K and Zhou J: Advanced oxidation protein products
induce hepatocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition via a
ROS-dependent, TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int.
41:842–853. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Schulzke JD, Ploeger S, Amasheh M, Fromm
A, Zeissig S, Troeger H, Richter J, Bojarski C, Schumann M and
Fromm M: Epithelial tight junctions in intestinal inflammation. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 1165:294–300. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Low D, Mino-Kenudson M and Mizoguchi E:
Recent advancement in understanding colitis-associated
tumorigenesis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:2115–2123. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu X, Sun S, Xie F, Ma J, Tang J, He S and
Bai L: Advanced oxidation protein products induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of intestinal epithelial cells
via a PKC delta-mediated, redox-dependent signaling pathway.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 27:37–56. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhong ZM, Bai L and Chen JT: Advanced
oxidation protein products inhibit proliferation and
differentiation of rat osteoblast-like cells via NF-kappaB pathway.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 24:105–114. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yang SJ, Song ZJ, Wang XC, Zhang ZR, Wu SB
and Zhu GQ: Curculigoside facilitates fear extinction and prevents
depression-like behaviors in a mouse learned helplessness model
through increasing hippocampal BDNF. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
40:1269–1278. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Larue L and Bellacosa A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: Role
of phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene.
24:7443–7454. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhu G, Wang X, Wu S, Li X and Li Q:
Neuroprotective effects of puerarin on
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine induced Parkinson's
disease model in mice. Phytother Res. 28:179–186. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huber MA, Beug H and Wirth T:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: NF-kappaB takes center stage.
Cell Cycle. 3:1477–1480. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Song Z, Shen F, Zhang Z, Wu S and Zhu G:
Calpain inhibition ameliorates depression-like behaviors by
reducing inflammation and promoting synaptic protein expression in
the hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 174(108175)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ma C, Huang S, Xu L, Tian L, Yang Y and
Wang J: Transcription co-activator P300 activates Elk1-aPKC-iota
signaling mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
malignancy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogenesis.
9(32)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gasiule S, Dreize N, Kaupinis A, Ražanskas
R, Čiupas L, Stankevičius V, Kapustina Ž, Laurinavičius A, Valius M
and Vilkaitis G: Molecular insights into miRNA-driven resistance to
5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin chemotherapy: miR-23b modulates the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells. J
Clin Med. 8(2115)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Roda G, Sartini A, Zambon E, Calafiore A,
Marocchi M, Caponi A, Belluzzi A and Roda E: Intestinal epithelial
cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol.
16:4264–4271. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|