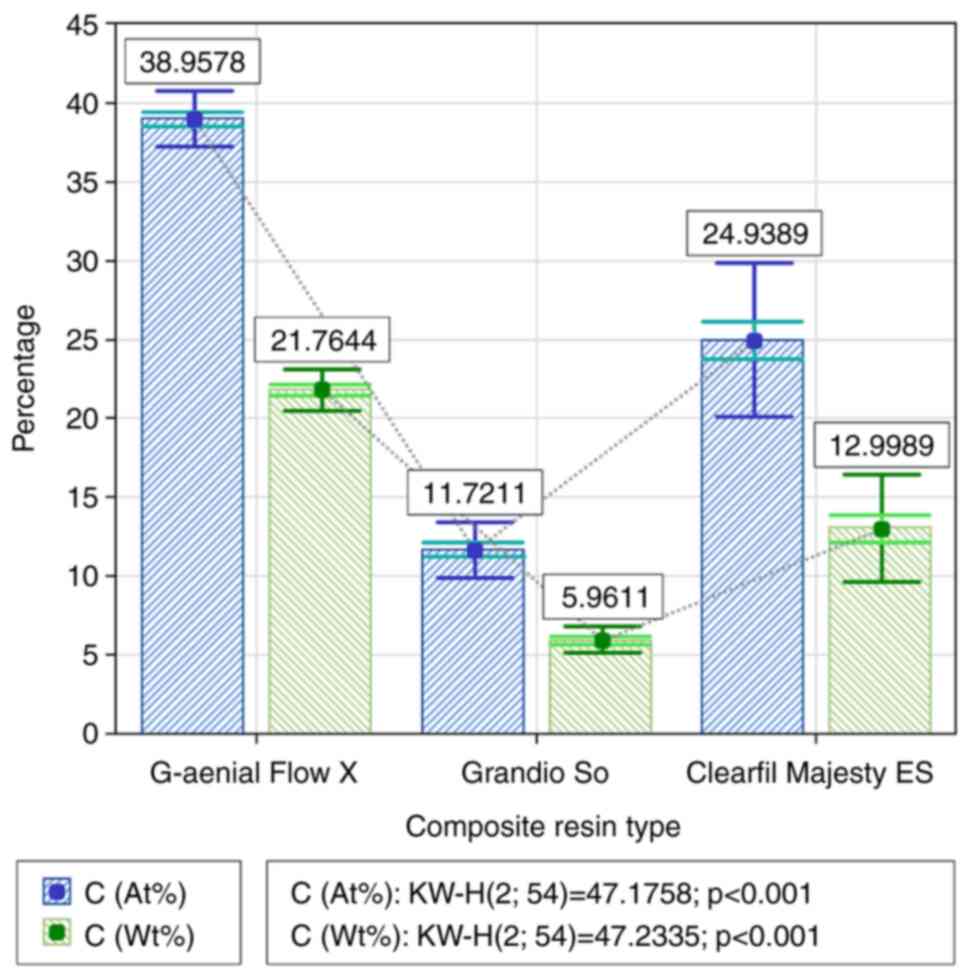
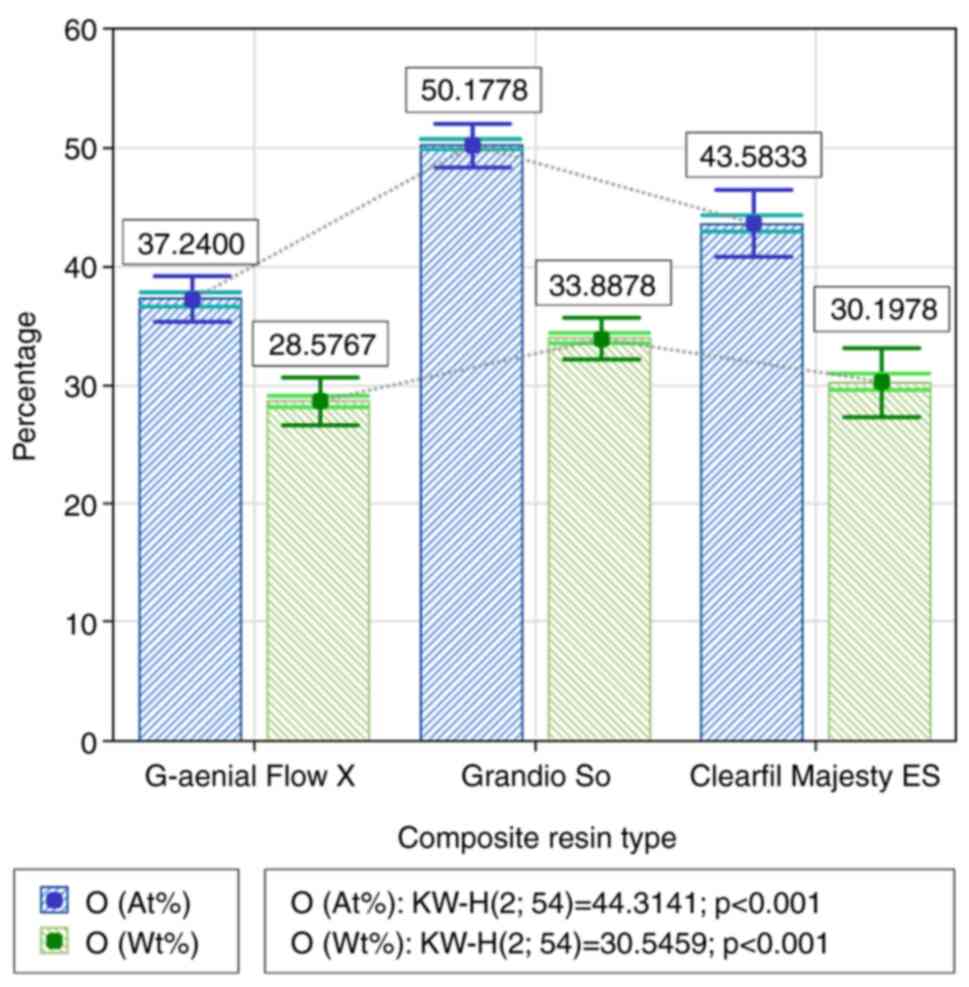
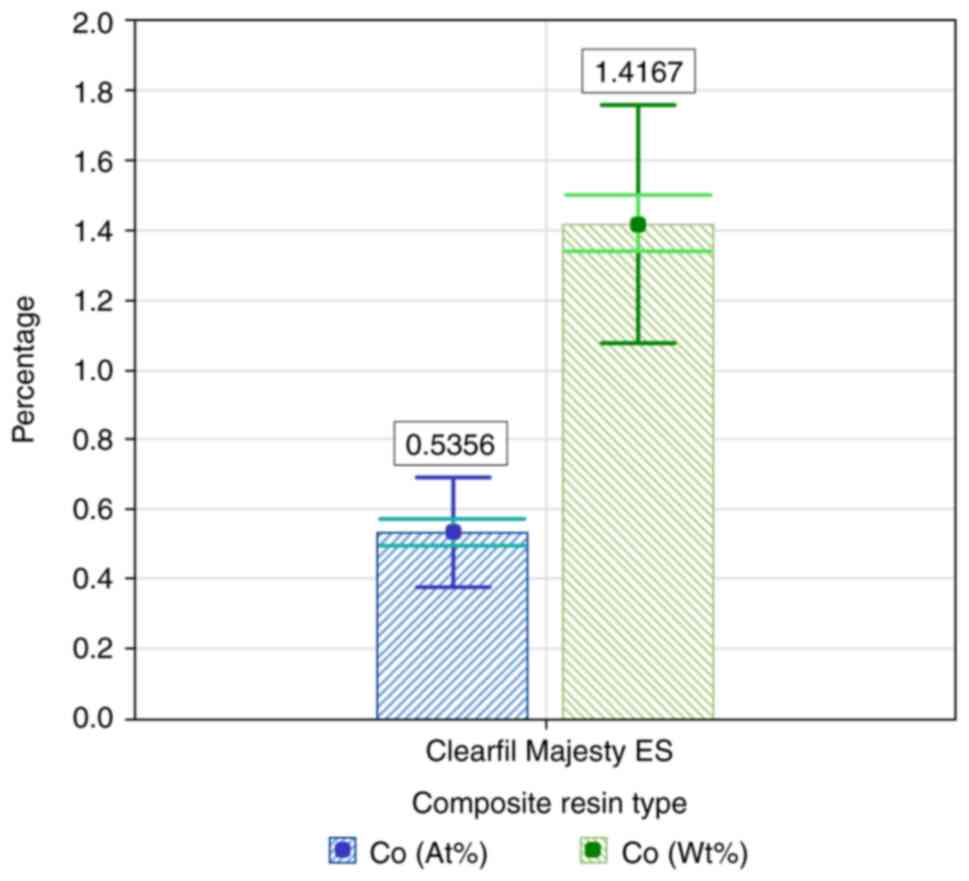
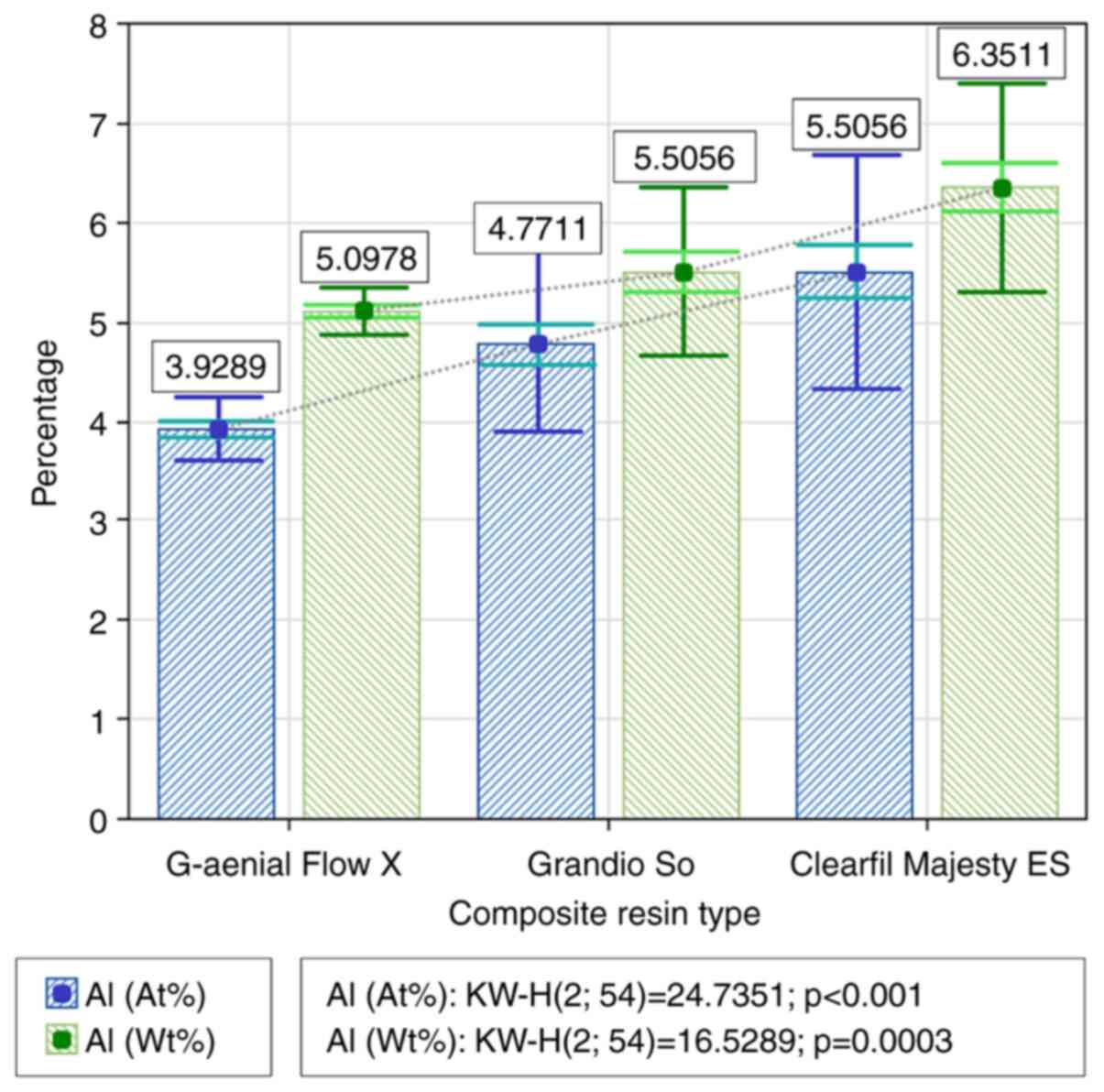
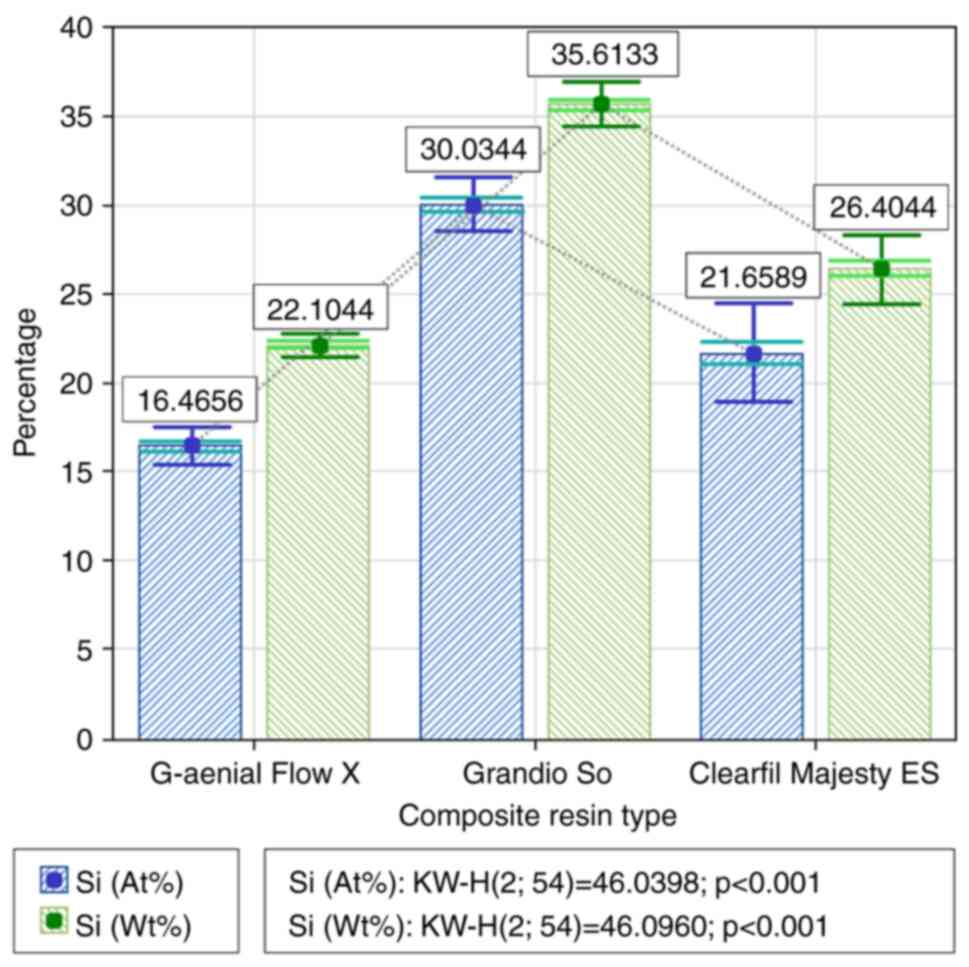
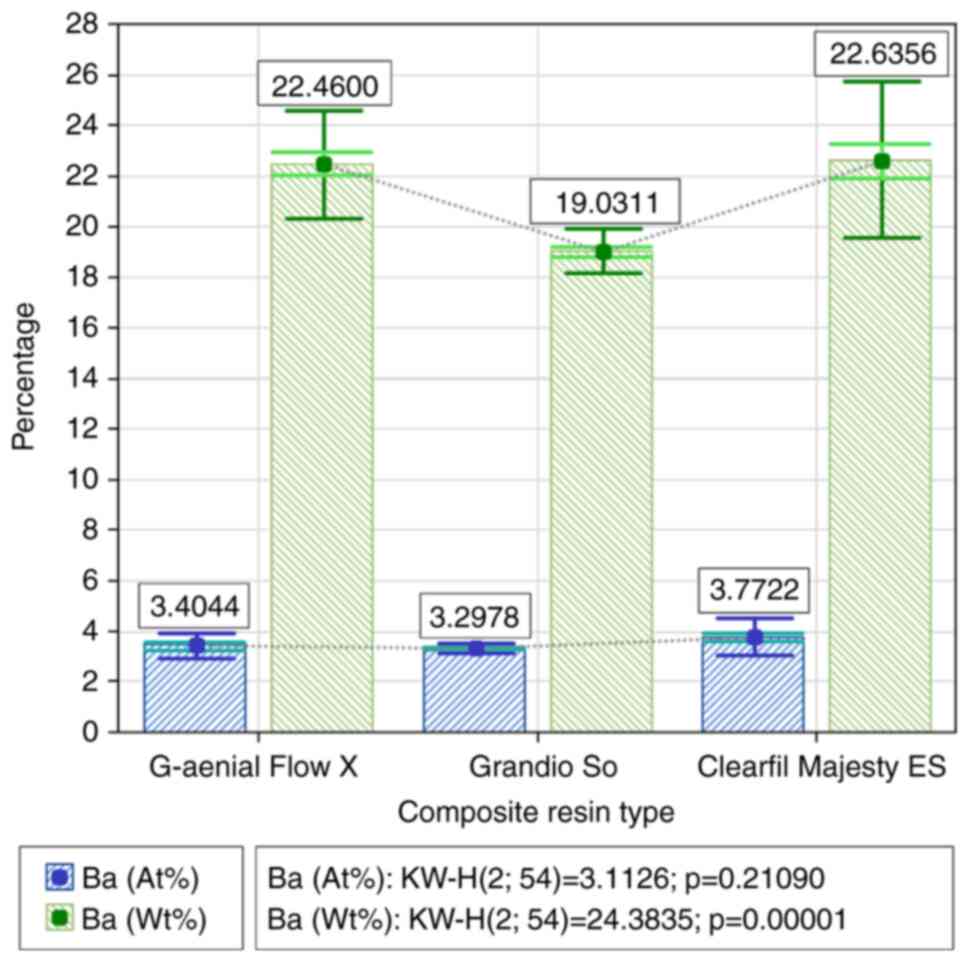
|
1
|
Cardoso EM, Reis C and Manzanares-Céspedes
MC: Chronic periodontitis, inflammatory cytokines, and
interrelationship with other chronic diseases. Postgrad Med.
130:98–104. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Giannakoura A, Pepelassi E, Kotsovilis S,
Nikolopoulos G and Vrotsos I: Tooth mobility parameters in chronic
periodontitis patients prior to periodontal therapy: A
cross-sectional study. Dent Oral Craniofac Res. 5:1–8. 2019.
|
|
3
|
Soares PB, Fernandes Neto AJ, Magalhães D,
Versluis A and Soares CJ: Effect of bone loss simulation and
periodontal splinting on bone strain: Periodontal splints and bone
strain. Arch Oral Biol. 56:1373–1381. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kathariya R, Devanoorkar A, Golani R,
Shetty N, Vallakatla V and Bhat MY: To splint or not to splint: The
current status of periodontal splinting. J Int Acad Periodontol.
18:45–56. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Littlewood SJ, Millett DC, Doubleday B,
Bearn DR and Worthington HV: Orthodontic retention: A systematic
review. J Orthod. 33:205–212. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhou Z and Ma S:
Retrospective study of combined splinting restorations in the
aesthetic zone of periodontal patients. Br Dent J. 220:241–247.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vilchis RJ, Hotta Y and Yamamoto K:
Examination of six orthodontic adhesives with electron microscopy,
hardness tester and energy dispersive X-ray microanalyzer. Angle
Orthod. 78:655–661. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Scougall-Vilchis RJ, Hotta M, Hotta M,
Idono T and Yamamoto K: Examination of composite resins with
electron microscopy, microhardness tester and energy dispersive
X-ray microanalyzer. Dent Mater J. 28:102–112. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Karadas M: The effect of different
beverages on the color and translucency of flowable composites.
Scanning. 38:701–709. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Özcan M and Kumbuloglu O: Periodontal and
trauma splints using fiber reinforced resin composites. In:
Clinical Guide to Principles of Fiber-Reinforced Composites in
Dentistry. 1st edition. Woodhead Publishing, pp111-130, 2017.
|
|
11
|
Vallittu PK: An overview of development
and status of fiber-reinforced composites as dental and medical
biomaterials. Acta Biomater Odontol Scand. 4:44–55. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bechir ES, Pacurar M, Hantoiu TA, Bechir
A, Smatrea O, Burcea A, Gioga C and Monea M: Aspects in
effectiveness of glass- and polyethylene-fibre reinforced composite
resin in periodontal splinting. Mater Plast. 53:104–109. 2016.
|
|
13
|
Juloski J, Beloica M, Goracci C, Chieffi
N, Giovannetti A, Vichif A, Vulicevic ZR and Ferrari M: Shear bond
strength to enamel and flexural strength of different
fiber-reinforced composites. J Adhes Dent. 15:123–130.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Vieriu RM, Tanculescu O, Mocanu F, Solomon
SM, Savin C, Bosinceanu DG, Doloca A, Iordache C, Ifteni G and
Saveanu I: In vitro study regarding the biomechanical behaviour of
bone, fibre reinforced polymer and wire composite perio-dontal
splints. II. model analysis. Mater Plast. 57:253–262. 2020.
|
|
15
|
Luchian I, Nanu S, Martu I, Teodorescu C,
Pasarin L, Solomon S, Martu MA, Tatarciuc M and Martu S: The
influence of highly viscous flowable composite resins on the
survival rate of periodontal splints. Rom J Oral Rehabilitation.
10:63–69. 2018.
|
|
16
|
Luchian I, Nanu S, Martu I, Martu MA,
Nichitean G, Nitescu DC, Gurau C, Victorita S, Pasarin L, Tatarciuc
M and Solomon SM: The influence of the composite resin material on
the clinical working time in fiberglass reinforced periodontal
splints. Mater Plast. 57:316–320. 2020.
|
|
17
|
Shahi S, Özcan M, Maleki Dizaj S, Sharifi
S, Al-Haj Husain N, Eftekhari A and Ahmadian E: A review on
potential toxicity of dental material and screening their
biocompatibility. Toxicol Mech Methods. 29:368–377. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wataha JC: Predicting clinical biological
responses to dental materials. Dent Mater. 28:23–40.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Polyzois GL: In vitro evaluation of dental
materials. Clin Mater. 16:21–60. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Leyssens L, Vinck B, Van Der Straeten C,
Wuyts F and Maes L: Cobalt toxicity in humans-A review of the
potential sources and systemic health effects. Toxicology.
387:43–56. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Exley C: Human exposure to aluminium.
Environ Sci Process Impacts. 15:1807–1816. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Meryon S and Jakeman J: Aluminium and
dental materials-a study in vitro of its potential release and
toxicity. Int Endod J. 20:16–19. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hu JB: High-performance ceramic/epoxy
composite adhesives enabled by rational ceramic bandgaps. Sci Rep.
10(484)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim IJ, Kim D, Ahn B, Lee HJ, Kim HJ and
Kim W: Vulcanizate structures of SBR compounds with silica and
carbon black binary filler systems at different curing
temperatures. Polymers (Basel). 12(2343)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Yu Q and Yang Z: Effect of
hydrophobic surface treated fumed silica fillers on a one-bottle
etch and rinse model dental adhesive. J Mater Sci Mater Med.
29(10)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kostić M, Pejcic A, Igić M and
Gligorijević N: Adverse reactions to denture resin materials. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:5298–5305. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bationo R, Ablassé R, Diarra A,
Beugré-Kouassi ML, Jordana F and Beugré JB: In vitro Assessment of
cytotoxicity of orthodontic and dental composite resins using human
gingival fibroblast. Sch J Dent Sci. 6:352–355. 2019.
|