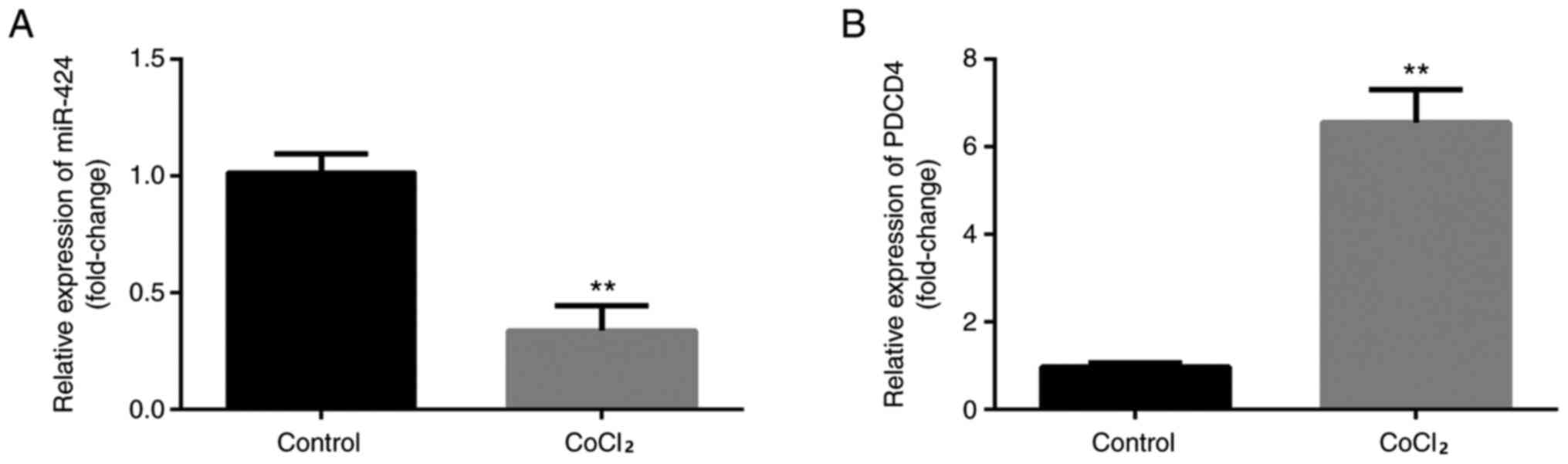
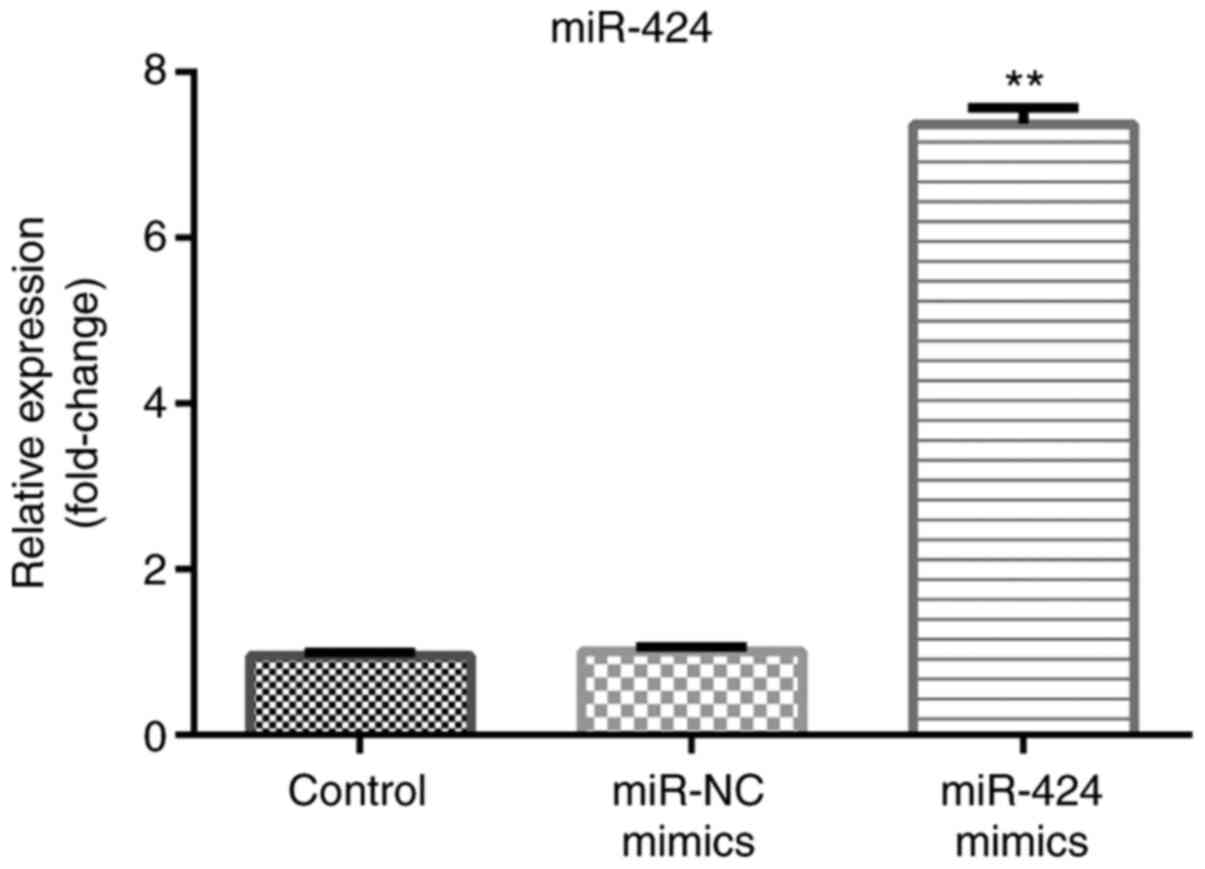
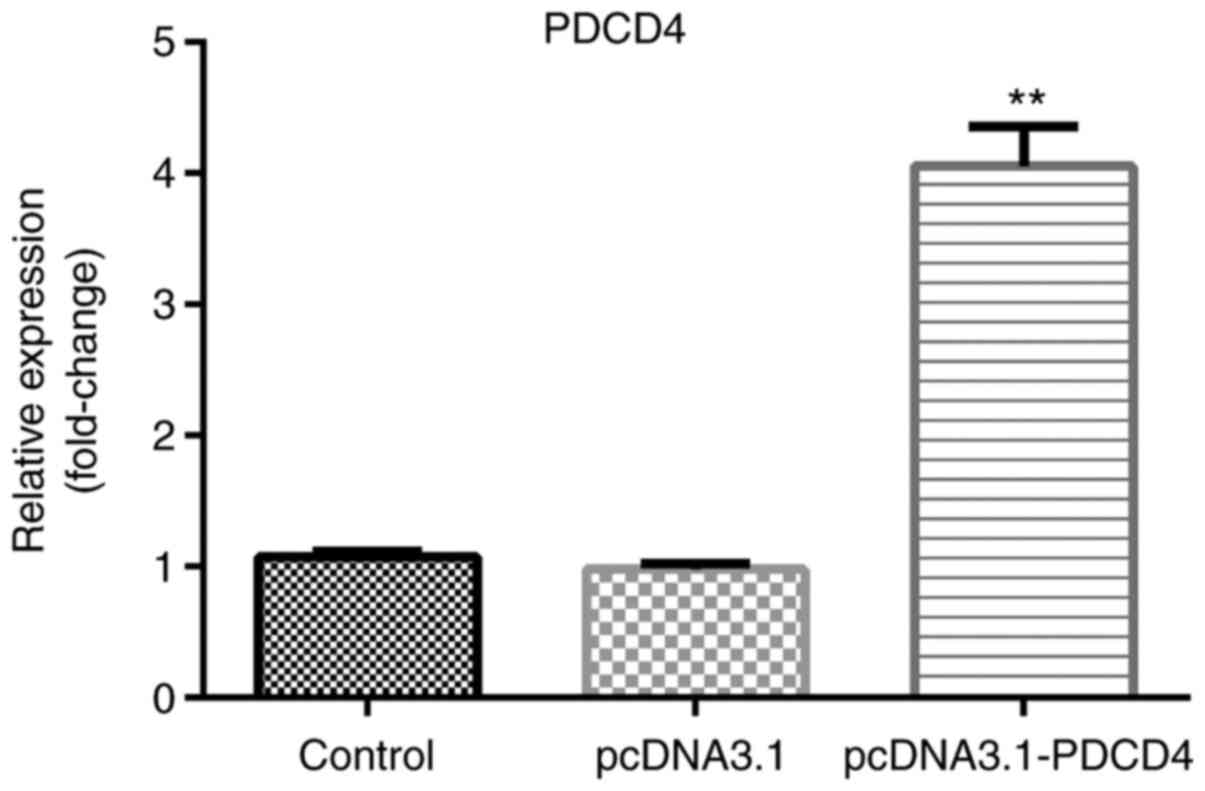
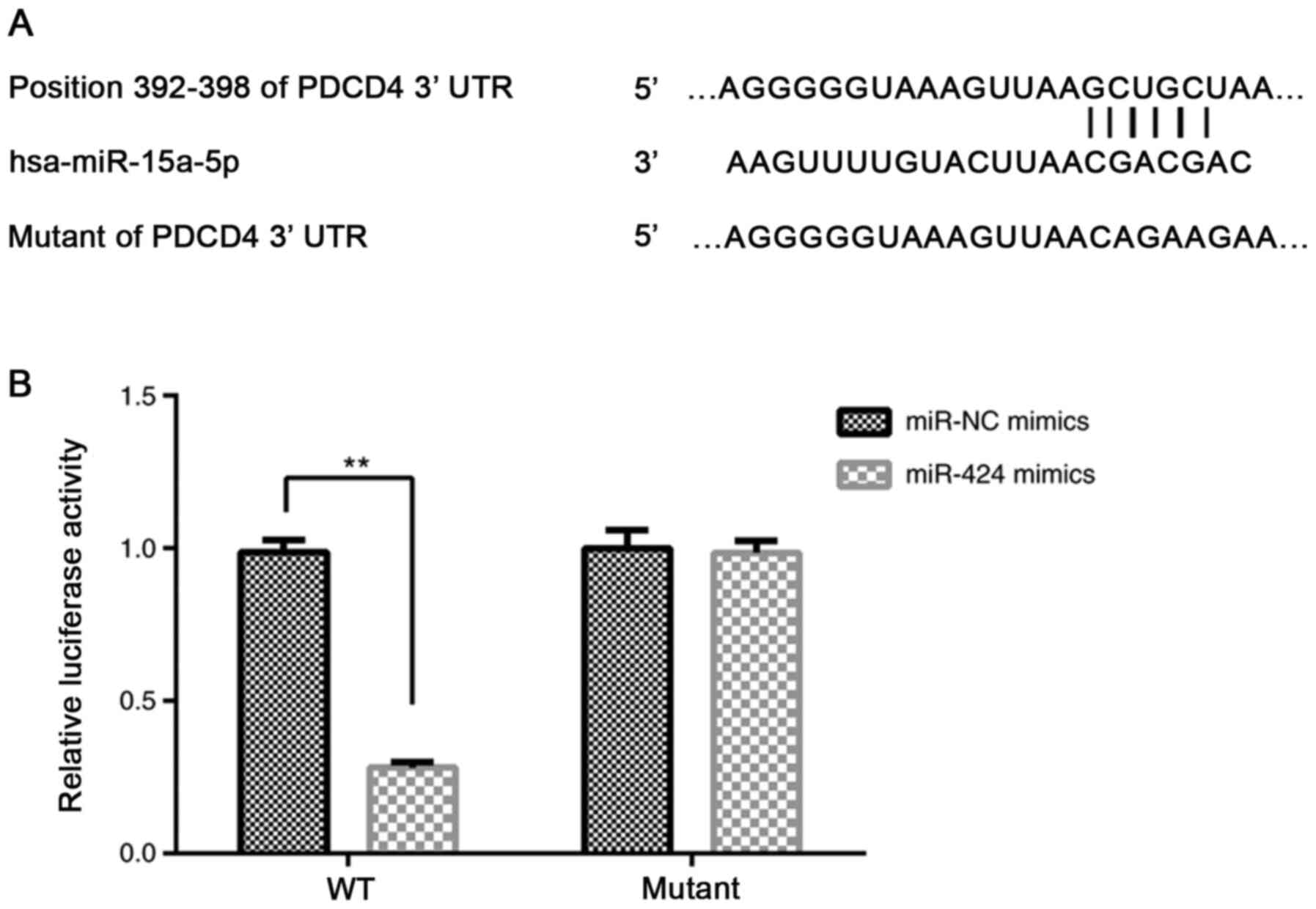
|
1
|
Johnston SC, Mendis S and Mathers CD:
Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: Estimates from
monitoring, surveillance, and modelling. Lancet Neurol. 8:345–354.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhao WJ, Zhang HF and Su JY:
Downregulation of microRNA-195 promotes angiogenesis induced by
cerebral infarction via targeting VEGFA. Mol Med Rep. 16:5434–5440.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lo EH, Dalkara T and Moskowitz MA:
Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 4:399–415. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M and Davis
SM: Stroke. Lancet. 371:1612–1623. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu G, Ma M, Liu X and Hankey GJ: Is there
a stroke belt in China and why? Stroke. 44:1775–1783.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kleindorfer D, de los Rios La Rosa F,
Khatri P, Kissela B, Mackey J and Adeoye O: Temporal trends in
acute stroke management. Stroke. 44 (Suppl 1):S129–S131.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vemuganti R: All's well that transcribes
well: Non-coding RNAs and post-stroke brain damage. Neurochem Int.
63:438–449. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Truelsen T and Bonita R: Epidemiological
transition of stroke in China? Stroke. 39:1653–1654.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang W, Jiang B, Sun H, Ru X, Sun D, Wang
L, Wang L, Jiang Y, Li Y, Wang Y, et al: NESS-China Investigators:
Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality of Stroke in China: Results
from a Nationwide Population-Based Survey of 480,687 Adults.
Circulation. 135:759–771. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xing B, Chen H, Zhang M, Zhao D, Jiang R,
Liu X and Zhang S: Ischemic postconditioning inhibits apoptosis
after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat.
Stroke. 39:2362–2369. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Townsend PA, Scarabelli TM, Pasini E,
Gitti G, Menegazzi M, Suzuki H, Knight RA, Latchman DS and
Stephanou A: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits STAT-1 activation
and protects cardiac myocytes from ischemia/reperfusion-induced
apoptosis. FASEB J. 18:1621–1623. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li P, Shen M, Gao F, Wu J, Zhang J, Teng F
and Zhang C: An Antagomir to MicroRNA-106b-5p Ameliorates Cerebral
Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Rats Via Inhibiting Apoptosis
and Oxidative Stress. Mol Neurobiol. 54:2901–2921. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ghelani HS, Rachchh MA and Gokani RH:
MicroRNAs as newer therapeutic targets: A big hope from a tiny
player. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 3:217–227. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zheng Y, Wang L, Chen M, Pei A, Xie L and
Zhu S: Upregulation of miR-130b protects against cerebral ischemic
injury by targeting water channel protein aquaporin 4 (AQP4). Am J
Transl Res. 9:3452–3461. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng L, Cheng W, Wang X, Yang Z, Zhou X
and Pan C: Overexpression of MicroRNA-145 Ameliorates Astrocyte
Injury by Targeting Aquaporin 4 in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. BioMed
Res Int. 2017(9530951)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yin KJ, Hamblin M and Chen YE: Non-coding
RNAs in cerebral endothelial pathophysiology: Emerging roles in
stroke. Neurochem Int. 77:9–16. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhao L, Hua C, Li Y, Sun Q and Wu W:
miR-525-5p inhibits ADAMTS13 and is correlated with
Ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced neuronal cell death. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:18115–18122. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wei N, Xiao L, Xue R, Zhang D, Zhou J, Ren
H, Guo S and Xu J: MicroRNA-9 Mediates the Cell Apoptosis by
Targeting Bcl2l11 in Ischemic Stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 53:6809–6817.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang YZ, Wang J and Xu F: Circulating
miR-29b and miR-424 as Prognostic Markers in Patients with Acute
Cerebral Infarction. Clin Lab. 63:1667–1674. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Darbinian N: Cultured Cell Line Models of
Neuronal Differentiation: NT2, PC12, and SK-N-MC. Methods Mol Biol.
2311:25–38. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Katarzyna B and Benita W: PC12 and THP-1
Cell Lines as Neuronal and Microglia Model in Neurobiological
Research. Appl Sci (Basel). 11(3729)2021.
|
|
24
|
Kudo TA, Tominami K, Izumi S, Hayashi Y,
Noguchi T, Matsuzawa A, Hong G and Nakai J: Characterization of
PC12 Cell Subclones with Different Sensitivities to Programmed
Thermal Stimulation. Int J Mol Sci. 21(8356)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wiatrak B and Balon K: Protective Activity
of Aβ on Cell Cultures (PC12 and THP-1 after Differentiation)
Preincubated with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Mol Neurobiol.
58:1453–1464. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Amalia L, Sadeli HA, Parwati I, Rizal A
and Panigoro R: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in acute ischemic
stroke: Neuroprotection for better clinical outcome. Heliyon.
6(e04286)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tripathi VK, Subramaniyan SA and Hwang I:
Molecular and Cellular Response of Co-cultured Cells toward Cobalt
Chloride (CoCl2)-Induced Hypoxia. ACS Omega.
4:20882–20893. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim HB, Yoo JY, Yoo SY, Lee JH, Chang W,
Kim HS, Baik TK and Woo RS: Neuregulin-1 inhibits
CoCl2-induced upregulation of excitatory amino acid
carrier 1 expression and oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells and the
hippocampus of mice. Mol Brain. 13(153)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Matsuhashi S, Manirujjaman M, Hamajima H
and Ozaki I: Control mechanisms of the tumor suppressor PDCD4:
Expression and functions. Int J Mol Sci. 20(2304)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Saugstad JA: MicroRNAs as effectors of
brain function. Stroke. 44 (Suppl 1):S17–S19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yan H, Fang M and Liu XY: Role of
microRNAs in stroke and poststroke depression.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2013(459692)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gui SH, Wang YM, Fan CY, Han LK, Wang TG,
Di MQ and Gu JQ: miR-424 Inhibits neuronal apoptosis in rats with
cerebral infarction through regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling
pathway. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 34:1285–1296. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sun H, Zhong D, Wang C, Sun Y, Zhao J and
Li G: MiR-298 Exacerbates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Following
Ischemic Stroke by Targeting Act1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
48:528–539. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Baczyńska D, Michałowska D and Witkiewicz
W: The role of microRNA in ischemic diseases - impact on the
regulation of inflammatory, apoptosis and angiogenesis processes.
Przegl Lek. 70:135–142. 2013.PubMed/NCBI(In Polish).
|
|
36
|
Yao S, Tang B, Li G, Fan R and Cao F:
miR-455 inhibits neuronal cell death by targeting TRAF3 in cerebral
ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 12:3083–3092.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xing G, Luo Z, Zhong C, Pan X and Xu X:
Influence of miR-155 on Cell Apoptosis in Rats with Ischemic
Stroke: Role of the Ras Homolog Enriched in Brain (Rheb)/mTOR
Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 22:5141–5153. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schwarzenbach H, Nishida N, Calin GA and
Pantel K: Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in
cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 11:145–156. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Guo YB, Ji TF, Zhou HW and Yu JL: Effects
of microRNA-21 on Nerve Cell Regeneration and Neural Function
Recovery in Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Cerebral Infarction
Rats by Targeting PDCD4. Mol Neurobiol. 55:2494–2505.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yan H, Rao J, Yuan J, Gao L, Huang W, Zhao
L and Ren J: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions as a competing
endogenous RNA to regulate ischemic neuronal death by targeting
miR-21/PDCD4 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis.
8(3211)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|