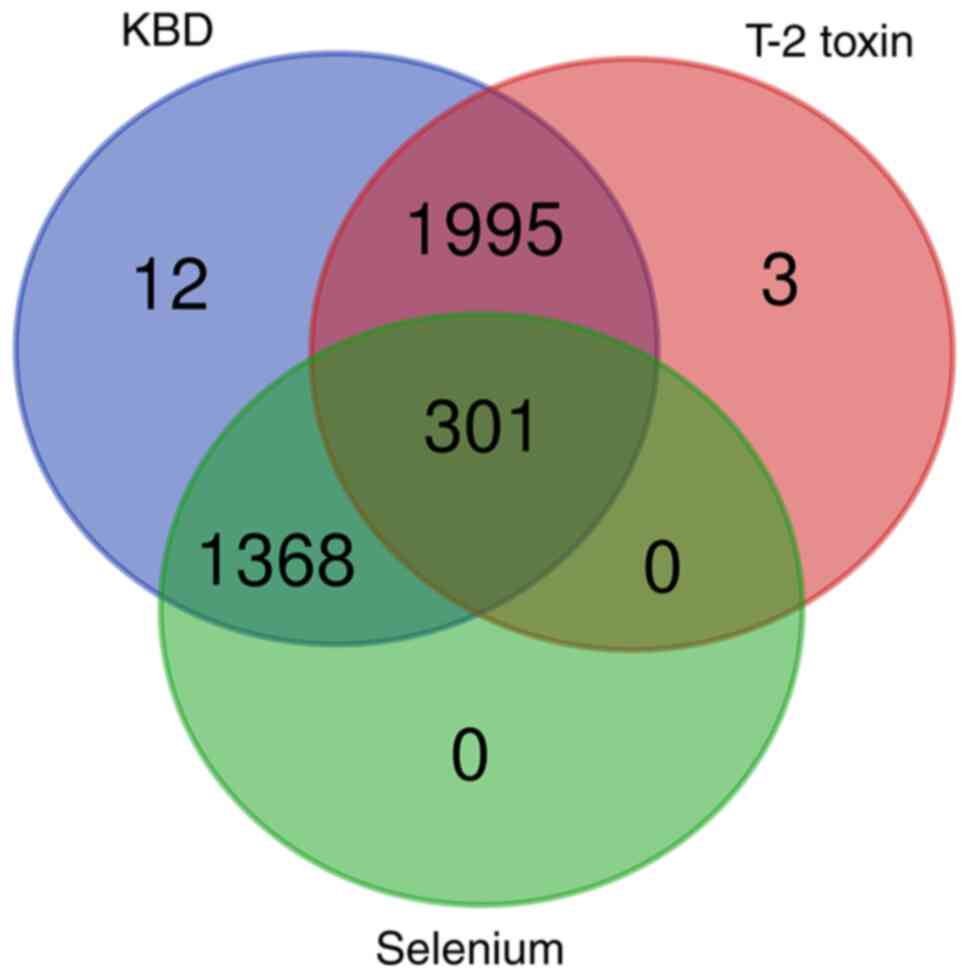
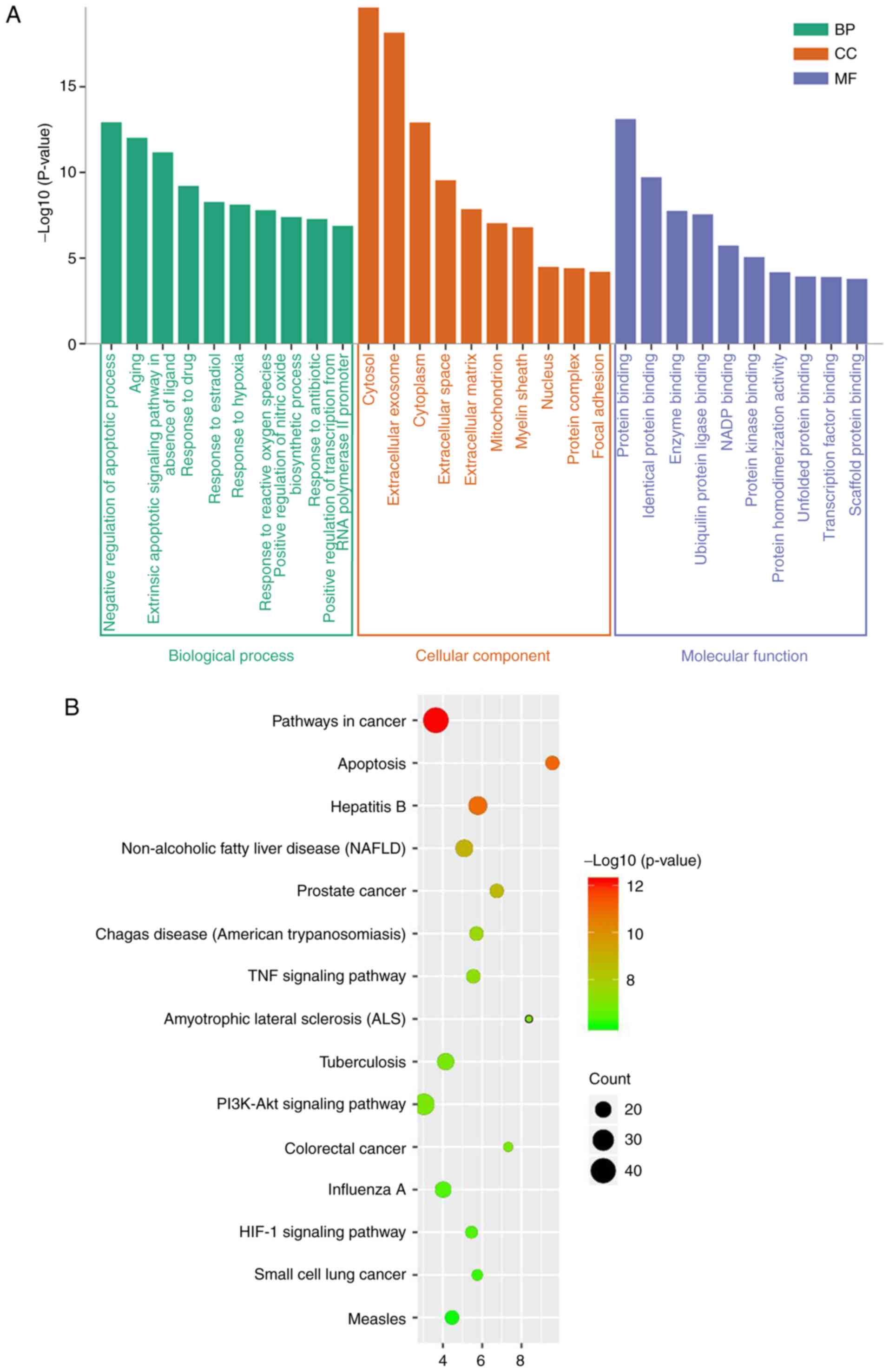
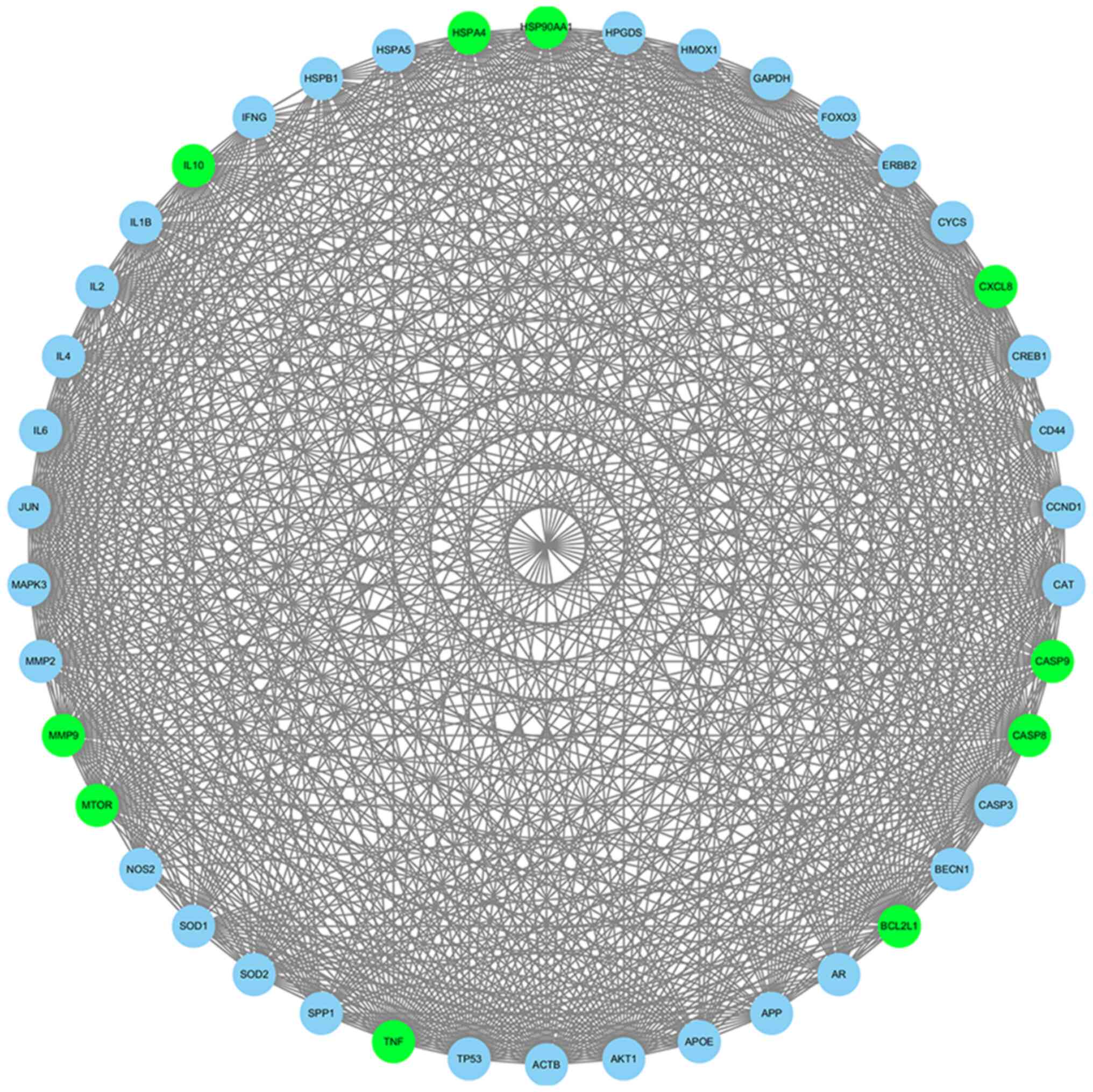
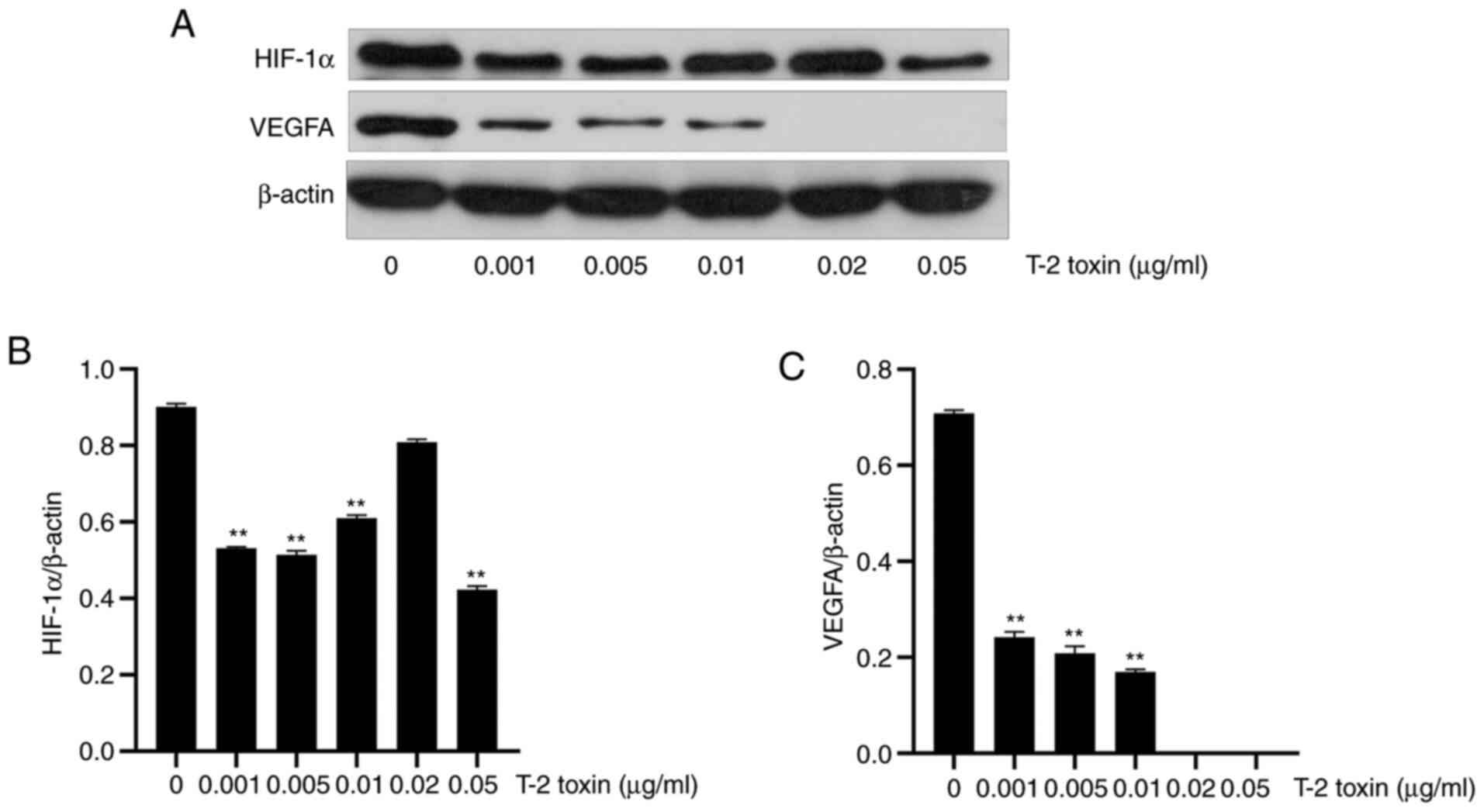
|
1
|
Xiong G: Diagnostic, clinical and
radiological characteristics of Kashin-Beck disease in Shaanxi
Province, PR China. Int Orthop. 25:147–150. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang K, Yu J, Liu H, Liu Y, Liu N, Cao Y,
Zhang X and Sun D: Endemic Kashin-Beck disease: A food-sourced
osteoarthropathy. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 50:366–372.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yang L, Zhang J, Li X, Xu C, Wang X and
Guo X: Expression profiles of selenium-related genes in human
chondrocytes exposed to T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 190:295–302. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sudre P and Mathieu F: Kashin-Beck
disease: From etiology to prevention or from prevention to
etiology? Int Orthop. 25:175–179. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gutleb AC, Morrison E and Murk AJ:
Cytotoxicity assays for mycotoxins produced by Fusarium strains: A
review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 11:309–320. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lei Y, Guanghui Z, Xi W, Yingting W, Xialu
L, Fangfang Y, Goldring MB, Xiong G and Lammi MJ: Cellular
responses to T-2 toxin and/or deoxynivalenol that induce cartilage
damage are not specific to chondrocytes. Sci Rep.
7(2231)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang SJ, Guo X, Zuo H, Zhang YG, Xu P,
Ping ZG, Zhang Z and Geng D: Chondrocyte apoptosis and expression
of Bcl-2, Bax, Fas, and iNOS in articular cartilage in patients
with Kashin-Beck disease. J Rheumatol. 33:615–619. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lei R, Jiang N, Zhang Q, Hu S, Dennis BS,
He S and Guo X: Prevalence of selenium, T-2 toxin, and
deoxynivalenol in kashin-beck disease areas in qinghai province,
Northwest China. Biol Trace Elem Res. 171:34–40. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jirong Y, Huiyun P, Zhongzhe Y, Birong D,
Weimin L, Ming Y and Yi S: Sodium selenite for treatment of
Kashin-Beck disease in children: A systematic review of randomised
controlled trials. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:605–613.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu Q, Wu W and Kuca K: From hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) to oxidative stress: A new
understanding of the toxic mechanism of mycotoxins. Food Chem
Toxicol. 135(110968)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang F, Guo X, Wang W, Yan H and Li C:
Genome-wide gene expression analysis suggests an important role of
hypoxia in the pathogenesis of endemic osteochondropathy
Kashin-Beck disease. PLoS One. 6(e22983)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu W, He A, Wen Y, Xiao X, Hao J, Zhang F
and Guo X: Comparison of microRNA expression profiles of
Kashin-Beck disease, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Sci
Rep. 7(540)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ and Simon MC:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol
Cell. 40:294–309. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Schönenberger MJ, Krek W and Kovacs WJ:
EPAS1/HIF-2α is a driver of mammalian pexophagy. Autophagy.
11:967–969. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gao RY, Wang M, Liu Q, Feng D, Wen Y, Xia
Y, Colgan SP, Eltzschig HK and Ju C: Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α
reprograms liver macrophages to protect against acute liver injury
through the production of interleukin-6. Hepatology. 71:2105–2117.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tian J, Yan J, Wang W, Zhong N, Tian L,
Sun J, Min Z, Ma J and Lu S: T-2 toxin enhances catabolic activity
of hypertrophic chondrocytes through ROS-NF-κB-HIF-2α pathway.
Toxicol In Vitro. 26:1106–1113. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xu J, Jiang C, Zhu W, Wang B, Yan J, Min
Z, Geng M, Han Y, Ning Q, Zhang F, et al: NOD2 pathway via RIPK2
and TBK1 is involved in the aberrant catabolism induced by T-2
toxin in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1575–1585.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi M, He Y, Zhang Y, Guo X, Lin J, Wang W
and Chen J: LncRNA MIAT regulated by selenium and T-2 toxin
increases NF-κB-p65 activation, promoting the progress of
Kashin-Beck disease. Hum Exp Toxicol. 40:869–881. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang T, Zhu X, Wu H, Jiang K and Zhao G:
Targeting the ROS/PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/HK2 axis of breast cancer cells:
Combined administration of polydatin and 2-Deoxy-d-glucose. J Cell
Mol Med. 23:3711–3723. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Guan R, Wang J, Li Z, Ding M, Li D, Xu G,
Wang T, Chen Y, Yang Q, Long Z, et al: Sodium tanshinone IIA
sulfonate decreases cigarette smoke-induced inflammation and
oxidative stress via blocking the activation of MAPK/HIF-1α
signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 9(263)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Deng M, Huang J, Wu J, Li Z, Xing
M, Wang J, Guo Q and Zou W: Microglial annexin A3 downregulation
alleviates bone cancer-induced pain through inhibiting the
Hif-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway. Pain.
161:2750–2762. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Carmeliet P: VEGF as a key mediator of
angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 69 (Suppl 3):S4–S10.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guo X, Zuo H, Cao CX, Zhang Y, Geng D,
Zhang ZT, Zhang YG, von der Mark K and von der Mark H: Abnormal
expression of Col X, PTHrP, TGF-beta, bFGF, and VEGF in cartilage
with Kashin-Beck disease. J Bone Miner Metab. 24:319–328.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang F, Guo X, Duan C, Wu S, Yu H and
Lammi M: Identification of differentially expressed genes and
pathways between primary osteoarthritis and endemic osteoarthritis
(Kashin-Beck disease). Scand J Rheumatol. 42:71–79. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Balamurugan K: HIF-1 at the crossroads of
hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:1058–1066.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Maes C, Carmeliet G and Schipani E:
Hypoxia-driven pathways in bone development, regeneration and
disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:358–366. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Johnson RJ, Sciaky
D, McMorran R, Wiegers J, Wiegers TC and Mattingly CJ: The
comparative toxicogenomics database: Update 2019. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D948–D954. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Ning Y, Zhang P, Yang L, Wang Y
and Guo X: Chondrocytes damage induced by T-2 toxin via
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in the pathogenesis of
an endemic osteochondropathy, Kashin-Beck disease. Exp Cell Res.
361:141–148. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu YN, Jiang ZC, Li SY, Li ZZ, Wang H,
Liu Y, Liao YC, Han J and Chen JH: Integrin α2β1 is involved in T-2
toxin-induced decrease of type II collagen in C28/I2 chondrocytes.
Toxicon. 186:12–18. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Janky R, Verfaillie A, Imrichová H, Van de
Sande B, Standaert L, Christiaens V, Hulselmans G, Herten K, Naval
Sanchez M, Potier D, et al: iRegulon: From a gene list to a gene
regulatory network using large motif and track collections. PLoS
Comput Biol. 10(e1003731)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang WZ, Guo X, Duan C, Ma WJ, Zhang YG,
Xu P, Gao ZQ, Wang ZF, Yan H, Zhang YF, et al: Comparative analysis
of gene expression profiles between the normal human cartilage and
the one with endemic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
17:83–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Duan C, Guo X, Zhang XD, Yu HJ, Yan H, Gao
Y, Ma WJ, Gao ZQ, Xu P and Lammi M: Comparative analysis of gene
expression profiles between primary knee osteoarthritis and an
osteoarthritis endemic to Northwestern China, Kashin-Beck disease.
Arthritis Rheum. 62:771–780. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wu Q, Qin Z, Kuca K, You L, Zhao Y, Liu A,
Musilek K, Chrienova Z, Nepovimova E, Oleksak P, et al: An update
on T-2 toxin and its modified forms: Metabolism, immunotoxicity
mechanism, and human exposure assessment. Arch Toxicol.
94:3645–3669. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Du XA, Wang HM, Dai XX, Kou Y, Wu RP, Chen
Q, Cao JL, Mo XY and Xiong YM: Role of selenoprotein S
(SEPS1)-105G>A polymorphisms and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in
Kashin-Beck disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:210–216.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Movafagh S, Crook S and Vo K: Regulation
of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a by reactive oxygen species: New
developments in an old debate. J Cell Biochem. 116:696–703.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Feng FB and Qiu HY: Effects of artesunate
on chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy through the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in rat models with rheumatoid
arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 102:1209–1220. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang W, Wei S, Luo M, Yu B, Cao J, Yang Z,
Wang Z, Goldring MB and Chen J: Oxidative stress and status of
antioxidant enzymes in children with Kashin-Beck disease.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1781–1789. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang FJ, Luo W and Lei GH: Role of HIF-1α
and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 82:144–147.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yudoh K, Nakamura H, Masuko-Hongo K, Kato
T and Nishioka K: Catabolic stress induces expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes:
Involvement of HIF-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 7:R904–R914. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Guo X, Zhang ZT, Wang M and Wang
SJ: Expression of Caspase-8 and Bcl-2 in the cartilage loose bodies
in patients with Kashin-Beck disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 31:1314–1317. 2011.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
43
|
Wen Y, Li P, Hao J, Duan C, Han J, He A,
Du Y, Liu L, Liang X, Zhang F and Guo X: Integrating genome-wide
DNA methylation and mRNA expression profiles identified different
molecular features between Kashin-Beck disease and primary
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 20(41)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wu C, Liu H, Zhang F, Shao W, Yang L, Ning
Y, Wang S, Zhao G, Lee BJ, Lammi M and Guo X: Long noncoding RNA
expression profile reveals lncRNAs signature associated with
extracellular matrix degradation in kashin-beck disease. Sci Rep.
7(17553)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ning Y, Wang X, Lammi MJ and Guo X:
Changes in the NF-κB signaling pathway in juvenile and adult
patients with Kashin-Beck disease. Exp Cell Res. 379:140–149.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xiong YM, Mo XY, Zou XZ, Song RX, Sun WY,
Lu W, Chen Q, Yu YX and Zang WJ: Association study between
polymorphisms in selenoprotein genes and susceptibility to
Kashin-Beck disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:817–824.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chang Y, Wang X, Sun Z, Jin Z, Chen M,
Wang X, Lammi MJ and Guo X: Inflammatory cytokine of IL-1β is
involved in T-2 toxin-triggered chondrocyte injury and metabolism
imbalance by the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol
Immunol. 91:195–201. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li Y, Mo X and Xiong Y: The study on
polymorphism of TrxR and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in
Kaschin-Beck disease. Biol Trace Elem Res. 190:303–308.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wu R, Zhang R, Xiong Y, Sun W, Li Y, Yang
X, Liu J, Jiang Y, Guo H, Mo X and Cao J: The study on
polymorphisms of Sep15 and TrxR2 and the expression of AP-1
signaling pathway in Kashin-Beck disease. Bone. 120:239–245.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Han L, Yang X, Sun W, Li Z, Ren H, Li B,
Zhang R, Zhang D, Shi Z, Liu J, et al: The study of GPX3
methylation in patients with Kashin-Beck disease and its mechanism
in chondrocyte apoptosis. Bone. 117:15–22. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|