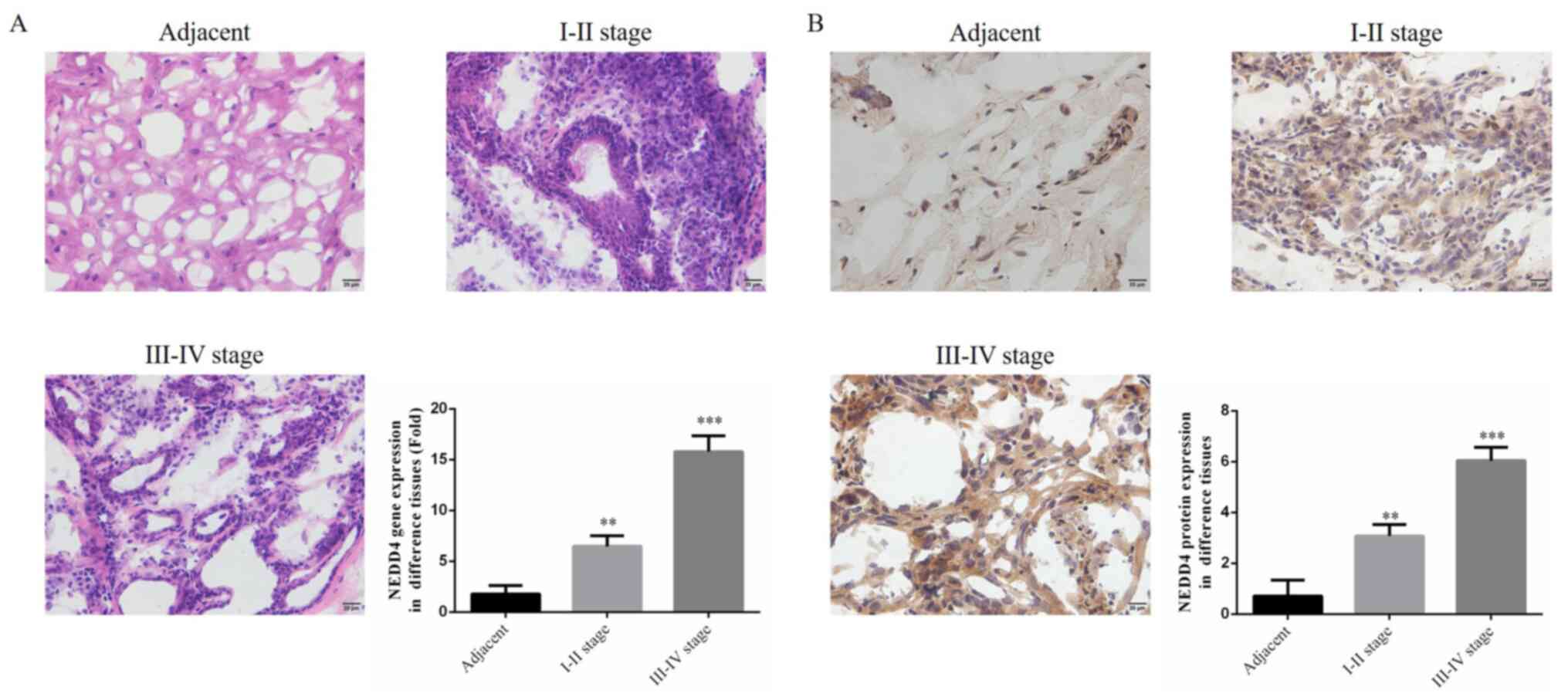
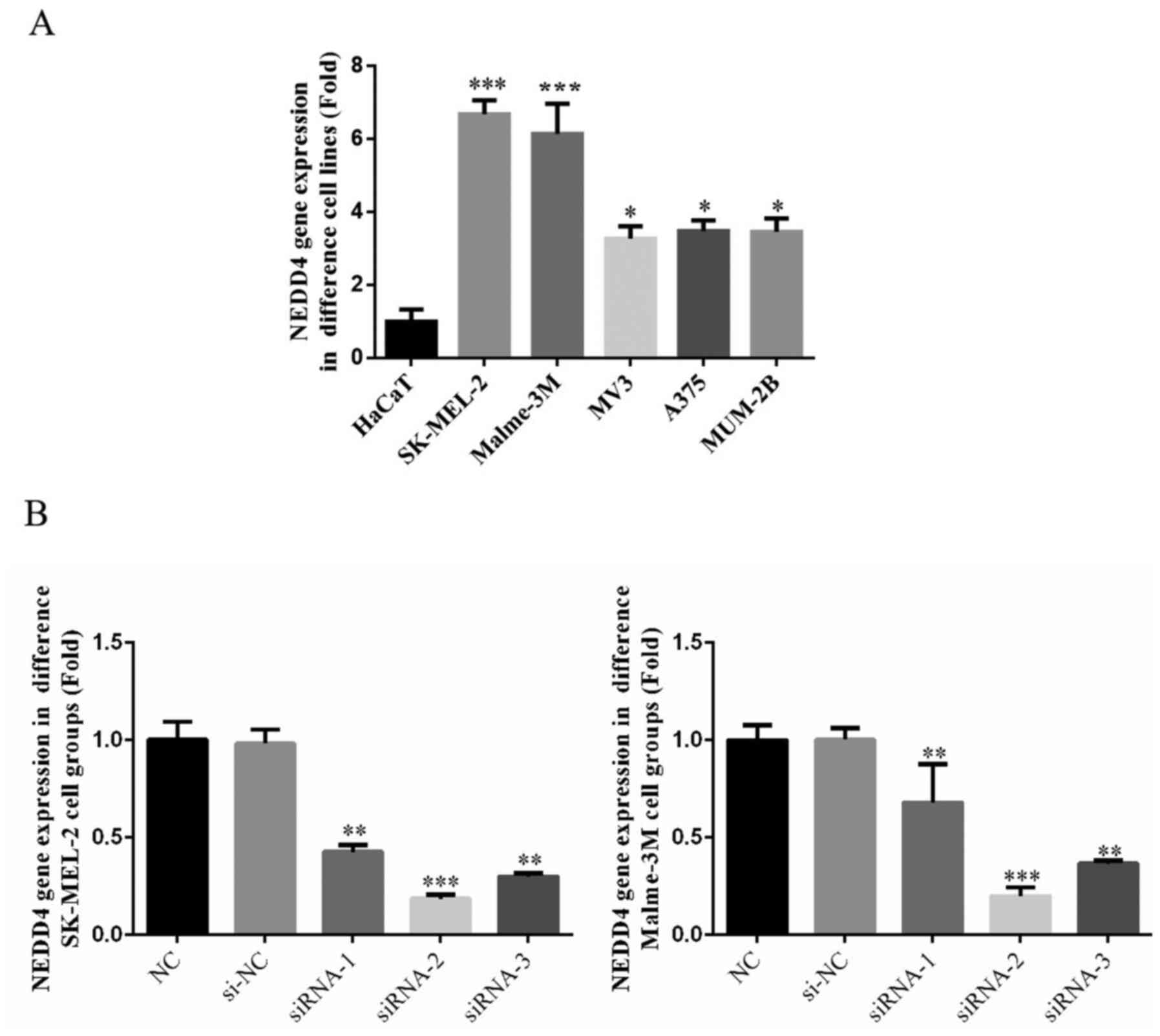
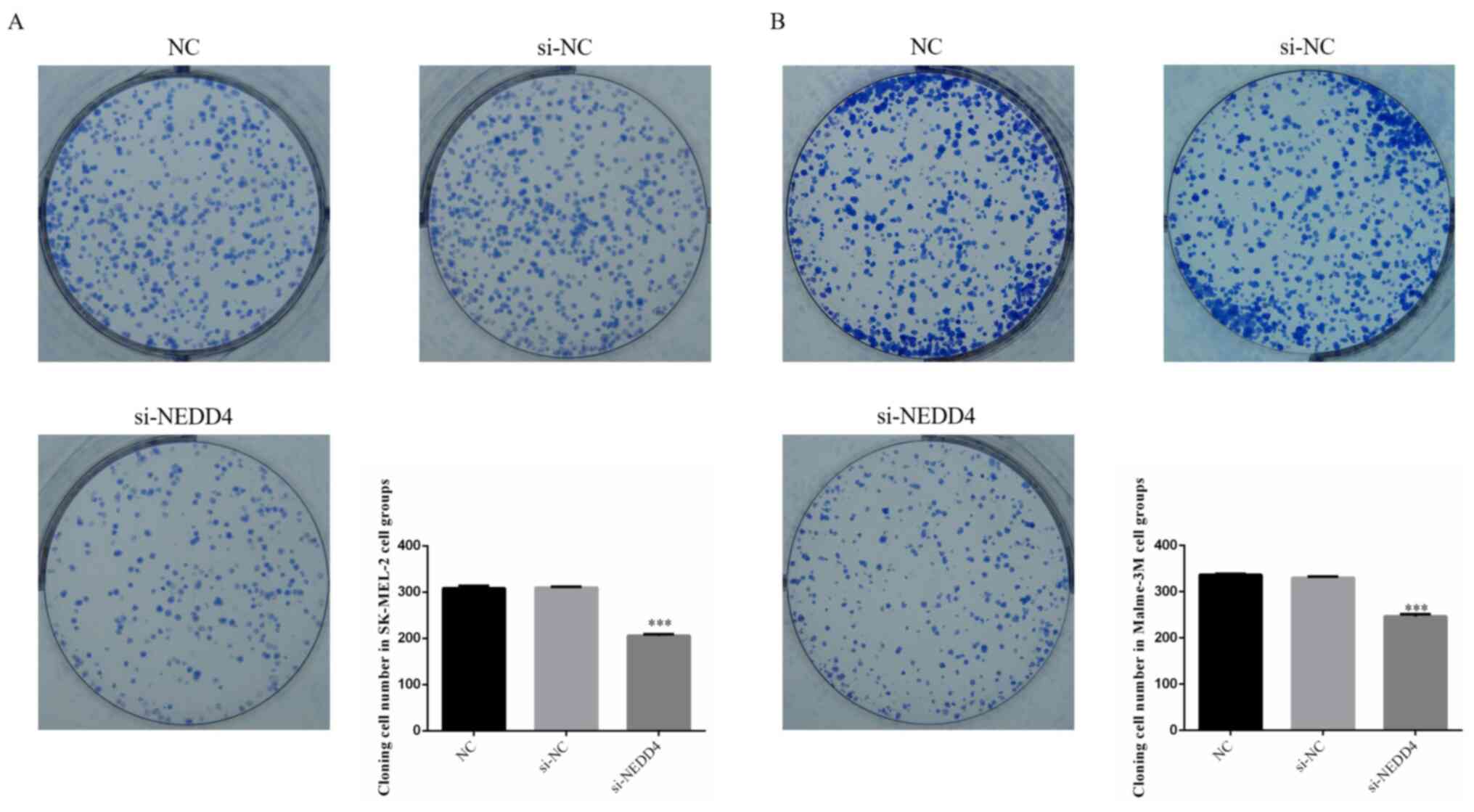
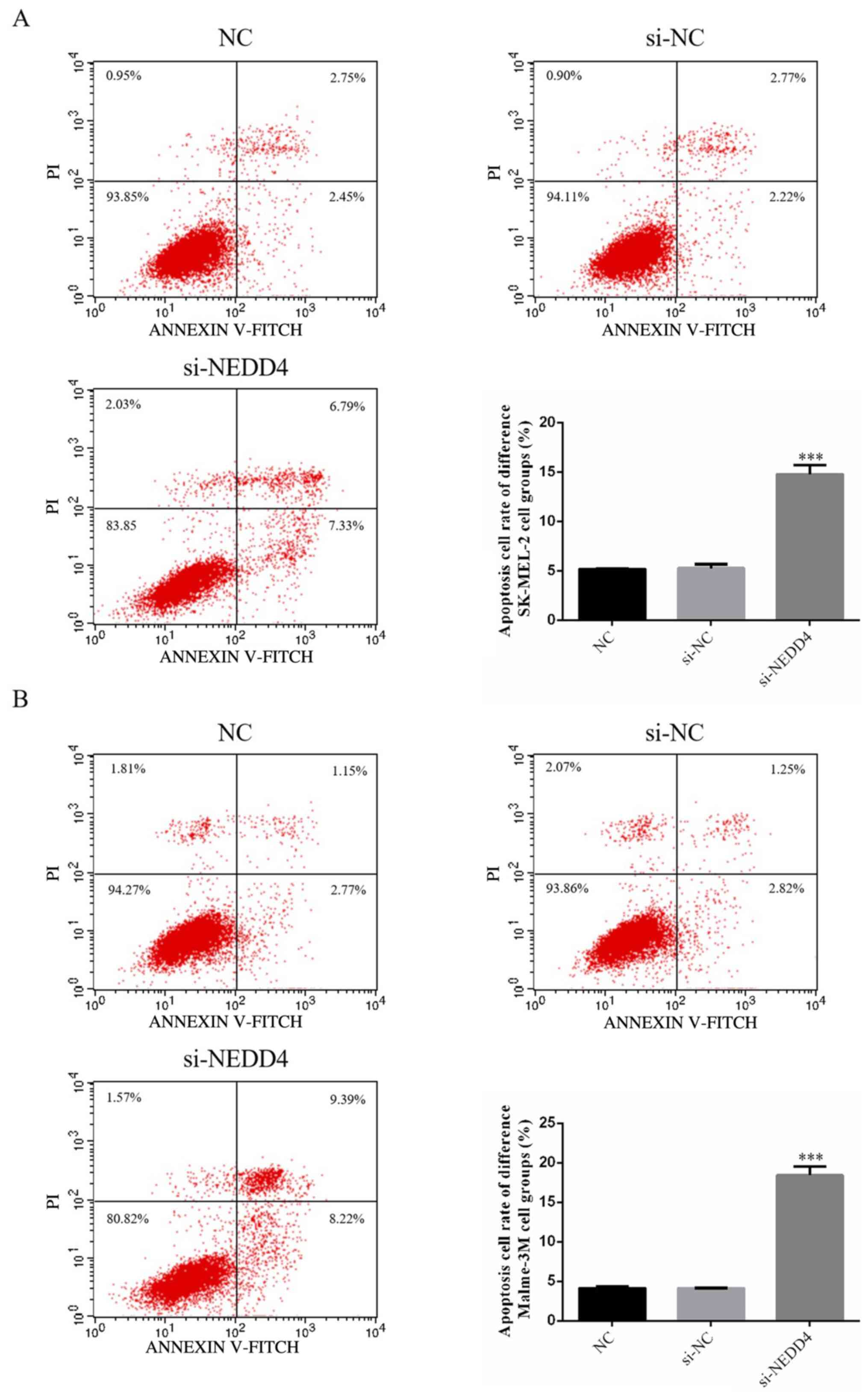
|
1
|
Riley RS, June CH, Langer R and Mitchell
MJ: Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 18:175–196. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
National Cancer Institute (NCI): SEER Stat
Fact Sheet: Melanoma of the skin. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.html.
Accessed June 20, 2015.
|
|
3
|
Joshua AM, Evans A, Van der Kwast T,
Zielenska M, Meeker AK, Chinnaiyan A and Squire JA: Prostatic
preneoplasia and beyond. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1785:156–181.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hershko A: The ubiquitin system for
protein degradation and some of its roles in the control of the
cell-division cycle (Nobel lecture). Angew Chem Int Ed.
44:5932–5943. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee AY and Brady MS: Neoadjuvant
immunotherapy for melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 123:782–788.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hjerpe R and Rodríguez MS: Alternative UPS
drug targets upstream the 26S proteasome. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
40:1126–1140. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tsvetkov P, Reuven N and Shaul Y:
Ubiquitin-independent p53 proteasomal degradation. Cell Death
Differ. 17:103–108. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Allende-Vega N and Saville MK: Targeting
the ubiquitin-proteasome system to activate wild-type p53 for
cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 20:29–39. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yu ZK, Gervais JL and Zhang H: Human CUL-1
associates with the SKP1/SKP2 complex and regulates p21(CIP1/WAF1)
and cyclin D proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:11324–11329.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ciechanover A: The 2008 Lindau Nobel
Laureate Meeting: Aaron Ciechanover, Chemistry 2004. J Vis Exp.
29(1559)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hoeller D and Dikic I: Targeting the
ubiquitin system in cancer therapy. Nature. 458:438–444.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hochstrasser M: Origin and function of
ubiquitin-like proteins. Nature. 458:422–429. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bhoj VG and Chen ZJ: Ubiquitylation in
innate and adaptive immunity. Nature. 458:430–437. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hirsch C, Gauss R, Horn SC, Neuber O and
Sommer T: The ubiquitylation machinery of the endoplasmic
reticulum. Nature. 458:453–460. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bergink S and Jentsch S: Principles of
ubiquitin and SUMO modifications in DNA repair. Nature.
458:461–467. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Raiborg C and Stenmark H: The ESCRT
machinery in endosomal sorting of ubiquitylated membrane proteins.
Nature. 458:445–452. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Paoluzzi L and O'Connor OA: Mechanistic
rationale and clinical evidence for the efficacy of proteasome
inhibitors against indolent and mantle cell lymphomas. BioDrugs.
20:13–23. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
O'Connor OA: Marked clinical activity of
the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in patients with follicular and
mantle-cell lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 6:191–199.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang Y, Kitagaki J, Dai RM, Tsai YC,
Lorick KL, Ludwig RL, Pierre SA, Jensen JP, Davydov IV, Oberoi P,
et al: Inhibitors of ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), a new class
of potential cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res. 67:9472–9481.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Soucy TA, Smith PG and Rolfe M: Targeting
NEDD8-activated cullin-RING ligases for the treatment of cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:3912–3916. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Soucy TA, Smith PG, Milhollen MA, Berger
AJ, Gavin JM, Adhikari S, Brownell JE, Burke KE, Cardin DP,
Critchley S, et al: An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a
new approach to treat cancer. Nature. 458:732–736. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Brownell JE, Sintchak MD, Gavin JM, Liao
H, Bruzzese FJ, Bump NJ, Soucy TA, Milhollen MA, Yang X, Burkhardt
AL, et al: Substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-like
protein-activating enzymes: The NEDD8 E1 inhibitor MLN4924 forms a
NEDD8-AMP mimetic in situ. Mol Cell. 37:102–111. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lin JJ, Milhollen MA, Smith PG, Narayanan
U and Dutta A: NEDD8-targeting drug MLN4924 elicits DNA
rereplication by stabilizing Cdt1 in S phase, triggering checkpoint
activation, apoptosis, and senescence in cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:10310–10320. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rabut G and Peter M: Function and
regulation of protein neddylation. ‘Protein modifications: Beyond
the usual suspects' review series. EMBO Rep. 9:969–976.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Leonardi GC, Candido S, Falzone L,
Spandidos DA and Libra M: Cutaneous melanoma and the immunotherapy
revolution (Review). Int J Oncol. 57:609–618. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Review).
|
|
26
|
Kuryk L, Bertinato L, Staniszewska M,
Pancer K, Wieczorek M, Salmaso S, Caliceti P and Garofalo M: From
conventional therapies to immunotherapy: Melanoma treatment in
review. Cancers (Basel). 12(3057)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tanda ET, Vanni I, Boutros A, Andreotti V,
Bruno W, Ghiorzo P and Spagnolo F: Current state of target
treatment in BRAF mutated melanoma. Front Mol Biosci.
7(154)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Qiu Y, Zheng Y, Wu KP and Schulman BA:
Insights into links between autophagy and the ubiquitin system from
the structure of LC3B bound to the LIR motif from the E3 ligase
NEDD4. Protein Sci. 26:1674–1680. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Huang DT, Ayrault O, Hunt HW, Taherbhoy
AM, Duda DM, Scott DC, Borg LA, Neale G, Murray PJ, Roussel MF, et
al: E2-RING expansion of the NEDD8 cascade confers specificity to
cullin modification. Mol Cell. 33:483–495. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Butt G, Yaylim I, Attar R, Aras A, Romero
MA, Qureshi MZ, Purenovic J and Farooqi AA: NEDD4 family of E3
ubiquitin ligases in breast cancer: Spotlight on SMURFs, WWPs and
NEDD4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1152:365–375. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang ZW, Hu X, Ye M, Lin M, Chu M and Shen
X: NEDD4 E3 ligase: Functions and mechanism in human cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 67:92–101. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Qian H, Wu B, You S, Wu S, Lu S,
Wang P, Cao L, Zhang N and Sun Y: E3 Ubiquitin ligase NEDD4
family-regulatory network in cardiovascular disease. Int J Biol
Sci. 16:2727–2740. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Soysouvanh F, Giuliano S, Habel N,
El-Hachem N, Pisibon C, Bertolotto C and Ballotti R: An Update on
the role of ubiquitination in melanoma development and therapies. J
Clin Med. 10(1133)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xie P, Peng Z, Chen Y, Li H, Du M, Tan Y,
Zhang X, Lu Z, Cui CP, Liu CH, et al: Neddylation of PTEN regulates
its nuclear import and promotes tumor development. Cell Res.
31:291–311. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Guo Y, Yang L, Lei S, Tan W and Long J:
NEDD4 negatively regulates GITR via ubiquitination in immune
microenvironment of melanoma. OncoTargets Ther. 12:10629–10637.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Huang X, Chen J, Cao W, Yang L, Chen Q, He
J, Yi Q, Huang H, Zhang E and Cai Z: The many substrates and
functions of NEDD4-1. Cell Death Dis. 10(904)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zou X, Levy-Cohen G and Blank M: Molecular
functions of NEDD4 E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1856:91–106. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang X, Zhang YL, Qiu G, Pian L, Guo L,
Cao H, Liu J, Zhao Y, Li X, Xu Z, et al: Hepatic neddylation
targets and stabilizes electron transfer flavoproteins to
facilitate fatty acid β-oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:2473–2483. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Luhtala S, Staff S, Kallioniemi A, Tanner
M and Isola J: Clinicopathological and prognostic correlations of
HER3 expression and its degradation regulators, NEDD4-1 and NRDP1,
in primary breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 18(1045)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shao G, Wang R, Sun A, Wei J, Peng K, Dai
Q, Yang W and Lin Q: The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 mediates cell
migration signaling of EGFR in lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
17(24)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wen W, Li J, Wang L, Xing Y, Li X, Ruan H,
Xi X, Xiong J and Kuang R: Inhibition of NEDD4 inhibits cell growth
and invasion and induces cell apoptosis in bladder cancer cells.
Cell Cycle. 16:1509–1514. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Meurette O: Shaping of the tumor
microenvironment by Notch signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1223:1–16.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Rubey M, Chhabra NF, Gradinger D,
Sanz-Moreno A, Lickert H, Przemeck GKH and Hrabě de Angelis M:
DLL1- and DLL4-mediated Notch signaling is essential for adult
pancreatic islet homeostasis. Diabetes. 69:915–926. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fleming T, Balderas-Márquez JE, Epardo D,
Ávila-Mendoza J, Carranza M, Luna M, Harvey S, Arámburo C and
Martínez-Moreno CG: Growth hormone neuroprotection against kainate
excitotoxicity in the retina is mediated by Notch/PTEN/Akt
signaling. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 60:4532–4547. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zheng D, Tao M, Liang X, Li Y, Jin J and
He Q: p66Shc regulates podocyte autophagy in high glucose
environment through the Notch-PTEN-PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Histol
Histopathol. 35:405–415. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|