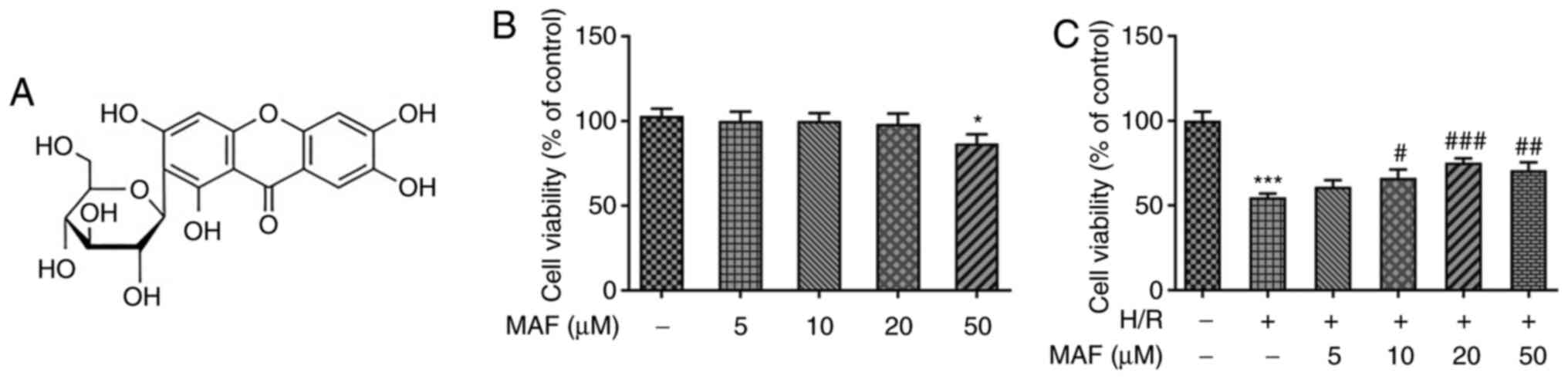
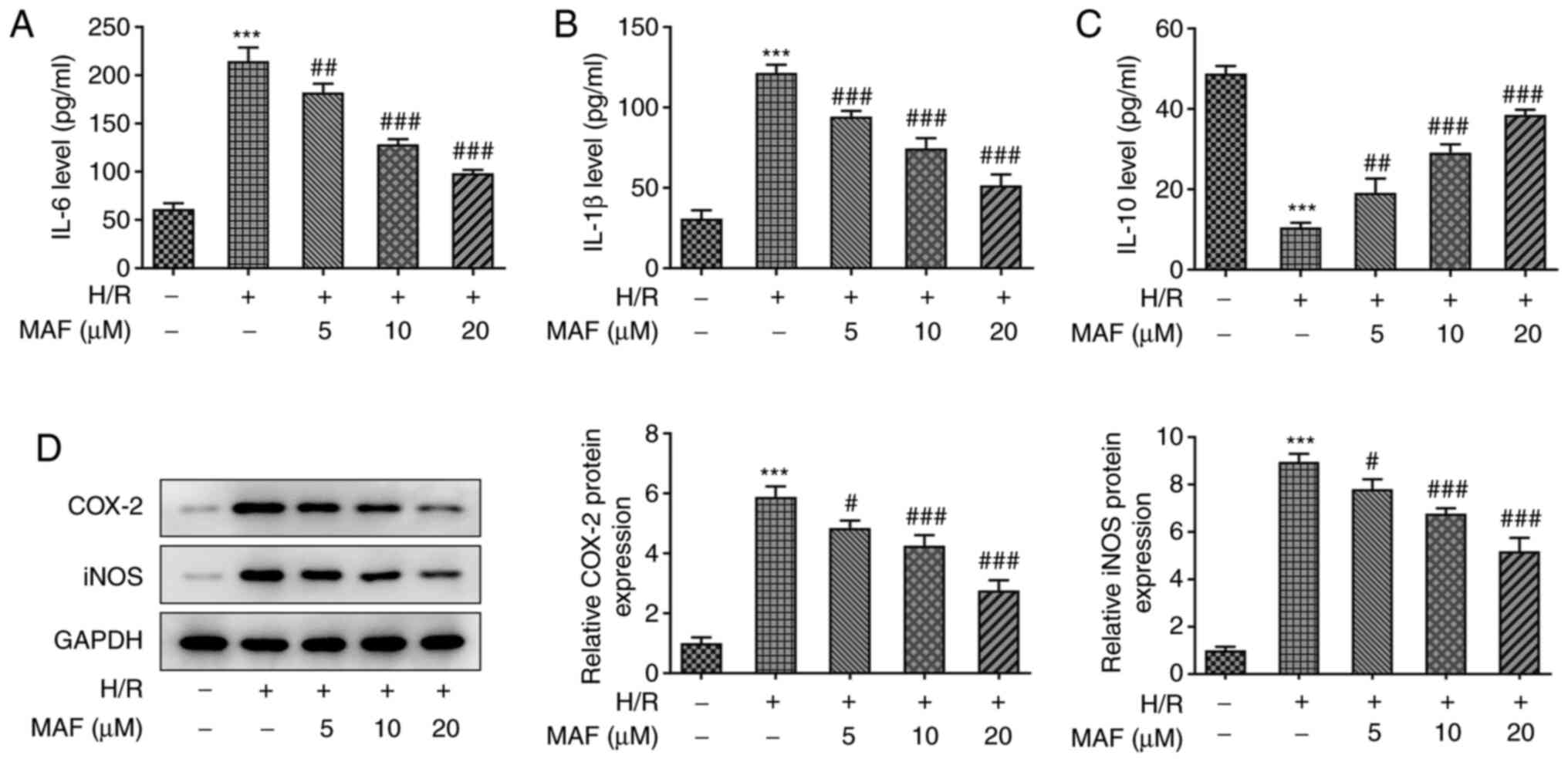
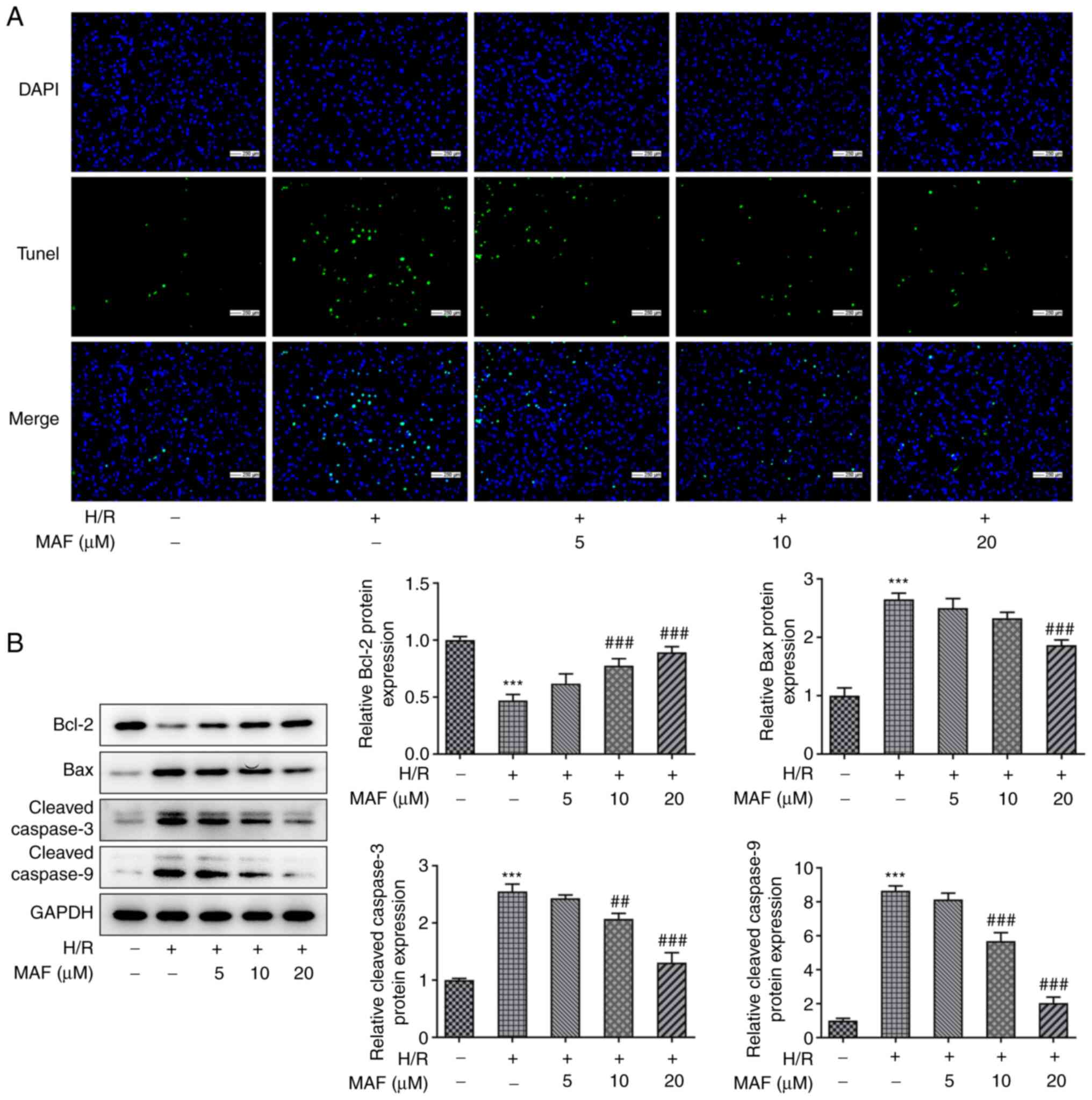
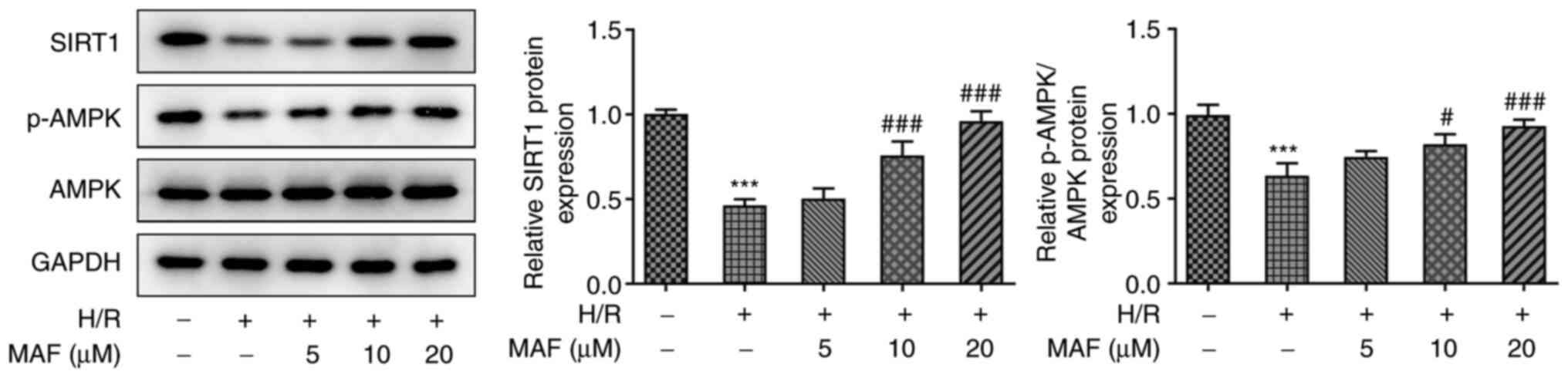
|
1
|
Laubach VE and Sharma AK: Mechanisms of
lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Opin Organ Transplant.
21:246–252. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Saito M, Chen-Yoshikawa TF, Suetsugu K,
Okabe R, Takahagi A, Masuda S and Date H: Pirfenidone alleviates
lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 158:289–296. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shah RJ and Diamond JM: Primary graft
dysfunction (PGD) following lung transplantation. Semin Respir Crit
Care Med. 39:148–154. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
You J, Cheng J, Yu B, Duan C and Peng J:
Baicalin, a Chinese herbal medicine, inhibits the proliferation and
migration of human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) Cells,
A549 and H1299, by activating the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. Med
Sci Monit. 24:2126–2133. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jin MS, Hyun CL, Park IA, Kim JY, Chung
YR, Im SA, Lee KH, Moon HG and Ryu HS: SIRT1 induces tumor invasion
by targeting epithelial mesenchymal transition-related pathway and
is a prognostic marker in triple negative breast cancer. Tumour
Biol. 37:4743–4753. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Suzuki K, Hayashi R, Ichikawa T, Imanishi
S, Yamada T, Inomata M, Miwa T, Matsui S, Usui I, Urakaze M, et al:
SRT1720, a SIRT1 activator, promotes tumor cell migration, and lung
metastasis of breast cancer in mice. Oncol Rep. 27:1726–1732.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lovaas JD, Zhu L, Chiao CY, Byles V,
Faller DV and Dai Y: SIRT1 enhances matrix metalloproteinase-2
expression and tumor cell invasion in prostate cancer cells.
Prostate. 73:522–530. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu Z, Meng Y, Miao Y, Yu L and Yu Q:
Propofol reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung
injury by stimulating sirtuin 1 and inhibiting pyroptosis. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:865–876. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yang C, Yang W, He Z, He H, Yang X, Lu Y
and Li H: Kaempferol improves lung ischemia-reperfusion injury via
antiinflammation and antioxidative stress regulated by
SIRT1/HMGB1/NF-κB axis. Front Pharmacol. 10(1635)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fu C, Hao S, Xu X, Zhou J, Liu Z, Lu H,
Wang L, Jin W and Li S: Activation of SIRT1 ameliorates LPS-induced
lung injury in mice via decreasing endothelial tight junction
permeability. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 40:630–641. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Salomone F, Barbagallo I, Godos J, Lembo
V, Currenti W, Cinà D, Avola R, D'Orazio N, Morisco F, Galvano F
and Li Volti G: Silibinin restores NAD+ levels and
induces the SIRT1/AMPK pathway in non-alcoholic fatty liver.
Nutrients. 9(1086)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mulchandani N, Yang WL, Khan MM, Zhang F,
Marambaud P, Nicastro J, Coppa GF and Wang P: Stimulation of brain
AMP-activated protein kinase attenuates inflammation and acute lung
injury in sepsis. Mol Med. 21:637–644. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li X, Jamal M, Guo P, Jin Z, Zheng F, Song
X, Zhan J and Wu H: Irisin alleviates pulmonary epithelial barrier
dysfunction in sepsis-induced acute lung injury via activation of
AMPK/SIRT1 pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.
118(109363)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ajila CM, Rao LJ and Rao UJ:
Characterization of bioactive compounds from raw and ripe Mangifera
indica L. peel extracts. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:3406–3411.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Du S, Liu H, Lei T, Xie X, Wang H, He X,
Tong R and Wang Y: Mangiferin: An effective therapeutic agent
against several disorders (Review). Mol Med Rep. 18:4775–4786.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dar A, Faizi S, Naqvi S, Roome T,
Zikr-ur-Rehman S, Ali M, Firdous S and Moin ST: Analgesic and
antioxidant activity of mangiferin and its derivatives: The
structure activity relationship. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:596–600.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Duang XY, Wang Q, Zhou XD and Huang DM:
Mangiferin: A possible strategy for periodontal disease to therapy.
Med Hypotheses. 76:486–488. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Imran M, Arshad MS, Butt MS, Kwon JH,
Arshad MU and Sultan MT: Mangiferin: A natural miracle bioactive
compound against lifestyle related disorders. Lipids Health Dis.
16(84)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li J, Liu M, Yu H, Wang W, Han L, Chen Q,
Ruan J, Wen S, Zhang Y and Wang T: Mangiferin improves hepatic
lipid metabolism mainly through its metabolite-norathyriol by
modulating SIRT-1/AMPK/SREBP-1c signaling. Front Pharmacol.
9(201)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jia L, Sun P, Gao H, Shen J, Gao Y, Meng
C, Fu S, Yao H and Zhang G: Mangiferin attenuates Bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in mice through inhibiting TLR4/p65 and
TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol. 71:1017–1028.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liao WI, Wu SY, Wu GC, Pao HP, Tang SE,
Huang KL and Chu SJ: Ac2-26, an Annexin A1 peptide, attenuates
ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury. Int J Mol Sci.
18(1771)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hung KY, Liao WI, Pao HP, Wu SY, Huang KL
and Chu SJ: Targeting F-box protein Fbxo3 attenuates lung injury
induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Front Pharmacol.
10(583)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kang H, Lee Y, Bae M, Park YK and Lee JY:
Astaxanthin inhibits alcohol-induced inflammation and oxidative
stress in macrophages in a sirtuin 1-dependent manner. J Nutr
Biochem. 85(108477)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yabuki H, Watanabe T, Oishi H, Katahira M,
Kanehira M and Okada Y: Muse cells and ischemia-reperfusion lung
injury. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1103:293–303. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kreisel D and Goldstein DR: Innate
immunity and organ transplantation: Focus on lung transplantation.
Transpl Int. 26:2–10. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rognlien AGW, Wollen EJ, Atneosen-Asegg M,
Suganthan R, Bjoras M and Saugstad OD: Neonatal Ogg1/Mutyh knockout
mice have altered inflammatory gene response compared to wildtype
mice in the brain and lung after hypoxia-reoxygenation. J Perinat
Med. 47:114–124. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu PL, Chong IW, Lee YC, Tsai JR, Wang
HM, Hsieh CC, Kuo HF, Liu WL, Chen YH and Chen HL:
Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol on
Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-induced alveolar epithelial cell dysfunction.
J Agric Food Chem. 63:9480–9487. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xie W, Zhou P, Sun Y, Meng X, Dai Z, Sun G
and Sun X: Protective effects and target network analysis of
ginsenoside Rg1 in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury: A
comprehensive overview of experimental studies. Cells.
7(270)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun Z and Wang X: Protective effects of
polydatin on multiple organ ischemia-reperfusion injury. Bioorg
Chem. 94(103485)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ye J, Lu S, Wang M, Ge W, Liu H, Qi Y, Fu
J, Zhang Q, Zhang B, Sun G and Sun X: Hydroxysafflor yellow a
protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via
suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome and activating autophagy. Front
Pharmacol. 11(1170)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Luczkiewicz P, Kokotkiewicz A, Dampc A and
Luczkiewicz M: Mangiferin: A promising therapeutic agent for
rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Med Hypotheses. 83:570–574.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu K, Wang F, Wang S, Li WN and Ye Q:
Mangiferin attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via
MAPK/Nrf-2/HO-1/NF-κ B in vitro and in vivo. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(7285434)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li N, Xiong R, He R, Liu B, Wang B and
Geng Q: Mangiferin mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury
by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Inflamm Res.
14:2289–2300. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang B, Wan J, Gong X, Kuang G, Cheng X
and Min S: Mangiferin attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
by inhibiting inflammation and inducing adenosine production. Int
Immunopharmacol. 25:148–154. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Du M, Wen G, Jin J, Chen Y, Cao J and Xu
A: Mangiferin prevents the growth of gastric carcinoma by blocking
the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 29:167–175.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xia G, Li X, Zhu X, Yin X, Ding H and Qiao
Y: Mangiferin protects osteoblast against oxidative damage by
modulation of ERK5/Nrf2 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
491:807–813. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jiang T, Han F, Gao G and Liu M:
Mangiferin exert cardioprotective and anti-apoptotic effects in
heart failure induced rats. Life Sci. 249(117476)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen L, Li S, Zhu J, You A, Huang X, Yi X
and Xue M: Mangiferin prevents myocardial infarction-induced
apoptosis and heart failure in mice by activating the Sirt1/FoxO3a
pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2944–2955. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen M, Wang Z, Zhou W, Lu C, Ji T, Yang
W, Jin Z, Tian Y, Lei W, Wu S, et al: SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling
activation by mangiferin attenuates cerebral hypoxia/reoxygenation
injury in neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
907(174236)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Michan S and Sinclair D: Sirtuins in
mammals: Insights into their biological function. Biochem J.
404:1–13. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu S, Xu J, Fang C, Shi C, Zhang X, Yu B
and Yin Y: Over-expression of heat shock protein 70 protects mice
against lung ischemia/reperfusion injury through SIRT1/AMPK/eNOS
pathway. Am J Transl Res. 8:4394–4404. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li D, Wang X, Huang Q, Li S, Zhou Y and Li
Z: Cardioprotection of CAPE-oNO2 against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion induced ROS generation via regulating the
SIRT1/eNOS/NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Redox Biol.
15:62–73. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ding S, Liu D, Wang L, Wang G and Zhu Y:
Inhibiting microRNA-29a protects myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury by targeting SIRT1 and suppressing oxidative stress and
NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
372:128–135. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Han Y, Sun W, Ren D, Zhang J, He Z,
Fedorova J, Sun X, Han F and Li J: SIRT1 agonism modulates cardiac
NLRP3 inflammasome through pyruvate dehydrogenase during ischemia
and reperfusion. Redox Biol. 34(101538)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lempiainen J, Finckenberg P, Levijoki J
and Mervaala E: AMPK activator AICAR ameliorates ischaemia
reperfusion injury in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol.
166:1905–1915. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|