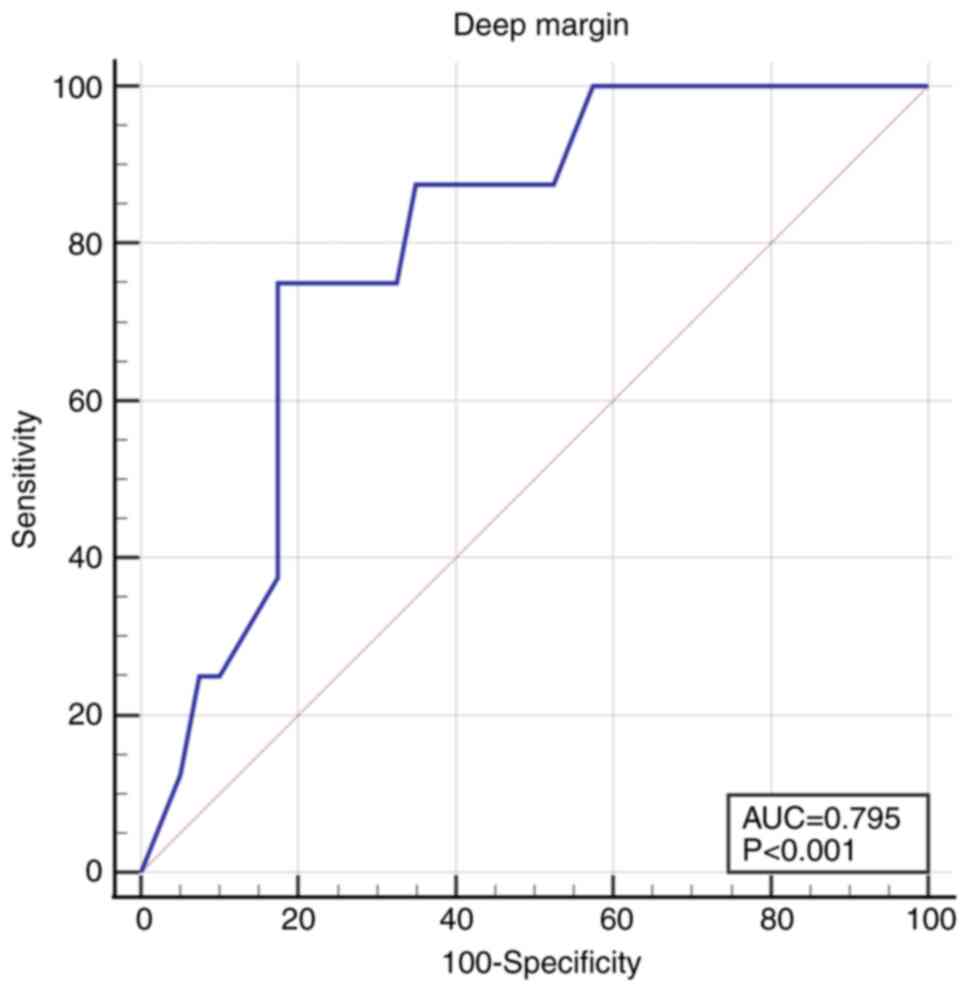
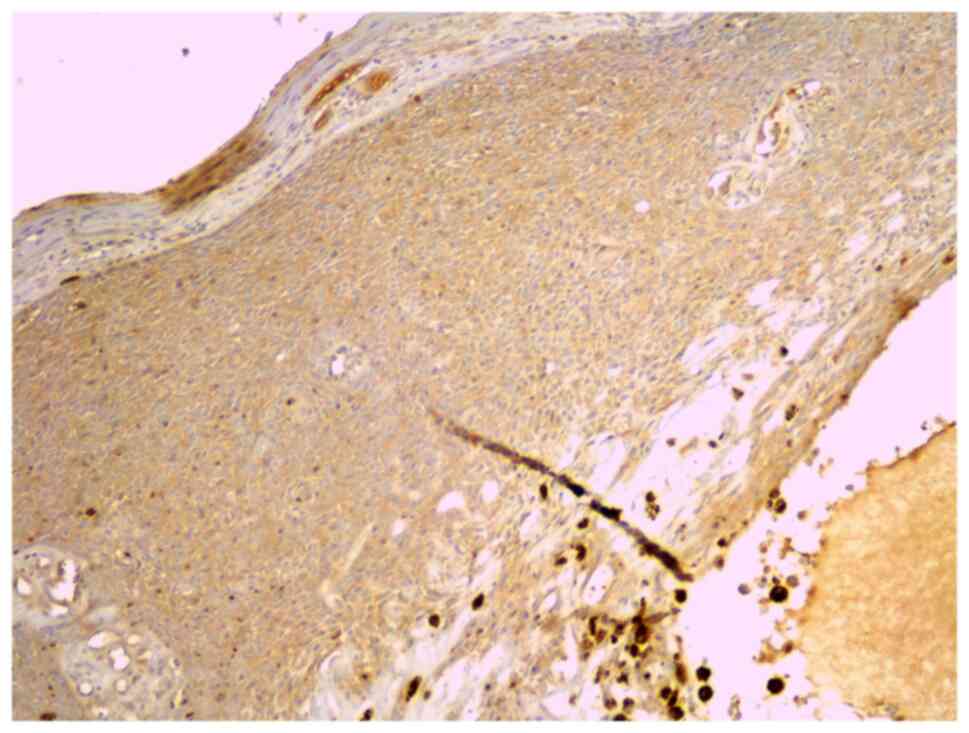
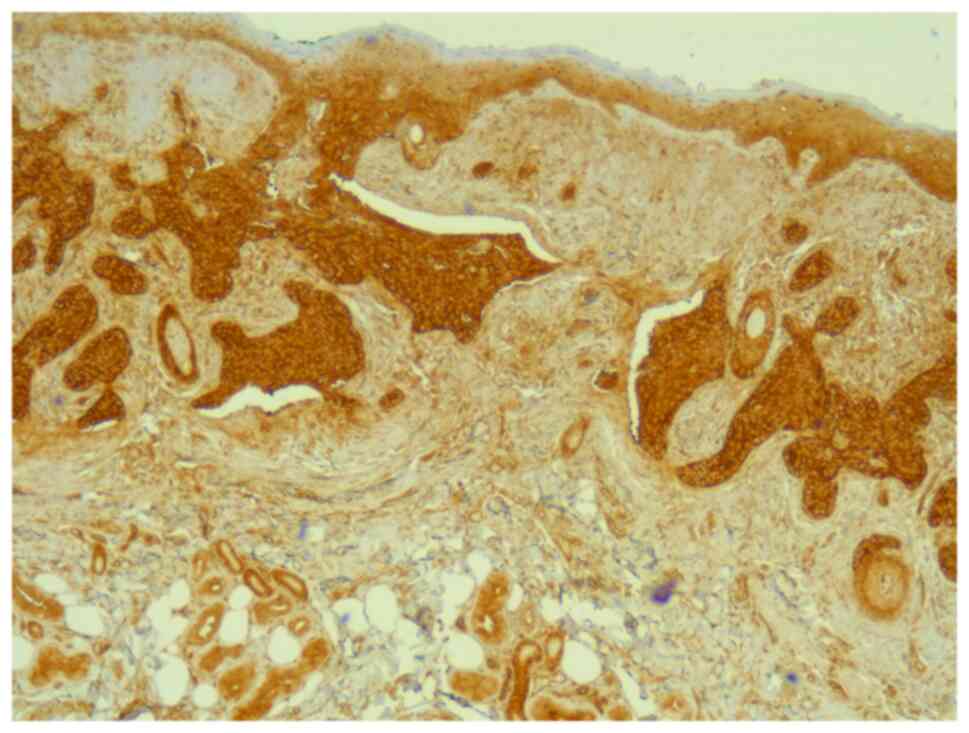
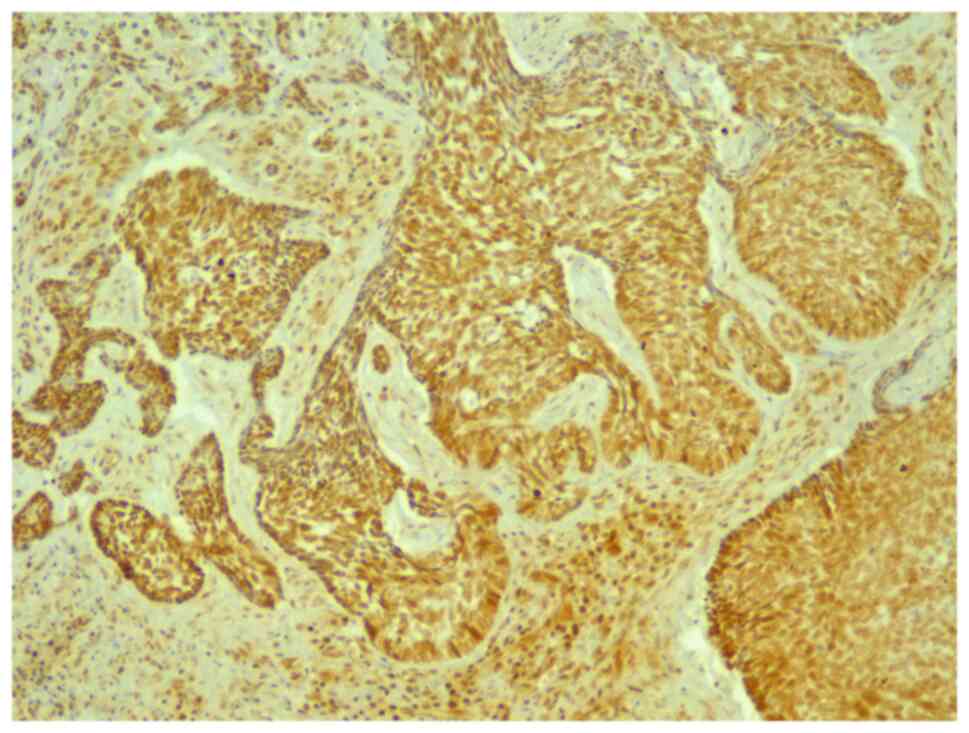
|
1
|
Peris K, Fargnoli MC, Garbe C, Kaufmann R,
Bastholt L, Seguin NB, Bataille V, Marmol V del, Dummer R, Harwood
CA, et al: Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma:
European consensus-based interdisciplinary guidelines. Eur J
Cancer. 118:10–34. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Verkouteren JAC, Ramdas KHR, Wakkee M and
Nijsten T: Epidemiology of basal cell carcinoma: Scholarly review.
Br J Dermatol. 177:359–372. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weedon D: Tumors of the epidermis. In:
Skin Pathology, 3rd edition. Elsevier, pp668-703, 2010.
|
|
4
|
Wortsman X: Sonography of facial cutaneous
basal cell carcinoma. J Ultrasound Med. 32:567–572. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network
(NCCN): Basal Cell Skin Cancer (version 1.2020). Available from:
https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nmsc.pdf.
|
|
6
|
Lara F, Santamaría JR and Garbers LE:
Recurrence rate of basal cell carcinoma with positive
histopathological margins and related risk factors. An Bras
Dermatol. 92:58–62. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lima NL, Verli FD, De Miranda JL and
Marinho SA: Basosquamous carcinoma: Histopathological features.
Indian J Dermatol. 57:382–383. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Trakatelli M, Morton C, Nagore E, Ulrich
C, Del Marmol V, Peris K and Basset-Seguin N: BCC subcommittee of
the Guidelines Committee of the European Dermatology Forum. Update
of the European guidelines for basal cell carcinoma management. Eur
J Dermatol. 24:312–329. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Van Loo E, Mosterd K, Krekels GA,
Roozeboom MH, Ostertag JU, Dirksen CD, Steijlen PM, Neumann HA,
Nelemans PJ and Kelleners-Smeets NW: Surgical excision versus Mohs'
micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face: A
randomised clinical trial with 10 year follow-up. Eur J Cancer.
50:3011–3020. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mastrangelo E and Milani M: Role and
inhibition of GLI1 protein in cancer. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 9:35–43.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pan D: The hippo signaling pathway in
development and cancer. Dev Cell. 19:491–505. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Szelachowska J, Donizy P,
Ratajczak-Wielgomas K, Halon A, Zielecka-Debska D, Lichon K,
Maciejczyk A, Lata-Wozniak E, Piotrowska A and Matkowski R: The
effect of YAP expression in tumor cells and tumor stroma on the
prognosis of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral
cavity floor and oral surface of the tongue. Oncol Lett.
18:3561–3570. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Quan T, Xu Y, Qin Z, Robichaud P, Betcher
S, Calderone K, He T, Johnson TM, Voorhees JJ and Fisher GJ:
Elevated YAP and its downstream targets CCN1 and CCN2 in basal cell
carcinoma: Impact on keratinocyte proliferation and stromal cell
activation. Am J Pathol. 184:937–943. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chu CY, Chang CC, Prakash E and Kuo ML:
Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and cancer progression. J
Biomed Sci. 15:675–685. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hall-Glenn F and Lyons KM: Roles for CCN2
in normal physiological processes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:3209–3217.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim NG, Koh E, Chen X and Gumbiner BM:
E-cadherin mediates contact inhibition of proliferation through
Hippo signaling-pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:11930–5. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vornicescu C, Șenila SC, Bejinariu NI,
Vesa SC, Boșca BA, Chirilă DN, Melincovici CS, Sorițău O and Mihu
CM: The role of GLI1, YAP, CTGF and E-cadherin in the pathogenesis
of basal cell carcinoma - our preliminary results. HVM Bioflux.
13:25–32. 2021.
|
|
18
|
Totonchy M and Leffell D: Emerging
concepts and recent advances in basal cell carcinoma.
F1000Research. 6(2085)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Girardi FM, Wagner VP, Martins MD,
Abentroth AL and Hauth LA: Factors associated with incomplete
surgical margins in basal cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Braz
J Otorhinolaryngol: Apr 8, 2020 (Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.02.007.
|
|
20
|
Bartoš V, Pokorný D, Zacharová O, Haluska
P, Doboszová J, Kullová M, Adamicová K, Péč M and Péč J: Recurrent
basal cell carcinoma: A clinicopathological study and evaluation of
histomorphological findings in primary and recurrent lesions. Acta
Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 20:67–75. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saabye Bøgelund F, Ashlede Philipsen P and
Gniadecki R: Factors affecting the recurrence rate of basal cell
carcinoma. Acta Derm Venereol. 87:330–334. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nilsson M: Induction of basal cell
carcinomas and trichoepitheliomas in mice overexpressing GLI-1.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:3438–3443. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cui Y, Cui CA, Yang ZT, Ni WD, Jin Y and
Xuan YH: Gli1 expression in cancer stem-like cells predicts poor
prognosis in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol
Pathol. 102:347–353. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Park KS, Martelotto LG, Peifer M, Sos ML,
Karnezis AN, Mahjoub MR, Bernard K, Conklin JF, Szczepny A, Yuan J,
et al: A crucial requirement for Hedgehog signaling in small cell
lung cancer. Nat Med. 17:1504–1508. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Debaugnies M, Sánchez-Danés A, Rorive S,
Raphaël M, Liagre M, Parent M-A, Brisebarre A, Salmon I and
Blanpain C: YAP and TAZ are essential for basal and squamous cell
carcinoma initiation. EMBO Rep. 19(e45809)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xu MZ, Yao TJ, Lee NP, Ng IO, Chan YT,
Zender L, Lowe SW, Poon RT and Luk JM: Yes-associated protein is an
independent prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer.
115:4576–4585. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Guo L, Chen Y, Luo J, Zheng J and Shao G:
YAP1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis of breast
cancer patients and induces breast cancer cell growth by inhibiting
PTEN. FEBS Open Bio. 9:437–445. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Marx A, Schumann A, Höflmayer D, Bady E,
Hube-Magg C, Möller K, Tsourlakis MC, Steurer S, Büscheck F,
Eichenauer T, et al: Up regulation of the Hippo signalling effector
YAP1 is linked to early biochemical recurrence in prostate cancers.
Sci Rep. 10(8916)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shimbo A, Kajiyama H, Tamauchi S,
Yoshikawa N, Ikeda Y, Nishino K, Suzuki S, Niimi K, Sakata J and
Kikkawa F: Expression of connective tissue growth factor as a
prognostic indicator and its possible involvement in the aggressive
properties of epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
42:2323–2332. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lin BR, Chang CC, Che TF, Chen ST, Chen
RJC, Yang CY, Jeng YM, Liang JT, Lee PH, Chang KJ, et al:
Connective tissue growth factor inhibits metastasis and acts as an
independent prognostic marker in colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 128:9–23. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Vanjaka-Rogošić L, Puizina-Ivić N, Mirić
L, Rogošić V, Kuzmić-Prusac I, Babić MS, Vuković D and Mardešić S:
Matrix metalloproteinases and E-cadherin immunoreactivity in
different basal cell carcinoma histological types. Acta Histochem.
116:688–693. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bánkfalvi A, Kraßort M, Buchwalow IB, Végh
A, Felszeghy E and Piffkó J: Gains and losses of adhesion molecules
(CD44, E-cadherin, and β-catenin) during oral carcinogenesis and
tumour progression. J Pathol. 198:343–351. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yazdani J, Ghavimi MA, Jabbari Hagh E and
Ahmadpour F: The role of E-cadherin as a prognostic biomarker in
head and neck squamous carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Mol Diagnosis Ther. 22:523–535. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Balci MG and Tayfur M: Loss of E-cadherin
expression in recurrent non-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the
bladder. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 11:4163–4168. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|