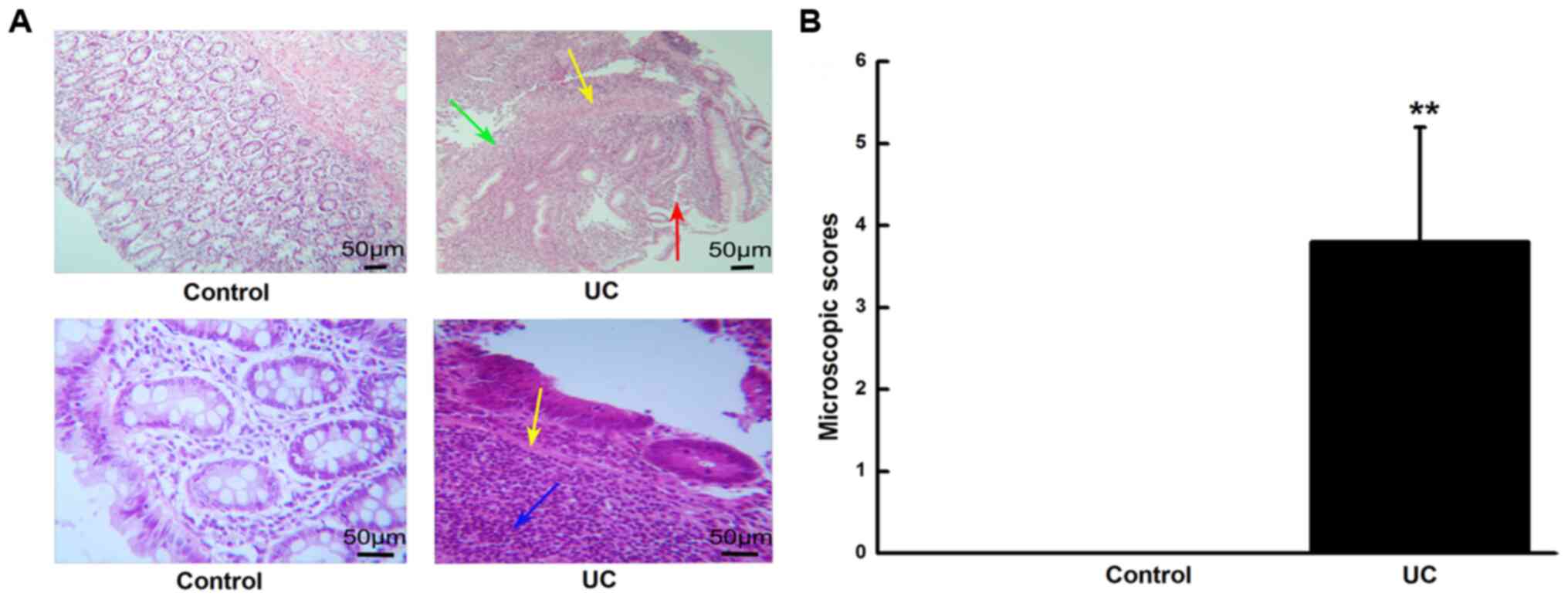
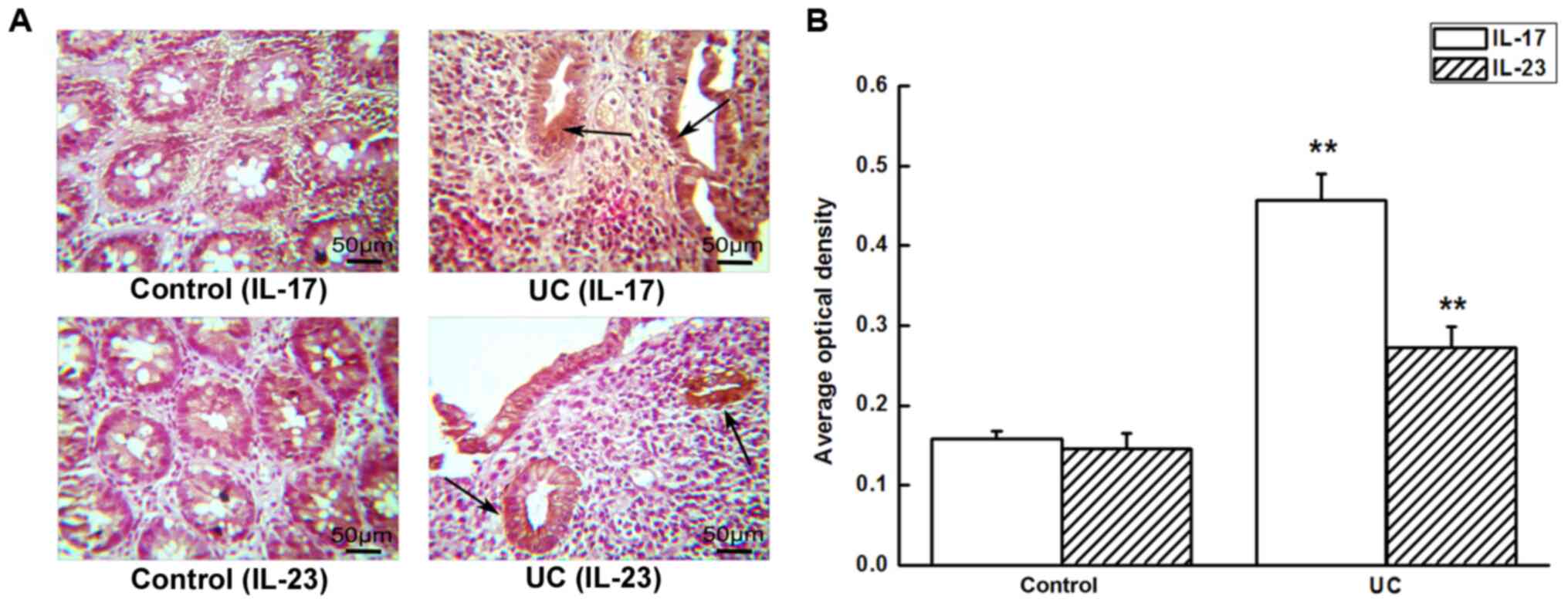
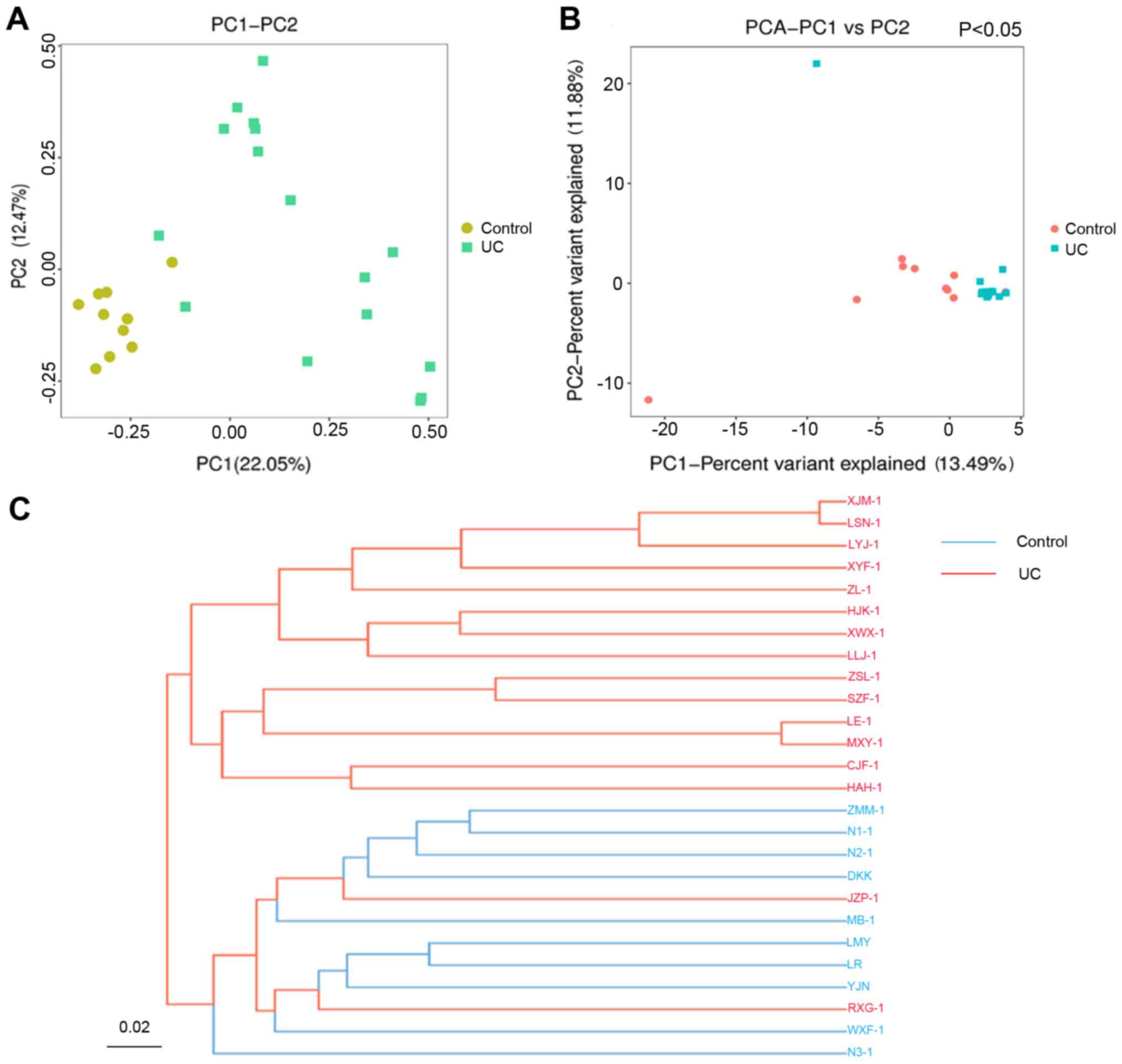
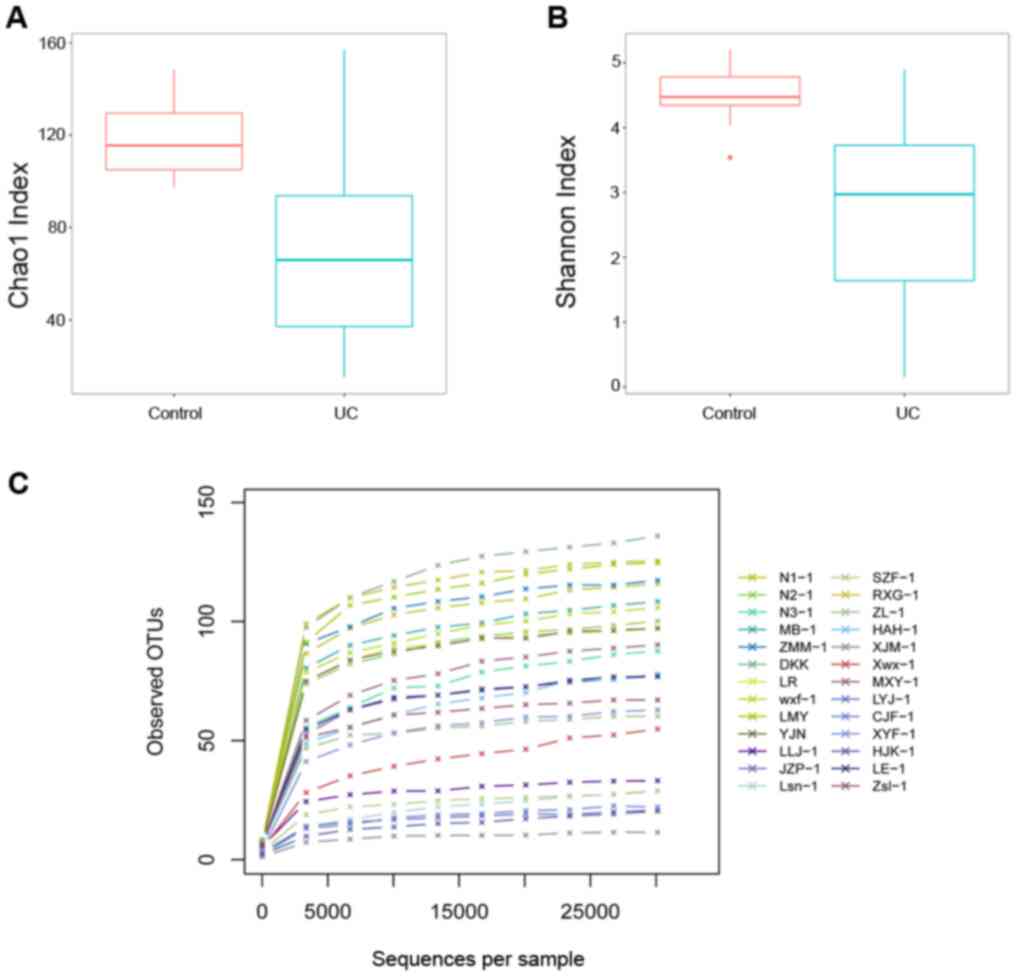
|
1
|
Sheehan D, Moran C and Shanahan F: The
microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol.
50:495–507. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sun M, Wu W, Liu Z and Cong Y: Microbiota
metabolite short chain fatty acids, GPCR, and inflammatory bowel
diseases. J Gastroenterol. 52:1–8. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rogler G: Chronic ulcerative colitis and
colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 345:235–241. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Adams SM and Bornemann PH: Ulcerative
colitis. Am Fam Physician. 87:699–705. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Al Bander Z, Nitert MD, Mousa A and
Naderpoor N: The gut microbiota and inflammation: An overview. Int
J Environ Res Public Health. 17(7618)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yap YA and Mariño E: An insight into the
intestinal web of mucosal immunity, microbiota, and diet in
inflammation. Front Immunol. 9(2617)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shen ZH, Zhu CX, Quan YS, Yang ZY, Wu S,
Luo WW, Tan B and Wang XY: Relationship between intestinal
microbiota and ulcerative colitis: Mechanisms and clinical
application of probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation.
World J Gastroenterol. 24:5–14. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH,
McGovern DP, Hui KY, Lee JC, Schumm LP, Sharma Y, Anderson CA, et
al: Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture
of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 491:119–124. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Macdonald TT and Monteleone G: Immunity,
inflammation, and allergy in the gut. Science. 307:1920–1925.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kostic AD, Xavier RJ and Gevers D: The
microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: Current status and the
future ahead. Gastroenterology. 146:1489–1499. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nishikawa J, Kudo T, Sakata S, Benno Y and
Sugiyama T: Diversity of mucosa-associated microbiota in active and
inactive ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroentero. l44:180–186.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ma XY, Dai ZF, Wang HC, Yang JN, Tang XY,
Kang YH, Ding CS, Li YX, Yang RL and Lin XH: Change of intestinal
flora and its relationship with IL-23 /IL-17 axis in patients with
ulcerative colitis. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology. 34:884–892.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Sartor RB and Wu GD: Roles for intestinal
bacteria, viruses, and fungi in pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel
diseases and therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterology.
152:327–339.e4. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gevers D, Kugathasan S, Denson LA,
Vázquez-Baeza Y, Van Treuren W, Ren B, Schwager E, Knights D, Song
SJ, Yassour M, et al: The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset
Crohn's disease. Cell Host Microbe. 15:382–392. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sokol H and Seksik P: The intestinal
microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases: Time to connect with the
host. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 26:327–331. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yu P, Shen F, Zhang X, Cao R, Zhao X, Liu
P, Tu H, Yang X, Shi R and Zhang H: Association of single
nucleotide polymorphisms of IL23R and IL17 with ulcerative colitis
risk in a Chinese Han population. PLoS One.
7(e44380)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li J, Tian H, Jiang HJ and Han B:
Interleukin-17 SNPs and serum levels increase ulcerative colitis
risk: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:15899–15909.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Larussa T, Oliverio M, Suraci E, Greco M,
Placida R, Gervasi S, Marasco R, Imeneo M, Paolino D, Tucci L, et
al: Oleuropein decreases cyclooxygenase-2 and interleukin-17
expression and attenuates inflammatory damage in colonic samples
from ulcerative colitis patients. Nutrients. 9(391)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Inflammatory bowel disease collaboration
group of Chinese Society of Gastroenterology. Consensus on the
diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in China.
Chin J Intern Med. 47:73–79. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Liang J, Zhou L, Sha SM, Lei SN, Luo GH
and Wu KC: Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Inflammatory
Bowel Disease (Guangzhou, 2012), an interpretation on the diagnosis
of UC. Chin J Gastroenterol. 17:712–720. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Siegmund B, Lehr HA, Fantuzzi G and
Dinarello CA: IL-1β-converting enzyme (caspase-1) in intestinal
inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13249–13254.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim BR, Shin J, Guevarra R, Lee JH, Kim
DW, Seol KH, Lee JH, Kim HB and Isaacson R: Deciphering diversity
indices for a better understanding of microbial communities. J
Microbiol Biotechnol. 27:2089–2093. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ren G, Yu M, Li K, Hu Y, Wang Y, Xu X and
Qu J: Seleno-lentinan prevents chronic pancreatitis development and
modulates gut microbiota in mice. J Funct Foods. 22:177–188.
2016.
|
|
24
|
Schmidt M, Unterer S, Suchodolski JS,
Honneffer JB, Guard BC, Lidbury JA, Steiner JM, Fritz J and Kölle
P: The fecal microbiome and metabolome differs between dogs fed
bones and raw food (BARF) diets and dogs fed commercial diets. PLoS
One. 13(e201279)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sender R, Fuchs S and Milo R: Are we
really vastly outnumbered? Revisiting the ratio of bacterial to
host cells in humans. Cell. 164:337–340. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tomasello G, Bellavia M, Palumbo VD,
Gioviale MC, Damiani P and Lo Monte AI: From gut microflora
imbalance to mycobacteria infection: Is there a relationship with
chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases? Ann Ital Chir.
82:361–368. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen J, Zuo ZX and Mao AP: Effect of
probiotics on inducing remission and maintaining therapy in
ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and pouchitis: Meta-analysis
of randomized controlled trials. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:21–35.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Verma R, Verma AK, Ahuja V and Paul J:
Real-time analysis of mucosal flora in patients with inflammatory
bowel disease in India. J Clin Microbiol. 48:4279–4282.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Marteau P: Bacterial flora in inflammatory
bowel disease. Dig Dis. 27 (Suppl 1):S99–S103. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mosca A, Leclerc M and Hugot JP: Gut
microbiota diversity and human diseases: Should we reintroduce key
predators in our ecosystem? Front Microbiol. 7(455)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Manichanh C, Rigottier-Gois L, Bonnaud E,
Gloux K, Pelletier E, Frangeul L, Nalin R, Jarrin C, Chardon P,
Marteau P, et al: Reduced diversity of faecal microbiota in Crohn's
disease revealed by a metagenomic approach. Gut. 55:205–211.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Balish E and Warner T: Enterococcus
faecalis induces inflammatory bowel disease in interleukin-10
knockout mice. Am J Pathol. 160:2253–2257. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gradel KO, Nielsen HL, Schonheyder HC,
Ejlertsen T, Kristensen B and Nielsen H: Increased short- and
long-term risk of inflammatory bowel disease after salmonella or
campylobacter gastroenteritis. Gastroenterology. 137:495–501.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li KY, Wang JL, Wei JP, Gao SY, Zhang YY,
Wang LT and Liu G: Fecal microbiota in pouchitis and ulcerative
colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 22:8929–8939. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rajilić-Stojanović M, Shanahan F, Guarner
F and de Vos WM: Phylogenetic analysis of dysbiosis in ulcerative
colitis during remission. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 19:481–488.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cucchiara S, Iebba V, Conte MP and Schippa
S: The microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease in different age
groups. Dig Dis. 27:252–258. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Swidsinski A, Loening-Baucke V,
Vaneechoutte M and Doerffel Y: Active Crohn's disease and
ulcerative colitis can be specifically diagnosed and monitored
based on the biostructure of the fecal flora. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
14:147–161. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sokol H, Seksik P, Furet JP, Firmesse O,
Nion-Larmurier I, Beaugerie L, Cosnes J, Corthier G, Marteau P and
Doré J: Low counts of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in
colitis microbiota. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 15:1183–1189.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Schwiertz A, Jacobi M, Frick JS, Richter
M, Rusch K and Köhler H: Microbiota in pediatric inflammatory bowel
disease. J Pediatr. 157:240–244.e1. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kabeerdoss J, Jayakanthan P, Pugazhendhi S
and Ramakrishna BS: Alterations of mucosal microbiota in the colon
of patients with inflammatory bowel disease revealed by real time
polymerase chain reaction amplification of 16S ribosomal
ribonucleic acid. Indian J Med Res. 142:23–32. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dziarski R, Park SY, Kashyap DR, Dowd SE
and Gupta D: Pglyrp-regulated gut microflora prevotella falsenii,
parabacteroides distasonis and Bacteroides eggerthii enhance
and alistipes finegoldii attenuates colitis in mice. PLoS One.
11(e146162)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Swidsinski A, Weber J, Loening-Baucke V,
Hale LP and Lochs H: Spatial organization and composition of the
mucosal flora in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin
Microbiol. 43:3380–3389. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Bamola VD, Ghosh A, Kapardar RK, Lal B,
Cheema S, Sarma P and Chaudhry R: Gut microbial diversity in health
and disease: Experience of healthy Indian subjects, and colon
carcinoma and inflammatory bowel disease patients. Microb Ecol
Health Dis. 28(1322447)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Frank DN, St Amand AL, Feldman RA,
Boedeker EC, Harpaz N and Pace NR: Molecular-phylogenetic
characterization of microbial community imbalances in human
inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:13780–13785. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dong LN, Wang M, Guo J and Wang JP: Role
of intestinal microbiota and metabolites in inflammatory bowel
disease. Chin Med J (Engl). 132:1610–1614. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Becker C, Neurath MF and Wirtz S: The
intestinal microbiota in inflammatory Bowel Disease. ILAR J.
56:192–204. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Nagao-Kitamoto H and Kamada N:
Host-microbial cross-talk in inflammatory bowel disease. Immune
Netw. 17:1–12. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Neurath MF: Cytokines in inflammatory
bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:329–342. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
McDermott AJ and Huffnagle GB: The
microbiome and regulation of mucosal immunity. Immunology.
142:24–31. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ott SJ, Musfeldt M, Wenderoth DF, Hampe J,
Brant O, Fölsch UR, Timmis KN and Schreiber S: Reduction in
diversity of the colonic mucosa associated bacterial microflora in
patients with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 53:685–693.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kabeerdoss J, Sankaran V, Pugazhendhi S
and Ramakrishna BS: Clostridium leptum group bacteria
abundance and diversity in the fecal microbiota of patients with
inflammatory bowel disease: A case-control study in India. BMC
Gastroenterol. 13(20)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Imhann F, Vich Vila A, Bonder MJ, Fu J,
Gevers D, Visschedijk MC, Spekhorst LM, Alberts R, Franke L, van
Dullemen HM, et al: Interplay of host genetics and gut microbiota
underlying the onset and clinical presentation of inflammatory
bowel disease. Gut. 67:108–119. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Nishino K, Nishida A, Inoue R, Kawada Y,
Ohno M, Sakai S, Inatomi O, Bamba S, Sugimoto M, Kawahara M, et al:
Analysis of endoscopic brush samples identified mucosa-associated
dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol.
53:95–106. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Danilova NA, Abdulkhakov SR, Grigoryeva
TV, Markelova MI, Vasilyev IY, Boulygina EA, Ardatskaya MD,
Pavlenko AV, Tyakht AV, Odintsova AK and Abdulkhakov RA: Markers of
dysbiosis in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Ter Arkh. 91:17–24. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Huttenhower C, Knight R, Brown CT,
Caporaso JG, Clemente JC, Gevers D, Franzosa EA, Kelley ST, Knights
D, Ley RE, et al: Advancing the microbiome research community.
Cell. 159:227–230. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lynch SV and Pedersen O: The human
intestinal microbiome in health and disease. N Engl J Med.
375:2369–2379. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Daniels L, Budding AE, de Korte N, Eck A,
Bogaards JA, Stockmann HB, Consten EC, Savelkoul PH and Boermeester
MA: Fecal microbiome analysis as a diagnostic test for
diverticulitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 33:1927–1936.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hirano A, Umeno J, Okamoto Y, Shibata H,
Ogura Y, Moriyama T, Torisu T, Fujioka S, Fuyuno Y, Kawarabayasi Y,
et al: Comparison of the microbial community structure between
inflamed and non-inflamed sites in patients with ulcerative
colitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol: Feb 20, 2018 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
59
|
Pace F, Pace M and Quartarone G:
Probiotics in digestive diseases: Focus on Lactobacillus GG.
Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 61:273–292. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Takamura T, Harama D, Fukumoto S, Nakamura
Y, Shimokawa N, Ishimaru K, Ikegami S, Makino S, Kitamura M and
Nakao A: Lactobacillus bulgaricus OLL1181 activates the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor pathway and inhibits colitis. Immunol Cell
Biol. 89:817–822. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Liu YW, Su YW, Ong WK, Cheng TH and Tsai
YC: Oral administration of Lactobacillus plantarum K68
ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in BALB/c mice via the
anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:2159–2166. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Atkins HL, Geier MS, Prisciandaro LD,
Pattanaik AK, Forder RE, Turner MS and Howarth GS: Effects of a
Lactobacillus reuteri BR11 mutant deficient in the
cystine-transport system in a rat model of inflammatory bowel
disease. Dig Dis Sci. 57:713–719. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Clarke G, Sandhu KV, Griffin BT, Dinan TG,
Cryan JF and Hyland NP: Gut reactions: Breaking down
xenobiotic-microbiome interactions. Pharmacol Rev. 71:198–224.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Suez J, Zmora N, Segal E and Elinav E: The
pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat Med. 25:716–729.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Meijer BJ and Dieleman LA: Probiotics in
the treatment of human inflammatory bowel diseases: Update 2011. J
Clin Gastroenterol. 45 (Suppl 1):S139–S144. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Shi N, Li N, Duan X and Niu H: Interaction
between the gut microbiome and mucosal immune system. Mil Med Res.
4(14)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Steck N, Hoffmann M, Sava IG, Kim SC,
Hahne H, Tonkonogy SL, Mair K, Krueger D, Pruteanu M, Shanahan F,
et al: Enterococcus faecalis metalloprotease compromises epithelial
barrier and contributes to intestinal inflammation.
Gastroenterology. 141:959–971. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhou Y, Chen H, He H, Du Y, Hu J, Li Y, Li
Y, Zhou Y, Wang H, Chen Y and Nie Y: Increased Enterococcus
faecalis infection is associated with clinically active Crohn
disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 95(e5019)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Xie Z, Qu Y, Leng Y, Sun W, Ma S, Wei J,
Hu J and Zhang X: Human colon carcinogenesis is associated with
increased interleukin-17-driven inflammatory responses. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 9:1679–1689. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
D'Ambrosio A, Cossu A, Amendola A, Zandri
A, Butera A, Sanchez M, Biffoni M, Pronio A, Montesani C, Kohn A,
et al: Lamina propria CD4+LAP+ regulatory T
cells are increased in active ulcerative colitis but show increased
IL-17 expression and reduced suppressor activity. J Crohns Colitis.
10:346–353. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Zhu Q, Zheng P, Chen X, Zhou F, He Q and
Yang Y: Andrographolide presents therapeutic effect on ulcerative
colitis through the inhibition of IL-23/IL-17 axis. Am J Transl
Res. 10:465–473. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kevans D, Tyler AD, Holm K, Jørgensen KK,
Vatn MH, Karlsen TH, Kaplan GG, Eksteen B, Gevers D, Hov JR and
Silverberg MS: Characterization of intestinal microbiota in
ulcerative colitis patients with and without primary sclerosing
cholangitis. J Crohns Colitis. 10:330–337. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Bajer L, Kverka M, Kostovcik M, Macinga P,
Dvorak J, Stehlikova Z, Brezina J, Wohl P, Spicak J and Drastich P:
Distinct gut microbiota profiles in patients with primary
sclerosing cholangitis and ulcerative colitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:4548–4558. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Rubio CA, Langner C and Schmidt PT:
Partial to complete abrogation of the subepithelial macrophage
barrier against the gut microbiota in patients with ulcerative
colitis and Crohn's colitis. Histopathology. 72:580–587.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Kiely CJ, Pavli P and O'Brien CL: The role
of inflammation in temporal shifts in the inflammatory bowel
disease mucosal microbiome. Gut Microbes. 9:477–485.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Yang Y and Jobin C: Novel insights into
microbiome in colitis and colorectal cancer. Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 33:422–427. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Huttenhower C, Kostic AD and Xavier RJ:
Inflammatory bowel disease as a model for translating the
microbiome. Immunity. 40:843–854. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Slatko BE, Gardner AF and Ausubel FM:
Overview of next-generation sequencing technologies. Curr Protoc
Mol Biol. 122(e59)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom
E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE and Relman DA:
Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science.
308:1635–1638. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|