|
1
|
Klein J and Schanstra JP: Implementation
of proteomics biomarkers in nephrology: From animal models to human
application? Proteomics Clin Appl. 13(e1800089)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferenbach DA and Bonventre JV: Acute
kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: From the laboratory to
the clinic. Nephrol Ther. 12 (Suppl 1):S41–S48. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ferenbach DA and Bonventre JV: Mechanisms
of maladaptive repair after AKI leading to accelerated kidney
ageing and CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol. 11:264–276. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Eirin A, Lerman A and Lerman LO: The
emerging role of mitochondrial targeting in kidney disease. Handb
Exp Pharmacol. 240:229–250. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z,
Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY and Yang CW: Chronic kidney
disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 382:260–272.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre
JV and Bates DW: Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay,
and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:3365–3370.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mumby MC and Walter G: Protein
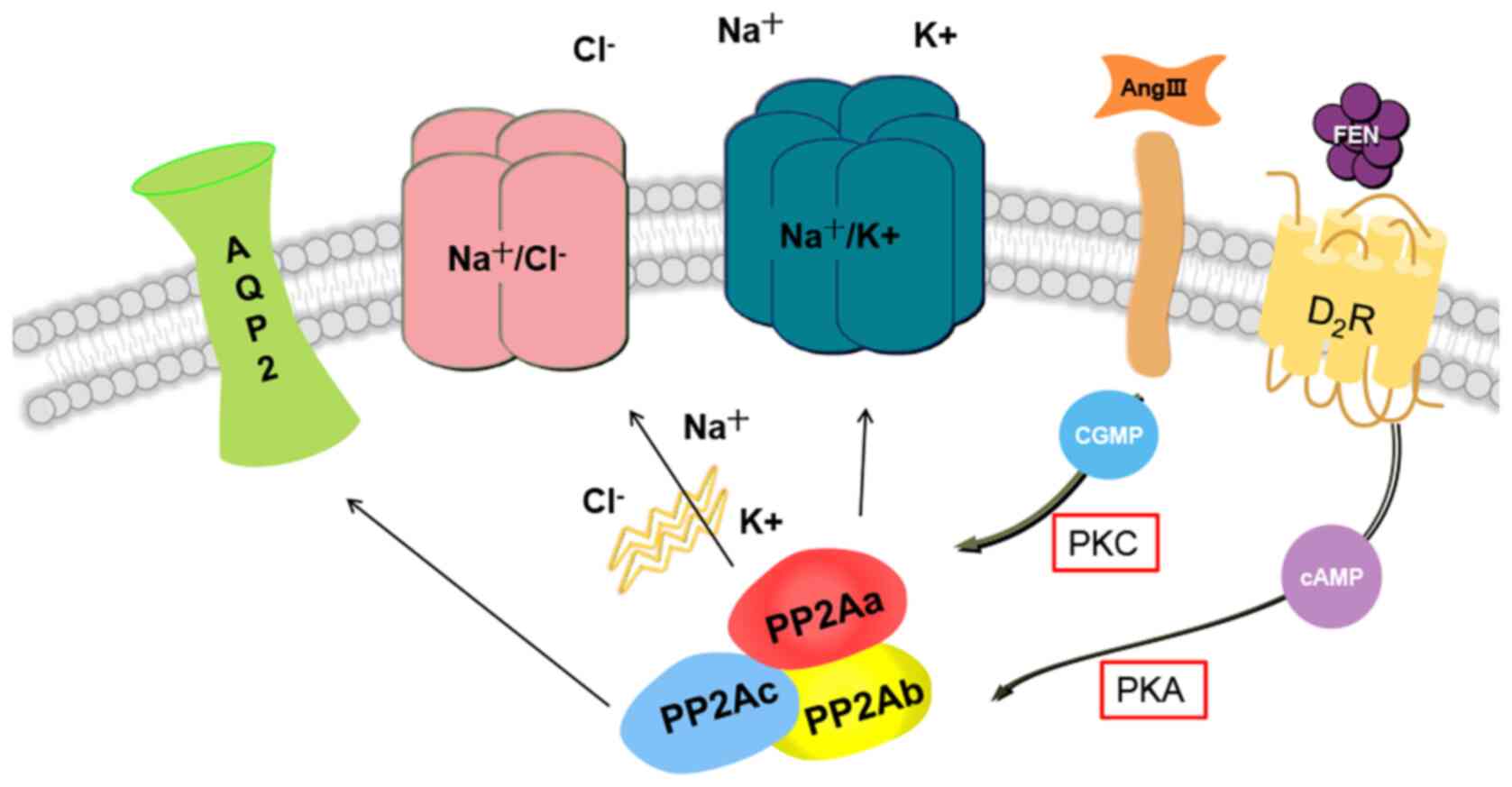
serine/threonine phosphatases: Structure, regulation, and functions
in cell growth. Physiol Rev. 73:673–699. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Eichhorn PJ, Creyghton MP and Bernards R:
Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1795:1–15. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tsao CC, Nica AF, Kurinna SM, Jiffar T,
Mumby M and Ruvolo PP: Mitochondrial protein phosphatase 2A
regulates cell death induced by simulated ischemia in kidney
NRK-52E cells. Cell Cycle. 6:2377–2385. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Deng Y, Guo Y, Liu P, Zeng R, Ning Y, Pei
G, Li Y, Chen M, Guo S, Li X, et al: Blocking protein phosphatase
2A signaling prevents endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
renal fibrosis: A peptide-based drug therapy. Sci Rep.
6(19821)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jin Jung K, Hyun Kim D, Kyeong Lee E, Woo
Song C, Pal Yu B and Young Chung H: Oxidative stress induces
inactivation of protein phosphatase 2A, promoting proinflammatory
NF-kappaB in aged rat kidney. Free Radic Biol Med. 61:206–217.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li J, Sheng C, Li W and Zheng JH: Protein
phosphatase-2A is down-regulated in patients within clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:1147–1153.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sen CK: Cellular thiols and
redox-regulated signal transduction. Curr Top Cell Regul. 36:1–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Barik S: Protein phosphorylation and
signal transduction. Subcell Biochem. 26:115–164. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shi Y: Serine/threonine phosphatases:
Mechanism through structure. Cell. 139:468–484. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
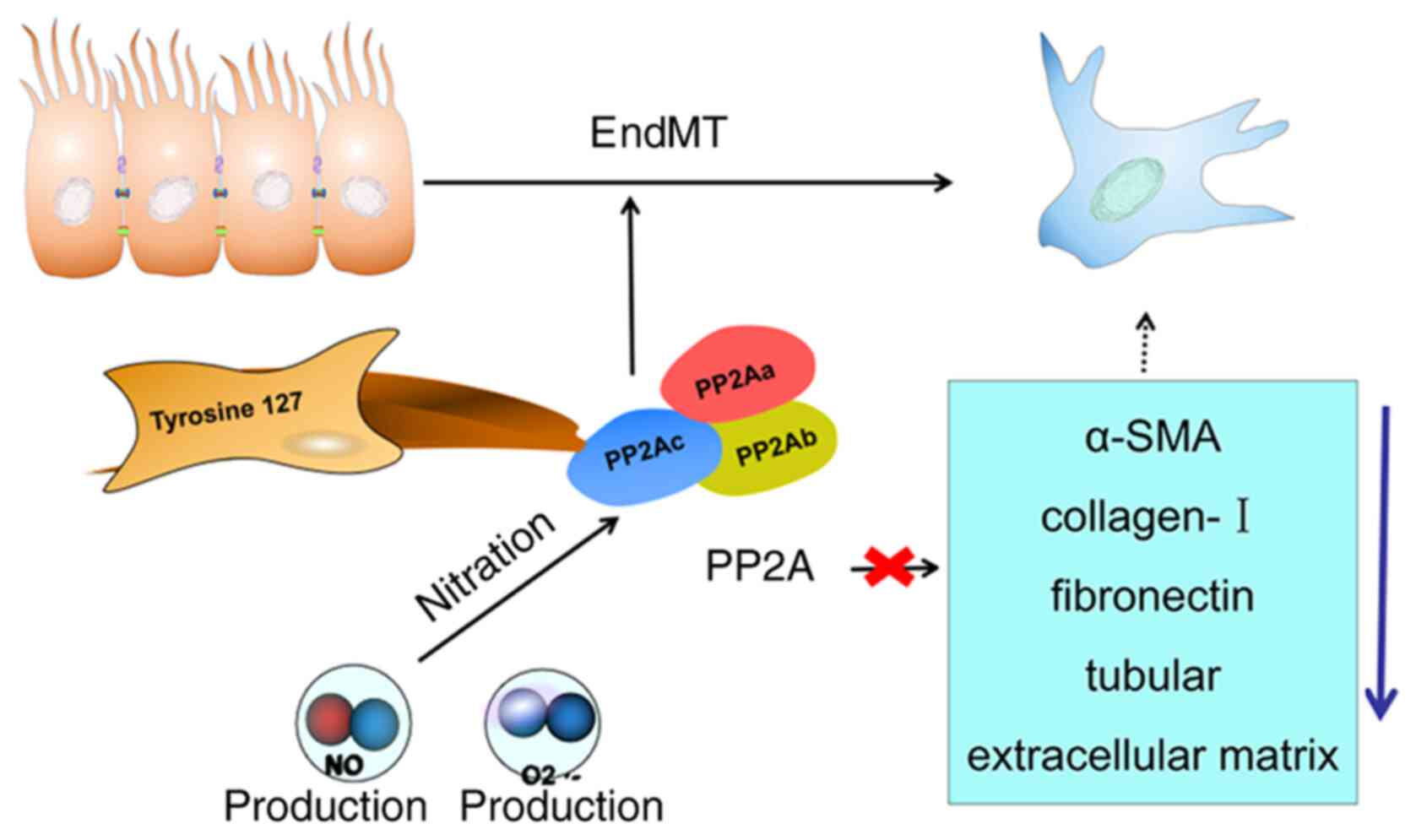
|
|
16
|
Barford D, Das AK and Egloff MP: The
structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: Insights into
catalysis and regulation. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct.
27:133–164. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Barford D: Colworth medal lecture.
Structural studies of reversible protein phosphorylation and
protein phosphatases. Biochem Soc Trans. 27:751–766.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
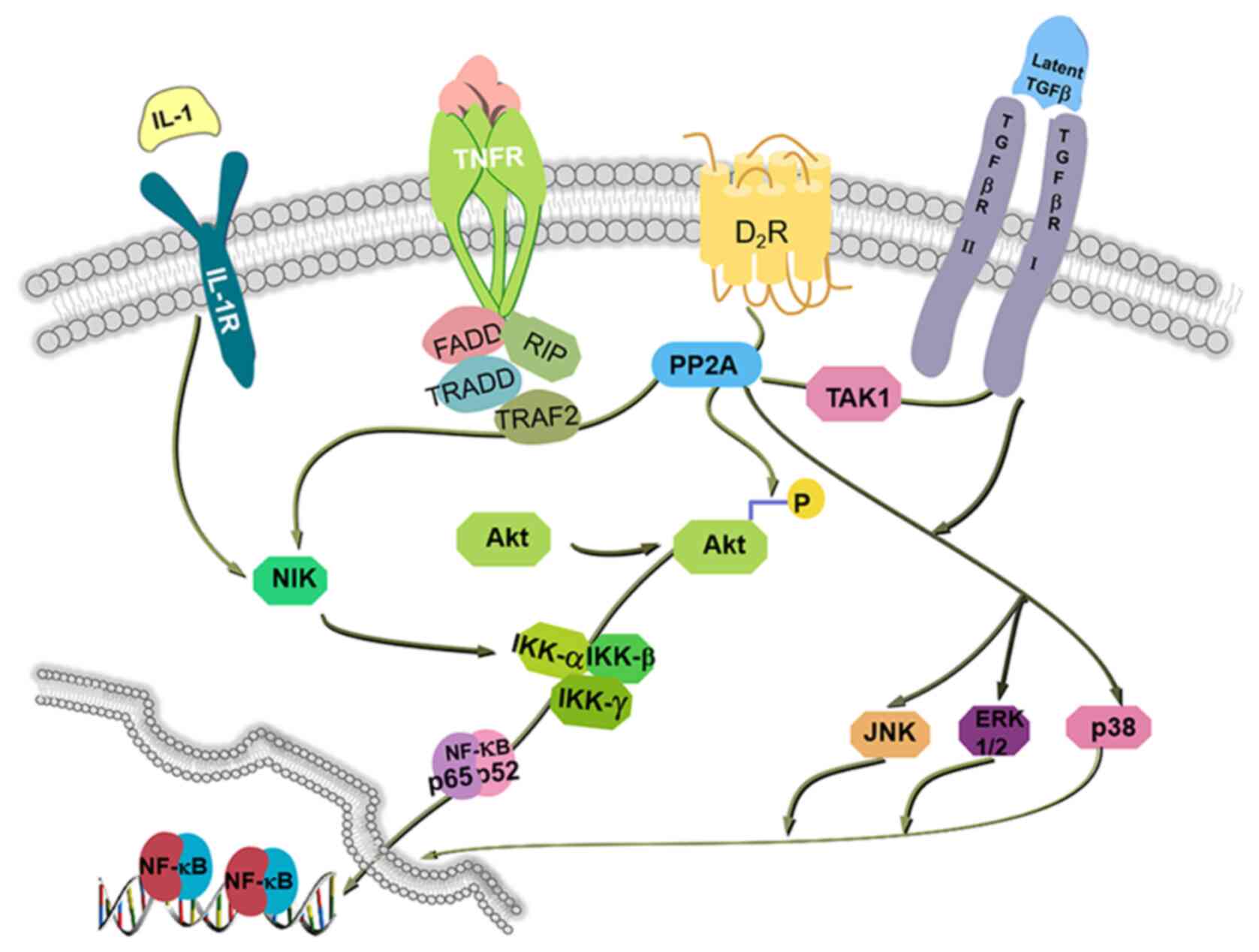
|
|
18
|
Hornbeck PV, Kornhauser JM, Tkachev S,
Zhang B, Skrzypek E, Murray B, Latham V and Sullivan M:
PhosphoSitePlus: A comprehensive resource for investigating the
structure and function of experimentally determined
post-translational modifications in man and mouse. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40:D261–D270. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Geraldes P: Protein phosphatases and
podocyte function. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 27:49–55.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kumar S and Tikoo K: Independent role of
PP2A and mTORc1 in palmitate induced podocyte death. Biochimie.
112:73–84. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Reiser J, Pixley FJ, Hug A, Kriz W, Smoyer
WE, Stanley ER and Mundel P: Regulation of mouse podocyte process
dynamics by protein tyrosine phosphatases rapid communication.
Kidney Int. 57:2035–2042. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Svennilson J, Durbeej M, Celsi G,
Laestadius A, da Cruz e Silva EF, Ekblom P and Aperia A: Evidence
for a role of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A during early
nephrogenesis. Kidney Int. 48:103–110. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Everett AD, Xue C and Stoops T:
Developmental expression of protein phosphatase 2A in the kidney. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 10:1737–1745. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gotz J, Probst A, Mistl C, Nitsch RM and
Ehler E: Distinct role of protein phosphatase 2A subunit Calpha in
the regulation of E-cadherin and beta-catenin during development.
Mech Dev. 93:83–93. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mumby M: The 3D structure of protein
phosphatase 2A: New insights into a ubiquitous regulator of cell
signaling. ACS Chem Biol. 2:99–103. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Janssens V and Goris J: Protein
phosphatase 2A: A highly regulated family of serine/threonine
phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem J.
353:417–439. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Turowski P, Favre B, Campbell KS, Lamb NJ
and Hemmings BA: Modulation of the enzymatic properties of protein
phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit by the recombinant 65-kDa
regulatory subunit PR65alpha. Eur J Biochem. 248:200–208.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sontag E: Protein phosphatase 2A: The
Trojan horse of cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 13:7–16.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
O'Connor CM, Perl A, Leonard D, Sangodkar
J and Narla G: Therapeutic targeting of PP2A. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 96:182–193. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Forester CM, Maddox J, Louis JV, Goris J
and Virshup DM: Control of mitotic exit by PP2A regulation of
Cdc25C and Cdk1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:19867–19872.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Slupe AM, Merrill RA and Strack S:
Determinants for substrate specificity of protein phosphatase 2A.
Enzyme Res. 2011(398751)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Flegg CP, Sharma M, Medina-Palazon C,
Jamieson C, Galea M, Brocardo MG, Mills K and Henderson BR: Nuclear
export and centrosome targeting of the protein phosphatase 2A
subunit B56alpha: Role of B56alpha in nuclear export of the
catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 285:18144–18154. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bononi A, Agnoletto C, De Marchi E, Marchi
S, Patergnani S, Bonora M, Giorgi C, Missiroli S, Poletti F,
Rimessi A and Pinton P: Protein kinases and phosphatases in the
control of cell fate. Enzyme Res. 2011(329098)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Riedel CG, Katis VL, Katou Y, Mori S, Itoh
T, Helmhart W, Gálová M, Petronczki M, Gregan J and Cetin B:
Protein phosphatase 2A protects centromeric sister chromatid
cohesion during meiosis I. Nature. 441:53–61. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jin Z, Shi J, Saraf A, Mei W, Zhu GZ,
Strack S and Yang J: The 48-kDa alternative translation isoform of
PP2A:B56epsilon is required for Wnt signaling during
midbrain-hindbrain boundary formation. J Biol Chem. 284:7190–7200.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Seshacharyulu P, Pandey P, Datta K and
Batra SK: Phosphatase: PP2A structural importance, regulation and
its aberrant expression in cancer. Cancer Lett. 335:9–18.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kanno T, Tsuchiya A, Shimizu T, Nakao S,
Tanaka A and Nishizaki T: Effects of newly synthesized
DCP-LA-phospholipids on protein kinase C and protein phosphatases.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:555–564. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kurimchak A and Grana X: PP2A
counterbalances phosphorylation of pRB and mitotic proteins by
multiple CDKs: Potential implications for PP2A disruption in
cancer. Genes Cancer. 3:739–748. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Svennilson J, Sandberg-Nordqvist A and
Aperia A: Age-dependent expression of protein phosphatase 2A in the
developing rat kidney. Pediatr Nephrol. 13:800–805. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yang J, Wu J, Tan C and Klein PS:
PP2A:B56epsilon is required for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during
embryonic development. Development. 130:5569–5578. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Jørgensen PL: Sodium and potassium ion
pump in kidney tubules. Physiol Rev. 60:864–917. 1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Rangel LB, Lopes AG, Lara LS, Carvalho TL,
Silva IV, Oliveira MM, Einicker-Lamas M, Vieyra A, Nogaroli L and
Caruso-Neves C: PI-PLCbeta is involved in the modulation of the
proximal tubule Na+-ATPase by angiotensin II. Regul Pept.
127:177–182. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gates J Jr, Ferguson SM, Blakely RD and
Apparsundaram S: Regulation of choline transporter surface
expression and phosphorylation by protein kinase C and protein
phosphatase 1/2A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 310:536–545.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Vieira-Filho LD, Cabral EV, Farias JS,
Silva PA, Muzi-Filho H, Vieyra A and Paixão AD: Renal molecular
mechanisms underlying altered Na+ handling and genesis of
hypertension during adulthood in prenatally undernourished rats. Br
J Nutr. 111:1932–1944. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dias J, Ferrao FM, Axelband F, Carmona AK,
Lara LS and Vieyra A: ANG-(3-4) inhibits renal
Na+-ATPase in hypertensive rats through a mechanism that
involves dissociation of ANG II receptors, heterodimers, and PKA.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F855–F863. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Vieira-Filho LD, Lara LS, Silva PA, Santos
FT, Luzardo R, Oliveira FS, Paixão AD and Vieyra A: Placental
malnutrition changes the regulatory network of renal Na-ATPase in
adult rat progeny: Reprogramming by maternal α-tocopherol during
lactation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 505:91–97. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Silva PA, Muzi-Filho H, Pereira-Acacio A,
Dias J, Martins JF, Landim-Vieira M, Verdoorn KS, Lara LS,
Vieira-Filho LD, Cabral EV, et al: Altered signaling pathways
linked to angiotensin II underpin the upregulation of renal
Na(+)-ATPase in chronically undernourished rats. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:2357–2366. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gildea JJ, Xu P, Kemp BA, Carey RM, Jose
PA and Felder RA: The dopamine D1 receptor and angiotensin II
type-2 receptor are required for inhibition of sodium transport
through a protein phosphatase 2A pathway. Hypertension.
73:1258–1265. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lecuona E, Garcia A and Sznajder JI: A
novel role for protein phosphatase 2A in the dopaminergic
regulation of Na, K-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 481:217–220. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li D, Cheng SX, Fisone G, Caplan MJ,
Ohtomo Y and Aperia A: Effects of okadaic acid, calyculin A, and
PDBu on state of phosphorylation of rat renal
Na+-K+-ATPase. Am J Physiol. 275:F863–F869.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Tiran Z, Peretz A, Sines T, Shinder V, Sap
J, Attali B and Elson A: Tyrosine phosphatases epsilon and alpha
perform specific and overlapping functions in regulation of
voltage-gated potassium channels in Schwann cells. Mol Biol Cell.
17:4330–4342. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Capdevila J and Wang W: Role of cytochrome
P450 epoxygenase in regulating renal membrane transport and
hypertension. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 22:163–169.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Nielsen S and Agre P: The aquaporin family
of water channels in kidney. Kidney Int. 48:1057–1068.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Christensen BM, Zelenina M, Aperia A and
Nielsen S: Localization and regulation of PKA-phosphorylated AQP2
in response to V(2)-receptor agonist/antagonist treatment. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 278:F29–F42. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hoffert JD, Pisitkun T, Wang G, Shen RF
and Knepper MA: Quantitative phosphoproteomics of
vasopressin-sensitive renal cells: Regulation of aquaporin-2
phosphorylation at two sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:7159–7164. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Tamma G, Robben JH, Trimpert C, Boone M
and Deen PM: Regulation of AQP2 localization by S256 and S261
phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
300:C636–C646. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Moeller HB, Knepper MA and Fenton RA:
Serine 269 phosphorylated aquaporin-2 is targeted to the apical
membrane of collecting duct principal cells. Kidney Int.
75:295–303. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Brown D: The ins and outs of aquaporin-2
trafficking. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 284:F893–F901.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kamsteeg EJ, Heijnen I, van Os CH and Deen
PM: The subcellular localization of an aquaporin-2 tetramer depends
on the stoichiometry of phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated
monomers. J Cell Biol. 151:919–930. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hoffert JD, Fenton RA, Moeller HB, Simons
B, Tchapyjnikov D, McDill BW, Yu MJ, Pisitkun T, Chen F and Knepper
MA: Vasopressin-stimulated increase in phosphorylation at Ser269
potentiates plasma membrane retention of aquaporin-2. J Biol Chem.
283:24617–24627. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Ren H, Yang B, Ruiz JA, Efe O, Ilori TO,
Sands JM and Klein JD: Phosphatase inhibition increases AQP2
accumulation in the rat IMCD apical plasma membrane. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 311:F1189–F1197. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Tamma G, Lasorsa D, Trimpert C, Ranieri M,
Di Mise A, Mola MG, Mastrofrancesco L, Devuyst O, Svelto M, Deen PM
and Valenti G: A protein kinase A-independent pathway controlling
aquaporin 2 trafficking as a possible cause for the syndrome of
inappropriate antidiuresis associated with polycystic kidney
disease 1 haploinsufficiency. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:2241–2253.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Valenti G, Procino G, Carmosino M, Frigeri
A, Mannucci R, Nicoletti I and Svelto M: The phosphatase inhibitor
okadaic acid induces AQP2 translocation independently from AQP2
phosphorylation in renal collecting duct cells. J Cell Sci.
113:1985–1992. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Millward TA, Zolnierowicz S and Hemmings
BA: Regulation of protein kinase cascades by protein phosphatase
2A. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:186–191. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Lee TH, Solomon MJ, Mumby MC and Kirschner
MW: INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein
phosphatase 2A. Cell. 64:415–423. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Izumi T, Walker DH and Maller JL: Periodic
changes in phosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc25 phosphatase
regulate its activity. Mol Biol Cell. 3:927–939. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Haystead TA, Weiel JE, Litchfield DW,
Tsukitani Y, Fischer EH and Krebs EG: Okadaic acid mimics the
action of insulin in stimulating protein kinase activity in
isolated adipocytes. The role of protein phosphatase 2a in
attenuation of the signal. J Biol Chem. 265:16571–16580.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tsao H and Greene LA: The roles of
macromolecular synthesis and phosphorylation in the regulation of a
protein kinase activity transiently stimulated by nerve growth
factor. J Biol Chem. 266:12981–12988. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Stark K, Vainio S, Vassileva G and McMahon
AP: Epithelial transformation of metanephric mesenchyme in the
developing kidney regulated by Wnt-4. Nature. 372:679–683.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Zeng L, Fagotto F, Zhang T, Hsu W, Vasicek
TJ, Perry WL III, Lee JJ, Tilghman SM, Gumbiner BM and Costantini
F: The mouse Fused locus encodes Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt
signaling pathway that regulates embryonic axis formation. Cell.
90:181–192. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Altintas MM and Reiser J: Bridges to
cross, burn, and mend: Cells of renin lineage as podocyte
progenitors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 309:F499–F500.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Pagtalunan ME, Miller PL, Jumping-Eagle S,
Nelson RG, Myers BD, Rennke HG, Coplon NS, Sun L and Meyer TW:
Podocyte loss and progressive glomerular injury in type II
diabetes. J Clin Invest. 99:342–348. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Huber TB and Benzing T: The slit
diaphragm: A signaling platform to regulate podocyte function. Curr
Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 14:211–216. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Sedor JR, Madhavan SM, Kim JH and
Konieczkowski M: Out on a LIM: Chronic kidney disease, podocyte
phenotype and the Wilm's tumor interacting protein (WTIP). Trans Am
Clin Climatol Assoc. 122:184–197. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liu M, Liang K, Zhen J, Zhou M, Wang X,
Wang Z, Wei X, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Zhou Z, et al: Sirt6 deficiency
exacerbates podocyte injury and proteinuria through targeting Notch
signaling. Nat Commun. 8(413)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Kobayashi N, Reiser J, Schwarz K, Sakai T,
Kriz W and Mundel P: Process formation of podocytes: Morphogenetic
activity of microtubules and regulation by protein serine/threonine
phosphatase PP2A. Histochem Cell Biol. 115:255–266. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Zhu X, Ye Y, Xu C, Gao C, Zhang Y, Zhou J,
Lin W and Mao J: Protein phosphatase 2A modulates podocyte
maturation and glomerular functional integrity in mice. Cell Commun
Signal. 17(91)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Hanssen L, Frye BC, Ostendorf T, Alidousty
C, Djudjaj S, Boor P, Rauen T, Floege J, Mertens PR and Raffetseder
U: Y-box binding protein-1 mediates profibrotic effects of
calcineurin inhibitors in the kidney. J Immunol. 187:298–308.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Zhong Y, Lee K, Deng Y, Ma Y, Chen Y, Li
X, Wei C, Yang S, Wang T, Wong NJ, et al: Arctigenin attenuates
diabetic kidney disease through the activation of PP2A in
podocytes. Nat Commun. 10(4523)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Qiu M, Liu L, Chen L, Tan G, Liang Z, Wang
K, Liu J and Chen H: MicroRNA-183 plays as oncogenes by increasing
cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting protein
phosphatase 2A in renal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
452:163–169. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Liu P, Xiang Y, Liu X, Zhang T, Yang R,
Chen S, Xu L, Yu Q, Zhao H, Zhang L, et al: Cucurbitacin B induces
the lysosomal degradation of EGFR and suppresses the CIP2A/PP2A/Akt
signaling axis in gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer.
Molecules. 24(647)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Cairns J, Ly RC, Niu N, Kalari KR, Carlson
EE and Wang L: CDC25B partners with PP2A to induce AMPK activation
and tumor suppression in triple negative breast cancer. NAR Cancer.
2(zcaa39)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Vicente C, Arriazu E, Martínez-Balsalobre
E, Peris I, Marcotegui N, García-Ramírez P, Pippa R, Rabal O,
Oyarzábal J, Guruceaga E, et al: A novel FTY720 analogue targets
SET-PP2A interaction and inhibits growth of acute myeloid leukemia
cells without inducing cardiac toxicity. Cancer Lett. 468:1–13.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Westermarck J and Hahn WC: Multiple
pathways regulated by the tumor suppressor PP2A in transformation.
Trends Mol Med. 14:152–160. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Xing ML, Lu YF, Wang DF, Zou XY, Zhang SX
and Yun Z: Clinical significance of sCIP2A levels in breast cancer.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:82–91. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Kauko O and Westermarck J: Non-genomic
mechanisms of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulation in cancer.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 96:157–164. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Lambrecht C, Haesen D, Sents W, Ivanova E
and Janssens V: Structure, regulation, and pharmacological
modulation of PP2A phosphatases. Methods Mol Biol. 1053:283–305.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Ou YC, Li JR, Wang JD, Chen WY, Kuan YH,
Yang CP, Liao SL, Lu HC and Chen CJ: Aspirin restores
ABT-737-mediated apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 502:187–193. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
de Fatima A, Zambuzzi WF, Modolo LV,
Tarsitano CA, Gadelha FR, Hyslop S, de Carvalho JE, Salgado I,
Ferreira CV and Pilli RA: Cytotoxicity of goniothalamin enantiomers
in renal cancer cells: Involvement of nitric oxide, apoptosis and
autophagy. Chem Biol Interact. 176:143–150. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Seo SU, Woo SM, Min KJ and Kwon TK:
Z-FL-COCHO, a cathepsin S inhibitor, enhances oxaliplatin-induced
apoptosis through upregulation of Bim expression. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 498:849–854. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Tsai YT, Chuang MJ, Tang SH, Wu ST, Chen
YC, Sun GH, Hsiao PW, Huang SM, Lee HJ, Yu CP, et al: Novel cancer
therapeutics with allosteric modulation of the mitochondrial
C-Raf-DAPK complex by raf inhibitor combination therapy. Cancer
Res. 75:3568–3582. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Ou YC, Kuan YH, Li JR, Raung SL, Wang CC,
Hung YY and Chen CJ: Induction of apoptosis by luteolin involving
akt inactivation in human 786-o renal cell carcinoma cells. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013(109105)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Liu Y: Renal fibrosis: New insights into
the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 69:213–217.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Daehn I and Bottinger EP: Microvascular
endothelial cells poised to take center stage in experimental renal
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:767–769. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Bohle A, Mackensen-Haen S and Wehrmann M:
Significance of postglomerular capillaries in the pathogenesis of
chronic renal failure. Kidney Blood Press Res. 19:191–195.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Fine LG, Orphanides C and Norman JT:
Progressive renal disease: The chronic hypoxia hypothesis. Kidney
Int Suppl. 65 (Suppl):S74–S78. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wu F and Wilson JX:
Peroxynitrite-dependent activation of protein phosphatase type 2A
mediates microvascular endothelial barrier dysfunction. Cardiovasc
Res. 81:38–45. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Kása A, Czikora I, Verin AD, Gergely P and
Csortos C: Protein phosphatase 2A activity is required for
functional adherent junctions in endothelial cells. Microvasc Res.
89:86–94. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Kriz W, Kaissling B and Le Hir M:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in kidney fibrosis: Fact or
fantasy? J Clin Invest. 121:468–474. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Lipphardt M, Dihazi H, Jeon NL, Dadafarin
S, Ratliff BB, Rowe DW, Müller GA and Goligorsky MS: Dickkopf-3 in
aberrant endothelial secretome triggers renal fibroblast activation
and endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
34:49–62. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta SE, Sugimoto H,
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:2282–2287. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Matsumoto K, Xavier S, Chen J, Kida Y,
Lipphardt M, Ikeda R, Gevertz A, Caviris M, Hatzopoulos AK,
Kalajzic I, et al: Instructive role of the microenvironment in
preventing renal fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 6:992–1005.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Chen CL, Chou KJ, Fang HC, Hsu CY, Huang
WC, Huang CW, Huang CK, Chen HY and Lee PT: Progenitor-like cells
derived from mouse kidney protect against renal fibrosis in a
remnant kidney model via decreased endothelial mesenchymal
transition. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6(239)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Xavier S, Vasko R, Matsumoto K, Zullo JA,
Chen R, Maizel J, Chander PN and Goligorsky MS: Curtailing
endothelial TGF-β signaling is sufficient to reduce
endothelial-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis in CKD. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 26:817–829. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Li J, Qu X and Bertram JF:
Endothelial-myofibroblast transition contributes to the early
development of diabetic renal interstitial fibrosis in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Am J Pathol. 175:1380–1388.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Xie T, Chen C, Peng Z, Brown BC, Reisz JA,
Xu P, Zhou Z, Song A, Zhang Y, Bogdanov MV, et al: Erythrocyte
metabolic reprogramming by sphingosine 1-phosphate in chronic
kidney disease and therapies. Circ Res. 127:360–375.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Hou T, Xiao Z, Li Y, You YH, Li H, Liu YP,
Xi YY, Li J, Duan SB, Liu H, et al: Norcantharidin inhibits renal
interstitial fibrosis by downregulating PP2Ac expression. Am J
Transl Res. 7:2199–2211. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Deng Y, Cai Y, Liu L, Lin X, Lu P, Guo Y,
Han M and Xu G: Blocking Tyr265 nitration of protein phosphatase 2A
attenuates nitrosative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction in
renal microvessels. FASEB J. 33:3718–3730. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Wright RS, Reeder GS, Herzog CA, Albright
RC, Williams BA, Dvorak DL, Miller WL, Murphy JG, Kopecky SL and
Jaffe AS: Acute myocardial infarction and renal dysfunction: A
high-risk combination. Ann Intern Med. 137:563–570. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Rodrigues FB, Bruetto RG, Torres US,
Otaviano AP, Zanetta DM and Burdmann EA: Effect of kidney disease
on acute coronary syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 5:1530–1536.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Barnes JL and Glass Ii WF: Renal
interstitial fibrosis: A critical evaluation of the origin of
myofibroblasts. Contrib Nephrol. 169:73–93. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Tobisawa T, Yano T, Tanno M, Miki T, Kuno
A, Kimura Y, Ishikawa S, Kouzu H, Nishizawa K, Yoshida H and Miura
T: Insufficient activation of Akt upon reperfusion because of its
novel modification by reduced PP2A-B55α contributes to enlargement
of infarct size by chronic kidney disease. Basic Res Cardiol.
112(31)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Sato Y and Yanagita M: Immune cells and
inflammation in AKI to CKD progression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
315:F1501–F1512. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Rahman MM, Rumzhum NN, Morris JC, Clark
AR, Verrills NM and Ammit AJ: Basal protein phosphatase 2A activity
restrains cytokine expression: Role for MAPKs and tristetraprolin.
Sci Rep. 5(10063)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Crispin JC, Apostolidis SA, Rosetti F,
Keszei M, Wang N, Terhorst C, Mayadas TN and Tsokos GC: Cutting
edge: Protein phosphatase 2A confers susceptibility to autoimmune
disease through an IL-17-dependent mechanism. J Immunol.
188:3567–3571. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Hsieh CY, Hsiao G, Hsu MJ, Wang YH and
Sheu JR: PMC, a potent hydrophilic α-tocopherol derivative,
inhibits NF-κB activation via PP2A but not IKBα-dependent signals
in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1278–1289.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Yang J, Fan GH, Wadzinski BE, Sakurai H
and Richmond A: Protein phosphatase 2A interacts with and directly
dephosphorylates RelA. J Biol Chem. 276:47828–47833.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Zhang Y, Cuevas S, Asico LD, Escano C,
Yang Y, Pascua AM, Wang X, Jones JE, Grandy D, Eisner G, et al:
Deficient dopamine D2 receptor function causes renal inflammation
independently of high blood pressure. PLoS One.
7(e38745)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Asghar M, Chugh G and Lokhandwala MF:
Inflammation compromises renal dopamine D1 receptor function in
rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 297:F1543–F1549. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Yang S, Yao B, Zhou Y, Yin H, Zhang MZ and
Harris RC: Intrarenal dopamine modulates progressive angiotensin
II-mediated renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
302:F742–F749. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Chugh G, Lokhandwala MF and Asghar M:
Oxidative stress alters renal D1 and AT1 receptor functions and
increases blood pressure in old rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
300:F133–F138. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Cuevas S, Villar VA,
Escano C, D Asico L, Yu P, Grandy DK, Felder RA, Armando I and Jose
PA: Paraoxonase 2 decreases renal reactive oxygen species
production, lowers blood pressure, and mediates dopamine D2
receptor-induced inhibition of NADPH oxidase. Free Radic Biol Med.
53:437–446. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Armando I, Wang X, Villar VA, Jones JE,
Asico LD, Escano C and Jose PA: Reactive oxygen species-dependent
hypertension in dopamine D2 receptor-deficient mice. Hypertension.
49:672–678. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Zhang Y, Jiang X, Qin C, Cuevas S, Jose PA
and Armando I: Dopamine D2 receptors' effects on renal inflammation
are mediated by regulation of PP2A function. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 310:F128–F134. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Marasa BS, Xiao L, Rao JN, Zou T, Liu L,
Wang J, Bellavance E, Turner DJ and Wang JY: Induced TRPC1
expression increases protein phosphatase 2A sensitizing intestinal
epithelial cells to apoptosis through inhibition of NF-kappaB
activation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 294:C1277–C1287.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Li S, Wang L, Berman MA, Zhang Y and Dorf
ME: RNAi screen in mouse astrocytes identifies phosphatases that
regulate NF-kappaB signaling. Mol Cell. 24:497–509. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Kim SI, Kwak JH, Wang L and Choi ME:
Protein phosphatase 2A is a negative regulator of transforming
growth factor-beta1-induced TAK1 activation in mesangial cells. J
Biol Chem. 283:10753–10763. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Jung KJ, Lee EK, Kim SJ, Song CW, Maruyama
N, Ishigami A, Kim ND, Im DS, Yu BP and Chung HY: Anti-inflammatory
activity of SMP30 modulates NF-κB through protein tyrosine
kinase/phosphatase balance. J Mol Med (Berl). 93:343–356.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|