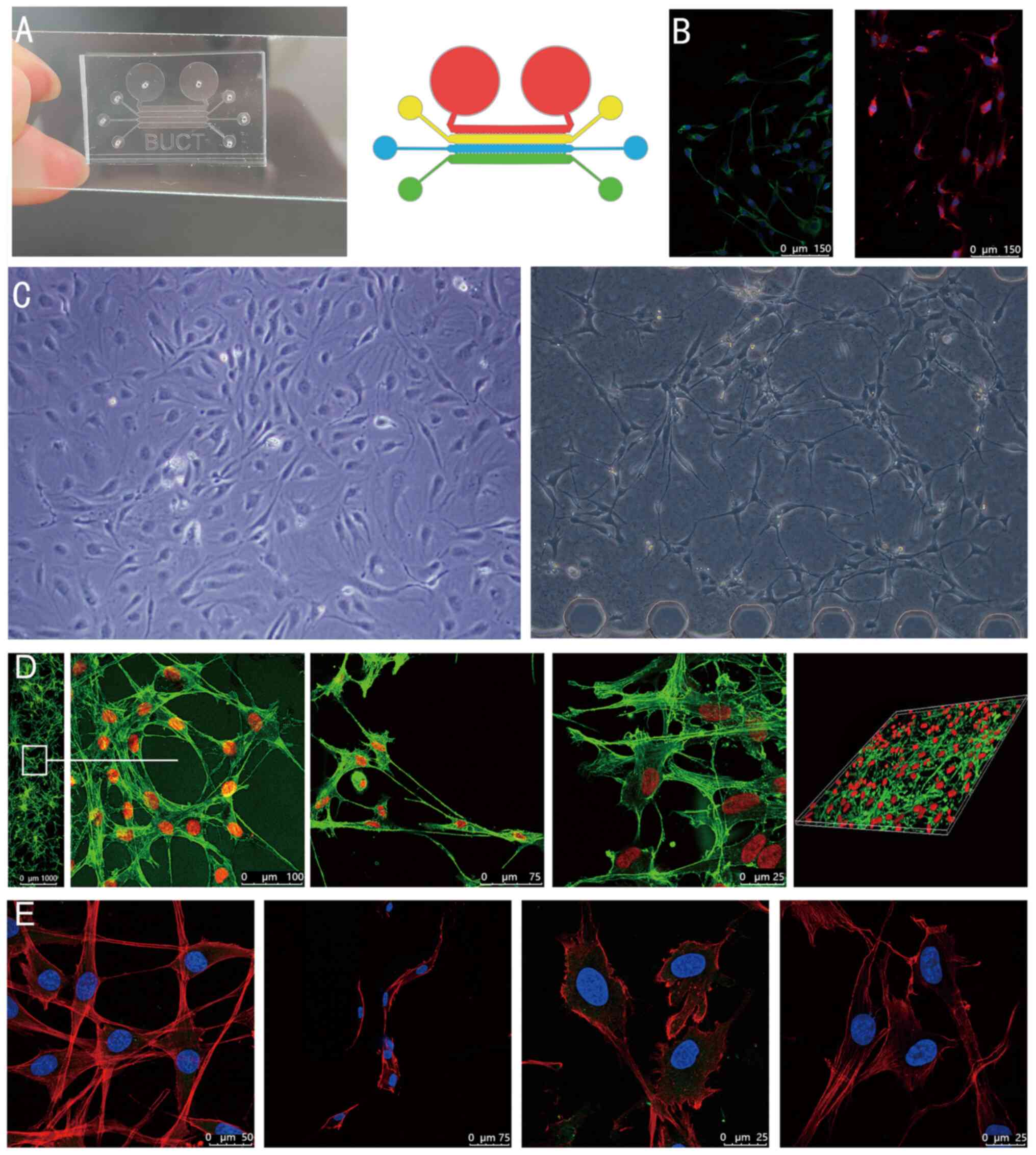
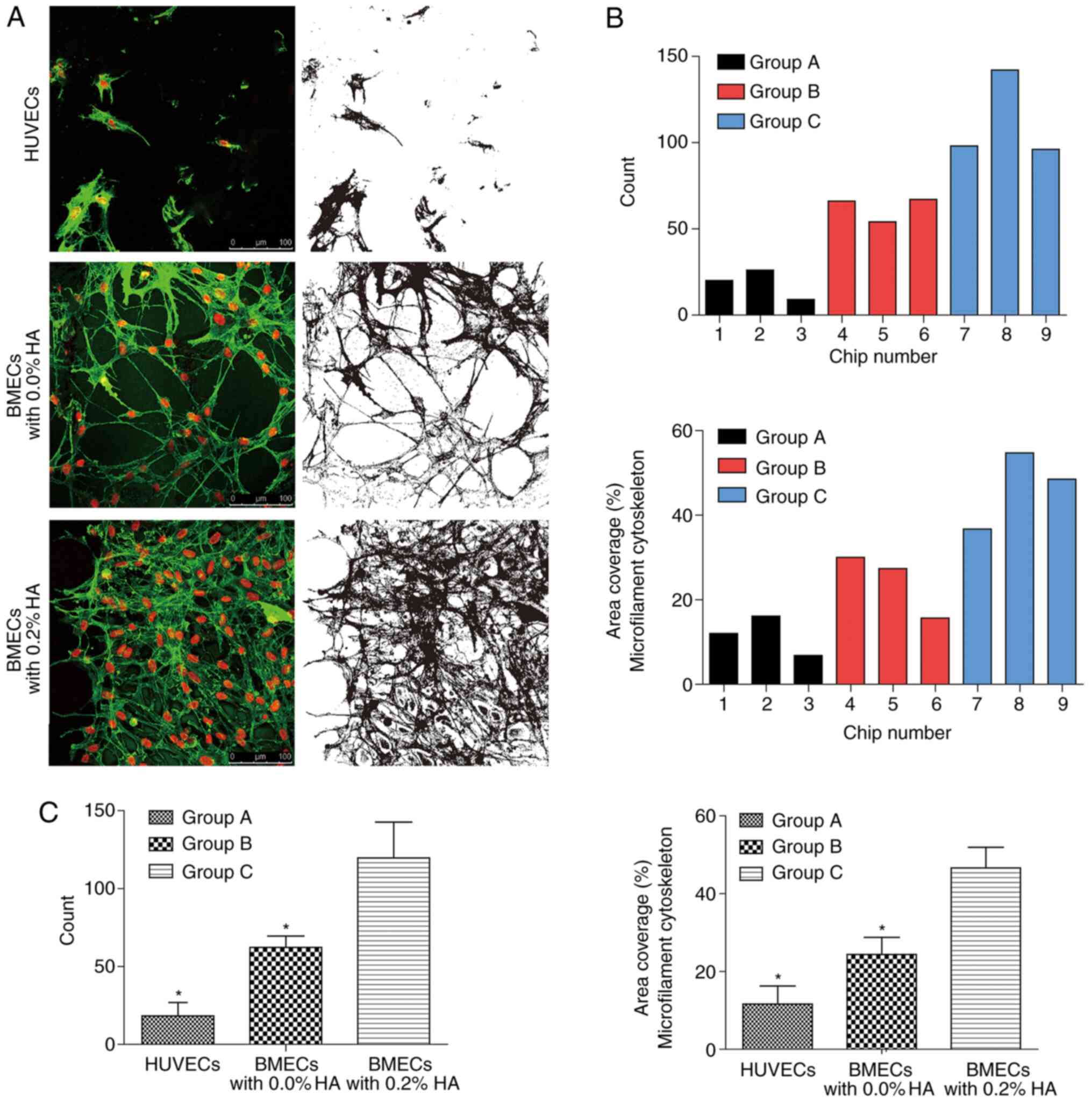
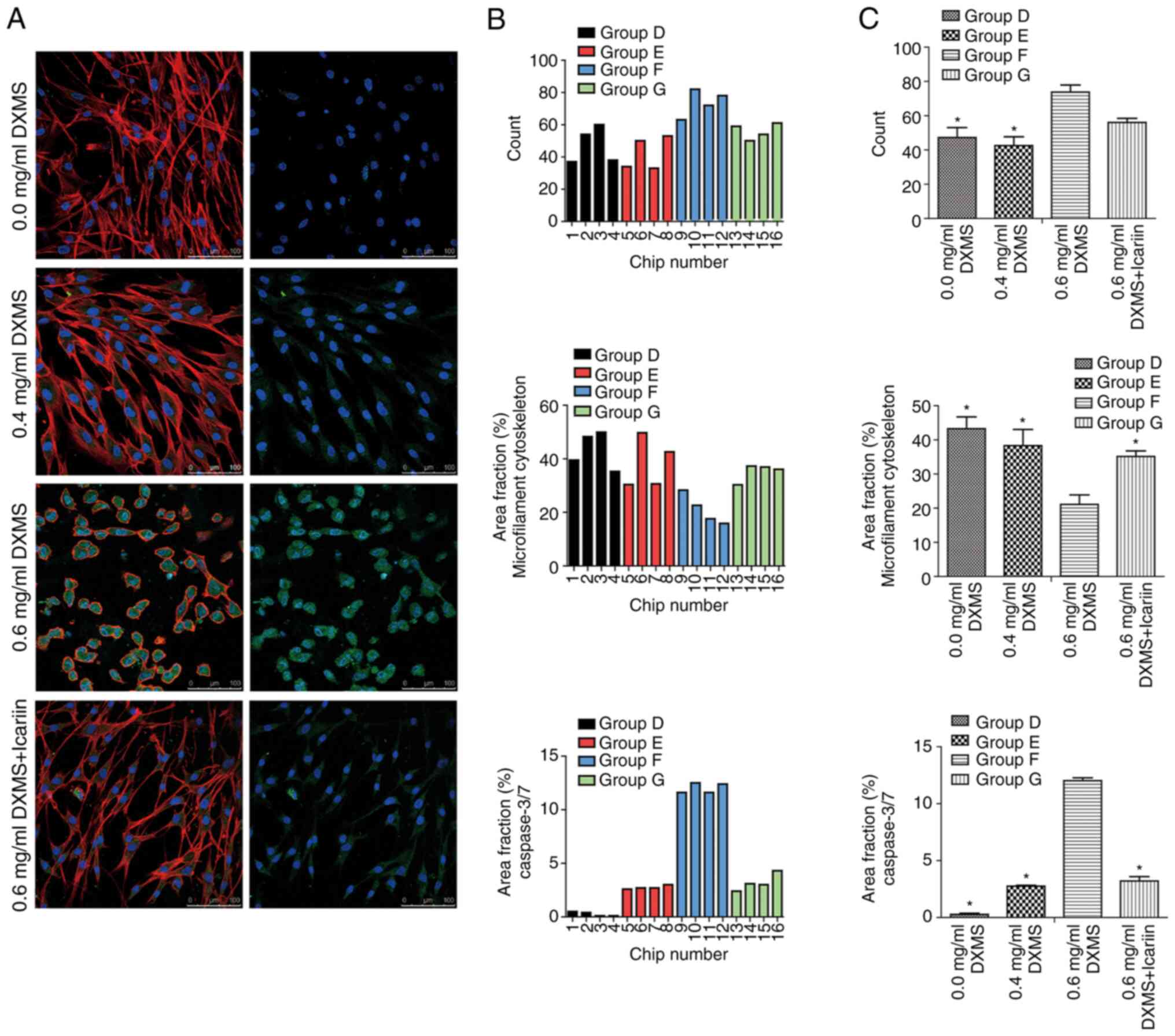
|
1
|
Zhao D, Liu Y, Ma C, Gu G and Han DF: A
mini review: Stem cell therapy for osteonecrosis of the femoral
head and pharmacological aspects. Curr Pharm Des. 25:1099–1104.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Maruyama M, Lin T, Pan CC, Moeinzadeh S,
Takagi M, Yang YP and Goodman SB: Cell-Based and scaffold-based
therapies for joint preservation in early-stage osteonecrosis of
the femoral head: A review of basic research. JBJS Rev.
7(e5)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yu Q, Guo W, Shen J and Lv Y: Effect of
glucocorticoids on lncRNA and mRNA expression profiles of the bone
microcirculatory endothelial cells from femur head of Homo sapiens.
Genom Data. 4:140–142. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yu QS, Guo WS, Cheng LM, Lu YF, Shen JY
and Li P: Glucocorticoids significantly influence the transcriptome
of bone microvascular endothelial cells of human femoral head. Chin
Med J (Engl). 128:1956–1963. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Urbaczek AC, Leão PAGC, Souza FZR, Afonso
A, Vieira Alberice J, Cappelini LTD, Carlos IZ and Carrilho E:
Endothelial cell culture under perfusion on A polyester-toner
microfluidic device. Sci Rep. 7(10466)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
van Engeland NCA, Pollet AMAO, den Toonder
JMJ, Bouten CVC, Stassen OMJA and Sahlgren CM: A biomimetic
microfluidic model to study signalling between endothelial and
vascular smooth muscle cells under hemodynamic conditions. Lab
Chip. 18:1607–1620. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
van der Helm MW, van der Meer AD, Eijkel
JC, van den Berg A and Segerink LI: Microfluidic organ-on-chip
technology for blood-brain barrier research. Tissue Barriers.
4(e1142493)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yu Q, Guo W, Cheng L, Lu Y and Li P:
Preliminary study of impact of steroids on expression profile and
transcriptome of bone microvascular endothelial cells. Zhonghua Yi
Xue Za Zhi. 94:3817–3820. 2014.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Zhang Q, Gao F, Cheng L, Liu L, Sun W and
Li Z: Effects of icariin on autophagy and exosome production of
bone microvascular endothelial cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 33:568–577. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Zhao DY, Yu QS, Guo WS and Cheng LM:
Effect of icariin on the proteomic expression profile of bone
microvascular endothelial cells of human femoral head against
steroids-induced lesion. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 96:1026–1030.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Sun Q and Pei J:
Microfluidic-Based 3D engineered microvascular networks and their
applications in vascularized microtumor models. Micromachines
(Basel). 9(493)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z, Chen YC, Cheng YH, Luan Y and
Yoon E: Microfluidics 3D gel-island chip for single cell isolation
and lineage-dependent drug responses study. Lab Chip. 16:2504–2512.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rh Owen G, Dard M and Larjava H:
Hydoxyapatite/beta-tricalcium phosphate biphasic ceramics as
regenerative material for the repair of complex bone defects. J
Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 106:2493–2512. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ramesh N, Moratti SC and Dias GJ:
Hydroxyapatite-polymer biocomposites for bone regeneration: A
review of current trends. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.
106:2046–2057. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jusoh N, Oh S, Kim S, Kim J and Jeon NL:
Microfluidic vascularized bone tissue model with
hydroxyapatite-incorporated extracellular matrix. Lab Chip.
15:3984–3988. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Whisler JA, Chen MB and Kamm RD: Control
of perfusable microvascular network morphology using a multiculture
microfluidic system. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 20:543–552.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen P, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Zhou W, Deng Y,
Hu X and Zhang L: Basic Fibroblast growth factor reduces
permeability and apoptosis of human brain microvascular endothelial
cells in response to oxygen and glucose deprivation followed by
reoxygenation via the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1
(FGFR1)/ERK pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:7191–7201. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Jiang Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Xiao M,
Song C, Bai Y, Yinuo Han N and Han F: Synapse impairment associated
with enhanced apoptosis in post-traumatic stress disorder. Synapse.
74(e22134)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gao X, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Zhao Z, Zhang H,
Wu J, Shen W and Zhong M: Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 disruption
inhibits angiogenesis by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Exp Ther Med. 18:3062–3070. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yuan W, Chang H, Liu X, Wang S, Liu H and
Xuan H: Brazilian green propolis inhibits Ox-LDL-Stimulated
Oxidative Stress In Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Partly
through PI3K/Akt/mTOR-Mediated Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2019(5789574)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tang L, Cheng JN, Long Y, He XM, Liang GN,
Tang XP, Jiang CX and Chen F: PCB 118-induced endothelial cell
apoptosis is partially mediated by excessive ROS production.
Toxicol Mech Methods. 27:394–399. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Munoz M, López-Oliva ME, Rodríguez C,
Martínez MP, Sáenz-Medina J, Sánchez A, Climent B, Benedito S,
García-Sacristán A, Rivera L, et al: Differential contribution of
Nox1, Nox2 and Nox4 to kidney vascular oxidative stress and
endothelial dysfunction in obesity. Redox Biol.
28(101330)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fernandez-Bertolez N, Costa C, Bessa MJ,
Park M, Carriere M, Dussert F, Teixeira JP, Pásaro E, Laffon B and
Valdiglesias V: Assessment of oxidative damage induced by iron
oxide nanoparticles on different nervous system cells. Mutat Res.
845(402989)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hu Y, Li H, Liu K, Zhang Y, Ren L and Fan
Z: Protective effects of icariin on human vascular endothelial
cells induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein via modulating
caspase-3 and Bcl-2. Mol Med Rep. 17:6835–6839. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen S, Wang Z, Zhou H, He B, Hu D and
Jiang H: Icariin reduces high glucose-induced endothelial
progenitor cell dysfunction via inhibiting the p38/CREB pathway and
activating the Akt/eNOS/NO pathway. Exp Ther Med. 18:4774–4780.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xiao HB, Liu ZK, Lu XY, Deng CN and Luo
ZF: Icariin regulates PRMT/ADMA/DDAH pathway to improve endothelial
function. Pharmacol Rep. 67:1147–1154. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang FY, Jia J, Song HH, Jia CM, Chen CB
and Ma J: Icariin protects vascular endothelial cells from
oxidative stress through inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. J
Integr Med. 17:205–212. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|