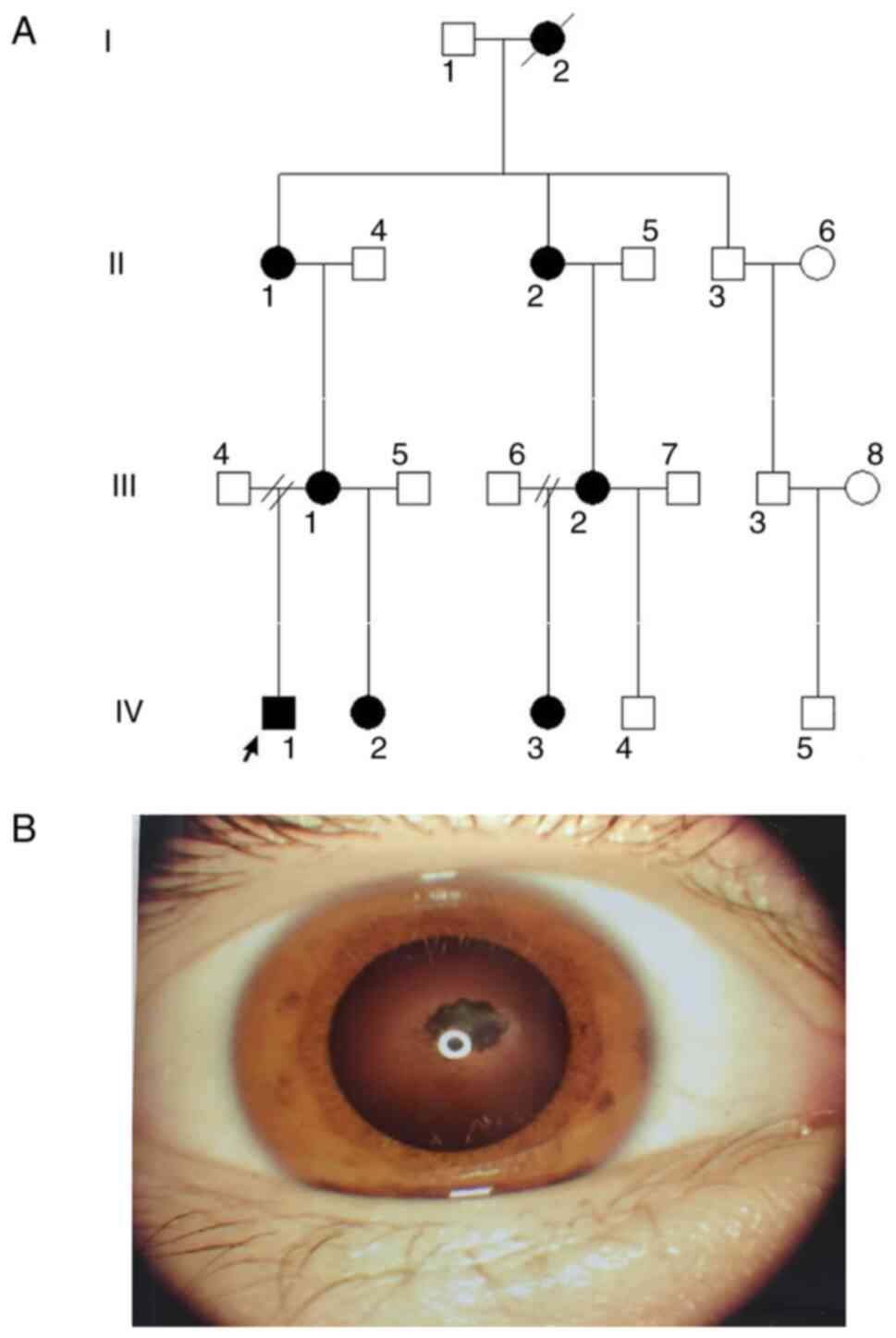
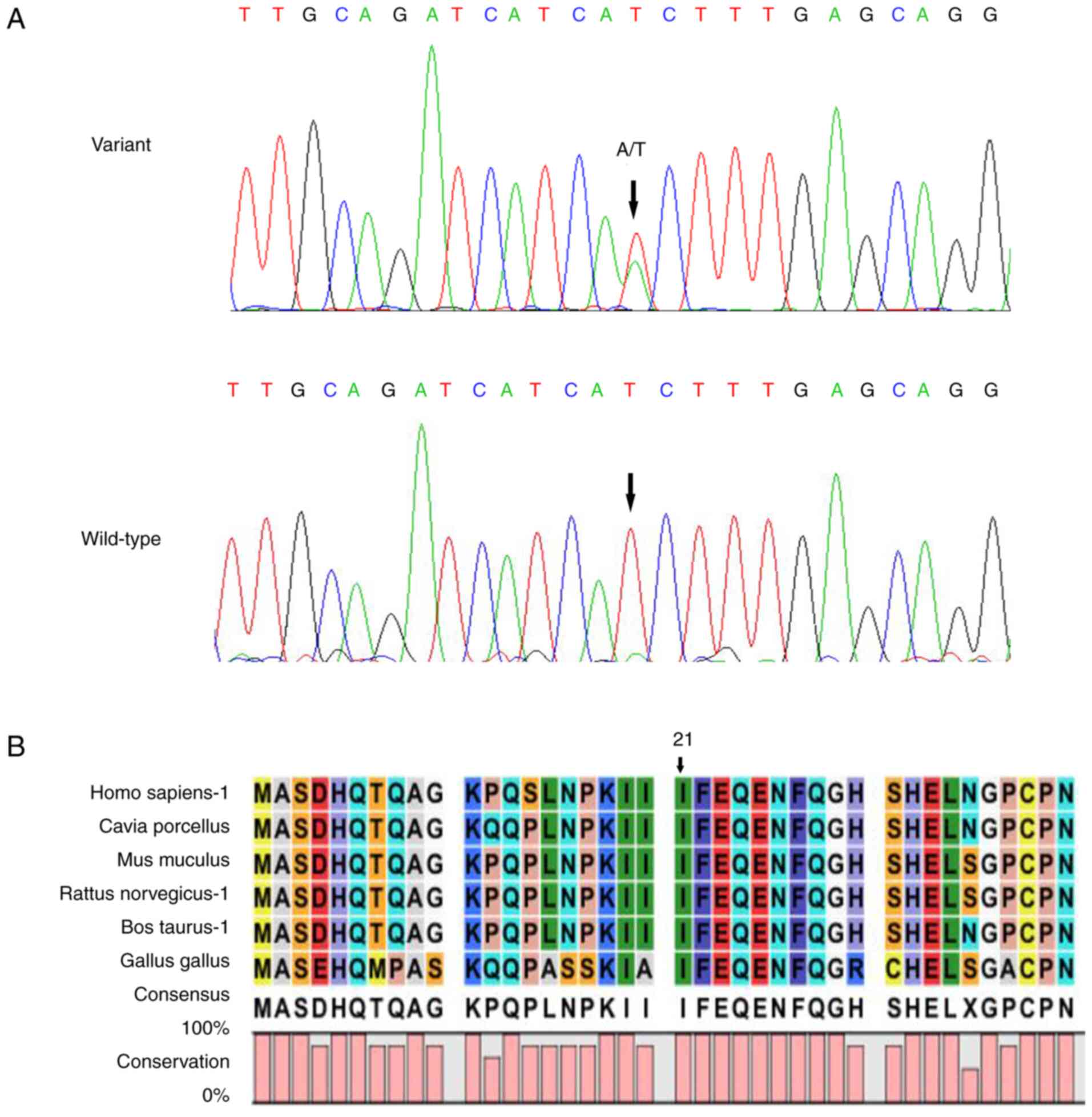
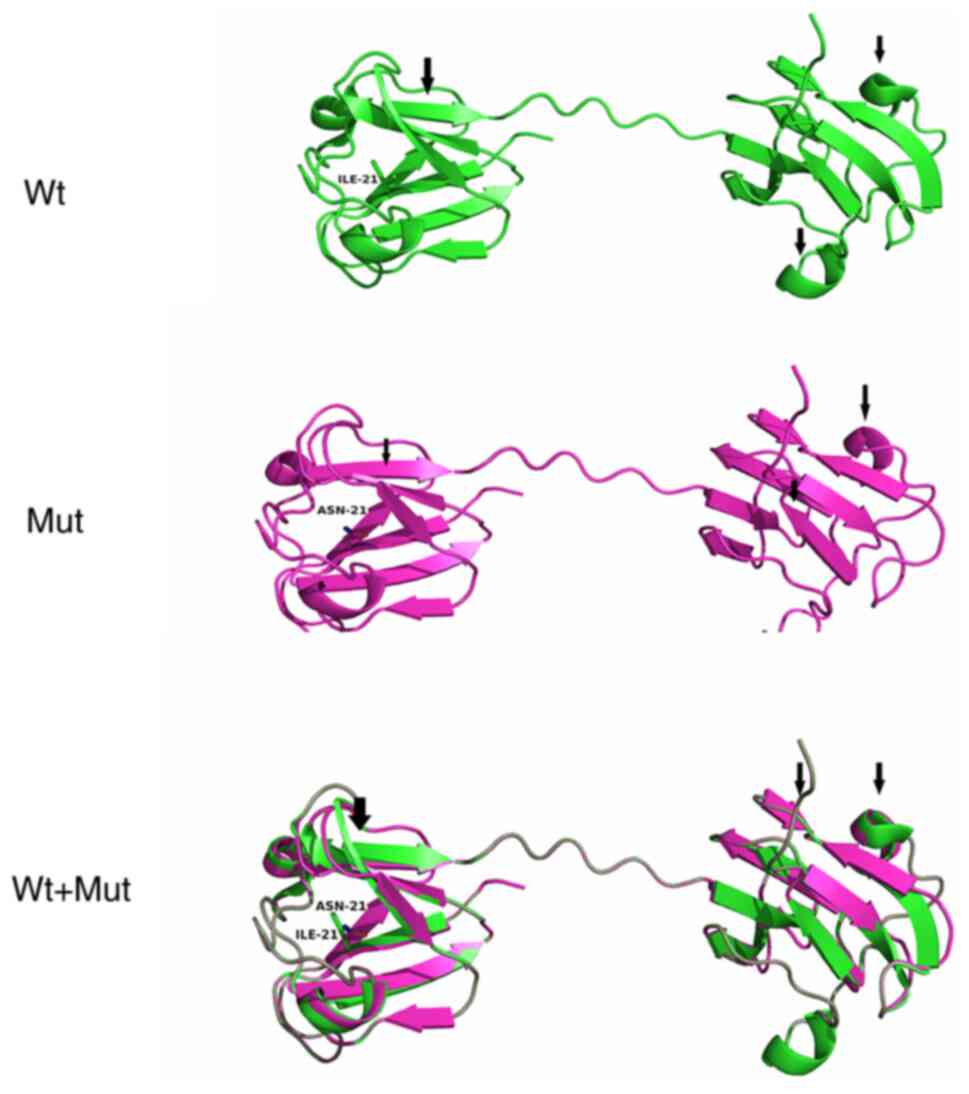
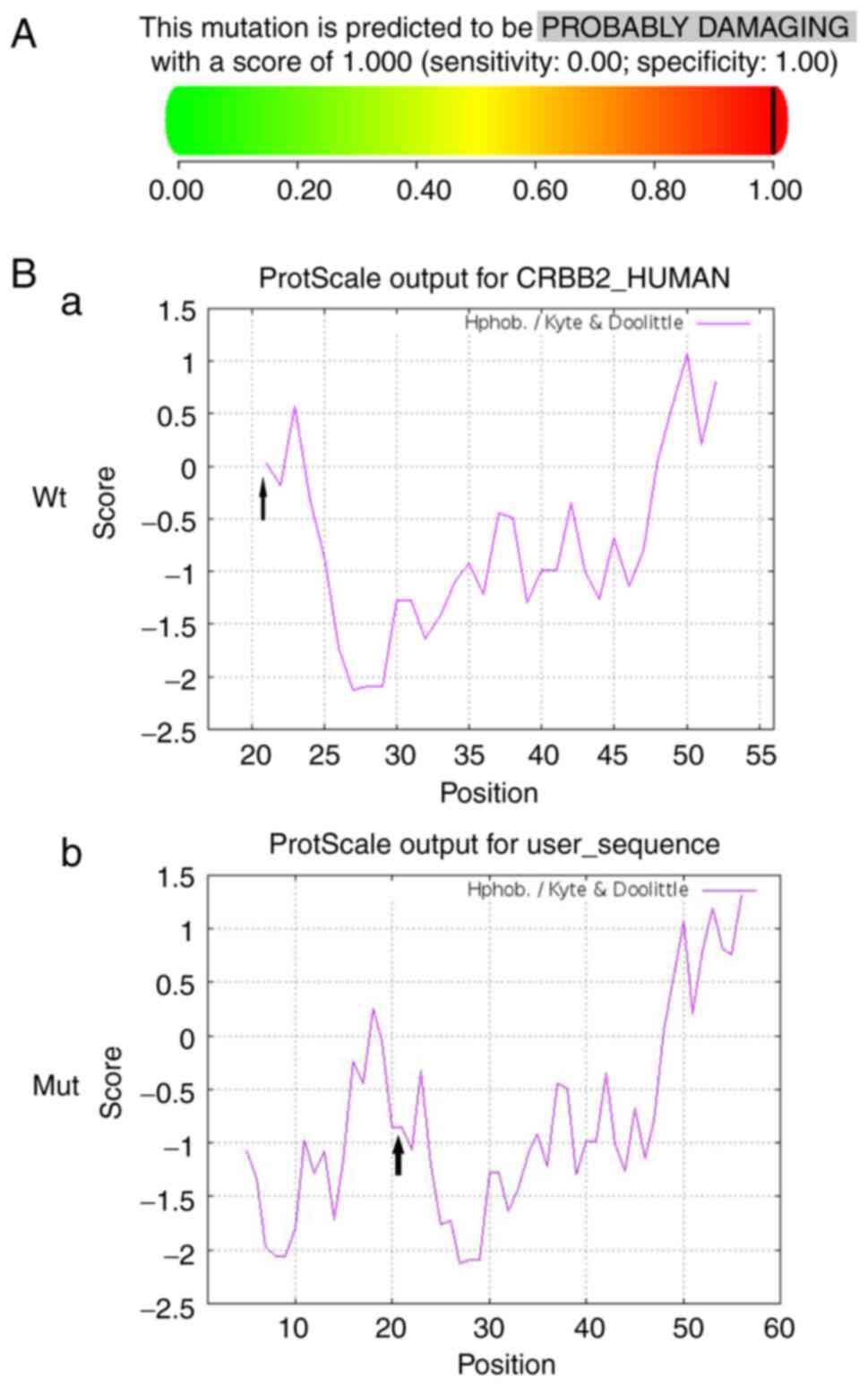
|
1
|
Naz S, Sharif S, Badar H, Rashid F, Kaleem
A and Iqtedar M: Incidence of environmental and genetic factors
causing congenital cataract in children of Lahore. J Pak Med Assoc.
66:819–822. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li J, Chen X, Yan Y and Yao K: Molecular
genetics of congenital cataracts. Exp Eye Res.
191(107872)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lhussiez V, Dubus E, Cesar Q, Acar N,
Nandrot EF, Simonutti M, Audo I, Lizé E, Nguyen S, Geissler A, et
al: Cohen syndrome-associated cataract is explained by VPS13B
functions in lens homeostasis and is modified by additional genetic
factors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 61(18)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sheeladevi S, Lawrenson JG, Fielder AR and
Suttle CM: Global prevalence of childhood cataract: A systematic
review. Eye (Lond). 30:1160–1169. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhuang J, Cao Z, Zhu Y, Liu L, Tong Y,
Chen X, Wang Y, Lu C, Ma X and Yang J: Mutation screening of
crystallin genes in Chinese families with congenital cataracts. Mol
Vis. 25:427–437. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gerasimovich ES, Strelkov SV and Gusev NB:
Some properties of three αB-crystallin mutants carrying point
substitutions in the C-terminal domain and associated with
congenital diseases. Biochimie. 142:168–178. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xu LJ, Lv ZG, Liu Y, Zhang XX, Cui YX, Li
XC, Zhu YJ and He J: A novel CRYBB2 mutation causes autosomal
dominant cataract: A report from a Chinese family. Eur J
Ophthalmol. 4(1120672120926450)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen W, Chen X, Hu Z, Lin H, Zhou F, Luo
L, Zhang X, Zhong X, Yang Y, Wu C, et al: A missense mutation in
CRYBB2 leads to progressive congenital membranous cataract by
impacting the solubility and function of βB2-crystallin. PLoS One.
8(e81290)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li L, Fan DB, Zhao YT, Li Y, Kong DQ, Cai
FF and Zheng GY: Two novel mutations identified in ADCC families
impair crystallin protein distribution and induce apoptosis in
human lens epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 7(17848)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Guo W, Lai Y, Yan Z, Wang Y, Nie Y, Guan
S, Kuo Y, Zhang W, Zhu X, Peng M, et al: Trio-whole-exome
sequencing and preimplantation genetic diagnosis for unexplained
recurrent fetal malformations. Hum Mutat. 41:432–448.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang KJ, Wang BB, Zhang F, Zhao Y, Ma X
and Zhu SQ: Novel beta-crystallin gene mutations in Chinese
families with nuclear cataracts. Arch Ophthalmol. 129:337–343.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
World Medical Association. World medical
association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chun SM, Sung CO, Jeon H, Kim TI, Lee JY,
Park H, Kim Y, Kim D and Jang SJ: Next-generation sequencing using
S1 nuclease for poor-quality formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded
tumor specimens. J Mol Diagn. 20:802–811. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhao S, Zhang C, Mu J, Zhang H, Yao W,
Ding X, Ding J and Chang Y: All-in-one sequencing: An improved
library preparation method for cost-effective and high-throughput
next-generation sequencing. Plant Methods. 16(74)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li H and Durbin R: Fast and accurate short
read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform. Bioinformatics.
25:1754–1760. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Broad Institute: Picard Tools. http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/. Accessed
September 10, 2019.
|
|
17
|
Van der Auwera GA, Carneiro MO, Hartl C,
Poplin R, Del Angel G, Levy-Moonshine A, Jordan T, Shakir K, Roazen
D, Thibault J, et al: From FastQ data to high confidence variant
calls: The genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr
Protoc Bioinformatics. 43:11.10.1–11.10.33. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang K, Li M and Hakonarson H: ANNOVAR:
Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput
sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38(e164)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kumar P, Henikoff S and Ng PC: Predicting
the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function
using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc. 4:1073–1081. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L,
Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS and Sunyaev SR: A
method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat
Methods. 7:248–249. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Schwarz JM, Cooper DN, Schuelke M and
Seelow D: MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the
deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods. 11:361–362. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cooper GM, Stone EA and Asimenos G: NISC
Comparative Sequencing Program. Green ED, Batzoglou S and Sidow A:
Distribution and intensity of constraint in mammalian genomic
sequence. Genome Res. 15:901–913. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
ACMG Board Of Directors: ACMG policy
statement. Updated recommendations regarding analysis and reporting
of secondary findings in clinical genome-scale sequencing. Genet
Med. 17:68–69. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S,
Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, et al:
Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence
variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American college
of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular
pathology. Genet Med. 17:405–424. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Seeliger D and de Groot BL: Ligand docking
and binding site analysis with PyMOL and autodock/vina. J Comput
Aided Mol Des. 24:417–422. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Balaji S and Vanniarajan A: Implication of
pseudo reference genes in normalization of data from reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR. Gene. 757(144948)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mooers B: Shortcuts for faster image
creation in PyMOL. Protein Sci. 29:268–276. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hetz C and Papa FR: The unfolded protein
response and cell fate control. Mol Cell. 69:169–181.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bashir S, Banday M, Qadri O, Bashir A,
Hilal N, Nida-I-Fatima Rader S and Fazili KM: The molecular
mechanism and functional diversity of UPR signaling sensor IRE1.
Life Sci. 265(118740)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sharma RB, Darko C and Alonso LC:
Intersection of the ATF6 and XBP1 ER stress pathways in mouse islet
cells. J Biol Chem. 295:14164–14177. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Berry V, Georgiou M, Fujinami K, Quinlan
R, Moore A and Michaelides M: Inherited cataracts: Molecular
genetics, clinical features, disease mechanisms and novel
therapeutic approaches. Br J Ophthalmol. 104:1331–1337.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu H, Wei X, Sha Y, Liu W, Gao H, Lin J,
Li Y, Tang Y, Wang Y, Wang Y and Su Z: Whole-exome sequencing in
patients with premature ovarian insufficiency: Early detection and
early intervention. J Ovarian Res. 13(114)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Astiazarán MC, García-Montaño LA,
Sánchez-Moreno F, Matiz-Moreno H and Zenteno JC: Next generation
sequencing-based molecular diagnosis in familial congenital
cataract expands the mutational spectrum in known congenital
cataract genes. Am J Med Genet A. 176:2637–2645. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hwang SS, Kim WS and Lee SJ: Clinical
features of strabismus and nystagmus in bilateral congenital
cataracts. Int J Ophthalmol. 11:813–817. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Magli A, Carelli R, Forte R, Vecchio EC,
Esposito F and Torre A: Congenital and developmental cataracts:
Focus on strabismus outcomes at long-term follow-up. Semin
Ophthalmol. 32:358–362. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kuhli-Hattenbach C, Fronius M and Kohnen
T: Timing of congenital cataract surgery: Amblyopia versus aphakic
glaucoma. Ophthalmologe. 117:190–198. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
38
|
Pauli S, Söker T, Klopp N, Illig T, Engel
W and Graw J: Mutation analysis in a German family identified a new
cataract-causing allele in the CRYBB2 gene. Mol Vis. 13:962–967.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao WJ, Xu J, Chen XJ, Liu HH, Yao K and
Yan YB: Effects of cataract-causing mutations W59C and W151C on
βB2-crystallin structure, stability and folding. Int J Biol
Macromol. 103:764–770. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Santhiya ST, Manisastry SM, Rawlley D,
Malathi R, Anishetty S, Gopinath PM, Vijayalakshmi P,
Namperumalsamy P, Adamski J and Graw J: Mutation analysis of
congenital cataracts in Indian families: Identification of SNPS and
a new causative allele in CRYBB2 gene. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
45:3599–3607. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li FF, Zhu SQ, Wang SZ, Gao C, Huang SZ,
Zhang M and Ma X: Nonsense mutation in the CRYBB2 gene causing
autosomal dominant progressive polymorphic congenital coronary
cataracts. Mol Vis. 14:750–755. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Weisschuh N, Aisenbrey S, Wissinger B and
Riess A: Identification of a novel CRYBB2 missense mutation causing
congenital autosomal dominant cataract. Mol Vis. 18:174–180.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim L, Kwon DH, Heo J, Park MR and Song
HK: Use of the LC3B-fusion technique for biochemical and structural
studies of proteins involved in the N-degron pathway. J Biol Chem.
295:2590–2600. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Friemel M, Marelja Z, Li K and Leimkühler
S: The N-terminus of iron-sulfur cluster assembly factor ISD11 is
crucial for subcellular targeting and interaction with l-cysteine
desulfurase NFS1. Biochemistry. 56:1797–1808. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Skach WR, Shi LB, Calayag MC, Frigeri A,
Lingappa VR and Verkman AS: Biogenesis and transmembrane topology
of the CHIP28 water channel at the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell
Biol. 125:803–815. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Song Z, Si N and Xiao W: A novel mutation
in the CRYAA gene associated with congenital cataract and
microphthalmia in a Chinese family. BMC Med Genet.
19(190)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Carver JA, Grosas AB, Ecroyd H and Quinlan
RA: The functional roles of the unstructured N- and C-terminal
regions in αB-crystallin and other mammalian small heat-shock
proteins. Cell Stress Chaperones. 22:627–638. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang J, Li J, Huang C, Xue L, Peng Y, Fu
Q, Gao L, Zhang J and Li W: Targeted knockout of the mouse
betaB2-crystallin gene (Crybb2) induces age-related cataract.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 49:5476–5483. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Song L and Luo ZQ: Post-translational
regulation of ubiquitin signaling. J Cell Biol. 218:1776–1786.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Frye M, Harada BT, Behm M and He C: RNA
modifications modulate gene expression during development. Science.
361:1346–1349. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang J, Cui WW, Du C, Huang Y, Pi X, Guo
W, Wang J, Huang W, Chen D, Li J, et al: Knockout of DNase1l1l
abrogates lens denucleation process and causes cataract in
zebrafish. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1866(165724)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Shiels A and Hejtmancik JF: Inherited
cataracts: Genetic mechanisms and pathways new and old. Exp Eye
Res. 209(108662)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chan WC, Tsang KY, Cheng YW, Ng VC, Chik
H, Tan ZJ, Boot-Handford R, Boyde A, Cheung KN, Cheah KS and Chan
D: Activating the unfolded protein response in osteocytes causes
hyperostosis consistent with craniodiaphyseal dysplasia. Hum Mol
Genet. 26:4572–4587. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Berry V, Pontikos N, Moore A, Ionides A,
Plagnol V, Cheetham ME and Michaelides M: A novel missense mutation
in HSF4 causes autosomal-dominant congenital lamellar cataract in a
British family. Eye (Lond). 32:806–812. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ghavami S, Yeganeh B, Zeki AA, Shojaei S,
Kenyon NJ, Ott S, Samali A, Patterson J, Alizadeh J, Moghadam AR,
et al: Autophagy and the unfolded protein response promote
profibrotic effects of TGF-β(1) in human lung fibroblasts. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 314:L493–L504. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Schinzel RT, Higuchi-Sanabria R, Shalem O,
Moehle EA, Webster BM, Joe L, Bar-Ziv R, Frankino PA, Durieux J,
Pender C, et al: The hyaluronidase, TMEM2, promotes ER homeostasis
and longevity independent of the UPR ER. Cell. 179:1306–1318.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Muñoz JP, Ivanova S, Sánchez-Wandelmer J,
Martínez-Cristóbal P, Noguera E, Sancho A, Díaz-Ramos A,
Hernández-Alvarez MI, Sebastián D, Mauvezin C, et al: Mfn2
modulates the UPR and mitochondrial function via repression of
PERK. EMBO J. 32:2348–2361. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Andley UP and Goldman JW: Autophagy and
UPR in alpha-crystallin mutant knock-in mouse models of hereditary
cataracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1860:234–239. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Nguyen KT, Lee CS, Mun SH, Truong NT, Park
SK and Hwang CS: N-terminal acetylation and the N-end rule pathway
control degradation of the lipid droplet protein PLIN2. J Biol
Chem. 294:379–388. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Nguyen KT, Mun SH, Lee CS and Hwang CS:
Control of protein degradation by N-terminal acetylation and the
N-end rule pathway. Exp Mol Med. 50:1–8. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|