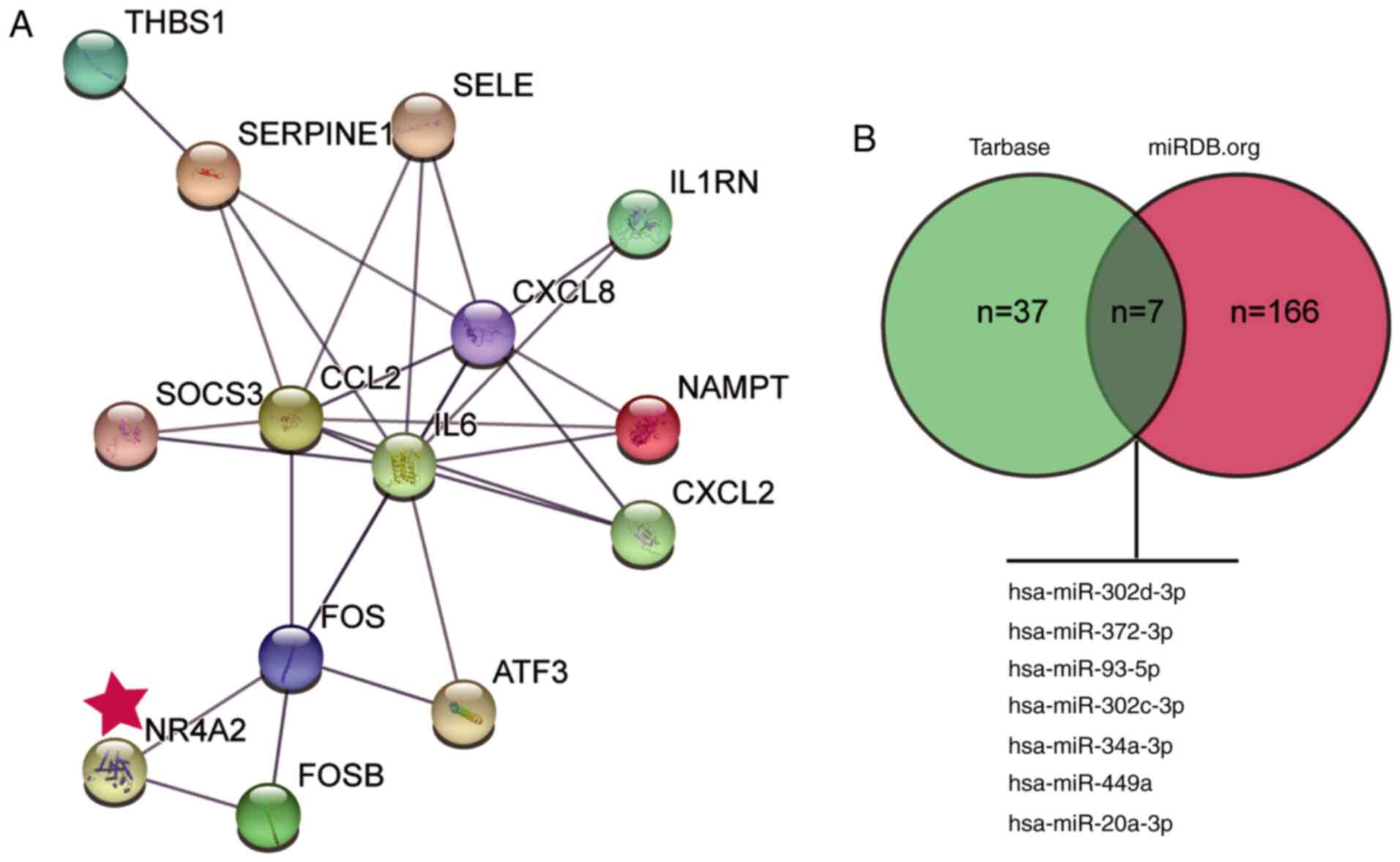
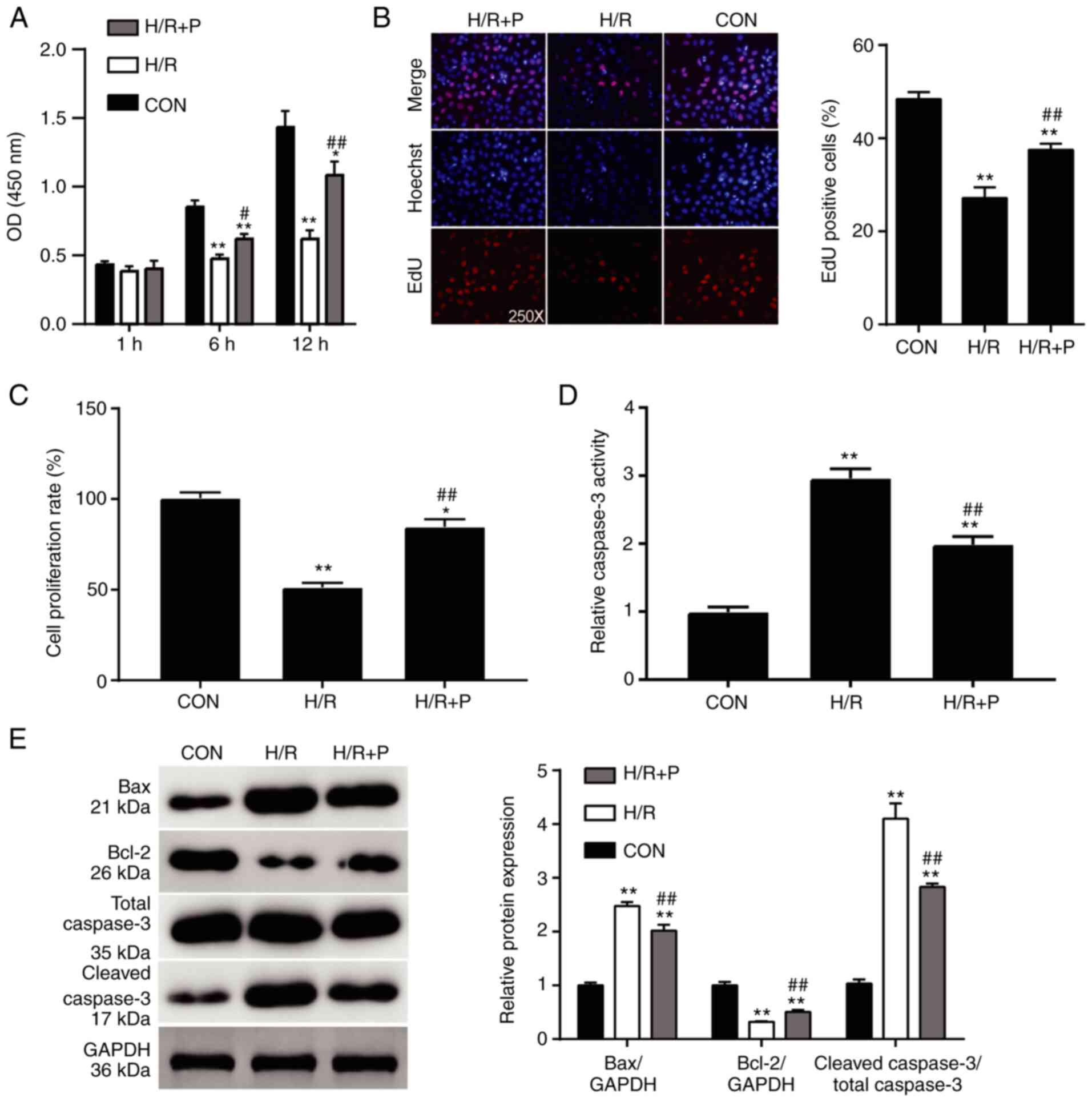
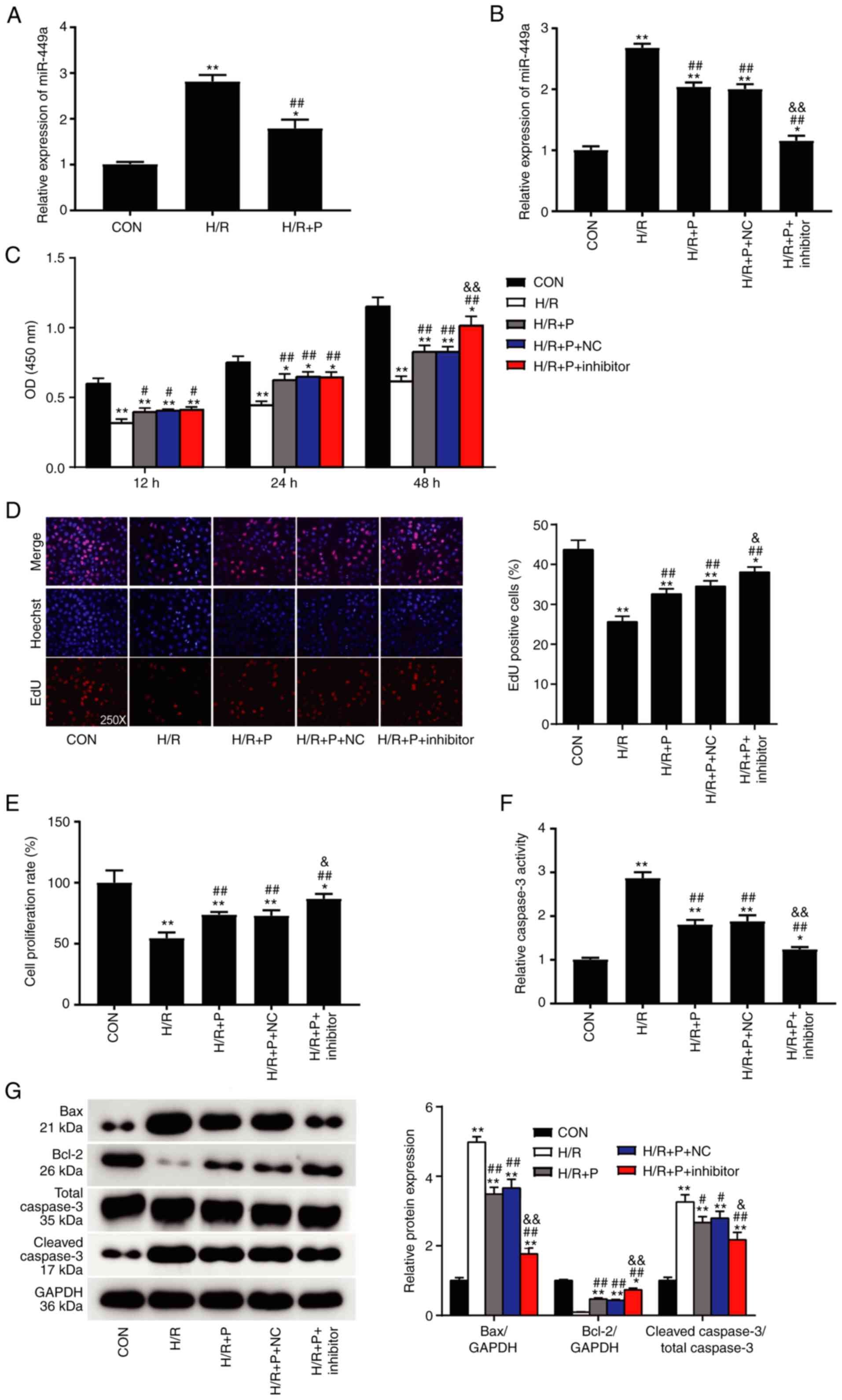
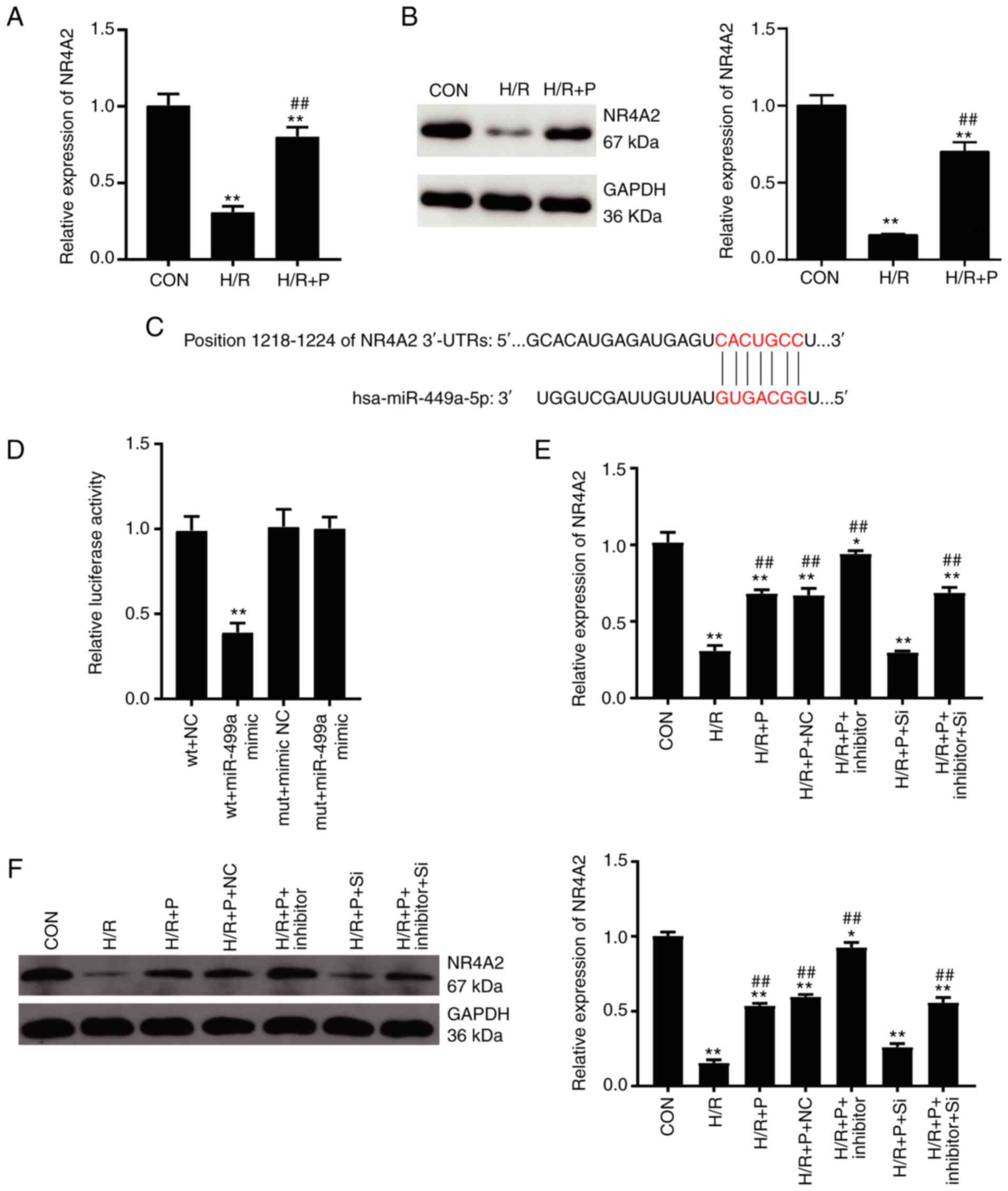
|
1
|
Nadatani Y, Watanabe T, Shimada S, Otani
K, Tanigawa T and Fujiwara Y: Microbiome and intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 63:26–32.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Binder A, Ali A, Chawla R, Aziz HA, Abbate
A and Jovin IS: Myocardial protection from ischemia-reperfusion
injury post coronary revascularization. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther.
13:1045–1057. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ferdinandy P, Schulz R and Baxter GF:
Interaction of cardiovascular risk factors with myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury, preconditioning, and postconditioning.
Pharmacol Rev. 59:418–458. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhao ZQ and Vinten-Johansen J:
Postconditioning: Reduction of reperfusion-induced injury.
Cardiovasc Res. 70:200–211. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Qiao SG, Sun Y, Sun B, Wang A, Qiu J, Hong
L, An JZ, Wang C and Zhang HL: Sevoflurane postconditioning
protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
restoring autophagic flux via an NO-dependent mechanism. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 40:35–45. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li Z, Zhang Y, Ding N, Zhao Y, Ye Z, Shen
L, Yi H and Zhu Y: Inhibition of lncRNA XIST improves myocardial
I/R injury by targeting miR-133a through inhibition of autophagy
and regulation of SOCS2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 18:764–773.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yao L, Chen H, Wu Q and Xie K:
Hydrogen-rich saline alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in
myocardial I/R injury via PINK-mediated autophagy. Int J Mol Med.
44:1048–1062. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li W, Li Y, Chu Y, Wu W, Yu Q, Zhu X and
Wang Q: PLCE1 promotes myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in
H/R H9c2 cells and I/R rats by promoting inflammation. Biosci Rep.
39(BSR20181613)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lotz C, Stumpner J and Smul TM:
Sevoflurane as opposed to propofol anesthesia preserves
mitochondrial function and alleviates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biomed Pharmacother.
129(110417)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li YM, Sun JG, Hu LH, Ma XC, Zhou G and
Huang XZ: Propofol-mediated cardioprotection dependent of
microRNA-451/HMGB1 against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
J Cell Physiol. 234:23289–23301. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li H, Zhang X, Tan J, Sun L, Xu LH, Jiang
YG, Lou JS, Shi XY and Mi WD: Propofol postconditioning protects
H9c2 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inducing autophagy
via the SAPK/JNK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:4573–4580.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhao D, Li Q, Huang Q, Li X, Yin M, Wang Z
and Hong J: Cardioprotective effect of propofol against oxygen
glucose deprivation and reperfusion injury in H9c2 cells. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2015(184938)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vasileiou I, Xanthos T, Koudouna E, Perrea
D, Klonaris C, Katsargyris A and Papadimitriou L: Propofol: A
review of its non-anaesthetic effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 605:1–8.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Green TR, Bennett SR and Nelson VM:
Specificity and properties of propofol as an antioxidant free
radical scavenger. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 129:163–169.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hanouz JL, Yvon A, Flais F, Rouet R,
Ducouret P, Bricard H and Gérard JL: Propofol decreases
reperfusion-induced arrhythmias in a model of ‘border zone’ between
normal and ischemic-reperfused guinea pig myocardium. Anesth Analg.
97:1230–1238. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hu S, Cao S, Tong Z and Liu J: FGF21
protects myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through reduction
of miR-145-mediated autophagy. Am J Transl Res. 10:3677–3688.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang Y, Yang J, Liu XW, Ding JW, Li S, Guo
X, Yang CJ, Fan ZX, Wang HB, Li Q, et al: Down-regulation of
miR-327 alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial damage
by targeting RP105. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:1049–1063.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ye Y, Hu Z, Lin Y, Zhang C and Perez-Polo
JR: Downregulation of microRNA-29 by antisense inhibitors and a
PPAR-gamma agonist protects against myocardial
ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 87:535–544.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cheng J, Wu Q, Lv R, Huang L, Xu B, Wang
X, Chen A and He F: MicroRNA-449a inhibition protects H9C2 cells
against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury by targeting the
Notch-1 signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:2587–2600.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Dong H, Liu Y, Han J, Tang S and
Si J: Tetramethylpyrazine partially relieves hypoxia-caused damage
of cardiomyocytes H9c2 by downregulation of miR-449a. J Cell
Physiol, Feb 15, 2019 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
21
|
Spathis AD, Asvos X, Ziavra D, Karampelas
T, Topouzis S, Cournia Z, Qing X, Alexakos P, Smits LM, Dalla C, et
al: Nurr1:RXRα heterodimer activation as monotherapy for
Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:3999–4004.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Medzikovic L, Schumacher CA, Verkerk AO,
van Deel ED, Wolswinkel R, van der Made I, Bleeker N, Cakici D, van
den Hoogenhof MM, Meggouh F, et al: Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77
affects cardiomyocyte calcium homeostasis and adverse cardiac
remodelling. Sci Rep. 5(15404)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xiao G, Sun T, Songming C and Cao Y: NR4A1
enhances neural survival following oxygen and glucose deprivation:
An in vitro study. J Neurol Sci. 330:78–84. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu H, Liu P, Shi X, Yin D and Zhao J:
NR4A2 protects cardiomyocytes against myocardial infarction injury
by promoting autophagy. Cell Death Discov. 4(27)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lucchinetti E, Hofer C, Bestmann L,
Hersberger M, Feng J, Zhu M, Furrer L, Schaub MC, Tavakoli R,
Genoni M, et al: Gene regulatory control of myocardial energy
metabolism predicts postoperative cardiac function in patients
undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery:
Inhalational versus intravenous anesthetics. Anesthesiology.
106:444–457. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ming N, Na HST, He JL, Meng QT and Xia ZY:
Propofol alleviates oxidative stress via upregulating
lncRNA-TUG1/Brg1 pathway in hypoxia/reoxygenation hepatic cells. J
Biochem. 166:415–421. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim EJ, Choi IS, Yoon JY, Park BS, Yoon JU
and Kim CH: Effects of propofol-induced autophagy against oxidative
stress in human osteoblasts. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 16:39–47.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang Z, Yang P and Qi Y: Role of
microRNA-134 in the neuroprotective effects of propofol against
oxygen-glucose deprivation and related mechanisms. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:20617–20623. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma K, Qiu J, Zhou M, Yang Y and Ye X:
Cox-2 Negatively affects the protective role of propofol against
hypoxia/reoxygenation induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis through
suppressing Akt signaling. Biomed Res Int.
2019(7587451)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xu B, Zhang X, Wang S and Shi B: MiR-449a
suppresses cell migration and invasion by targeting PLAGL2 in
breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 214:790–795. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Yu F, Wang S, Zhao X, Jiang F, Xie
J and Deng M: circGFRA1 promotes ovarian cancer progression by
sponging miR-449a. J Cancer. 10:3908–3913. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kardys I, van Tiel CM, de Vries CJ,
Pannekoek H, Uitterlinden AG, Hofman A, Witteman JC and de Maat MP:
Haplotypes of the NR4A2/NURR1 gene and cardiovascular disease: The
Rotterdam Study. Hum Mutat. 30:417–423. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|