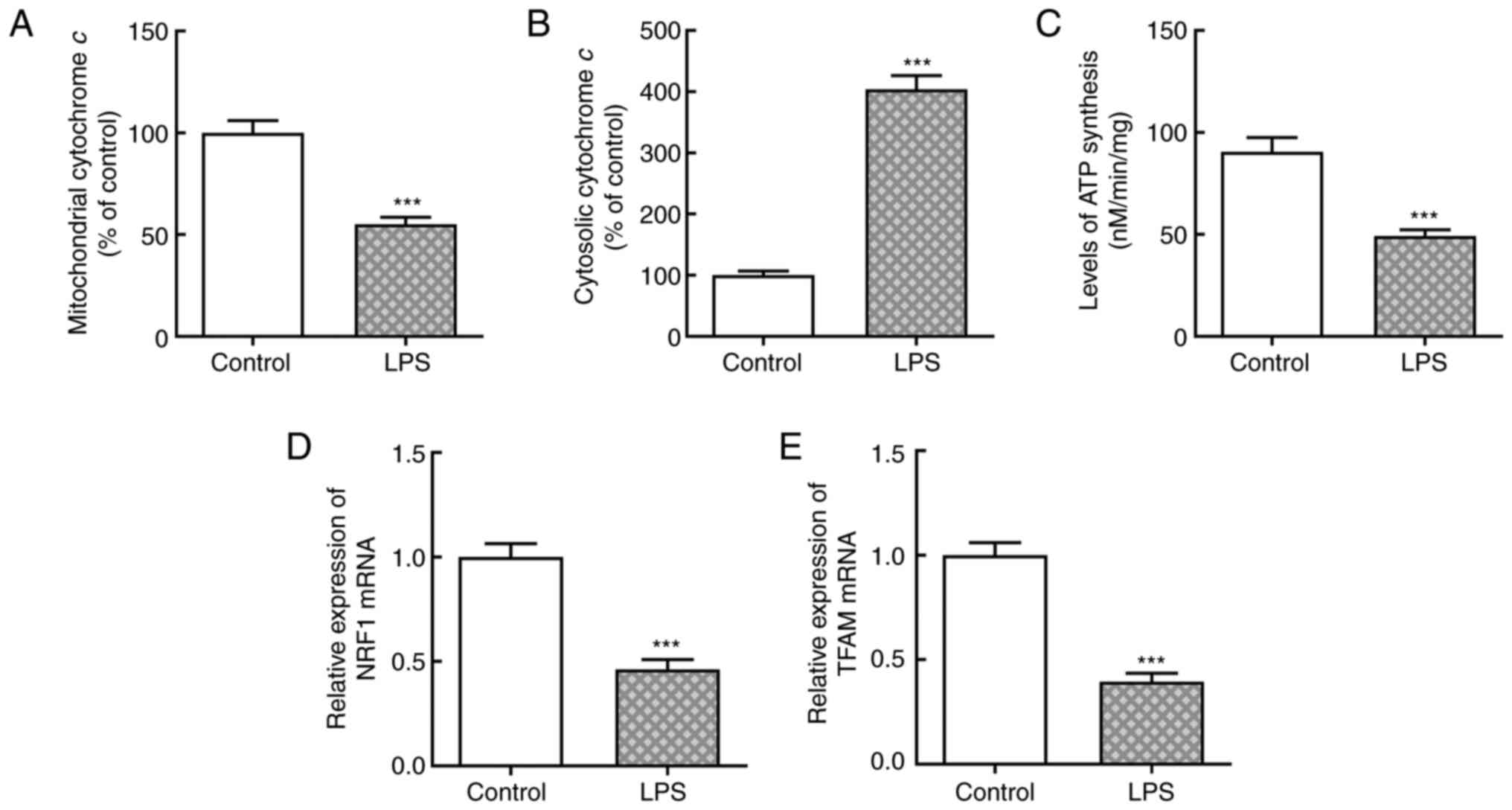
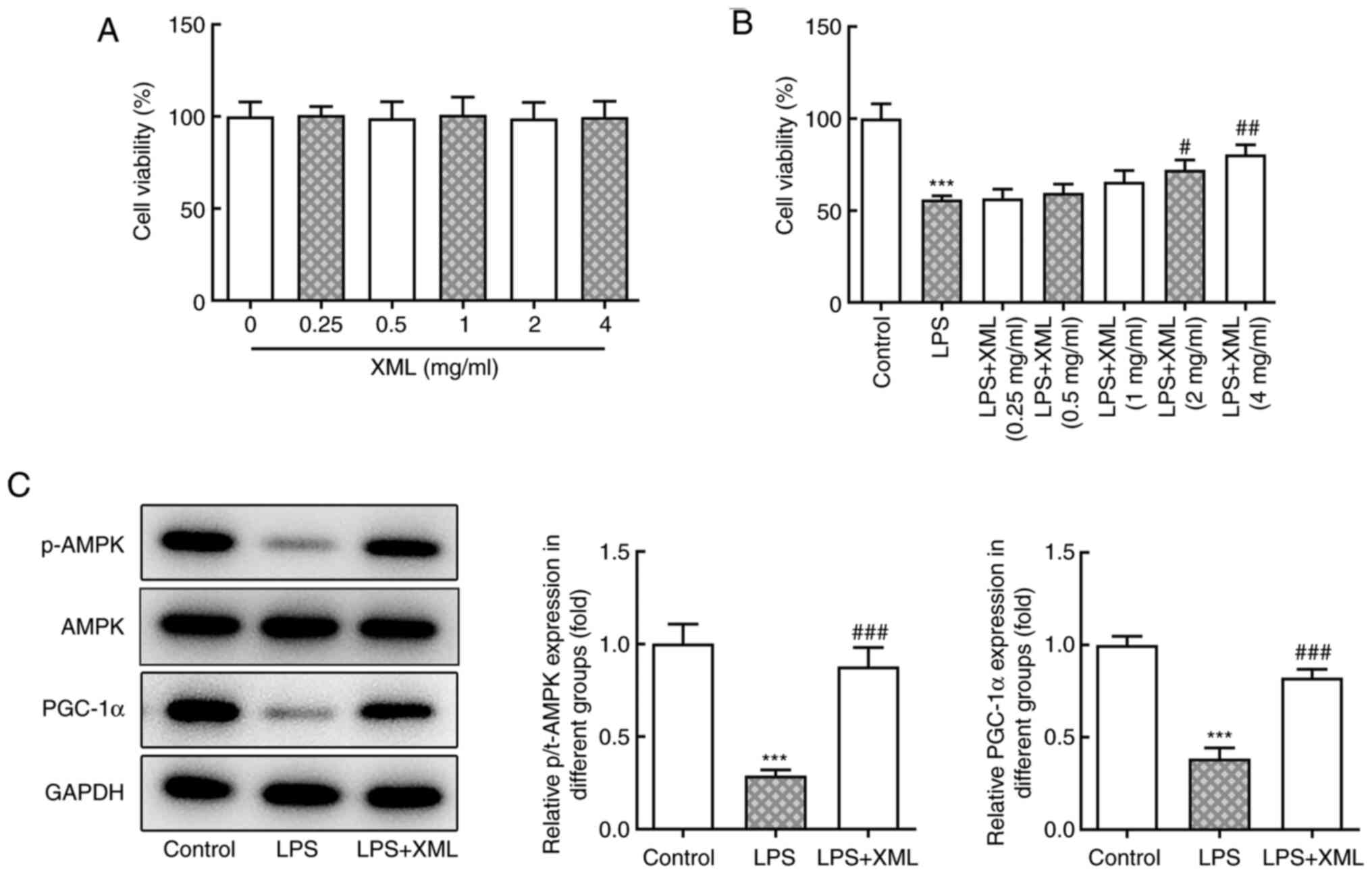
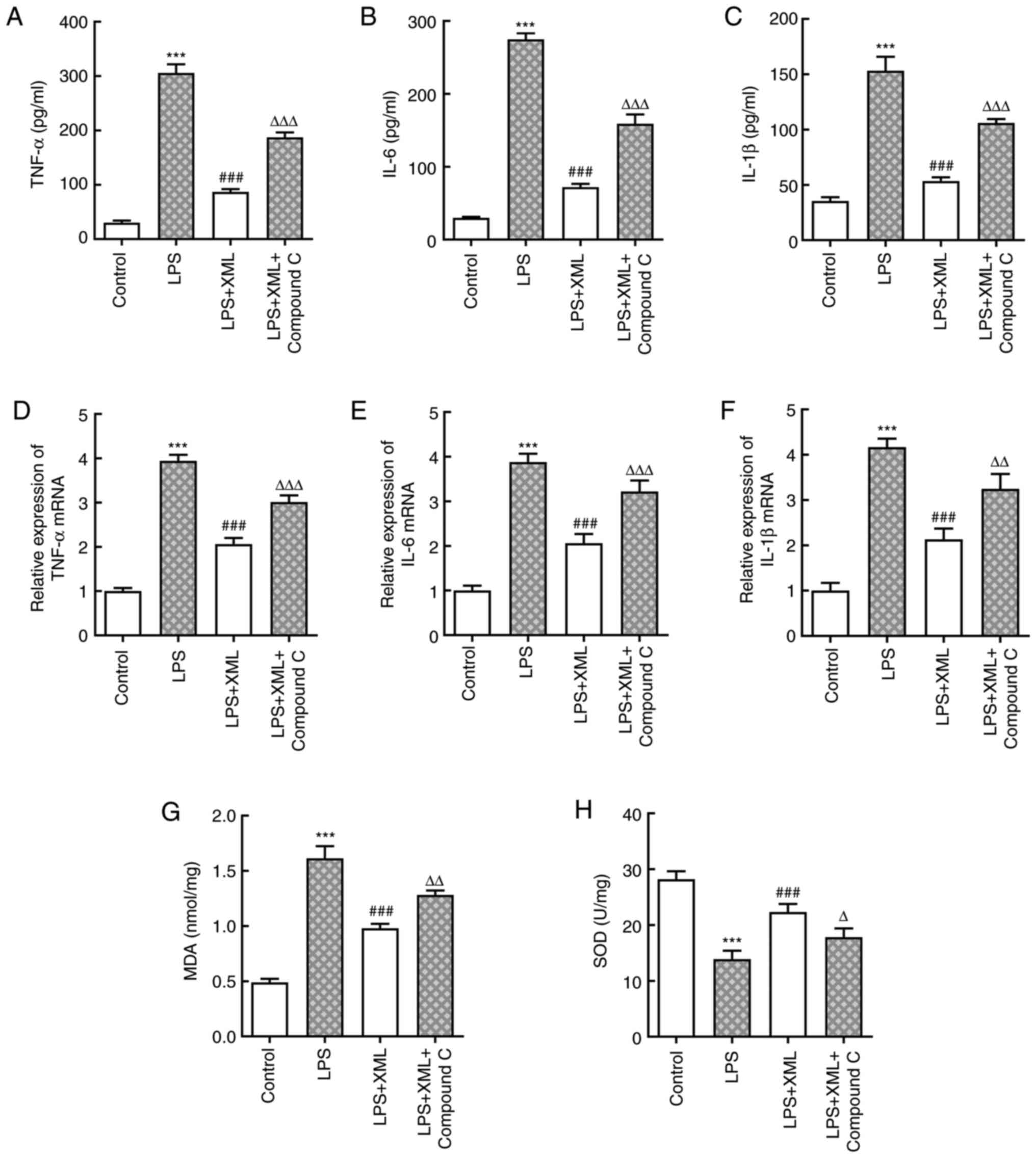
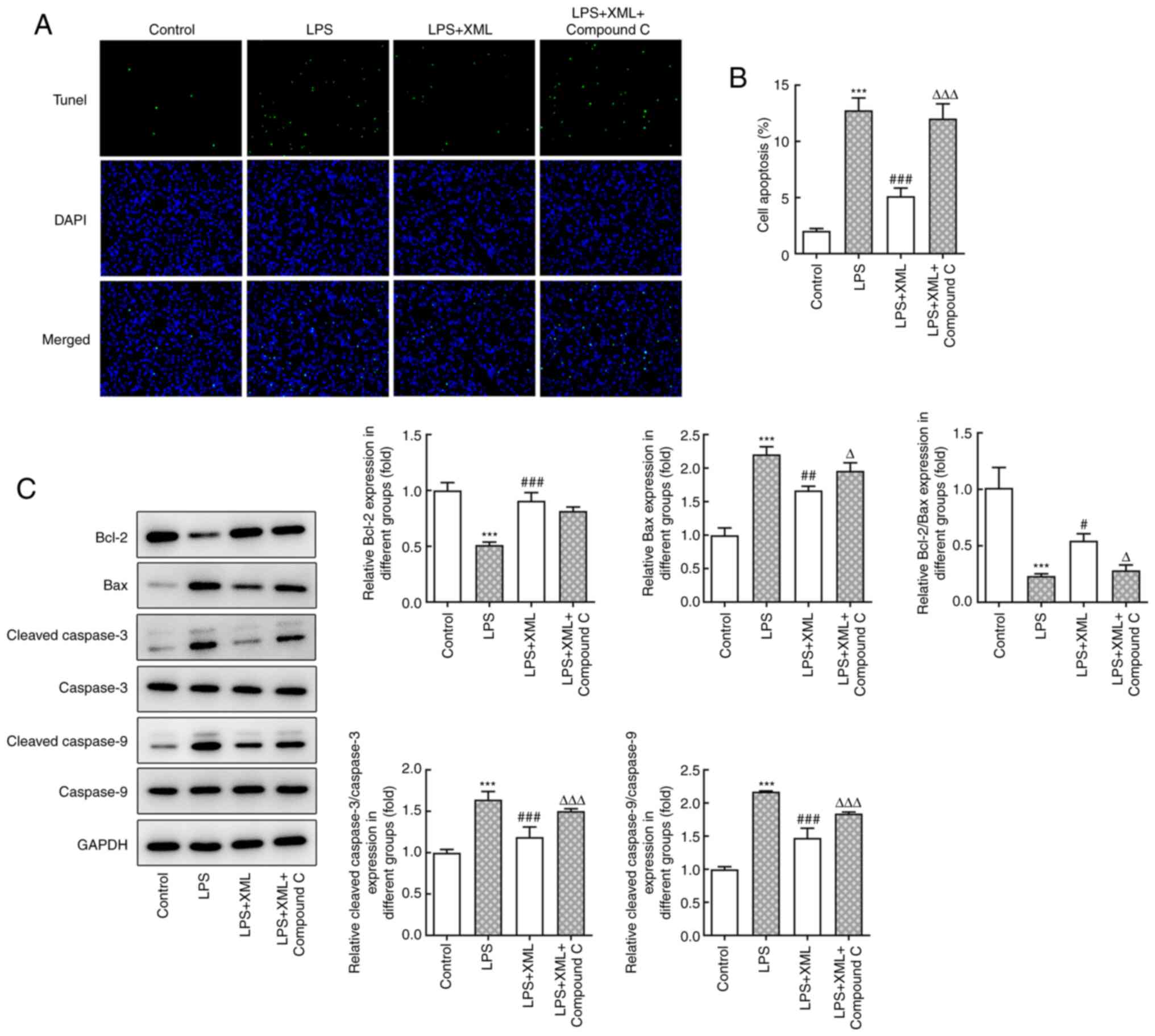
|
1
|
Trefts E, Gannon M and Wasserman DH: The
liver. Curr Biol. 27:R1147–R1151. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Miyajima A, Tanaka M and Itoh T:
Stem/progenitor cells in liver development, homeostasis,
regeneration, and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 14:561–574.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Strnad P, Tacke F, Koch A and Trautwein C:
Liver-guardian, modifier and target of sepsis. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:55–66. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J,
Clermont G, Carcillo J and Pinsky MR: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 29:1303–1310.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Savio LEB, de Andrade Mello P, Figliuolo
VR, de Avelar Almeida TF, Santana PT, Oliveira SDS, Silva CLM,
Feldbrügge L, Csizmadia E, Minshall RD, et al: CD39 limits P2X7
receptor inflammatory signaling and attenuates sepsis-induced liver
injury. J Hepatol. 67:716–726. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang H, Wei L, Zhang Z, Liu S, Zhao G,
Zhang J and Hu Y: Protective effect of Periplaneta americana
extract on intestinal mucosal barrier function in patients with
sepsis. J Tradit Chin Med. 33:70–73. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhao Y, Yang A, Tu P and Hu Z: Anti-tumor
effects of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana.
Chin Med. 12(26)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li QJ, Wang ZG, Liu Q, Xie Y and Hu HL:
Research status of Periplaneta americana with analyses and
prospects of key issues. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 43:1507–1516.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Ma X, Hu Y, Li X, Zheng X, Wang Y, Zhang
J, Fu C and Geng F: Periplaneta americana ameliorates
dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by
Keap1/Nrf-2 activation, intestinal barrier function, and gut
microbiota regulation. Front Pharmacol. 9(944)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li J, Shi W, Zhang J and Ren L: To explore
the protective mechanism of PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1)/parkin
mitophagy-mediated extract of Periplaneta americana on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Med Sci Monit.
25:1383–1391. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang HW, Wei LY, Zhao G, Yang YJ, Liu SZ,
Zhang ZY, Jing Z and Hu YL: Periplaneta americana extract
used in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
World J Emerg Med. 7:50–54. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li D, Li W, Chen Y, Liu L, Ma D, Wang H,
Zhang L, Zhao S and Peng Q: Anti-fibrotic role and mechanism of
Periplaneta americana extracts in CCl4-induced hepatic
fibrosis in rats. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 50:491–498.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zou Y, Zhang M, Zeng D, Ruan Y, Shen L, Mu
Z, Zou J, Xie C, Yang Z, Qian Z, et al: Periplaneta
americana extracts accelerate liver regeneration via a complex
network of pathways. Front Pharmacol. 11(1174)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xing W, Yang L, Peng Y, Wang Q, Gao M,
Yang M and Xiao X: Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates sepsis-induced injury
and mitochondrial dysfunction in liver via AMPK-mediated autophagy
flux. Biosci Rep. 37(BSR20170934)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang Q, Han B, Xue J, Lv Y, Li S, Liu Y,
Wu P, Wang X and Zhang Z: Hexavalent chromium induces mitochondrial
dynamics disorder in rat liver by inhibiting AMPK/PGC-1α signaling
pathway. Environ Pollut. 265(114855)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Singer M: The role of mitochondrial
dysfunction in sepsis-induced multi-organ failure. Virulence.
5:66–72. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yan J and Li S and Li S: The role of the
liver in sepsis. Int Rev Immunol. 33:498–510. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nguyen T, Chen X, Chai J, Li R, Han X,
Chen X, Liu S, Chen M and Xu X: Antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and
analgesic activities of Periplaneta americana extract and
underlying mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother.
123(109753)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Alcantara-Neves NM, Veiga RV, Ponte JC, da
Cunha SS, Simões SM, Cruz ÁA, Yazdanbakhsh M, Matos SM, Silva TM,
Figueiredo CA, et al: Dissociation between skin test reactivity and
anti-aeroallergen IgE: Determinants among urban Brazilian children.
PLoS One. 12(e0174089)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen P, Shen Y, Shi H, Ma X, Lin B, Xiao
T, Wu F, Zhu J, Li Z, Xiao J, et al: Gastroprotective effects of
kangfuxin-against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer via attenuating
oxidative stress and ER stress in mice. Chem Biol Interact.
260:75–83. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Song Q, Xie Y, Gou Q, Guo X, Yao Q and Gou
X: JAK/STAT3 and smad3 activities are required for the wound
healing properties of Periplaneta americana extracts. Int J
Mol Med. 40:465–473. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Paradies G, Paradies V, Ruggiero FM and
Petrosillo G: Oxidative stress, cardiolipin and mitochondrial
dysfunction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:14205–14218. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kelly DP and Scarpulla RC: Transcriptional
regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and
function. Genes Dev. 18:357–368. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Evans MJ and Scarpulla RC: Interaction of
nuclear factors with multiple sites in the somatic cytochrome
c promoter. Characterization of upstream NRF-1, ATF, and
intron Sp1 recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 264:14361–14368.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Levine B, Packer M and Codogno P:
Development of autophagy inducers in clinical medicine. J Clin
Invest. 125:14–24. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Doria A, Gatto M and Punzi L: Autophagy in
human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368(1845)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pickles S, Vigié P and Youle RJ: Mitophagy
and quality control mechanisms in mitochondrial maintenance. Curr
Biol. 28:R170–R185. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kim JS, Nitta T, Mohuczy D, O'Malley KA,
Moldawer LL, Dunn WA Jr and Behrns KE: Impaired autophagy: A
mechanism of mitochondrial dysfunction in anoxic rat hepatocytes.
Hepatology. 47:1725–1736. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li Y and Chen Y: AMPK and autophagy. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 1206:85–108. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM,
Gelino S, Kohnz RA, Mair W, Vasquez DS, Joshi A, Gwinn DM, Taylor
R, et al: Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein
kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science. 331:456–461.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bergeron R, Ren JM, Cadman KS, Moore IK,
Perret P, Pypaert M, Young LH, Semenkovich CF and Shulman GI:
Chronic activation of AMP kinase results in NRF-1 activation and
mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
281:E1340–E1346. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jäger S, Handschin C, St-Pierre J and
Spiegelman BM: AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) action in
skeletal muscle via direct phosphorylation of PGC-1alpha. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:12017–12022. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gerhart-Hines Z, Rodgers JT, Bare O, Lerin
C, Kim SH, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW, Wu Z and Puigserver P: Metabolic
control of muscle mitochondrial function and fatty acid oxidation
through SIRT1/PGC-1alpha. EMBO J. 26:1913–1923. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Reznick RM, Zong H, Li J, Morino K, Moore
IK, Yu HJ, Liu ZX, Dong J, Mustard KJ, Hawley SA, et al:
Aging-associated reductions in AMP-activated protein kinase
activity and mitochondrial biogenesis. Cell Metab. 5:151–156.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|