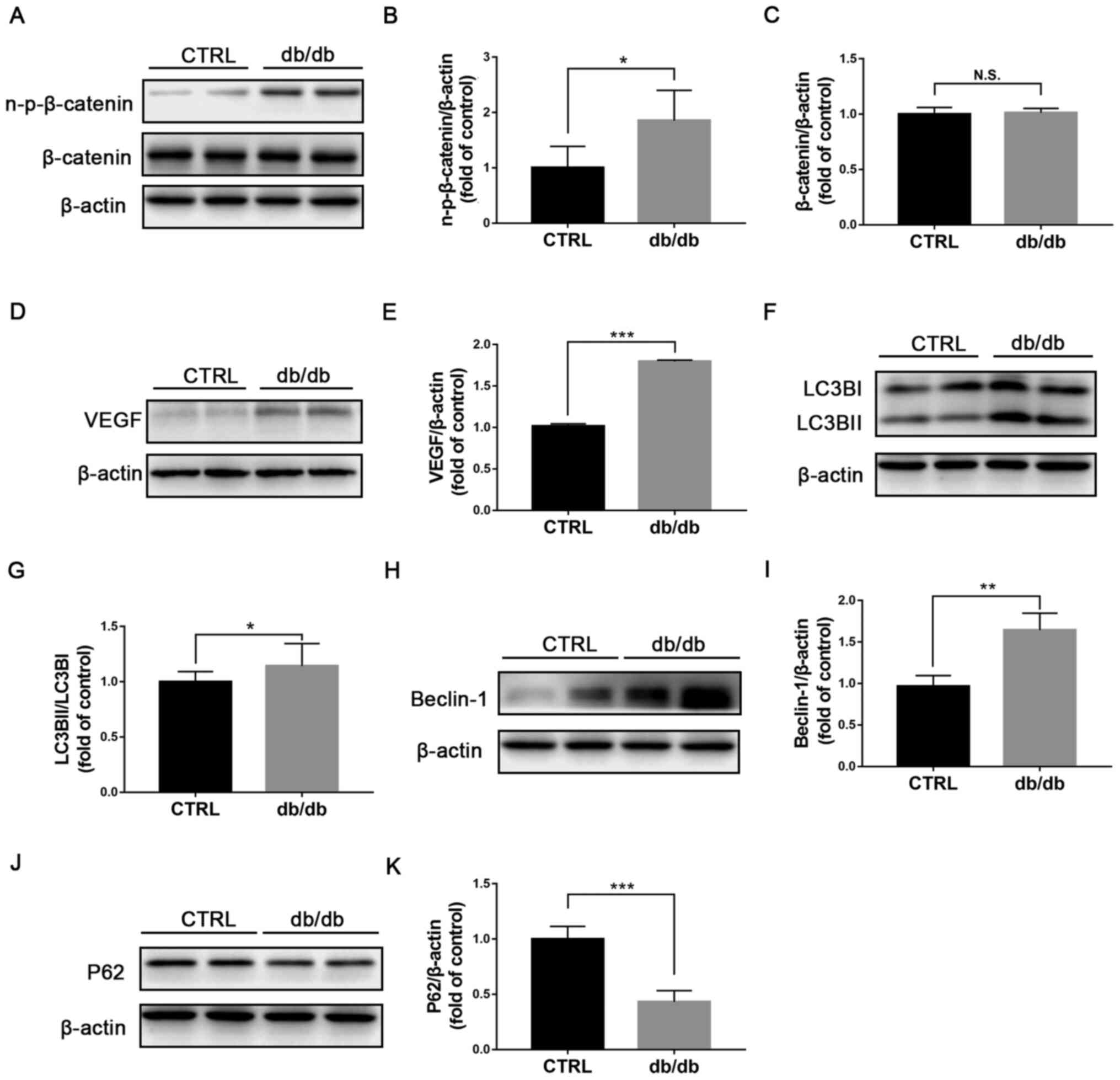
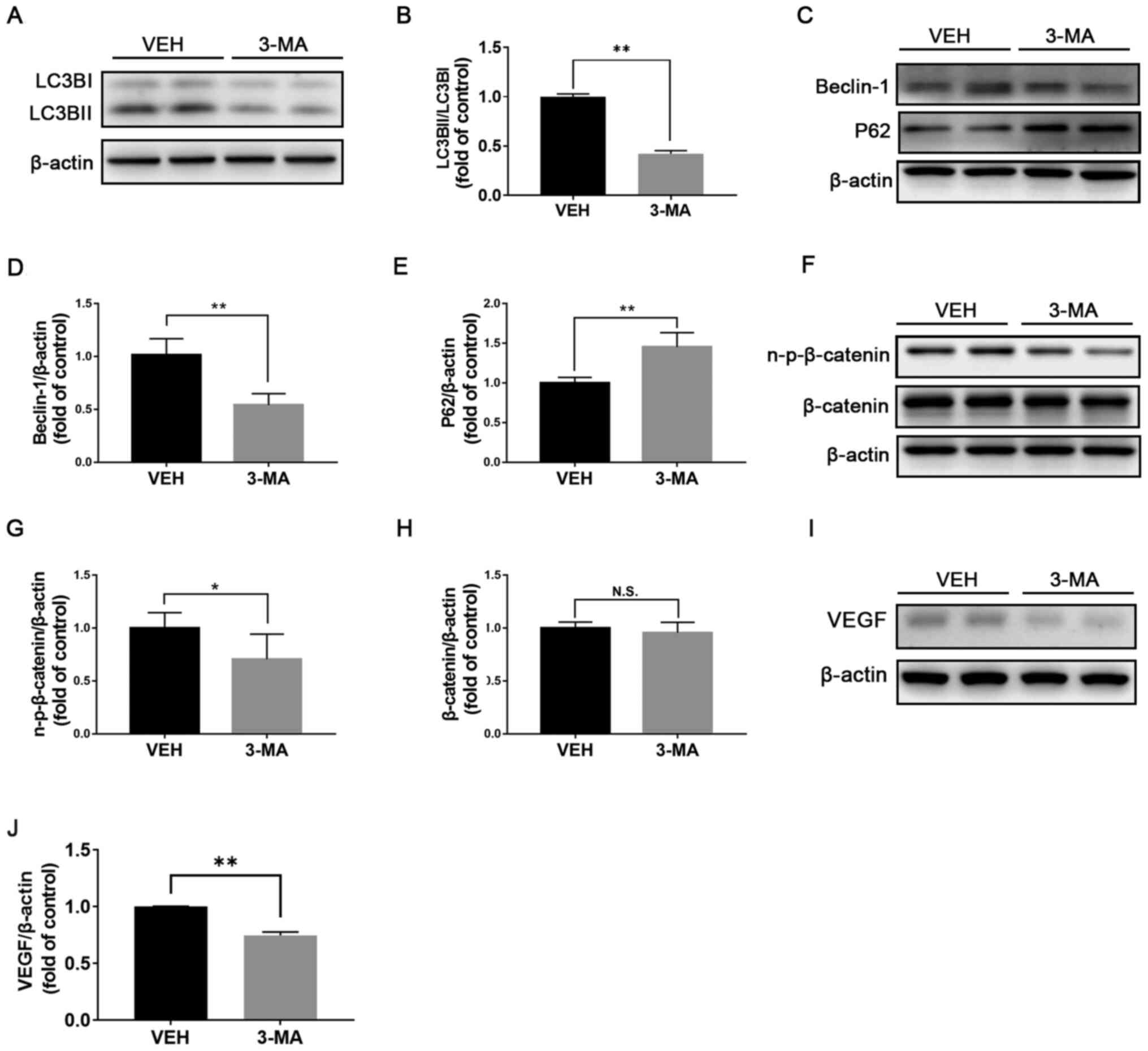
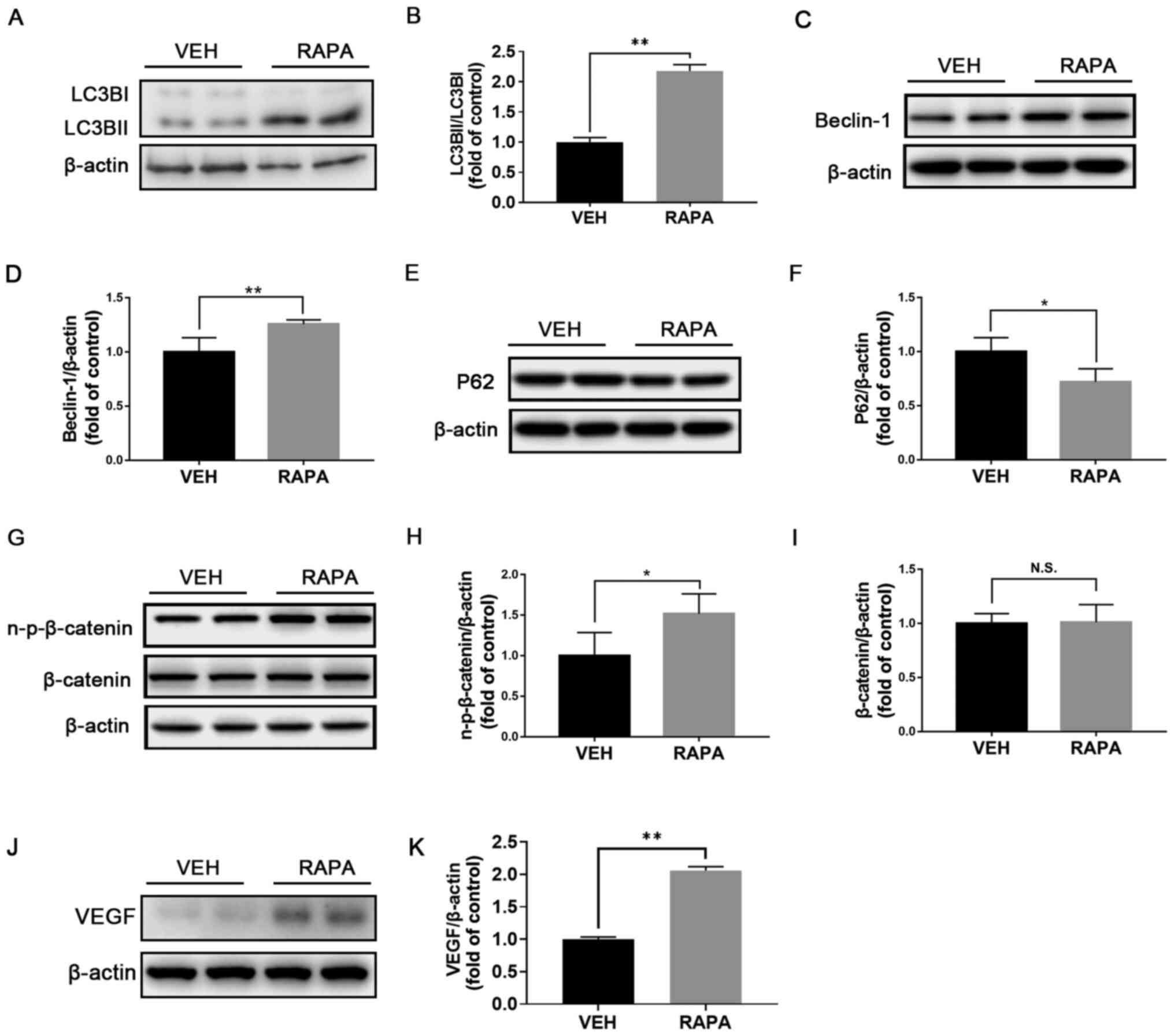
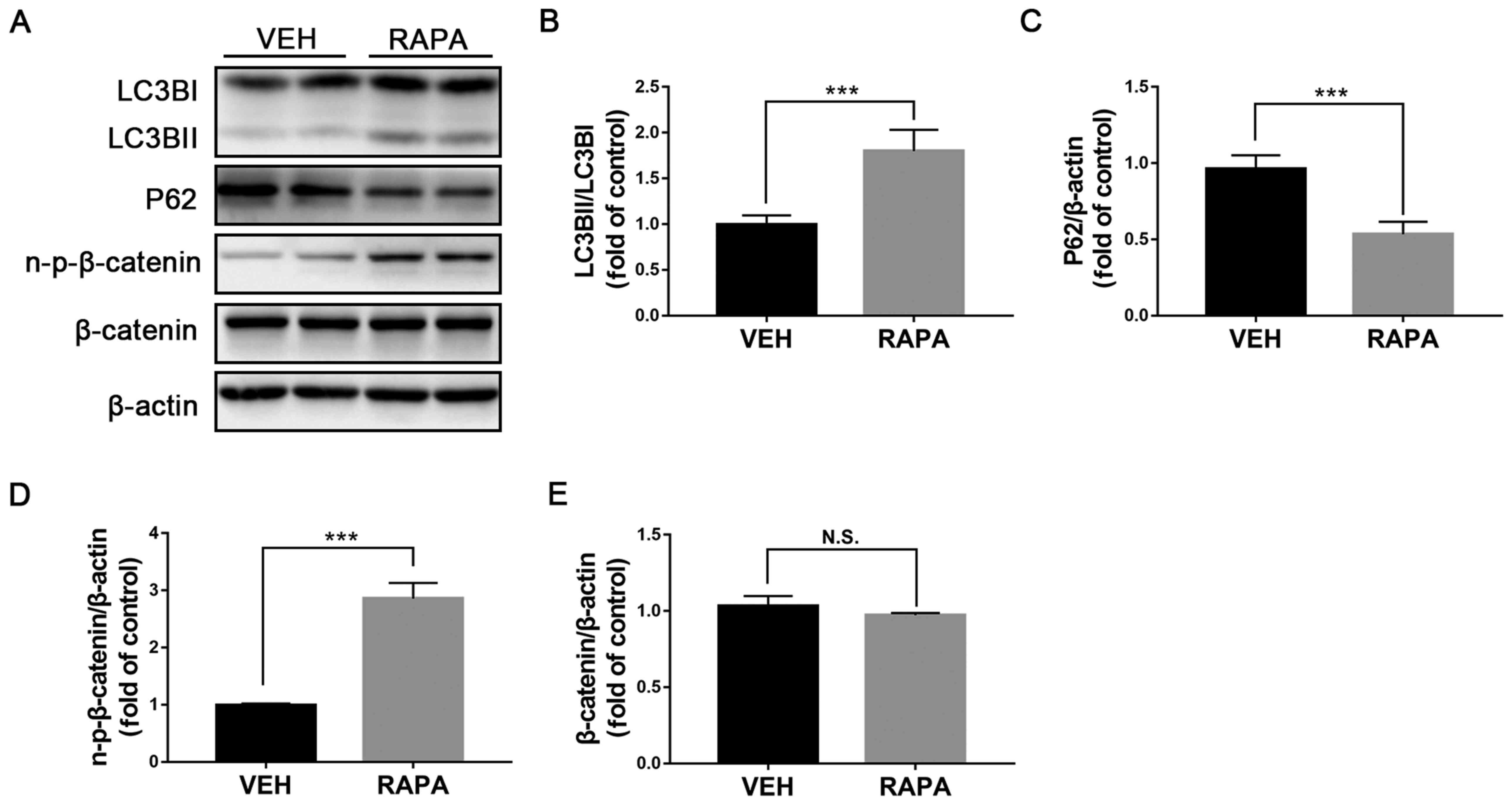
|
1
|
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R and
King H: Global prevalence of diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000
and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 27:1047–1053.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Klein R, Knudtson MD, Lee KE, Gangnon R
and Klein BE: The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic
Retinopathy: XXII the twenty-five-year progression of retinopathy
in persons with type 1 diabetes. Ophthalmology. 115:1859–1868.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ting DSW and Wong TY: Proliferative
diabetic retinopathy: Laser or eye injection? Lancet.
389:2165–2166. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen Q and Ma JX: Canonical Wnt signaling
in diabetic retinopathy. Vision Res. 139:47–58. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen Y, Hu Y, Zhou T, Zhou KK, Mott R, Wu
M, Boulton M, Lyons TJ, Gao G and Ma JX: Activation of the Wnt
pathway plays a pathogenic role in diabetic retinopathy in humans
and animal models. Am J Pathol. 175:2676–2685. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu X, Zhang B, McBride JD, Zhou K, Lee K,
Zhou Y, Liu Z and Ma JX: Antiangiogenic and antineuroinflammatory
effects of kallistatin through interactions with the canonical Wnt
pathway. Diabetes. 62:4228–4238. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee K, Hu Y, Ding L, Chen Y, Takahashi Y,
Mott R and Ma JX: Therapeutic potential of a monoclonal antibody
blocking the Wnt pathway in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes.
61:2948–2957. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Eskelinen EL and Saftig P: Autophagy: A
lysosomal degradation pathway with a central role in health and
disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:664–673. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Boya P, Esteban-Martínez L, Serrano-Puebla
A, Gómez-Sintes R and Villarejo-Zori B: Autophagy in the eye:
Development, degeneration, and aging. Prog Retin Eye Res.
55:206–245. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rosa MD, Distefano G, Gagliano C, Rusciano
D and Malaguarnera L: Autophagy in Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 14:810–825. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fu D, Yu JY, Yang S, Wu M, Hammad SM,
Connell AR, Du M, Chen J and Lyons TJ: Survival or death: A dual
role for autophagy in stress-induced pericyte loss in diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetologia. 59:2251–2261. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lopes de Faria JM, Duarte DA, Montemurro
C, Papadimitriou A, Consonni SR and Lopes de Faria JB: Defective
Autophagy in Diabetic Retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
57:4356–4366. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li P, Guo Y, Bledsoe G, Yang Z, Chao L and
Chao J: Kallistatin induces breast cancer cell apoptosis and
autophagy by modulating Wnt signaling and microRNA synthesis. Exp
Cell Res. 340:305–314. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Peng Y, Cao J, Yao XY, Wang JX, Zhong MZ,
Gan PP and Li JH: TUSC3 induces autophagy in human non-small cell
lung cancer cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget.
8:52960–52974. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gao C, Cao W, Bao L, Zuo W, Xie G, Cai T,
Fu W, Zhang J, Wu W, Zhang X, et al: Autophagy negatively regulates
Wnt signalling by promoting Dishevelled degradation. Nat Cell Biol.
12:781–790. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Lei H, Shi Y, Wang JJ, Chen N, Li
ZH, Chen YF, Ye QF and Yang Y: Autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine
alleviates overload-exercise-induced cardiac injury in rats. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 38:990–997. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
James MH, Quinn RK, Ong LK, Levi EM, Smith
DW, Dickson PW and Dayas CV: Rapamycin reduces motivated responding
for cocaine and alters GluA1 expression in the ventral but not
dorsal striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 784:147–154. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li X, Shan J, Chang W, Kim I, Bao J, Lee
HJ, Zhang X, Samuel VT, Shulman GI, Liu D, et al: Chemical and
genetic evidence for the involvement of Wnt antagonist Dickkopf2 in
regulation of glucose metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:11402–11407. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen Q, Qiu F, Zhou K, Matlock HG,
Takahashi Y, Rajala RVS, Yang Y, Moran E and Ma JX: Pathogenic Role
of microRNA-21 in Diabetic Retinopathy Through Downregulation of
PPARα. Diabetes. 66:1671–1682. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Seglen PO and Gordon PB: 3-Methyladenine:
Specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in
isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:1889–1892.
1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Coughlin BA, Feenstra DJ and Mohr S:
Müller cells and diabetic retinopathy. Vision Res. 139:93–100.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhou KK, Benyajati S, Le Y, Cheng R, Zhang
W and Ma JX: Interruption of Wnt signaling in Müller cells
ameliorates ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization. PLoS One.
9(e108454)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mauthe M, Orhon I, Rocchi C, Zhou X, Luhr
M, Hijlkema KJ, Coppes RP, Engedal N, Mari M and Reggiori F:
Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing
autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Autophagy. 14:1435–1455.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cicchini M, Chakrabarti R, Kongara S,
Price S, Nahar R, Lozy F, Zhong H, Vazquez A, Kang Y and Karantza
V: Autophagy regulator BECN1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis
driven by WNT1 activation and following parity. Autophagy.
10:2036–2052. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fan Q, Yang L, Zhang X, Ma Y, Li Y, Dong
L, Zong Z, Hua X, Su D, Li H, et al: Autophagy promotes metastasis
and glycolysis by upregulating MCT1 expression and Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37(9)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ríos JA, Godoy JA and Inestrosa NC: Wnt3a
ligand facilitates autophagy in hippocampal neurons by modulating a
novel GSK-3β-AMPK axis. Cell Commun Signal. 16(15)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Burke SJ, Batdorf HM, Burk DH, Noland RC,
Eder AE, Boulos MS, Karlstad MD and Collier JJ: db/db mice exhibit
features of human type 2 diabetes that are not present in
weight-matched C57BL/6J mice fed a Western diet. J Diabetes Res.
2017(8503754)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bogdanov P, Corraliza L, Villena JA,
Carvalho AR, Garcia-Arumí J, Ramos D, Ruberte J, Simó R and
Hernández C: The db/db mouse: A useful model for the study of
diabetic retinal neurodegeneration. PLoS One.
9(e97302)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Midena E, Segato T, Radin S, di Giorgio G,
Meneghini F, Piermarocchi S and Belloni AS: Studies on the retina
of the diabetic db/db mouse. I. Endothelial cell-pericyte ratio.
Ophthalmic Res. 21:106–111. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bringmann A, Pannicke T, Grosche J,
Francke M, Wiedemann P, Skatchkov SN, Osborne NN and Reichenbach A:
Müller cells in the healthy and diseased retina. Prog Retin Eye
Res. 25:397–424. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tien T, Zhang J, Muto T, Kim D, Sarthy VP
and Roy S: High Glucose Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction in
Retinal Müller Cells: Implications for Diabetic Retinopathy. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 58:2915–2921. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ao H, Li H, Zhao X, Liu B and Lu L: TXNIP
positively regulates the autophagy and apoptosis in the rat müller
cell of diabetic retinopathy. Life Sci. 267(118988)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Iwai-Kanai E, Yuan H, Huang C, Sayen MR,
Perry-Garza CN, Kim L and Gottlieb RA: A method to measure cardiac
autophagic flux in vivo. Autophagy. 4:322–329. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|