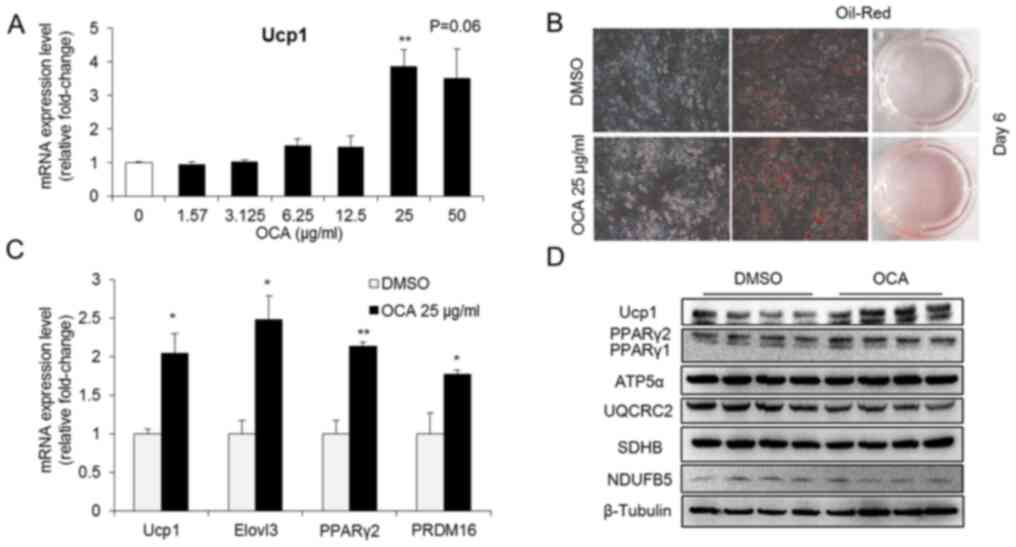
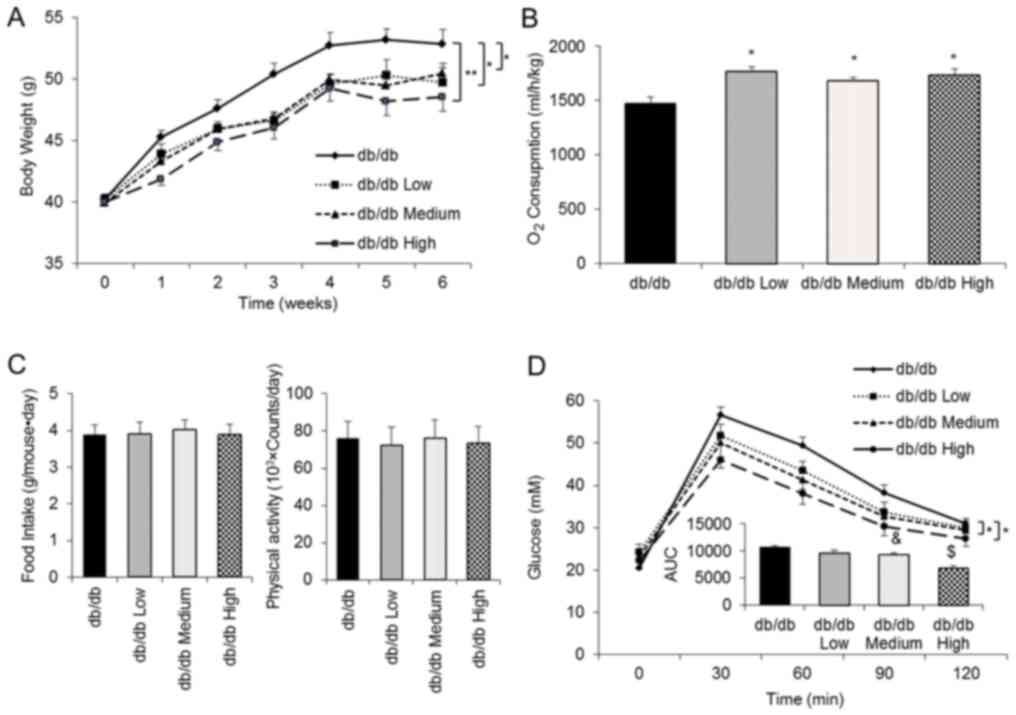
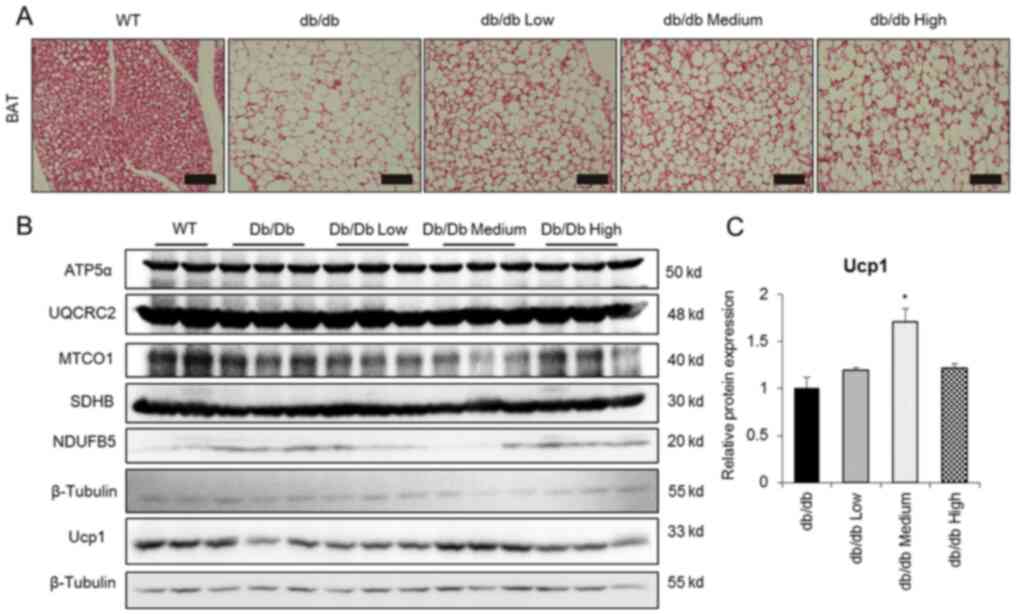
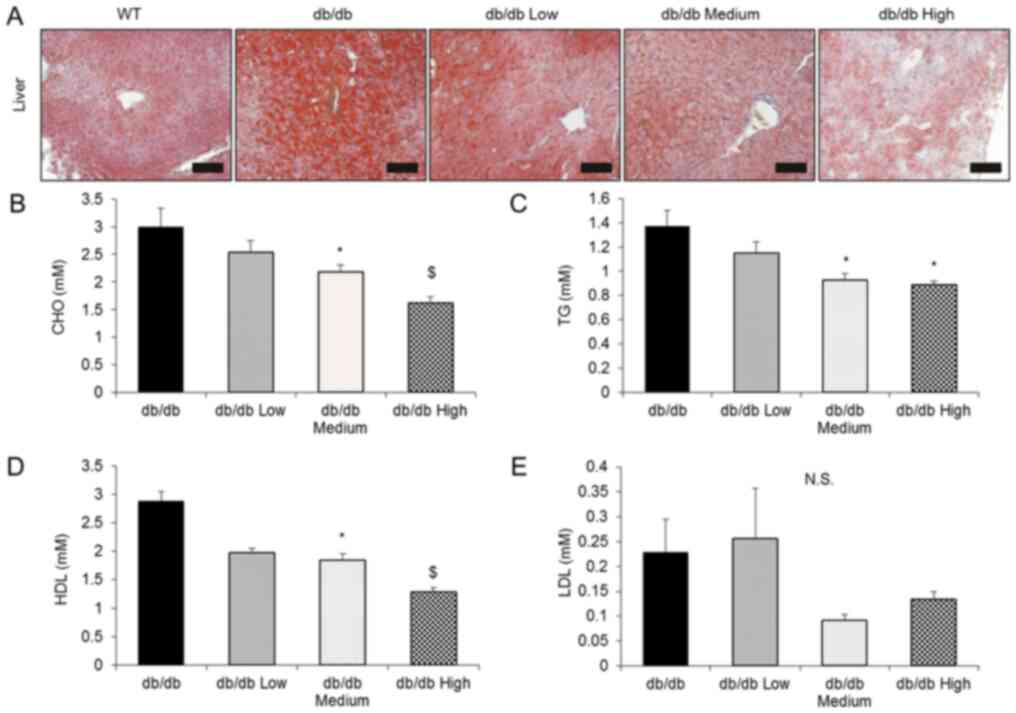
|
1
|
Srivastava G and Apovian CM: Current
pharmacotherapy for obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:12–24.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Haslam DW and James WP: Obesity. Lancet.
366:1197–1209. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cypess AM, Haft CR, Laughlin MR and Hu
HCH: Brown fat in humans: Consensus points and experimental
guidelines. Cell Metab. 20:408–415. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu X, Zheng Z, Zhu X, Meng M, Li L, Shen
Y, Chi Q, Wang D, Zhang Z, Li C, et al: Brown adipose tissue
transplantation improves whole-body energy metabolism. Cell Res.
23:851–854. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu X, Wang S, You Y, Meng M, Zheng Z,
Dong M, Lin J, Zhao Q, Zhang C, Yuan X, et al: Brown adipose tissue
transplantation reverses obesity in Ob/Ob mice. Endocrinology.
156:2461–2469. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rinella ME: Nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: A systematic review. JAMA. 313:2263–2273. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy
T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J and Bugianesi E: Global burden of
NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:11–20. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE,
Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, Harrison SA, Brunt EM and Sanyal AJ:
The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
Practice guidance from the American association for the study of
liver diseases. Hepatology. 67:328–357. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Antuna-Puente B, Feve B, Fellahi S and
Bastard JP: Adipokines: The missing link between insulin resistance
and obesity. Diabetes Metab. 34:2–11. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chong AY, Lupsa BC, Cochran EK and Gorden
P: Efficacy of leptin therapy in the different forms of human
lipodystrophy. Diabetologia. 53:27–35. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Polyzos SA, Toulis KA, Goulis DG, Zavos C
and Kountouras J: Serum total adiponectin in nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism.
60:313–326. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rotman Y and Sanyal AJ: Current and
upcoming pharmacotherapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Gut. 66:180–190. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Watanabe M, Houten SM, Wang L, Moschetta
A, Mangelsdorf DJ, Heyman RA, Moore DD and Auwerx J: Bile acids
lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and
SREBP-1c. J Clin Invest. 113:1408–1418. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Luo YH, Wang XX, Orlicky DJ and Levi M:
Bile acid sequestrant prevents NAFLD and NASH in western diet fed
mice independent of FXR. Hepatology. 62:280A–282A. 2015.
|
|
15
|
Yuan L and Bambha K: Bile acid receptors
and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol. 7:2811–2818.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Massafra V, Milona A, Vos HR, Ramos RJJ,
Gerrits J, Willemsen ECL, Ramos Pittol JM, Ijssennagger N,
Houweling M, Prinsen HCMT, et al: Farnesoid X receptor activation
promotes hepatic amino acid catabolism and ammonium clearance in
mice. Gastroenterology. 152:1462–1476.e10. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Haczeyni F, Poekes L, Wang H, Mridha AR,
Barn V, Geoffrey Haigh W, Ioannou GN, Yeh MM, Leclercq IA, Teoh NC
and Farrell GC: Obeticholic acid improves adipose morphometry and
inflammation and reduces steatosis in dietary but not metabolic
obesity in mice. Obesity (Silver Spring). 25:155–165.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yuan X, Wei G, You Y, Huang Y, Lee HJ,
Dong M, Lin J, Hu T, Zhang H, Zhang C, et al: Rutin ameliorates
obesity through brown fat activation. FASEB J. 31:333–345.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang C, Wang J, Zhang H, Liu S, Lee HJ,
Jin W and Cheng J: Hepatitis C virus core protein induces hepatic
steatosis via Sirt1-dependent pathway. Liver Int. 38:803–812.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Trayhurn P, Thurlby PL and James WP:
Thermogenic defect in pre-obese ob/ob mice. Nature. 266:60–62.
1977.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kozak LP and Anunciado-Koza R: UCP1: Its
involvement and utility in obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 32 (Suppl
7):S32–S38. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Masuo K, Straznicky NE, Lambert GW,
Katsuya T, Sugimoto K, Rakugi H, Socratous F, Hastings J, Lambert
EA, Ogihara T and Esler MD: Leptin-receptor polymorphisms relate to
obesity through blunted leptin-mediated sympathetic nerve
activation in a Caucasian male population. Hypertens Res.
31:1093–1100. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cannon B and Nedergaard J: Brown adipose
tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol Rev.
84:277–359. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Carey AL and Kingwell BA: Brown adipose
tissue in humans: Therapeutic potential to combat obesity.
Pharmacol Ther. 140:26–33. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yoneshiro T, Aita S, Matsushita M,
Kayahara T, Kameya T, Kawai Y, Iwanaga T and Saito M: Recruited
brown adipose tissue as an antiobesity agent in humans. J Clin
Invest. 123:3404–3408. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tian L, Qiu H, Sun S and Lin H: Emergency
cardiovascular hospitalization risk attributable to cold
temperatures in Hong Kong. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes.
9:135–142. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Marin JJ, Macias RI, Briz O, Banales JM
and Monte MJ: Bile acids in physiology, pathology and pharmacology.
Curr Drug Metab. 17:4–29. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Broeders EP, Nascimento EB, Havekes B,
Brans B, Roumans KH, Tailleux A, Schaart G, Kouach M, Charton J,
Deprez B, et al: The bile acid chenodeoxycholic acid increases
human brown adipose tissue activity. Cell Metab. 22:418–426.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen X, Yan L, Guo Z, Chen Y, Li M, Huang
C, Chen Z and Meng X: Chenodeoxycholic acid attenuates high-fat
diet-induced obesity and hyperglycemia via the G protein-coupled
bile acid receptor 1 and proliferator-activated receptor γ pathway.
Exp Ther Med. 14:5305–5312. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rizzo G, Disante M, Mencarelli A, Renga B,
Gioiello A, Pellicciari R and Fiorucci S: The farnesoid X receptor
promotes adipocyte differentiation and regulates adipose cell
function in vivo. Mol Pharmacol. 70:1164–1173. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rahman MS, Imran KM, Hossain M, Lee TJ and
Kim YS: Biochanin A induces a brown-fat phenotype via improvement
of mitochondrial biogenesis and activation of AMPK signaling in
murine C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells. Phytother Res. 35:920–931.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang HL, Huang YY, Lee HJ and Jin WZ:
Zic1 negatively regulates brown adipogenesis in C3H10T1/2 cells.
Sci Bull. 60:1033–1035. 2015.
|
|
34
|
Watanabe M, Houten SM, Mataki C,
Christoffolete MA, Kim BW, Sato H, Messaddeq N, Harney JW, Ezaki O,
Kodama T, et al: Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting
intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Nature. 439:484–489.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mudaliar S, Henry RR, Sanyal AJ, Morrow L,
Marschall HU, Kipnes M, Adorini L, Sciacca CI, Clopton P, Castelloe
E, et al: Efficacy and safety of the farnesoid X receptor agonist
obeticholic acid in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 145:574–582.e1.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Papazyan R, Liu X, Liu J, Dong B, Plummer
EM, Lewis RD II, Roth JD and Young MA: FXR activation by
obeticholic acid or nonsteroidal agonists induces a human-like
lipoprotein cholesterol change in mice with humanized chimeric
liver. J Lipid Res. 59:982–993. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pencek R, Marmon T, Roth JD, Liberman A,
Hooshmand-Rad R and Young MA: Effects of obeticholic acid on
lipoprotein metabolism in healthy volunteers. Diabetes Obes Metab.
18:936–940. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu Y, Li F, Zalzala M, Xu J, Gonzalez FJ,
Adorini L, Lee YK, Yin L and Zhang Y: Farnesoid X receptor
activation increases reverse cholesterol transport by modulating
bile acid composition and cholesterol absorption in mice.
Hepatology. 64:1072–1085. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Cipriani S, Mencarelli A, Palladino G and
Fiorucci S: FXR activation reverses insulin resistance and lipid
abnormalities and protects against liver steatosis in Zucker
(fa/fa) obese rats. J Lipid Res. 51:771–784. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Owsley E and Chiang JY: Guggulsterone
antagonizes farnesoid X receptor induction of bile salt export pump
but activates pregnane X receptor to inhibit cholesterol 7
alpha-hydroxylase gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 304:191–195.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lorbek G, Lewinska M and Rozman D:
Cytochrome P450s in the synthesis of cholesterol and bile
acids-from mouse models to human diseases. FEBS J. 279:1516–1533.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Modica S, Petruzzelli M, Bellafante E,
Murzilli S, Salvatore L, Celli N, Di Tullio G, Palasciano G,
Moustafa T, Halilbasic E, et al: Selective activation of nuclear
bile acid receptor FXR in the intestine protects mice against
cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 142:355–365.e1-e4. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang GX, Zhao XY, Meng ZX, Kern M,
Dietrich A, Chen Z, Cozacov Z, Zhou D, Okunade AL, Su X, et al: The
brown fat-enriched secreted factor Nrg4 preserves metabolic
homeostasis through attenuation of hepatic lipogenesis. Nat Med.
20:1436–1443. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lee P, Linderman JD, Smith S, Brychta RJ,
Wang J, Idelson C, Perron RM, Werner CD, Phan GQ, Kammula US, et
al: Irisin and FGF21 are cold-induced endocrine activators of brown
fat function in humans. Cell Metab. 19:302–309. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
van den Beukel JC, Boon MR, Steenbergen J,
Rensen PC, Meijer OC, Themmen AP and Grefhorst A: Cold exposure
partially corrects disturbances in lipid metabolism in a male mouse
model of glucocorticoid excess. Endocrinology. 156:4115–4128.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yilmaz Y, Ones T, Purnak T, Ozguven S,
Kurt R, Atug O, Turoglu HT and Imeryuz N: Association between the
presence of brown adipose tissue and non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease in adult humans. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 34:318–323.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Blondin DP, Labbé SM, Noll C, Kunach M,
Phoenix S, Guérin B, Turcotte ÉE, Haman F, Richard D and Carpentier
AC: Selective impairment of glucose but not fatty acid or oxidative
metabolism in brown adipose tissue of subjects with type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 64:2388–2397. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gunawardana SC and Piston DW:
Insulin-independent reversal of type 1 diabetes in nonobese
diabetic mice with brown adipose tissue transplant. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 308:E1043–E1055. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|