|
1
|
Thompson J and Lakhani N: Cataracts. Prim
Care. 42:409–423. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shiels A and Hejtmancik JF: Biology of
inherited cataracts and opportunities for treatment. Annu Rev Vis
Sci. 5:123–149. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Vrensen GF: Early cortical lens opacities:
A short overview. Acta Ophthalmol. 87:602–610. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ten Berge JC, Fazil Z, van den Born I,
Wolfs RCW, Schreurs MWJ, Dik WA and Rothova A: Intraocular cytokine
profile and autoimmune reactions in retinitis pigmentosa,
age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma and cataract. Acta
Ophthalmol. 97:185–192. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee CM and Afshari NA: The global state of
cataract blindness. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 28:98–103.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Olson RJ, Braga-Mele R, Chen SH, Miller
KM, Pineda R II, Tweeten JP and Musch DC: Cataract in the adult eye
preferred practice pattern®. Ophthalmology. 124:P1–P119.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yuan XB, Zhang DY, Chen SJ, Wu PC and
Zhang WF: Prevalence of cataract among the population aged 50 years
and over at different altitudes in Gansu Province. Zhonghua Yan Ke
Za Zhi. 55:589–594. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Asbell PA, Dualan I, Mindel J, Brocks D,
Ahmad M and Epstein S: Age-related cataract. Lancet. 365:599–609.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shiels A and Hejtmancik JF: Mutations and
mechanisms in congenital and age-related cataracts. Exp Eye Res.
156:95–102. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu YC, Wilkins M, Kim T, Malyugin B and
Mehta JS: Cataracts. Lancet. 390:600–612. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Keel S and He M: Risk factors for
age-related cataract. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 46:327–328.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hashemi H, Pakzad R, Yekta A, Aghamirsalim
M, Pakbin M, Ramin S and Khabazkhoob M: Global and regional
prevalence of age-related cataract: A comprehensive systematic
review and meta-analysis. Eye (Lond). 34:1357–1370. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
National Institute for Health and Care
Excellence (UK): Cataracts in adults: Management. National
Institute for Health and Care Excellence, London, 2017.
|
|
14
|
Truscott RJW and Friedrich MG: Molecular
processes implicated in human age-related nuclear cataract. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 60:5007–5021. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Klein BE, Klein R and Lee KE: Incidence of
age-related cataract: The beaver dam eye study. Arch Ophthalmol.
116:219–225. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lu B, Christensen IT, Yu T, Wang C, Yan Q
and Wang X: SUMOylation evoked by oxidative stress reduced lens
epithelial cell antioxidant functions by increasing the stability
and transcription of TP53INP1 in age-related cataracts. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2019(7898069)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang H, Cui Y, Tang Y, Tang X, Yu X, Zhou
J, Yin Q and Shentu X: Cytoprotective role of humanin in lens
epithelial cell oxidative stress-induced injury. Mol Med Rep.
22:1467–1479. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Panni S, Lovering RC, Porras P and Orchard
S: Non-coding RNA regulatory networks. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene
Regul Mech. 1863(194417)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Puvvula PK: LncRNAs regulatory networks in
cellular senescence. Int J Mol Sci. 20(2615)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
He Z, Yang D, Fan X, Zhang M, Li Y, Gu X
and Yang M: The roles and mechanisms of lncRNAs in liver fibrosis.
Int J Mol Sci. 21(1482)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang J and Cen S: Roles of lncRNAs in
influenza virus infection. Emerg Microbes Infect. 9:1407–1414.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka
D, Sobolewski C and Foti M: Deciphering miRNAs' action through
miRNA editing. Int J Mol Sci. 20(6249)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H and Taheri M:
miRNA profile in ovarian cancer. Exp Mol Pathol.
113(104381)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Permenter MG, McDyre BC, Ippolito DL and
Stallings JD: Alterations in tissue microRNA after heat stress in
the conscious rat: Potential biomarkers of organ-specific injury.
BMC Genomics. 20(141)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen X, Xiao W, Chen W, Liu X, Wu M, Bo Q,
Luo Y, Ye S, Cao Y and Liu Y: MicroRNA-26a and -26b inhibit lens
fibrosis and cataract by negatively regulating Jagged-1/Notch
signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 24:1431–1442. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang F, Meng W and Tong B:
Down-regulation of MicroRNA-133b suppresses apoptosis of lens
epithelial cell by up-regulating BCL2L2 in age-related cataracts.
Med Sci Monit. 22:4139–4145. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
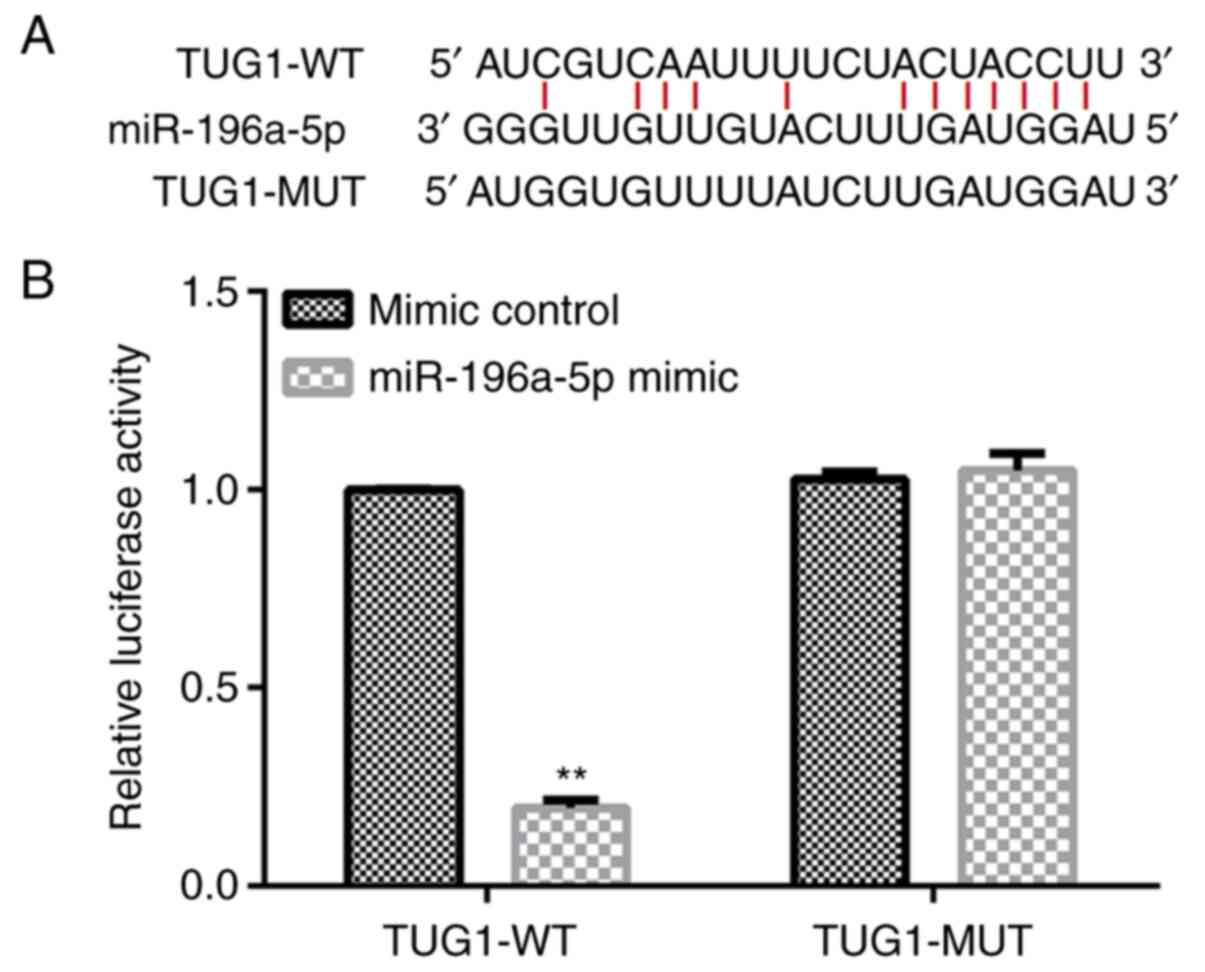
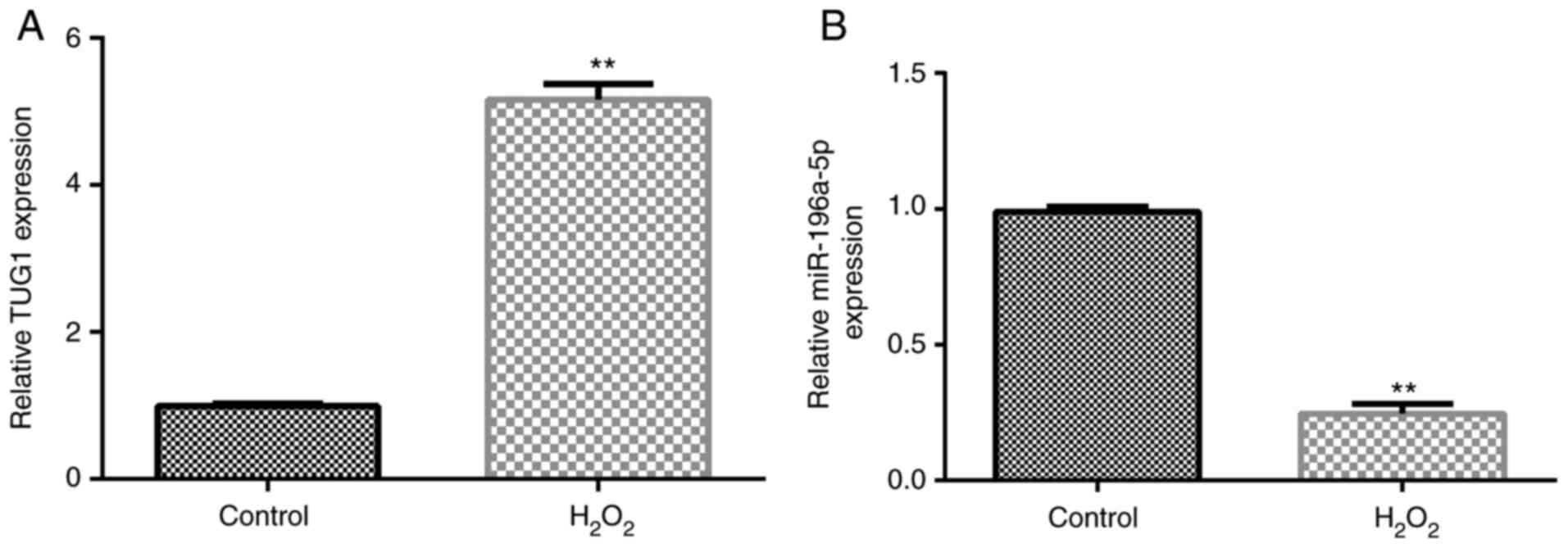
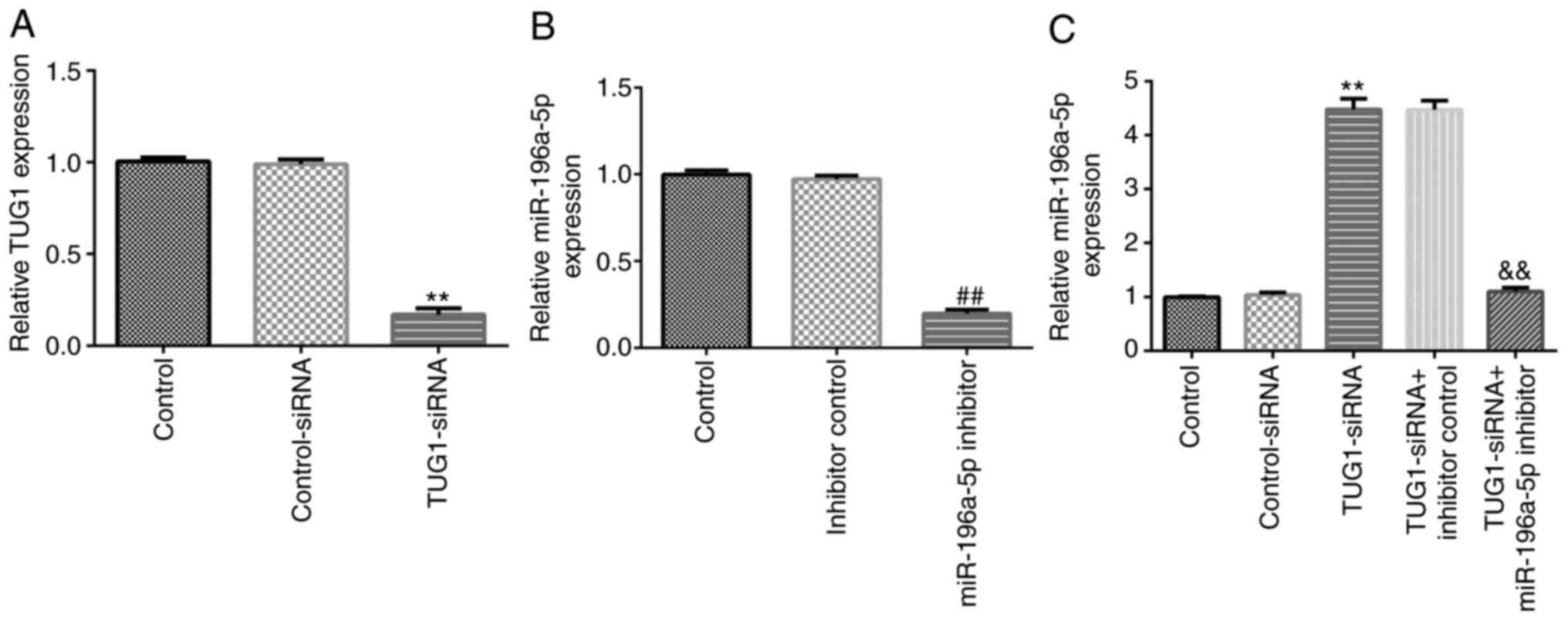
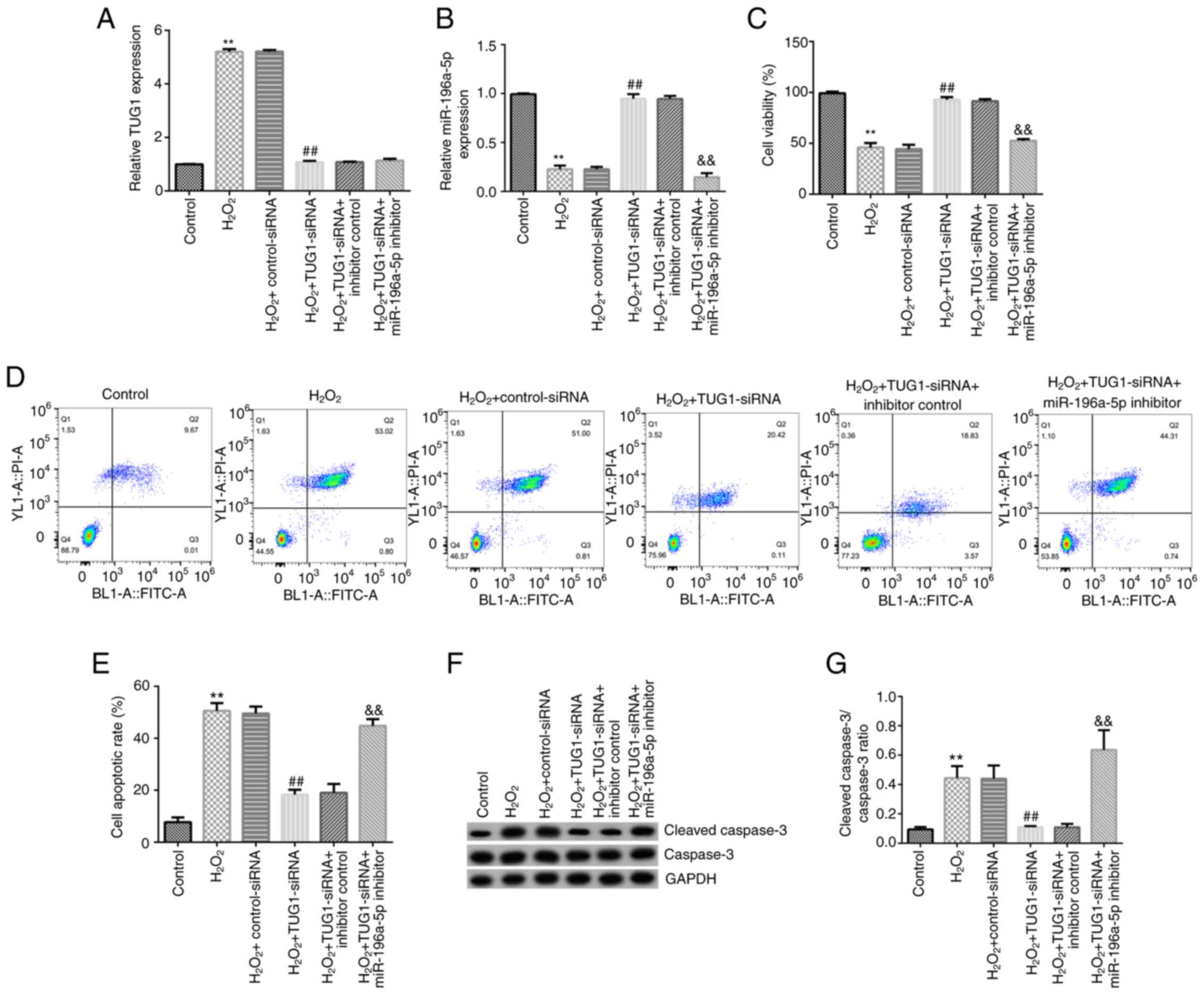
Li G, Song H, Chen L, Yang W, Nan K and Lu
P: TUG1 promotes lens epithelial cell apoptosis by regulating
miR-421/caspase-3 axis in age-related cataract. Exp Cell Res.
356:20–27. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xin H, Wang C and Liu Z: miR-196a-5p
promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via targeting IκBα. BMC
Cancer. 19(30)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mi C, Ye B, Gao Z, Du J, Li R and Huang D:
BHLHE40 plays a pathological role in pre-eclampsia through
upregulating SNX16 by transcriptional inhibition of miR-196a-5p.
Mol Hum Reprod. 26:532–548. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang L, Xie H and Li S: LncRNA LOXL1-AS1
controls osteogenic and adipocytic differentiation of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis through
regulating the miR-196a-5p/Hmga2 axis. J Bone Miner Metab.
38:794–805. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang L, Wei Y, Yan Y, Wang H, Yang J,
Zheng Z, Zha J, Bo P, Tang Y, Guo X, et al: CircDOCK1 suppresses
cell apoptosis via inhibition of miR-196a-5p by targeting BIRC3 in
OSCC. Oncol Rep. 39:951–966. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yang JP, Yang JK, Li C, Cui ZQ, Liu HJ,
Sun XF, Geng SM, Lu SK, Song J, Guo CY and Jiao BH: Downregulation
of ZMYND11 induced by miR-196a-5p promotes the progression and
growth of GBM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 494:674–680.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tu Y, Li L, Qin B, Wu J, Cheng T, Kang L
and Guan H: Long noncoding RNA glutathione peroxidase 3-antisense
inhibits lens epithelial cell apoptosis by upregulating glutathione
peroxidase 3 expression in age-related cataract. Mol Vis.
25:734–744. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fukuoka H and Afshari NA: The impact of
age-related cataract on measures of frailty in an aging global
population. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 28:93–97. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chainy GBN and Sahoo DK: Hormones and
oxidative stress: An overview. Free Radic Res. 54:1–26.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chirumbolo S: Oxidative stress, nutrition
and cancer: Friends or foes? World J Mens Health. 39:19–30.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shao A, Lin D, Wang L, Tu S, Lenahan C and
Zhang J: Oxidative stress at the crossroads of aging, stroke and
depression. Aging Dis. 11:1537–1566. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wu C, Liu Z, Ma L, Pei C, Qin L, Gao N, Li
J and Yin Y: MiRNAs regulate oxidative stress related genes via
binding to the 3' UTR and TATA-box regions: A new hypothesis for
cataract pathogenesis. BMC Ophthalmol. 17(142)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu XF, Hao JL, Xie T, Malik TH, Lu CB,
Liu C, Shu C, Lu CW and Zhou DD: Nrf2 as a target for prevention of
age-related and diabetic cataracts by against oxidative stress.
Aging Cell. 16:934–942. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang Z, Su D, Sun Z, Liu S, Sun L, Li Q,
Guan L, Liu Y, Ma X and Hu S: MDM2 phosphorylation mediates
H2O2-induced lens epithelial cells apoptosis
and age-related cataract. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 528:112–119.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hu S, Su D, Sun L, Wang Z, Guan L, Liu S,
Zhao B, Liu Y, Shi C, Yu J and Ma X: High-expression of ROCK1
modulates the apoptosis of lens epithelial cells in age-related
cataracts by targeting p53 gene. Mol Med. 26(124)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yan Z, Bi M, Zhang Q, Song Y and Hong S:
LncRNA TUG1 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer via the
miR-138-5p/ZEB2 axis. Biosci Rep. 40(BSR20201025)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zong M, Feng W, Wan L, Yu X and Yu W:
LncRNA TUG1 promotes esophageal cancer development through
regulating PLK1 expression by sponging miR-1294. Biotechnol Lett.
42:2537–2549. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yu G, Zhou H, Yao W, Meng L and Lang B:
lncRNA TUG1 promotes cisplatin resistance by regulating CCND2 via
epigenetically silencing miR-194-5p in bladder cancer. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 16:257–271. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|